Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Cobalt-based molecular electrocatalysis of nitrile reduction: evolving sustainability beyond hydrogen†
Simon N.
Child
a,
Radoslav
Raychev
a,
Nathan
Moss
a,
Benjamin
Howchen
a,
Peter N.
Horton
 b,
Christopher C.
Prior
a,
Vasily S.
Oganesyan
b,
Christopher C.
Prior
a,
Vasily S.
Oganesyan
 a and
John
Fielden
a and
John
Fielden
 *a
*a
aSchool of Chemistry, University of East Anglia, Norwich, NR4 7TJ, UK. E-mail: John.Fielden@uea.ac.uk
bUK National Crystallography Service, School of Chemistry, University of Southampton, Southampton, SO17 1BJ, UK
First published on 11th June 2019
Abstract
Two new cobalt bis-iminopyridines, [Co(DDP)(H2O)2](NO3)2 (1, DDP = cis-[1,3-bis(2-pyridinylenamine)] cyclohexane) and [Co(cis-DDOP)(NO3)](NO3) (2, cis-DDOP = cis-3,5-bis[(2-Pyridinyleneamin]-trans-hydroxycyclohexane) electrocatalyse the 4-proton, 4-electron reduction of acetonitrile to ethylamine. For 1, this reduction occurs in preference to reduction of protons to H2. A coordinating hydroxyl proton relay in 2 reduces the yield of ethylamine and biases the catalytic system back towards H2.
The last decade has seen an explosion of interest in molecular electrocatalysts for production of dihydrogen (HECs).1–5 Tremendous progress has been made in increasing speed,1,3 lowering overpotential,1,4 and understanding the mechanism of HECs.1,5 However, we are still some distance from molecule-based systems that can produce H2 at industrial scale, and at a cost low enough for hydrogen to play a major role in a nascent mixed energy vector economy. Thus, it is worth considering additional applications in sustainable chemistry for the knowledge and materials developed in molecular HEC research.
Efficient, fast, electrochemically driven manipulation of protons and hydrides is intrinsic to the performance of HECs.5 This implies that under appropriate conditions, many HECs or derivatives thereof will be active in organic reductions, where delivery of H atoms to the correct site is essential to achieving the desired product.6 Thus, exploring HECs as catalysts for organic chemistry could uncover new high value processes where the advantages of molecular catalysts – exquisite structural control, providing for unrivalled tuneability and selectivity – outweigh their drawbacks in cost and stability. Such processes could be reductions using sustainable reagents (i.e. acetic acid plus solar electricity) that avoid the need for high H2 pressures, high temperatures and enable control through adjustment of electrochemical potential. Moreover, for multi-electron processes, electrolysis driven by photovoltaics may prove more efficient than direct photoredox catalysis requiring multiple, reversible photoinduced electron transfers.7
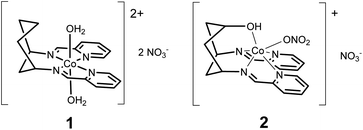
Herein, we present the electrocatalytic behaviour of two new cyclohexane-supported cobalt bis-pyridyl imine complexes: [Co(DDP)(H2O)2](NO3)2 (1) and [Co(cis-DDOP)(NO3)](NO3) (2) (Scheme 1). Cobalt bis-pyridyl imines are known as low-cost, easily accessible molecular HECs,2b but we find that in acetonitrile electrolyte with weak (acetic) acid, 1 is a better catalyst for the 4 proton, 4 electron reduction of acetonitrile to ethylamine than the kinetically more straightforward two-electron reduction of protons to dihydrogen. Introduction of a coordinating hydroxyl group, and resulting change of geometry to trigonal prismatic in 2 biases the system back towards H2, and increases current density, while still producing ethylamine. To our knowledge this is the first confirmed demonstration of turnover for acetonitrile reduction with a molecular electrocatalyst.
