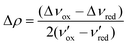Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleSpectroscopic and thermodynamic characterization of a cobalt-verdazyl valence tautomeric system. influence of crystal structure, solvent and counterion†
David J. R.
Brook
 *a,
Jeffrey
DaRos
a,
Aamani
Ponnekanti
a,
Stefano
Agrestini
*a,
Jeffrey
DaRos
a,
Aamani
Ponnekanti
a,
Stefano
Agrestini
 b and
Eric
Pellegrin
b
b and
Eric
Pellegrin
b
aDepartment of Chemistry, San Jose State University, San Jose, CA 95192, USA. E-mail: david.brook@sjsu.edu
bALBA Synchrotron Light Source, E-08290 Cerdanyola del Vallès, Barcelona, Spain
First published on 3rd April 2024
Abstract
Crystallization of the verdazyl-based valence tautomeric ion [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ (where dipyvd is the radical ligand 1-isopropyl-3,5-di(2′-pyridyl)-6-oxoverdazyl) with a variety of different counterions results in materials that show varying degrees of valence tautomeric (VT) transition in the solid state. The X-ray structure of the SbF6 salt at 150 K reveals a localized structure for the S = 1/2 tautomer, with a Co3+ cation and distinct anionic and radical ligands. Comparison with the structure of the same material at 300 K reveals large structural changes in the ligand as a result of the valence tautomeric equilibrium. Data for the S = 3/2 form is less conclusive; X-ray spectroscopy on the PF6 salt suggests a degree of low spin Co2+ character for the S = 3/2 tautomer at very low temperature though this is inconsistent with EPR data at similar temperatures and structural information at 150 K. Magnetic measurements on the [BArF4]− and triflate salts in organic solvents show that the VT equilibrium is dependent on solvent and ion pairing effects.
Introduction
Valence tautomeric (VT) compounds (compounds that switch between states that have a different electronic distribution) are interesting for their complex electronic structure as well as their possible applications.1–3 Fundamentally, VT compounds are asymmetric mixed valence systems; the small energy difference between tautomers results in an electronic structure that can be critically dependent on small environmental changes, and the coupling of molecular geometry with electron transfer results in an energy barrier for the tautomeric interconversion. This coupling also means that for VT systems the Born-Oppenheimer approximation may no longer be valid, and vibronic coupling must be included in a theoretical description.4,5The combination of an energy barrier and environmental sensitivity also means that VT systems have the potential for bistability. Under particular conditions a bistable sample may exist in one of two (or more) forms that interconvert only slowly; the particular form observed depends not only on the current conditions but the history of the sample. As a result, these systems have possible application as molecular sensors, in information storage, and molecular and quantum computing.
Understanding the barrier in metal–ligand VT systems requires understanding the geometry changes occurring at both ligand and metal sites. The majority of reported valence tautomers involve a cobalt ion coordinated to an oxolene (catecholate/semiquinone/quinone) ligand system.2 In many of these cases, electron transfer also results in spin crossover at the metal ion, though for some recent examples the two processes are separate.6–8 Spin crossover at the metal ion results in relatively large changes in bond length but changes in the ligand geometry are relatively small. Recent studies have explored other ligand systems in order to better control valence tautomerization and related geometry changes.9 In particular we recently reported a cobalt-verdazyl system, cobalt bis(1-isopropyl,3,5-di-(2′pyridyl)-6-oxoverdazyl), [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ that showed valence tautomerism between doublet and quartet states in solution, but in the solid state (as the PF6− salt) it was trapped as the quartet (Scheme 1).10
 | ||
| Scheme 1 Synthesis of [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ showing ligand numbering scheme (top) and the [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ valence tautomeric equilibrium (bottom). | ||
Studies on related species indicate the oxidized form of the ligand (a verdazyl radical) is essentially rigid and planar, however reduction by a single electron gives an antiaromatic ring that shows strong bond length alternation and deviation from planarity.10,11 Because such large geometry changes may become the basis of new bistable systems, we have undertaken a more detailed analysis of this valence tautomeric system. In particular, we have endeavored to explore in more detail the different tautomeric structures, and further investigate the role of counterion and solvent on the position of the tautomeric equilibrium.
Results and discussion
The S = 1/2 state
Though our previous results unambiguously identified the low spin state as a spin doublet (S = 1/2) species, its characterization is incomplete. In particular, if the tautomeric transition involves electron transfer to the ligand manifold, the resulting species is mixed valence in the ligands but its classification using the Robin-Day scheme is not immediately obvious. The isoelectronic iron species [Fe(dipyvd)2]+ appears to be a completely delocalized (class III) system12 while the related mixed valence systems [Ni(dipyvd)2]+ and [Zn(dipyvd)2]+ appear to be completely localized (class I, or possibly class II).11 Since the VT equilibrium is typically very sensitive to the molecular environment and crystal packing, changing the counterion is a possible way to isolate the low spin state and characterize it by X-ray diffraction. Consequently we synthesized salts of [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ with four counterions in addition to the previously reported10 PF6−; trifluoromethanesulfonate (OTf−), tetrafluoroborate (BF4−), hexafluoroantimonate (SbF6−) and tetrakis[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]borate ([BArF4]−). Of four newly synthesized salts, the IR spectra of the BF4− and SbF6− salts show multiple carbonyl stretches at room temperature, while the for the OTf− and [BArF4]− (and previouly synthesized PF6−) salts, only a single carbonyl stretch is apparent (Fig. 1).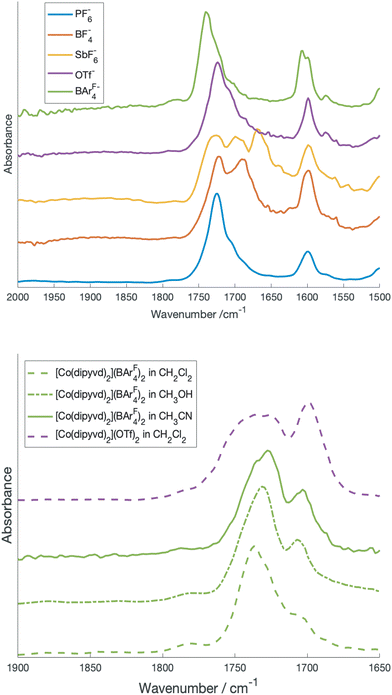 | ||
| Fig. 1 Top: carbonyl region of the IR spectrum of crystalline [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ salts. Bottom: carbonyl region of [Co(dipyvd)2]2+(BArF4)2 and [Co(dipyvd)2]2+(OTf)2 in solution. | ||
Previous studies have shown that the carbonyl stretching frequency of 6-oxoverdazyls is sensitive to changes in electron density on the verdazyl ring, in particular resulting from metal coordination and oxidation/reduction.13,14 Consequently the presence of multiple carbonyl stretches for the BF4− and SbF6− salts suggests the coexistence of valence tautomers in the solid at ambient temperatures, though other causes, such as crystal packing should be ruled out.
