Rapamycin–PLGA microparticles prevent senescence, sustain cartilage matrix production under stress and exhibit prolonged retention in mouse joints†
Abstract
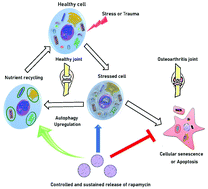
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a joint disease characterized by progressive damage of articular cartilage and the adjoining subchondral bone. Chondrocytes, the primary cells of the cartilage, have limited regenerative capacity and when they undergo stress due to trauma or with aging, they senesce or become apoptotic. Rapamycin, a potent immunomodulator, has shown promise in OA treatment. It activates autophagy and is known to prevent senescence. However, its clinical translation for OA is hampered due to systemic toxicity as high and frequent doses are required. Here, we have fabricated rapamycin encapsulated poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) based carriers that induced autophagy and prevented cellular senescence in human chondrocytes. The microparticle (MP) delivery system showed sustained release of the drug for several weeks. Rapamycin microparticles protected in vitro cartilage mimics (micromass cultures) from degradation, allowing sustained production of sGAG, and demonstrated a prolonged senescence preventive effect under oxidative and genomic stress conditions. These microparticles also exhibited a residence time of ∼30 days after intra-articular injections in murine knee joints. Such particulate systems are promising candidates for intra-articular delivery of rapamycin for the treatment of osteoarthritis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...