Myricetin alleviated hepatic steatosis by acting on microRNA-146b/thyroid hormone receptor b pathway in high-fat diet fed C57BL/6J mice†
Abstract
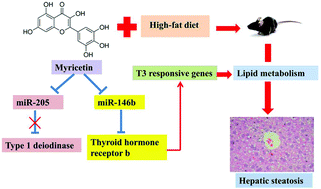
Hepatic microRNAs (miRs) regulate local thyroid hormone (TH) action and TH-related lipid metabolism. We previously found that myricetin effectively ameliorated hepatic steatosis by targeting PPAR signaling pathway, in which the differentially expressed genes were TH-responsive. The present study was designed to explore the mechanism by which myricetin regulated miR-dependent TH action and lipid metabolism on high-fat diet (HFD)-induced hepatic steatosis. C57BL/6J mice were fed a HFD with or without 100 mg kg−1 myricetin by oral gavage for 16 weeks (n = 8 for each group). The results showed that myricetin improved HFD-induced hepatic steatosis, increased serum TH levels and hepatic type 1 deiodinase (DIO1) activities, and elevated energy expenditure in relation to the HFD mice. Meanwhile, myricetin inhibited miR-205 and miR-146b up-regulation induced by HFD, and also up-regulated their targets, Dio1 and thyroid hormone receptor b (TRb) expression, at both the transcriptional and translational levels, accompanied by the regulation of TH responsive lipid metabolism genes. Overexpression or knockdown of miR-205 failed to affect Dio1 mRNA and protein levels in primary mouse hepatocytes. Myricetin directly decreased miR-146b expression in miR-146b mimic-treated hepatocytes to elevate TRb levels. However, the beneficial effects of myricetin on hepatic TH action and lipid metabolism were abolished by TRb siRNA in free fatty acid (FFA)-treated hepatocytes. Our results indicated that myricetin attenuated hepatic steatosis via the miR-146b/TRb pathway and should be considered for the management of NAFLD conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...