For the BF4−, SbF6−, [BArF4]− and possibly the triflate salts, magnetic measurements reveal a decrease in χ·T with temperature consistent with a valence tautomeric transition. In all cases this transition is incomplete, χ·T reaching low temperature plateau values of 0.56, 0.5 and 1.1 for the BF4−, SbF6− and [BArF4]− salts respectively, while the triflate transition only occurs below 150 K and does not reach a plateau above 50 K. Plots of χ·T vs. T for the solid samples are shown in Fig. 2.
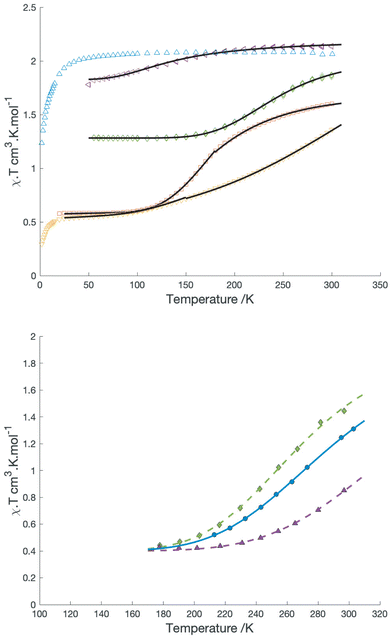 | ||
| Fig. 2 Top: χT vs T for different salts of [Co(dipyvd)2]2+: PF6− (blue), SbF6−(yellow) BF4− (red), OTf− (purple), BArF4−(green). Black solid lines are the best fits to the simple equilibrium model described in the text. Bottom: plots of χ·T vs. T in solution for [Co(dipyvd)2]2+(BArF4)2 in dichloromethane (green), [Co(dipyvd)2]2+(PF6)2 in acetonitrile (blue) (data from ref. 4) and [Co(dipyvd)2]2+(OTf)2 in dichloromethane (purple). Lines are best fits to the model in the text. | ||
Neither the triflate, nor the [BArF4]− salt gave crystals amenable to X-ray analysis, so our understanding of these structures is more limited; however, X-ray quality crystals could be obtained from the PF6−, BF4− and SbF6− salts. The PF6− salt was reported previously.10 Unit cell parameters for the BF4− and SbF6− salts are reported in Table 1.
| [Co(dipyvd)2](BF4)2 | [Co(dipyvd)2](BF4)2 | [Co(dipyvd)2](SbF6)2 | [Co(dipyvd)2](SbF6)2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCDC deposition number | 2332798 | 2332825 | 2332770 | 2332805 |
| Measurement temperature/K | 250 | 150 | 300 | 150 |
| Crystal system | Orthorhombic | Orthorhombic | Monoclinic | Monoclinic |
| Space group | Fddd | Fddd | P21/c | P21/c |
| a | 13.1032(8) | 13.0663(16) | 9.0686(7) | 9.1759(10) |
| b | 17.2017(10) | 17.1914(18) | 29.208(2) | 28.242(3) |
| c | 30.254(2) | 29.810(7) | 16.0218(12) | 15.6923(16) |
| α | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| β | 90 | 90 | 103.966(2) | 103.842(2) |
| ɣ | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| Z | 8 | 8 | 4 | 4 |
| R 1 | 8.44 | 8.44 | 7.76 | 6.36 |
The BF4− salt crystallizes in the orthorhombic space group Fddd with the cation centered on (and thus disordered about) the intersection of three perpendicular twofold axes. At 250 K, the verdazyl ring is essentially planar; the deviation of the verdazyl ring atoms from their mean plane is 0.03 Å. When the temperature is reduced to 150 K the deviation of the verdazyl atoms from their mean plane increases to 0.13 Å and the average metal–ligand bond length drops from 2.019 to 1.971 Å. Between 150 K and 100 K the crystal appears to undergo a phase change and at 100 K the structure can no longer be accurately determined. These observations suggest a transition to a low spin configuration of the metal ion and electron transfer to the ligand consistent with the magnetic data, but, because of the orientational disorder of the molecules about the twofold axes of the spacegroup, they do not provide insight into the localized or delocalized structure of the low spin state.
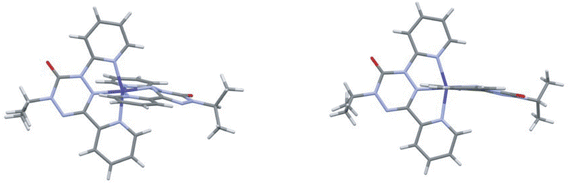
The SbF6− salt crystallizes from dichloromethane/acetonitrile in the monoclinic space group P21/c. There are three anion sites; one is located on a crystallographic inversion center and thus has a site occupancy of 0.5. To compensate for this fractional occupancy one of the remaining anion sites is half occupied by CH2Cl2 solvent. At 300 K one of the anions shows some rotational disorder, but this is no longer apparent at 150 K. The cation has two distinct ligands with no obvious orientational disorder. The two ligands have different geometries. In one ligand the central tetrazane ring is planar and the ring is relatively symmetric. For the second ligand the tetrazane ring is distinctly puckered and there is a pronounced bond length alternation consistent with an anti-aromatic 8π electron configuration. These differences become more pronounced at 150 K. Structures of the SbF6− salt at 300 K and 150 K are shown in Fig. 3.