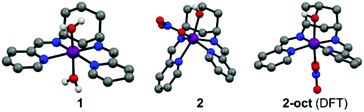
Compounds 1 and 2 are obtained by complexing the parent ligands with Co(II) nitrate in methanol, vapour diffusion isolates them as single crystalline materials suitable for X-ray diffraction. Synthesis of the ligands is detailed in the ESI.† The crystal structure of 1 (Fig. 1 and S1†) exhibits a very similar, distorted octahedral geometry to the previously published trans-hydroxy substituted complex,8 although the coordinated nitrate is replaced by a second water molecule – likely due to loss of the hydrogen bonding ligand trans-OH group and resulting changes to the crystal packing and hydrogen bonded network (Fig. S3†). In 2 (Fig. 1 and S2†), coordination of the –OH group pulls Co 0.9743(8) Å out of the plane of the N4 pocket, leading to a trigonal prismatic geometry where the two pyridyl imine chelators are ca. 90° to one another and the shortest coordinate bond (2.075(1) Å) is to the hydroxyl O. There is no coordinated water molecule, and Co-pyridyl, imine and nitrato bond lengths are all longer than in 1 (Table S2†). Large differences in the paramagnetic 1H-NMRs of 1 and 2 indicate that these structural differences are retained in solution (Fig. S4†). Even so, DFT calculations estimate a small (ca. 30 kJ mol−1) ΔE between the observed structure of 2, and an alternative 2-oct (Fig. 1) where the pyridyl imines return to the equatorial plane (analogous to 1) and the hydroxyl remains coordinated at a similar distance (ca. 2.078 Å). This modest energy difference, comparable to a strong hydrogen bond,9 suggests that 2 could change its configuration in response to protonation of –OH and/or reduction of Co, making the –OH group hemi-labile while retaining a short O-to-Co distance.
For both complexes, cyclic voltammetry (CV) reveals three quasi-reversible reductions between −0.8 and −1.8 V vs. Fc/Fc+, and an oxidation at ca. +0.5 V (Table 1, Fig. S6†). The large peak separation (ΔE) of the oxidation indicates CoII/III, owing to the associated spin-state change (Table 1). This ΔE for 2 is especially large, because d6 CoIII strongly disfavours the trigonal prismatic geometry10 and forces a structural change that slows down electron transfer. The first reduction is assigned to CoII/I for both 1 and 2, in accordance with prior work,2b and consistent with the large (300 mV) negative shift due to coordination of the electron-donating hydroxyl and change in geometry in 2, and DFT calculations indicating that the HOMOs of 1− and 2− are predominantly metal based (Fig. 2, Fig. S5†). The two subsequent reductions can be formally assigned to the ligands for both complexes, however DFT-calculated frontier orbitals suggest participation from both the imino-pyridines and the metal centres. DFT also suggests that the much larger ΔE for 2 on the last reduction results from a structural rearrangement involving de-coordination of both nitrate counterion and hydroxyl group. Thus, the hydroxyl group may act as a hemi-labile ligand that coordinates and de-coordinates during catalytic turnover.
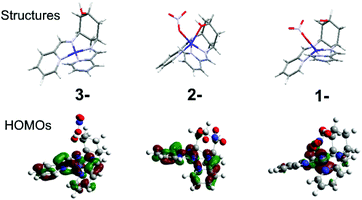 | ||
| Fig. 2 DFT calculated structures and HOMOs of 2 in its one (1-), two (2-) and three (3-) electron reduced states. | ||
| E 1/2, V vs. Fc/Fc+ (ΔE, mV)a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1+/0b | 0/1− | 0/2− | 0/3− | |
| a Solutions ca. 10−3 M in analyte and 0.1 M in [NBu4][BF4] in acetonitrile at a glassy carbon working electrode with a scan rate of 100 mV s−1. Potentials referenced to Ferrocene internal standard E1/2 = 0 V, ΔEp = 80 mV. b The “0” state is defined as the initially isolated Co2+ complex. | ||||
| 1 | 0.53 (130) | −0.85 (80) | −1.37 (70) | −1.77 (60) |
| 2 | 0.43 (393) | −1.16 (91) | −1.40 (81) | −1.80 (200) |
