Metabolomic study on the hepatoprotective effects of modified Sinisan using ultra-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization quadruple time-of-flight mass spectrometry coupled with pattern recognition approach
Abstract
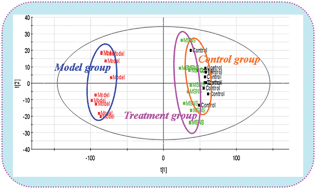
Metabolomics, the global analysis of small molecules in a biological system in a holistic context, has played increasingly important roles in studies on the potential mechanisms of drugs. Modified Sinisan (MSNS), a traditional Chinese medicine, has showed good clinical efficacy in the treatment of liver injury, and its mechanism remains unclear. The present study was undertaken to explore the metabolomic characters of liver injury induced by dimethylnitrosamine and the therapeutic effects of MSNS. The study utilized ultra-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization quadruple time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC/ESI-Q-TOF-MS) in positive electrospray ionization combined with pattern recognition approach including principal component analysis (PCA), partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) and orthogonal projection to latent structures discriminate analysis (OPLS-DA) to demonstrate comprehensive metabolic characteristics and discover differentiating metabolites. Significant changes of 11 biomarkers in rat urine were identified and they were associated with perturbations in riboflavin metabolism, arginine and proline metabolism, histidine metabolism, sphingolipid metabolism, alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism, cysteine and methionine metabolism and pyrimidine metabolism. Of note, MSNS administration could provide satisfactory effects on liver injury through partially reversing the level of biomarkers in the urine of liver injured rats. These results show the power of metabolomics in unraveling the potential mechanisms of MSNS and may help us to obtain a better understand of the underlying pathophysiological processes of liver injury.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...