The (IUPAC) atomic numbering scheme for the ligand is shown in Scheme 1. Details of the coordination geometries of the metal ion, along with other structures for comparison are listed in Table 2. Similarly, selected geometrical parameters of the ligands, along with parameters from related species, are listed in Table 3.
| Substance | [Co(dipyvd)2](SbF6)2 | [Co(dipyvd)2](SbF6)2 | [Co(dipyvd)2](BF4)2 | [Co(dipyvd)2](BF4)2 | [Co(dipyvd)2](PF6)2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) a a |
[Co(terpy)2] (BF4)2b | [Co(terpy)2] (BF4)2b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Data from ref. 4. b Data from ref. 24. c Determined using Octadist.16Σ and Θ are measures of distortion from an ideal octahedral geometry. | |||||||
| Temp./K | 300 | 150 | 250 | 150 | 150 | 375 | 100 |
| Mean Co-N distance | 2.019 | 1.938 | 2.019 | 1.971 | 2.120 | 2.115 | 2.031 |
| Σ | 111.0 | 85.0 | 108.3 | 96.9 | 139.1 | 120 | 90.4 |
Θ
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 15,16 15,16 |
356.4 | 289.3 | 347.8 | 344.4 | 440.0 | 387 | 305 |
| Parameter (IUPAC numbering) – see Scheme 1 | [Co(dipyvd)2] (SbF6)2 (radical ligand) | [Co(dipyvd)2] (SbF6)2 (anionic ligand) | [Co(dipyvd)2] (SbF6)2 (radical ligand) | [Co(dipyvd)2] (SbF6)2 (anionic ligand) | [Co(dipyvd)2] (PF6)a | dipyvdHb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Data from ref. 4. b Data from ref. 24. c Mean distance of the verdazyl ring atoms from their own mean plane. d Sum of bond angles around the N–H nitrogen. | ||||||
| Temp./K | 300 | 300 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 300 |
| N4–N5 | 1.355(9) | 1.383(9) | 1.359(5) | 1.415(6) | 1.425(3) | 1.434(3) |
| C3–N4 | 1.335(9) | 1.35(1) | 1.326(6) | 1.375(6) | 1.357(5) | 1.373(3) |
| N2–C3 | 1.314(8) | 1.32(1) | 1.310(6) | 1.309(7) | 1.284(3) | 1.282(3) |
| N1–N2 | 1.351(10) | 1.36(1) | 1.358(6) | 1.377(7) | 1.415(5) | 1.410(3) |
| Planarityc | 0.018 | 0.023 | 0.016 | 0.081 | 0.13 | 0.172 |
| Sum of bond angles of coordinated atom | 360.0 | 355.3 | 360.0 | 340.1 | 338.9 | 334.9d |
The structure of the SbF6− salt along with the three carbonyl stretches in the IR of this species (one for the S = 3/2 tautomer, the other two for the distinct ligands of the S = 1/2 tautomer) provides strong evidence that the structure of the low spin state is localized in at least this crystal structure, but considering the small energy differences between different electronic structures and geometries in spin transition systems, it is still possible that the valence tautomer is delocalized in solution.17 A more detailed investigation of the solution IR spectra as a function of solvent helps resolve this issue. In particular since [BArF4]− is a very weakly-coordinating anion, solutions of this salt are expected to show minimal ion pairing effects and reflect just cation solvent interaction.
Fig. 1b shows the carbonyl region of the IR for the [BArF4]− salt in the solvents dichloromethane, acetonitrile, and methanol along with the triflate salt in dichloromethane. In particular for acetonitrile there are prominent maxima in the spectrum at 1725 and 1700 cm−1 and more detailed inspection reveals a shoulder at 1740 cm−1. In comparison, in dichloromethane, there is one prominent C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretch at 1740 cm−1 and the peaks at 1725 cm−1 and 1700 cm−1 are reduced to inconspicuous shoulders. Since the [BArF4]− salt, which is largely high spin in the solid state at ambient temperature, shows only the peak at 1740 cm−1 in the solid state, this is likely associated with the high spin tautomer, while the two lower frequency peaks are from the low spin species. The presence of two carbonyl stretches associated with the low spin species is consistent with a localized structure with the peak at 1725 cm−1 due to the radical ligand, while that at 1700 cm−1 due to the anionic ligand. Vibrational frequencies of mixed valence species can provide insight into the strength of the interaction between the two redox sites (and thus the Robin-Day classification). In particular Atwood and Geiger18 developed a charge distribution parameter for mixed valence species based on IR measurements, Δρ, defined as:
O stretch at 1740 cm−1 and the peaks at 1725 cm−1 and 1700 cm−1 are reduced to inconspicuous shoulders. Since the [BArF4]− salt, which is largely high spin in the solid state at ambient temperature, shows only the peak at 1740 cm−1 in the solid state, this is likely associated with the high spin tautomer, while the two lower frequency peaks are from the low spin species. The presence of two carbonyl stretches associated with the low spin species is consistent with a localized structure with the peak at 1725 cm−1 due to the radical ligand, while that at 1700 cm−1 due to the anionic ligand. Vibrational frequencies of mixed valence species can provide insight into the strength of the interaction between the two redox sites (and thus the Robin-Day classification). In particular Atwood and Geiger18 developed a charge distribution parameter for mixed valence species based on IR measurements, Δρ, defined as:
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O at 1733 cm−1) and [Co(dipyvd)2]+ (C
O at 1733 cm−1) and [Co(dipyvd)2]+ (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O at 1685 cm−1)10 as ν′ox and ν′red respectively, and the values from the solution IR, 1725 cm−1 and 1700 cm−1 as νmeansox and νmeansred, we obtain Δρ = 0.24 indicating significant interaction between the ligands; i.e. a class II system. This analysis must be treated with a little caution however; unlike the related species [Ni(dipyvd)2]n+ and [Zn(dipyvd)2]n+ for which the C
O at 1685 cm−1)10 as ν′ox and ν′red respectively, and the values from the solution IR, 1725 cm−1 and 1700 cm−1 as νmeansox and νmeansred, we obtain Δρ = 0.24 indicating significant interaction between the ligands; i.e. a class II system. This analysis must be treated with a little caution however; unlike the related species [Ni(dipyvd)2]n+ and [Zn(dipyvd)2]n+ for which the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching frequencies are essentially invariant in solid and solution, the C
O stretching frequencies are essentially invariant in solid and solution, the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretches for [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ species are quite sensitive to the molecular environment, as can be seen by comparison of the solid and solution IR spectra. Even in solution, though the [BArF4]− salt seems to show the same three C
O stretches for [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ species are quite sensitive to the molecular environment, as can be seen by comparison of the solid and solution IR spectra. Even in solution, though the [BArF4]− salt seems to show the same three C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching frequencies at different intensities depending on solvent, examination of the OTf− spectrum indicates the C
O stretching frequencies at different intensities depending on solvent, examination of the OTf− spectrum indicates the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretch can also depend upon counterion.
O stretch can also depend upon counterion.