Both complexes respond strongly to addition of acetic acid (AcOH). For the first reduction of 1 (at 100 mV s−1) a shift of ca. −200 mV in the return wave is observed if the subsequent wave(s) are also scanned (Fig. 3, Fig. S7†). However, little change occurs to this first wave when studied in isolation (Fig. S8†), and at slow scan rates (Fig. S9†) it retains reversibility when scanning subsequent waves. For the second wave one equivalent of AcOH roughly doubles the current associated with the forward (reduction) process, but leaves the return wave unchanged. Addition of more AcOH (up to 5 eq.) nearly triples the current observed with no acid for the reduction wave, which from 5 eq. onwards shifts to more positive potential by ca. 60 mV per −log[AcOH] (Fig. S7†), without further significant increase in current at 100 mV s−1. At 10 mV s−1, however, current continues increasing up to 30 eq. AcOH (Fig. S9†). These observations are consistent with slow catalysis on the second wave, which we assign as 2-proton, 2-electron proton coupled electron transfer (PCET) followed by slow H2 evolution – as confirmed by detection of traces of H2 upon bulk electrolysis at −1.5 V vs. Fc/Fc+. The slow nature of this process (TOF ca. 0.3 s−1), occurring near the potential for imine reduction, implies that H2 evolution is occurring from a 2-electron, 2-proton reduced imine ligand. Ligand-based H2 evolution is documented for more electron rich bis-iminopyridines, at TOFs up to 19.4 s−1.11 Finally, a third, catalytic wave develops at more negative potential (Fig. S7†). Its potential shifts positive and current increases in proportion to the concentration of acid, indicating PCET, and is likely initiated through formation of a CoII hydride. Prior work on Co-bis-iminopyridines found that in weakly acidic conditions metal protonation only occured upon transfer of a second electron to Co, and postulated involvement of the imino-pyridines in the reaction pathway.2b
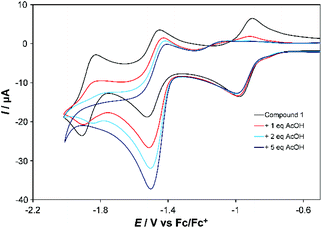 | ||
| Fig. 3 CV showing effect of adding 1, 2 and 5 equivalents of AcOH to the first two reduction waves of 1 in MeCN. Conditions as described under Table 1. | ||
The behaviour of 2 is more complex (Fig. S10–12†). With AcOH present, three waves occur before the main catalytic process, corresponding to a similar series of electron transfers to those of 1: CoII to CoI, followed by two PCETs that reduce the imino-pyridines and result in slow H2 evolution. The reason for the split in the imino-pyridine PCETs is not clear, but may relate to lower symmetry inequivalencing the two “arms” on the CV timescale, and/or a difference in the strength of communication between them. Notably, as more acid is added the PCETs begin to merge (Fig. S12†) and the catalytic half-wave potential for 2, initially ca. 230 mV more negative than that of 1, shifts such that by 30 eq. AcOH the difference is only 130 mV. This is consistent with acid encouraging de-coordination of –OH, producing behaviour more similar to 1, and potentially enabling it to act as a proton relay that lowers the potentials associated with the metal centre.12
The observed response to a weak proton source encouraged investigation of the main catalytic wave by bulk electrolysis (BE) of solutions of acetic acid in acetonitrile (Table 2). Both catalysts have a lower faradaic efficiency (ηF) for H2 evolution than the blank glassy carbon (GC) electrode, and for 1 the chemical yield of H2 was also lower than for GC alone. This indicates that H2 evolution cannot be a major pathway for 1, and is not the only one for 2. A ninhydrin test indicated the presence of amines in the catholyte, treatment with 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene (DNFB) enabled quantification of ethylamine (as N-ethyl-2,4-dinitroaniline) by 1H-NMR (Table 2, Fig. S18–20†), and also revealed small quantities of 2,4-dinitroaniline – confirmed by MS (Fig. S23–25†). The faradaic yield (ηF) of EtNH2 for 1 (22%) is double that of 2, and the TON is higher (7 vs. 5). While the ηFs and TONs obtained are modest, the 4-electron, 4-proton process involved is challenging. To our knowledge this is the first confirmation of MeCN → EtNH2 turnover with any molecular electrocatalyst, and the first evidence of any such reactivity with an earth abundant metal.13 Thus for 1, it seems remarkable that ηF for EtNH2 exceeds that for the more kinetically straightforward reduction of H+ to H2.