A class II Mixed valence system would be expected to show an intervalence charge transfer band; however, the overlapping spectra of the S = 3/2 and S = 1/2 tautomers make the identification of bands associated with the individual forms more complex. Inspection of the VT-vis-NIR spectra reveal that the relatively sharp peak at 617 nm gains intensity with lower temperatures and thus is associated with the low spin tautomer, while the broad feature at 560 nm loses intensity and is thus associated with the high spin tautomer. Surprisingly perhaps, the broad feature at 725 nm remains relatively unchanged with temperature. Approximate spectra for the low and high spin species can be derived by deconvolution using the concentrations determined by solution magnetic susceptibility. These are shown in Fig. 4.
As for the solution IR spectrum (above) the spectrum for the low spin tautomer can be compared with several cobalt(III) reference compounds; the terpyridine analog, [Co(terpy)2]3+ along with the reduced species [Co(dipyvd)2]+ and the oxidized species [Co(dipyvd)2]3+. All three reference compounds are low spin Co(III). Since [Co(terpy)2]3+ is essentially transparent in the visible aside from weak d–d transitions19 the visible transitions in the two corresponding dipyvd species are almost certainly ligand or charge transfer (CT) based. For the trication, the bandshape and vibronic structure are similar to the intraligand transitions in the Ni2+ and Zn2+ analogs11 and thus likely arises from a similar transition, that is, excitation into the verdazyl SOMO. The peak maximum is somewhat redshifted from the Zn2+ and Ni2+ species – this is probably due to the greater charge on the cation lowering the energy of the verdazyl SOMO. The broad absorbance in the spectrum of [Co(dipyvd)2]+ at 630 nm however likely arises from a ligand–metal charge transfer transition (LMCT) since the coordinated leucoverdazyl ligand itself only shows a tail into the visible range.11 The low temperature spectrum arising from deconvolution of the VT spectra shows both the sharper intra-ligand transitions associated with a coordinated radical and a broad band similar to the LMCT band observed for the coordinated anion. The expected intervalence charge transfer (IVCT) band probably overlaps with the LMCT band and may contribute to its asymmetric appearance.
The S = 3/2 state
Like the low spin state, the high spin state was incompletely characterized in our previous report. Crystallographic cobalt-ligand bond lengths and octahedral distortion parameters are comparable with other high spin octahedral cobalt species (Table 2), while the IR data and ligand geometries are consistent with radical ligands (Table 3). The problem is that traditional coupling of the radical ligands (S = 1/2) to the high spin cobalt ion (S = 3/2) would be expected to give either a sextet (S = 5/2, ferromagnetic coupling) or doublet (S = 1/2, antiferromagnetic coupling) while the high field EPR and magnetism data reported previously,10 along with magnetization vs. field measurements at low temperature (ESI†) are all consistent with a spin quartet (S = 3/2) with significant zero field splitting (D = +16 cm−1). A similar phenomenon was observed in the oxolene valence tautomer Co(3,5-DBSQ)2(TMED), for which Pierpont et al. proposed that the coupling was in fact weak, and all states were roughly equally populated.20 Other evidence suggests that coupling of high spin Co2+ to single semiquinones21 or verdazyl radicals22 is ferromagnetic, though as Gransbury and co-workers point out, the coupling is anisotropic with spin–orbit coupling playing a significant role, and is likely extremely dependent on subtle geometry changes.21 Furthermore, Robert and co-workers’ computational studies on this species23 provided the important insight that in a paramagnetic ligand field capable of two spin states, the metal ion cannot necessarily be described as purely ‘low spin’ or ‘high spin’ (a phenomenon labeled spinmerism). Despite this complexity we considered that a better understanding of the system might start through determination of traditional ligand field parameters and comparison with similar systems but with closed shell ligand manifolds.Earlier studies indicate that the ligand field splittings of [Ni(dipyvd)2]2+ and [Ni(terpy)2]2+ are comparable.11 Consequently, it is reasonable to assume that the electronic structures of [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ and [Co(terpy)2]2+ will show some similarity, at least with regard to the metal ion, and that [Co(terpy)2]2+ will provide a useful point of comparison.
[Co(terpy)2]2+ is a spin crossover compound with a high spin (S = 3/2) and low spin (S = 1/2) state in equilibrium depending upon the temperature and counterion.24–26 The coordination geometries of both the high spin and low spin states are detailed in Table 2. Several authors have examined the electronic structure of both the high spin and low spin states of [Co(terpy)2]2+. In particular, Kremer and co-workers24 estimated the ligand field splitting, 10Dq, for the high spin configuration as 13![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 500 cm−1, while for the low spin configuration 10Dq was reported as 15
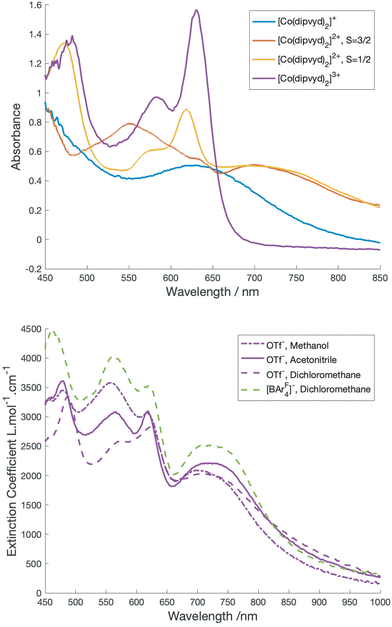
500 cm−1, while for the low spin configuration 10Dq was reported as 15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cm−1. The latter number was also reported by Krivokapic et al.25,26 As previously mentioned,10 the geometry of the high spin state of [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ is more consistent with the geometry of the high spin rather than the low spin structure of [Co(terpy)2]2+. However, determining other parameters that can further clarify the electronic structure is more challenging. Optical transitions that can confirm the ligand field splitting are obscured by intraligand transitions as well as the spectrum of the S = 1/2 tautomer. As we did for the nickel analog, we turned to X-ray spectroscopy to provide better insight. Fig. 5 shows L-edge X-ray absorption spectra (XAS) recorded on [Co(dipyvd)2]2+(PF6−)2 and [Co(dipyvd)2]2+(SbF6−)2 at 300 K as well as L edge XAS spectra of [Co(terpy)2]2+(PF6−)2 and [Co(dipyvd)2]+(PF6−) as reference compounds.
000 cm−1. The latter number was also reported by Krivokapic et al.25,26 As previously mentioned,10 the geometry of the high spin state of [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ is more consistent with the geometry of the high spin rather than the low spin structure of [Co(terpy)2]2+. However, determining other parameters that can further clarify the electronic structure is more challenging. Optical transitions that can confirm the ligand field splitting are obscured by intraligand transitions as well as the spectrum of the S = 1/2 tautomer. As we did for the nickel analog, we turned to X-ray spectroscopy to provide better insight. Fig. 5 shows L-edge X-ray absorption spectra (XAS) recorded on [Co(dipyvd)2]2+(PF6−)2 and [Co(dipyvd)2]2+(SbF6−)2 at 300 K as well as L edge XAS spectra of [Co(terpy)2]2+(PF6−)2 and [Co(dipyvd)2]+(PF6−) as reference compounds.
Not surprisingly considering the magnetic data, the SbF6− salt shows features associated with both Co3+ and Co2+ metal centers. In fact, the major features of the spectrum can be largely reproduced by a combination of the two reference spectra. More surprising is that the spectrum of the PF6− salt at 300 K also shows both Co3+ and Co2+ features, despite there being no evidence for population of the low spin state in the PF6− salt at this temperature. The PF6− salt was further examined at 2 K by XAS and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD). At low temperatures, the Co3+ features in the PF6− salt XAS spectrum become more prominent, though in prior studies there was no evidence for the low spin species in the low temperature EPR and magnetic data.10 There are two possible explanations for this phenomenon. The most likely results from the fact that X-ray spectroscopy is largely a surface phenomenon. At the surface of samples of [Co(dipyvd)2]2+(PF6−)2 the lattice forces that prevent relaxation of the molecules to the S = 1/2 state are reduced. Alternatively, this could be an example of Soft X-ray Induced Excited Spin State Trapping (SoXIESST), though this phenomenon has not been previously observed at ambient temperature.27
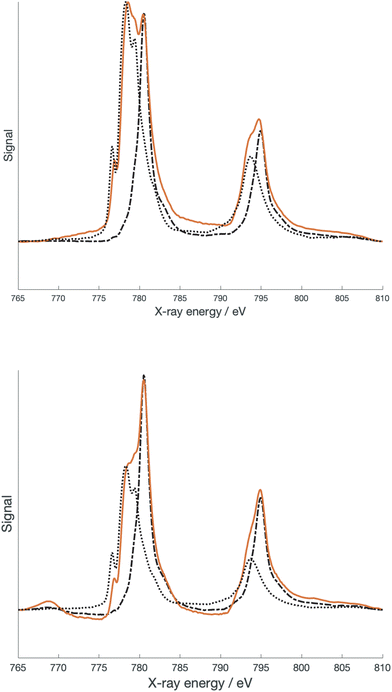
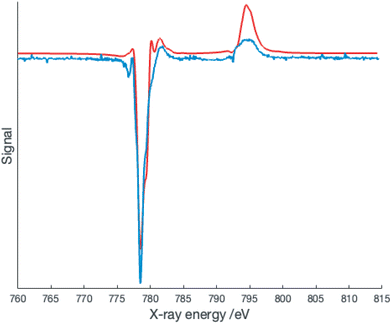
The presence of overlapping signals complicates the simulation of the XAS spectra; however, the XMCD signal is expected to arise almost entirely from the Co2+ species and thus simulation of this signal may provide better insight. The XMCD data collected at 2 K is shown in Fig. 6.
Surprisingly, the best fit to the XMCD signal is obtained with 10Dq = 2.0 eV (16![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 100 cm−1) and Slater–Condon integrals scaled by a factor of 0.69 corresponding to a Racah B parameter of 670 cm−1. These parameters are more consistent with a low spin Co2+ center, but this is inconsistent with the geometric parameters determined at 150 K, and more crucially the EPR spectrum at 5 K.10,24 Several recent publications have provided evidence for low spin cobalt ions in cobalt oxolene valence tautomers.6–8 A quartet state can arise from ferromagnetic coupling of a low spin Co2+ with the two radicals, and thus our data suggests an equilibrium population of two distinct quartet states. Alternatively this could be a manifestation of the spinmerism phenomenon described by Robert et al.23 Initial density functional calculations on the quartet state of [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ using the B3LYP functional favor the low spin Co2+ geometry as an energy minimum, but since the results of DFT calculations on VT systems are critically dependent upon the functional used, and the calculations must also take into account intermolecular interactions,28 we do not put much weight on this result; rather, we consider the complexity of this system requires a separate, dedicated computational study.
100 cm−1) and Slater–Condon integrals scaled by a factor of 0.69 corresponding to a Racah B parameter of 670 cm−1. These parameters are more consistent with a low spin Co2+ center, but this is inconsistent with the geometric parameters determined at 150 K, and more crucially the EPR spectrum at 5 K.10,24 Several recent publications have provided evidence for low spin cobalt ions in cobalt oxolene valence tautomers.6–8 A quartet state can arise from ferromagnetic coupling of a low spin Co2+ with the two radicals, and thus our data suggests an equilibrium population of two distinct quartet states. Alternatively this could be a manifestation of the spinmerism phenomenon described by Robert et al.23 Initial density functional calculations on the quartet state of [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ using the B3LYP functional favor the low spin Co2+ geometry as an energy minimum, but since the results of DFT calculations on VT systems are critically dependent upon the functional used, and the calculations must also take into account intermolecular interactions,28 we do not put much weight on this result; rather, we consider the complexity of this system requires a separate, dedicated computational study.
Other spectral measurements also hint at the complexity of the electronic structure of this species. Based on the analysis of the solution IR for [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ [BArF4−]2 (above), the solvated [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ cations exhibit a single C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretch at 1740 cm−1. This is significantly higher than the C
O stretch at 1740 cm−1. This is significantly higher than the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretch in other [M(dipvyd)2]2+ complexes (C
O stretch in other [M(dipvyd)2]2+ complexes (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O at 1725 cm−1, M
O at 1725 cm−1, M![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) Fe,12 Ni, Zn11) and also in [Co(dipyvd)2]3+, (C
Fe,12 Ni, Zn11) and also in [Co(dipyvd)2]3+, (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O at 1733 cm−1). The 1740 cm−1 stretching frequency is maintained in the solid state for the [BArF4]− salt, but not for the triflate or PF6− salt which both have a single C
O at 1733 cm−1). The 1740 cm−1 stretching frequency is maintained in the solid state for the [BArF4]− salt, but not for the triflate or PF6− salt which both have a single C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretch at 1725 cm−1 in line with observations for other [M(dipyvd)2]2+ species. The verdazylium cations derived from oxidation of 1,5-diisopropyl verdazyls have C
O stretch at 1725 cm−1 in line with observations for other [M(dipyvd)2]2+ species. The verdazylium cations derived from oxidation of 1,5-diisopropyl verdazyls have C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretches in 1740 cm−1 region,29 suggesting that in solution, or in the environment provided by the [BArF4]− counterions, the high spin form of [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ has some degree of positive charge on the verdazyl ligands. It is possible that this reflects contributions to the electronic structure of this system where the metal ion is formally d8 Co(I). Such electronic structures are still consistent with an overall spin of 3/2 and have a precedent in that the related reduced species, [Co(terpy)2]+, is best described as a Co(I) system,30 but more investigation is clearly necessary.