| Catalyst | E/V vs. Fc/Fc+ | Q/C | H2 | EtNH2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| η F | η Chem | η F | η Chem | |||
| Electrolysis performed with 0.2 mM catalyst, 40 mM AcOH, 0.1 M [NBu4][BF4] in MeCN at a GC block electrode.a Faradaic efficiency determined by gas chromatography.b Chemical yield based on AcOH.c Faradaic efficiency determined by reaction with 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene and 1H-NMR vs trimethoxybenzene standard.d Chemical yield based on AcOH.e Electrolysis on GC block alone at tabulated potential to match relevant catalyst.f Electrolysis conducted at catalytic half-wave potential, as tabulated. Data (H2 only) for the peak of the catalytic waves is presented in the ESI. | ||||||
| Blank 1 | −1.87 V | 6.7 | 56% | 19% | 0% | 0% |
| Blank 2 | −2.05 V | 7.3 | 72% | 27% | 0% | 0% |
| 1 | −1.87 V | 12.1 | 15% | 10% | 22% | 14% |
| 1 /CD3CN | −1.87 V | 12.8 | 20% | 13% | n.d. | n.d. |
| 2 | −2.05 V | 17.4 | 38% | 34% | 11% | 10% |
Unlike existing nitrile hydrogenation catalysts,141 and 2 produce no secondary or tertiary amines from MeCN. However, the total ηF of H2 and EtNH2 never exceeds 50%, indicating presence of other processes. Current evidence suggests: (i) Surface chemistry at GC may account for 25% or so of the charge – ηF for H2 in blank reactions is only 56–72% (>90% at higher potential), suggesting that some current reduces GC surface functionalities.15 This is supported by evidence of quinones in GC-MS of the solutions (Fig. S27†). (ii) Reduction of NBu4+ to NBu3 is indicated by GC-MS (Fig. S27†), and mass spectra of materials recovered after reaction with DNFB indicate trace quantities of butylamine and dibutylamine adducts (Fig. S23–24†). (iii) A negative NH3 test (indophenol) implies the 2,4-dinitroaniline forms from a readily hydrolysed (enamine) 3-aminocrotonitrile-DNFB adduct. 3-Aminocrotonitrile is a known product of electrochemical MeCN reduction,16 but both this and the triazine observed by GC-MS would be included in the ηF for H2 as they form via deprotonation of MeCN – BE of CD3CN electrolyte produced a higher H2 yield (Table 2), suggesting they are not major pathways. No other molecular products can be unambiguously identified (Fig. S18–27†), but CV of the catholyte after reaction (Fig. S13–15†) reveals that the catalysts are degraded by the process, accounting for some of the current. Importantly, BE performed with dirty electrodes from a prior run with 1 (Table S2†) produced no ethylamine. Although participation of solution phase or metastable Co nanomaterials cannot be excluded by this test,17 these are usually associated with efficient hydrogen evolution and our H2 yields are generally lowered vs. blank electrodes. Thus it seems that EtNH2 exclusively results from molecular electrocatalysis by 1 and 2.
Bulk electrolysis underestimates turnover frequency (TOF) as only a small portion of catalyst is active at any one time. So, to estimate TOFs for EtNH2 we used CV, adding AcOH until saturation was reached for 1, and until the concentration used for BE was reached for 2 (Fig. S16†). Adjusting for ηF, this gives estimates of TOF(EtNH2) of 2.3 s−1 for 1 and 1.5 s−1 for 2, under the BE conditions. While 2 appears capable of accessing faster rates, direct AcOH reduction current from the GC electrode becomes problematic as more acid is added. TOF(H2) is not estimated for either catalyst as it cannot be delineated from the electrode contribution. Use of H-terminated boron doped diamond (BDD) electrodes (Fig. S17†),18 which have less activity for AcOH reduction, indicates that 2 can indeed access maximum current densities close to an order of magnitude higher than those of 1, and thus much faster reaction rates (for both H2 and EtNH2).