O stretches in 1740 cm−1 region,29 suggesting that in solution, or in the environment provided by the [BArF4]− counterions, the high spin form of [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ has some degree of positive charge on the verdazyl ligands. It is possible that this reflects contributions to the electronic structure of this system where the metal ion is formally d8 Co(I). Such electronic structures are still consistent with an overall spin of 3/2 and have a precedent in that the related reduced species, [Co(terpy)2]+, is best described as a Co(I) system,30 but more investigation is clearly necessary.
Equilibrium and environment
With (somewhat) better descriptions of the two valence tautomers, we turned to examine possible factors that influence the equilibrium between them. The solvent dependence of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching frequency has already been noted. Solution magnetic susceptibility of the [BArF4]− salt in dichloromethane and acetonitrile (as determined by Evans method) is shown in Fig. 2b. Also shown is the data for the triflate salt in dichloromethane. The magnetic data was fitted to a simple equilibrium model31 to give estimates of ΔH and ΔS listed in Table 4.
O stretching frequency has already been noted. Solution magnetic susceptibility of the [BArF4]− salt in dichloromethane and acetonitrile (as determined by Evans method) is shown in Fig. 2b. Also shown is the data for the triflate salt in dichloromethane. The magnetic data was fitted to a simple equilibrium model31 to give estimates of ΔH and ΔS listed in Table 4.
| System | ΔH kJ mol−1 | ΔS J K−1 |
|---|---|---|
| [Co(dipyvd)2] (PF6)2 | 18 | 66 |
| CH3CN solution | ||
| [Co(dipyvd)2] (BArF4)2 | 17 | 65 |
| CH2Cl2 solution | ||
| [Co(dipyvd)2] (OTf)2 | 19 | 56 |
| CH2Cl2 solution | ||
| [Co(dipyvd)2] (BArF4)2 | 15 | 57 |
| [Co(dipyvd)2] (BF4)2 | 7.9 (<170 K) | 40 (<170 K) |
| 6.0 (>170 K) | 33 (>170 K) | |
| [Co(dipyvd)2] (SbF6)2 | 4.4 (<200 K) | 11(<200 K) |
| 9.7 (>200 K) | 20 (>200 K) | |
| [Co(dipyvd)2] (OTf)2 | 3.6 | 24 |
Fig. 4b shows the vis-NIR spectra of the triflate and [BArF4]− salt as a function of solvent. The magnetic data, along with the IR and vis-NIR spectra all indicate that the low spin form is slightly more favored by polar solvents. This is somewhat expected from the dipole generated by localization of charge on one ligand. However, this description is simplistic. The low spin state is not exceptionally favored in methanol, even though hydrogen bonding might be expected to stabilize the development of negative charge on the carbonyl carbon. Conversely in the less polar solvent dichloromethane, the equilibrium is strongly influenced by counterion, with triflate favoring the S = 1/2 form. It seems likely that ion pairing plays a big role in this behavior but at first glance the presence of negatively charged ions near the ligands would disfavor the development of a negative charge on the ligand.
The entropy associated with the VT transition is lower than that typically observed for the cobalt-oxolene valence tautomers.31,32 For the oxolene systems, the increase in entropy is generally attributed to increased vibrational entropy as a result of the lower force constants for the Co2+-ligand bonds. The lower entropy change in the present system probably reflects greater vibrational entropy associated with the more flexible geometry of the ligand in the low spin state.
The large change in ligand geometry upon tautomerization is also likely responsible for the variety of behavior observed in the solid state from entirely high spin throughout the temperature range (PF6−) to mostly low spin (SbF6−). In particular, the fact that in general the tautomeric transition does not go to completion at low temperature in the solid reflects the geometric requirements of the reduced ligand. Similar to the approach we used for the solution data, a simple equilibrium model can be used to fit the magnetic data in the solid state. For the [BArF4]− salt and triflate, this model provides acceptable fits for the entire range between 50 and 300 K. For the SbF6− and BF4− salts, such a simple model is inadequate, but reasonable fits are obtained by fitting the data in two separate temperature ranges. Values for ΔH and ΔS obtained from these fits are listed in Table 4; however, as noted by LaBute and co-workers,33 such fits assume that valence tautomerization occurs randomly throughout the sample, whereas in practice there may be clustering of tautomers as a result of intermolecular interactions within the lattice. Consequently, the values should be treated with a little skepticism. Nevertheless, the reduction in the apparent ΔH and ΔS at higher temperatures in the BF4− salt indicates a level of cooperativity between molecules which suggests the possibility of more abrupt transitions and hysteresis with careful tuning of this or related systems.
Conclusion
More extensive studies on the [Co(dipyvd)2]2+ system have provided more information on the two VT states in equilibrium. In particular, the low spin state has predominantly low spin Co3+ character with a localized, mixed valent ligand manifold and some degree of interaction between the ligands. The high spin state is a spin quartet, but a fully satisfactory description of its electronic structure is still elusive, with different analytical methods suggesting high spin Co2+, low spin Co2+ and even possibly Co+ character. The geometry changes associated with the VT transformation result in lower entropy changes compared to the more common oxolene systems, but suggest a potential for cooperative behavior in the solid state, though such behavior has not yet been realized. Together these observations suggest avenues for further study of this system, along with potential design criteria for tuning VT behavior of this and other verdazyl based coordination compounds.Experimental
General
DipyvdH, [Co(dipyvd)2](PF6) and [Co(dipyvd)2](PF6)2 were synthesized as reported previously.10 Other chemicals were purchased from commercial suppliers.Low temperature X-ray absorption spectra and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism spectra were recorded at the BOREAS beamline, ALBA synchrotron, Barcelona, Spain. Additional X-ray spectra were recorded at the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory (SSRL), Stanford, CA USA. Simulations of X-ray spectra were performed with the frontend program CRISPY34 and the package QUANTY.35
Spectroscopic characterization of [Co(dipyvd)2]3+
This species was generated electrochemically in solution from [Co(dipyvd)2](PF6)2 in acetonitrile using a Pt-honeycomb working electrode and 0.1 M Bu4N+PF6 supporting electrolyte. Formation of the cation was monitored by UV-vis spectroscopy. The C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O region of the IR spectrum was obtained by examination of the same solution when the oxidation was complete; a single C
O region of the IR spectrum was obtained by examination of the same solution when the oxidation was complete; a single C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretch was observed at 1733 cm−1.