Overall, current evidence supports a mechanism where 1 and 2 are first reduced from CoII to CoI, and then undergo a ligand (imine) based 2-electron, 2-proton reduction that results in slow H2 evolution. Additional PCET before H2 evolution occurs results in reduction of acetonitrile solvent to ethylamine, further reduction of the ligands, and for 2 likely also initiates a faster hydrogen evolution process. This, and the reaction by-products observed, indicates the likely involvement of hydrides, implying that fast catalysis is initiated by formation of [H2LCoII-H]. Tentatively, we suggest that 1 favours EtNH2 production more than 2 because it requires simultaneous coordination of both MeCN and hydride – in 2, the hydroxyl makes this more difficult to achieve. However, this additional hydroxyl donor may help 2 access higher reaction rates by stabilising against degradation as the acid concentration increases. It may also act as a proton relay in the de-coordinated geometries indicated by DFT (2−/23−, Fig. 1), notably rate enhancements (up to 103×) have been seen for inclusion of pendant amine groups in Fe and Ni based HECs.3a Moreover, subsequent re-coordination of -OH would increase the reactivity of resulting Co hydride species. However, current data do not exclude direct PCET to coordinated MeCN, or PCET from the reduced ligand to MeCN. Thus, work to eliminate the electrode contribution and elucidate mechanism is ongoing.
In conclusion, we have shown that two complexes designed as molecular HECs perform a challenging electrocatalytic hydrogenation with high selectivity for the organic product. Although this behaviour is previously unreported, it is likely not unique and thus presents an interesting perspective for investigation of HECs as electrocatalysts for more environmentally benign organic reactions.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We thank the UK EPSRC National Mass Spectrometry Facility for MS, RC Treatt Ltd for GC-MS, Dr Hani El Moll (UEA) for the X-ray structure of 2, and Prof. Chris Pickett and Dr Saad Ibrahim (UEA) for helpful discussions. This work was supported by: EPSRC (EP/L504944/1 DTA studentship to SNC), RSC (Summer Research Bursary to RR) and the University of East Anglia. As well as the ESI† and deposited cif files, data can be obtained by contacting the corresponding author.Notes and references
- (a) J. R. McKone, S. C. Marinescu, B. S. Brunschwig, J. R. Winkler and H. B. Gray, Chem. Sci., 2014, 5, 865 RSC; (b) V. Artero, M. Chavarot-Kerlidou and M. Fontcave, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 7238 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) N. Kaeffer, M. Chavarot-Kerlidou and V. Artero, Acc. Chem. Res., 2015, 48, 1286 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) N. Queyriaux, R. T. Jane, J. Massin, V. Artero and M. Chavarot-Kerlidou, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2015, 304–5, 3 CrossRef PubMed; (e) A. Dutta, A. M. Appel and W. J. Shaw, Nat. Rev. Chem., 2018, 2, 244 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) H. I. Karunadasa, C. J. Chang and J. R. Long, Nature, 2010, 464, 1329 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) B. D. Stubbert, J. C. Peters and H. B. Grey, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 18070 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) A. Dutta, S. Lense, J. Hou, M. H. Engelhard, J. A. S. Roberts and W. J. Shaw, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 18490 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) M. Nippe, R. S. Khnayzer, J. A. Panetier, D. Z. Zee, B. S. Olaiya, M. Head-Gordon, C. J. Chang, F. N. Castellano and J. R. Long, Chem. Sci., 2013, 4, 3934 RSC; (e) J. Xie, Q. Zhou, C. Li, W. Wang, Y. Hou, B. Zhang and X. Wang, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 6520 RSC; (f) E. Deponti, A. Luisa, M. Natali, E. Lengo and F. Scandola, Dalton Trans., 2014, 43, 16345 RSC.
- (a) M. L. Helm, M. Stewart, R. M. Bullock, M. Rakowski DuBois and D. L. Dubois, Science, 2011, 333, 863 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) D. Khusnutdinova, B. L. Wadsworth, M. Flores, A. M. Beiler, E. A. Reyes Cruz, Y. Zenkov and G. F. Moore, ACS Catal., 2018, 8, 9888 CrossRef CAS; (c) C. M. Clug, W. G. Dougherty, W. S. Kassell and E. S. Wiedner, Organometallics, 2019, 38, 1269–1279 CrossRef.
- (a) X. Hu, B. S. Brunschwig and J. C. Peters, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 8988 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) D. K. Bediako, B. H. Solis, D. K. Dogutan, M. M. Roubelakis, A. G. Maher, C. H. Lee, M. B. Chambers, S. Hammes-Schiffer and D. G. Nocera, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2014, 111, 15001 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) C. H. Lee, D. K. Dogutan and D. G. Nocera, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 8775 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) M. Vennampalli, G. Liang, L. Katta, C. E. Webster and X. Zhao, Inorg. Chem., 2014, 53, 10094 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) B. H. Solis, Y. Yu and S. Hammes-Schiffer, Inorg. Chem., 2013, 52, 6994 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) A. Lewandowska-Andralojc, T. Baine, X. Zhao, J. T. Muckerman, E. Fujita and D. Polyansky, Inorg. Chem., 2015, 54, 4310 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) B. Mondal, K. Sengupta, A. Rana, A. Mahammed, M. Botoshansky, S. G. Dey, Z. Gross and A. Dey, Inorg. Chem., 2013, 52, 3381 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) S. Raugei, S. Chen, M.-S. Ho, B. Ginovska-Pangovska, R. J. Rousseau, M. Dupuis, D. L. Dubois and R. M. Bullock, Chem. – Eur. J., 2012, 18, 6493 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) P. Wang, G. Liang, M. R. Reddy, M. Long, K. Driskill, C. Lyons, B. Donnadieu, J. C. Bollinger, C. E. Webster and X. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 9219 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) N. Elgrishi, B. D. McCarthy, E. S. Rountree and J. L. Dempsey, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 3644 CrossRef CAS.
- For example, hydrogenation: H. U. Blaser, B. Pugin, F. Spindler and M. Thommen, Acc. Chem. Res., 2007, 40, 1240 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Consider water splitting: an efficient (ca. 20%) commercial solar cell connected to a PEM electrolyser (ca. 80% efficient) will deliver a solar-to-H2 conversion efficiency of ca. 15%. This is yet to be beaten by integrated solar water-splitting devices or other photochemical systems.
- J. Fielden, D.-L. Long, M. Speldrich, P. Kögerler and L. Cronin, Dalton Trans., 2012, 41, 4927 RSC.
- G. A. Jeffery, An Introduction to Hydrogen Bonding (Topics in Physical Chemistry), Oxford University Press, New York, NY, 1997 Search PubMed.
- E. Cremades, J. Echeverría and S. Alvarez, Chem. – Eur. J., 2010, 16, 10380 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. J. Thompson and L. A. Berben, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 11642 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Xie, Q. Zhou, C. Li, W. Wang, Y. Hou, B. Zhang and X. Wang, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 6520 RSC.
- Electro-reduction of MeCN to EtNH2 has been demonstrated for an osmium complex but no TON was reported, see: M. H. V. Huynh, R. T. Baker, D. E. Morris, P. S. White and T. J. Meyer, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2002, 41, 3870 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) H. Li, Y. Wu, J. Zhang, W. Dai and M. Qiao, Appl. Catal., A, 2004, 275, 199 CrossRef CAS; (b) D. J. Segobia, A. F. Trasarti and C. R. Apesteguía, Appl. Catal., A, 2012, 445–6, 69 CrossRef.
- K. M. Sundberg, W. H. Smyrl, Lj. Atanasoska and R. Atanasoski, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1989, 136, 434 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) B. Batanero, F. Barba and A. Martin, J. Org. Chem., 2002, 67, 2369 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) J. K. Foley, C. Korzeniewski and S. Pons, Can. J. Chem., 1988, 66, 201 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Kaeffer, A. Morozan, J. Fize, E. Martinez, L. Guetaz and V. Artero, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 3727 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) H. B. Suffredini, V. A. Pedrosa, L. Codognoto, S. A. S. Machado, R. C. Rocha-Filho and L. A. Avaca, Electrochim. Acta, 2004, 49, 4021 CrossRef CAS; (b) G. R. Salazar-Banda, A. E. de Carvalho, L. S. Andrade, R. C. Rocha-Filho and L. A. Avaca, J. Appl. Electrochem., 2010, 40, 1817 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Synthetic and other experimental/computational details, CIF files. CCDC 1898421 and 1898426. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c9dt00773c |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 |