O stretch was observed at 1733 cm−1.
[Co(dipyvd)2](OTf)2
Cobalt triflate (72 mg, 0.2 mmol) and dipyvdH (118 mg, 0.4 mmol) were combined in 5 mL acetonitrile and the mixture stirred vigorously while open to the air at ambient temperature for 48 h. After this period crystallization was induced by diffusion of diethyl ether into the solution. The dark purple crystals were isolated by filtration: 121 mg, 64%, IR (ATR) 1722 cm−1 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 1597, 1468, 1438, 1260, 1220, 1142, 1028, 773, 706 cm−1; calcd for:C32H30CoF6N12O8S2·2 H2O C, 39.07; H, 3.48; N, 17.09. Found: C 39.01, H 3.08, N 16.53.
O), 1597, 1468, 1438, 1260, 1220, 1142, 1028, 773, 706 cm−1; calcd for:C32H30CoF6N12O8S2·2 H2O C, 39.07; H, 3.48; N, 17.09. Found: C 39.01, H 3.08, N 16.53.
[Co(dipyvd)2]X2
[Co(dipyvd)2](OTf)2 and the sodium or ammonium salt of the counterion were both dissolved in the minimum amount of methanol and the solutions combined. Distilled water was added to the resulting solution. If precipitation did not occur immediately, methanol was removed by rotary evaporation until precipitation occurred. The precipitate of the salt was removed by filtration and dried under vacuum, then recrystallized as described below.[Co(dipyvd)2](BF4)2
[Co(dipyvd)2](OTf)2 (18.0 mg, 0.02 mmol) and NaBF4 (10 mg, 0.1 mmol) gave 6.0 mg, (0.007 mmol, 36%) of [Co(dipyvd)2](BF4)2 recrystallized by vapor diffusion of ether into an acetonitrile solution. IR (ATR) 1725 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 1691 (C
O), 1691 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 1603, 1595, 1481, 1463, 1437, 1276, 1247, 1217, 1157, 1051 (B–F), 1030 (B–F), 785, 630 cm–1. Calcd for: C30H30B2CoF8N12O2: C, 43.77; H, 3.67; N, 20.42. Found: C, 43.48; H, 3.74; N 20.16. A single crystal of dimensions 0.089 × 0.123 × 0.584 mm was mounted for examination by crystallography at 150 K. A second crystal of dimensions 0.015 × 0.204 × 0.298 mm was mounted for examination by crystallography at 150 K. Unit cell dimensions for both data collections are listed in Table 1. Full details of data collection and refinement are available from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre in .cif format.
O), 1603, 1595, 1481, 1463, 1437, 1276, 1247, 1217, 1157, 1051 (B–F), 1030 (B–F), 785, 630 cm–1. Calcd for: C30H30B2CoF8N12O2: C, 43.77; H, 3.67; N, 20.42. Found: C, 43.48; H, 3.74; N 20.16. A single crystal of dimensions 0.089 × 0.123 × 0.584 mm was mounted for examination by crystallography at 150 K. A second crystal of dimensions 0.015 × 0.204 × 0.298 mm was mounted for examination by crystallography at 150 K. Unit cell dimensions for both data collections are listed in Table 1. Full details of data collection and refinement are available from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre in .cif format.
[Co(dipyvd)2](BArF4)2
[Co(dipyvd)2](OTf)2 18 mg, 0.02 mmol, and NaBArF4 (34 mg, 0.04 mmol) gave 20.7 mg (0.009 mmol, 44%) of [Co(dipyvd)2](BArF4)2, recrystallized by layering a dichloromethane solution with heptane and diffusion of the layers. IR (ATR) 1740 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 1606, 1464, 1440, 1353, 1274, 1110 (C–F), 887, 838, 775, 743, 711, 682, 669 cm−1. Calcd for: C94H54B2CoF48N12O2: C, 47.52; H, 2.29; N, 7.07. Found: C, 47.37; H, 2.18; N 6.48.
O), 1606, 1464, 1440, 1353, 1274, 1110 (C–F), 887, 838, 775, 743, 711, 682, 669 cm−1. Calcd for: C94H54B2CoF48N12O2: C, 47.52; H, 2.29; N, 7.07. Found: C, 47.37; H, 2.18; N 6.48.
[Co(dipyvd)2](SbF6)2
Cobalt triflate (72 mg, 0.2 mmol) and dipyvdH (118 mg, 0.4 mmol) were combined in 5 mL acetonitrile and the mixture stirred vigorously while open to the air at ambient temperature for 48 h, after which the solvent was removed by evaporation. The residue was redissolved in methanol and filtered before adding a solution of 108 mg NaSbF6 in water to the filtrate. Methanol was removed by rotary evaporator and the resulting precipitate removed by filtration. The precipitate was redissolved in acetonitrile and crystallization induced by diffusion of dichloromethane vapor into the solution giving the product as dark green crystals. (25.9 mg, 11% from Co(OTf)2) IR (ATR) 1725 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 1699 (C
O), 1699 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 1669 (C
O), 1669 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 1599, 1438, 1367, 1274, 1244, 1211, 1148, 1017, 779, 734, 659 cm−1 (Sb-F). Calcd for: C30H30CoF12N12O2Sb2·(CH2Cl2)0.5: C, 31.48; H, 2.69; N, 14.45. Found: C, 31.59; H, 2.72; N 14.31. A single crystal of dimensions 0.4 × 0.1 × 0.1 mm was mounted for examination by crystallography at 300 K and 150 K. Unit cell dimensions are listed in Table 1. Full details of data collection and refinement are available from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre in .cif format.
O), 1599, 1438, 1367, 1274, 1244, 1211, 1148, 1017, 779, 734, 659 cm−1 (Sb-F). Calcd for: C30H30CoF12N12O2Sb2·(CH2Cl2)0.5: C, 31.48; H, 2.69; N, 14.45. Found: C, 31.59; H, 2.72; N 14.31. A single crystal of dimensions 0.4 × 0.1 × 0.1 mm was mounted for examination by crystallography at 300 K and 150 K. Unit cell dimensions are listed in Table 1. Full details of data collection and refinement are available from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre in .cif format.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
Financial support was provided by the National Science Foundation (CHE-1900491 to DJRB). Magnetic data for [Co(dipyvd)2](BArF4)2 and [Co(dipyvd)2](OTf)2 were recorded on instrumentation supported by the National Science Foundation (grant MRI-1827433). Crystallographic data for [Co(dipyvd)2](SbF6)2 were recorded with instrumentation purchased with support from the US Department of Defense (grant W911NF1910520). We thank Dr Ghenadie Novitchi and CNRS-LNCMI (Grenoble, France) for collection of magnetic data on samples of [Co(dipyvd)2](BF4)2 and [Co(dipyvd)2](PF6)2. We thank Dr Jacques Pecaut (Université Grenoble Alpes) for X-ray crystallographic studies on [Co(dipyvd)2](BF4)2. Use of the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, is supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences under Contract No. DE-AC02-76SF00515.References
- C. G. Pierpont, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2001, 216–217, 99–125 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Tezgerevska, K. G. Alley and C. Boskovic, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2014, 268, 23–40 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Evangelio and D. Ruiz-Molina, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2005, 2005, 2957–2971 CrossRef.
- S. Klokishner, O. Reu and M. Roman, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021, 23, 21714–21728 RSC.
- S. I. Klokishner and O. S. Reu, Chem. Phys., 2003, 286, 115–126 CrossRef CAS.
- K. KC, T. Woods and L. Olshansky, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202311790 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Metzger, R. Dolai, S. Reh, H. Kelm, M. Schmitz, B. Oelkers, M. Sawall, K. Neymeyr and H.-J. Krüger, Chem. – Eur. J., 2023, 29, e202300091 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Mörtel, S. J. Goodner, J. Oschwald, A. Scheurer, T. Drewello and M. M. Khusniyarov, Dalton Trans., 2024, 53, 4098–4107 RSC.
- M. A. Hay, J. T. Janetzki, V. J. Kumar, R. W. Gable, R. Clérac, A. A. Starikova, P. J. Low and C. Boskovic, Inorg. Chem., 2022, 61, 17609–17622 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Fleming, D. Chung, S. Ponce, D. J. R. Brook, J. DaRos, R. Das, A. Ozarowski and S. A. Stoian, Chem. Commun., 2020, 56, 4400 RSC.
- C. Fleming, S. Vu, D. J. R. Brook, S. Agrestini, E. Pellegrin and J. DaRos, Front. Chem., 2023, 11 DOI:10.3389/fchem.2023.1295289.
- D. J. R. Brook, C. Fleming, D. Chung, C. Richardson, S. Ponce, R. Das, H. Srikanth, R. Heindl and B. C. Noll, Dalton Trans., 2018, 47, 6351–6360 RSC.
- S. D. J. McKinnon, B. O. Patrick, A. B. P. Lever and R. G. Hicks, Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 773–775 RSC.
- D. J. R. Brook, Comments Inorg. Chem., 2015, 35, 1–17 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Marchivie, P. Guionneau, J.-F. Letard and D. Chasseau, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B: Struct. Sci., 2005, 61, 25–28 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Ketkaew, Y. Tantirungrotechai, P. Harding, G. Chastanet, P. Guionneau, M. Marchivie and D. J. Harding, Dalton Trans., 2021, 50, 1086–1096 RSC.
- M. Parthey and M. Kaupp, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 5067–5088 RSC.
- C. G. Atwood and W. E. Geiger, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2000, 122, 5477–5485 CrossRef CAS.
- J. T. Yarranton and J. K. McCusker, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 12488–12500 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. W. Liang, T. Kroll, D. Nordlund, T.-C. Weng, D. Sokaras, C. G. Pierpont and K. J. Gaffney, Inorg. Chem., 2017, 56, 737–747 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. K. Gransbury, M.-E. Boulon, R. A. Mole, R. W. Gable, B. Moubaraki, K. S. Murray, L. Sorace, A. Soncini and C. Boskovic, Chem. Sci., 2019, 10, 8855–8871 RSC.
- T. M. Barclay, R. G. Hicks, M. T. Lemaire, L. K. Thompson and Z. Q. Xu, Chem. Commun., 2002, 1688–1689 RSC.
- P. Roseiro, N. B. Amor and V. Robert, ChemPhysChem, 2022, 23, e202100801 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Kremer, W. Henke and D. Reinen, Inorg. Chem., 1982, 21, 3013–3022 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Krivokapic, M. Zerara, M. L. Daku, A. Vargas, C. Enachescu, C. Ambrus, P. Tregenna-Piggott, N. Amstutz, E. Krausz and A. Hauser, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2007, 251, 364–378 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Enachescu, I. Krivokapic, M. Zerara, J. A. Real, N. Amstutz and A. Hauser, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 2007, 360, 3945–3950 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Poneti, M. Mannini, L. Sorace, P. Sainctavit, M.-A. Arrio, E. Otero, J. Criginski Cezar and A. Dei, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 1954–1957 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. K. Gransbury, M.-E. Boulon, S. Petrie, R. W. Gable, R. J. Mulder, L. Sorace, R. Stranger and C. Boskovic, Inorg. Chem., 2019, 58, 4230–4243 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. C. Haller, D. Chambers, R. Cheng, V. Chemistruck, T. F. Hom, Z. Li, J. Nguyen, A. Ichimura and D. J. R. Brook, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2015, 119, 10750–10760 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. England, E. Bill, T. Weyhermüller, F. Neese, M. Atanasov and K. Wieghardt, Inorg. Chem., 2015, 54, 12002–12018 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. M. Adams and D. N. Hendrickson, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1996, 118, 11515–11528 CrossRef CAS.
- C. G. Pierpont and O. S. Jung, Inorg. Chem., 1995, 34, 4281–4283 CrossRef CAS.
- M. X. LaBute, R. V. Kulkarni, R. G. Endres and D. L. Cox, J. Chem. Phys., 2002, 116, 3681–3689 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Retegan, Crispy: v0.7.4, 2019 Search PubMed.
- M. W. Haverkort, M. Zwierzycki and O. K. Andersen, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys, 2012, 85, 165113 Search PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Plot of magnetization vs. applied field between 2 and 5 K for [Co(dipyvd)2](PF6)2, XAS spectrum of [Co(dipyvd)2](PF6)2 recorded at 2 K. Full details of the structure determinations of [Co(dipyvd)2](SbF6)2 and [Co(dipyvd)2](BF4)2. CCDC 2332770, 2332798, 2332805 and 2332825. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4dt00465e |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |