Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Chemical principles underpinning the performance of the metal–organic framework HKUST-1
Christopher H.
Hendon
and
Aron
Walsh
*
Department of Chemistry, University of Bath, Claverton Down, Bath, BA2 7AY, UK. E-mail: a.walsh@bath.ac.uk; Tel: +44 (0)1225 384913
First published on 11th May 2015
Abstract
A common feature of multi-functional metal–organic frameworks is a metal dimer in the form of a paddlewheel, as found in the structure of Cu3(btc)2 (HKUST-1). The HKUST-1 framework demonstrates exceptional gas storage, sensing and separation, catalytic activity and, in recent studies, unprecedented ionic and electrical conductivity. These results are a promising step towards the real-world application of metal–organic materials. In this perspective, we discuss progress in the understanding of the electronic, magnetic and physical properties of HKUST-1, representative of the larger family of Cu⋯Cu containing metal–organic frameworks. We highlight the chemical interactions that give rise to its favourable properties, and which make this material well suited to a range of technological applications. From this analysis, we postulate key design principles for tailoring novel high-performance hybrid frameworks.
1 Introduction
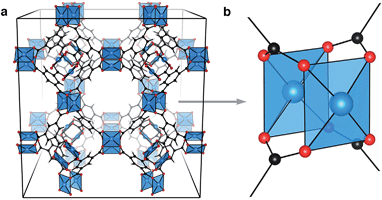
The structural diversity of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs)1 has stimulated research efforts in the fields of gas storage and sensing,2,3 catalysis,4,5 and more recently, as electroactive materials in devices.6–10 Many studies have focused on the syntheses of ‘ultra-high porosity’ materials11,12 with the prospect of tailor-made gas vessels for selective uptake and storage.13–18 Whilst it is recognised that these organic–inorganic compounds can exhibit an extensive range of properties relevant to solid-state chemistry and physics – including magnetism, ferroelectricity and electrochromism – electronic structure modulation has been a secondary consideration in hybrid materials design.19From the plethora of reported MOFs, some of the highest performing multi-application materials feature an array of Cu⋯Cu paddlewheel secondary building units (SBUs), shown truncated in Fig. 1b. There are many examples of organic–inorganic frameworks featuring this motif (e.g. HKUST-1,20 NU-111,21 PCN-14 (ref. 22) and NOTT-115 (ref. 23)), with varying porosity and aperture depending on the organic linker selection.24,25 Porous frameworks have been used in the storage of gas,26 but all have shown significant retention and selectivity of gaseous mixtures.27–29 It is not clear that the high porosity of these materials, attributed to the large organic linkers, correlates with high performance. Indeed, HKUST-1 is one of the more dense porous MOFs.
HKUST-1, (Cu3(btc)2, Fig. 1a), is a framework composed of an array of 32 Cu⋯Cu paddlewheels per crystallographic unit cell, connected in three dimensions by 1,3,5-benzene tricarboxylate (btc). Like cupric acetate, this ligand arrangement results in two coordinatively unsaturated Cu sites per paddlewheel which polar molecules can interact with. The paddlewheels are stable in both the coordinatively unsaturated and saturated arrangements.30 In the original preparation of HKUST-1, Cu3(btc)2 crystallises with stoichiometric amounts of water coordinated to each Cu2+ ion. Anhydrous (or activated) HKUST-1 is realised by gentle heating under low pressure, resulting in the chemically activated structure with exposed Cu2+ sites.
MOFs can be complex in both chemistry and geometry. In an attempt to simplify discussions of these frameworks several shorthand naming systems have been devised. The most common is an arbitrary alphanumeric string, often indicating the institution where the material was first isolated (e.g. HKUST-1 as a description of Cu3(btc)2). An alternative nomenclature describes the structural topology.31 For example, Cu3(btc)2 crystallises with so-called tbo topology in space group Fm![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m, which relates to ‘twisted’ boracite (the mineral form of calcium borate). There are many Cu-based MOFs that deviate from the tbo type. For example, Eddaoudi and co-workers reported a Cu-containing MOF of type rht,32 and there are further reports including nbo, cuo, ftw, eto, gea, rht and agw topologies.33–36 The electronic structure and applications described herein relate specifically to HKUST-1, but the principles should be transferable to any of the Cu⋯Cu containing MOFs.
m, which relates to ‘twisted’ boracite (the mineral form of calcium borate). There are many Cu-based MOFs that deviate from the tbo type. For example, Eddaoudi and co-workers reported a Cu-containing MOF of type rht,32 and there are further reports including nbo, cuo, ftw, eto, gea, rht and agw topologies.33–36 The electronic structure and applications described herein relate specifically to HKUST-1, but the principles should be transferable to any of the Cu⋯Cu containing MOFs.
Activated HKUST-1 has demonstrated remarkable gas separation and uptake. It has been shown to be both an ionic and electrical conductor, and an efficient heterogeneous catalyst, despite its pedestrian chemical composition. Both btc and Cu⋯Cu paddlewheels are not unique to HKUST-1. Indeed, btc is a familiar ligand in MOF chemistry.37,38 Thus, the properties of HKUST-1 that underpin its multifunctionality stem from the combination of metal and ligand, in this specific topology. In this perspective, we explore the chemical and electronic characteristics of HKUST-1 and use them to form guidelines for future application-specific hybrid materials design.
2 Electronic and magnetic structure
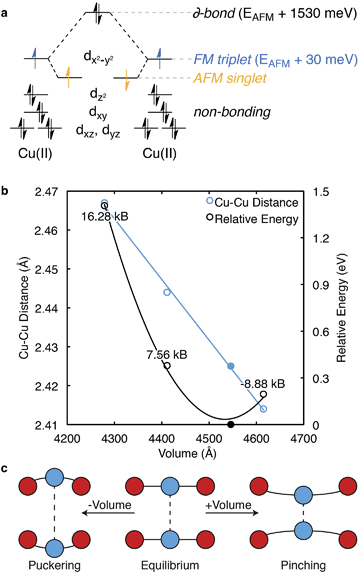
In 1989, an extensive description of the electronic structure and optical response of cupric acetate was presented by Solomon and co-workers.39 Solomon also described the electronic structure of these cupric oxide paddle wheels in relation to biological systems.40 Here, the Cu2+ ions have a d9 electronic configuration and are separated by 2.65 Å. This short bond-length results in a strong antiferromagnetic (AFM) interaction within the paddle-wheel (Cu↑⋯Cu↓), with no appreciable interaction between adjacent paddlewheels.One decade later, the synthesis and characterisation of HKUST-1 was achieved by Williams and co-workers.20 The local environment of Cu2+ is similar to cupric acetate, with the valence and conduction bands centred on cupric acetate-like orbitals (Fig. 2). A range of spin configurations are again possible for Cu⋯Cu, summarised in Fig. 3a. These can be isolated from first-principles electronic structure calculations and placed in order of increasing stability: a δ-bond state (a closed-shell singlet), a ferromagnetic (FM) state (an open-shell triplet), and an antiferromagnetic state (an open-shell singlet).41
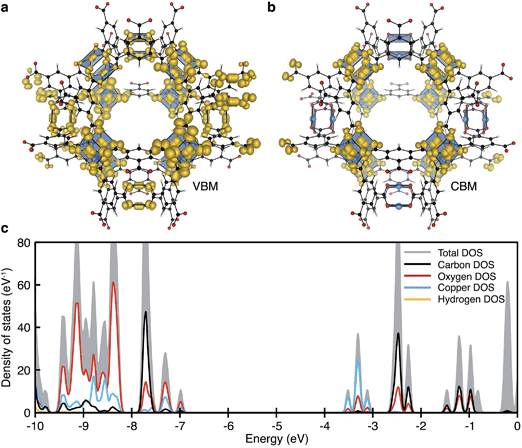 | ||
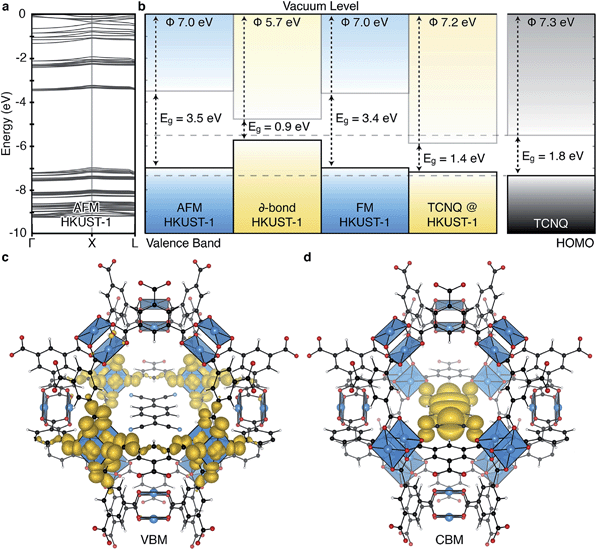
| Fig. 2 The electronic structure of HKUST-1 as computed from hybrid density functional theory (full details in ref. 41). The valence band maximum (a) and conduction band minimum (b) electronic contributions are localised on the cupric acetate motifs, with minimal influence of the aromatic groups. The electronic density of states (DOS) (c) for the ground-state antiferromagnetic configuration is characteristic of a wide band gap insulator. | ||
Following cupric acetate, HKUST-1 (both hydrated and activated) exhibits an AFM ground state, while the FM and δ-bond states may be populated by temperature and/or photo-excitation. Williams and co-workers demonstrated this effect, showing an increase of the magnetic susceptibility at temperatures greater than 100 K.42 In a recent study by Pöppl and co-workers, the AFM ground-state was confirmed with a range of electron spin resonance techniques, with evidence for an S = 1 excited spin state.43
From first-principles calculations, the AFM state is 1.53 eV (148 kJ mol−1) per paddlewheel more stable than the δ-bond state, and 0.03 eV (3 kJ mol−1) per paddlewheel more stable than the FM state, Fig. 3a. From the negative exchange interaction between nearest-neighbour Cu ions, a Néel temperature of 348 K was predicted.44 Treatment of the correct magnetic structure is critical in calculations of the electronic structure of HKUST-1 (and related open-shell frameworks). A closed-shell (spin restricted) calculation forces the δ-bond formation, which is one of many low energy excited electronic states.
There is evidence for magnetoelastic coupling in this system. The spin state of the Cu ions is sensitive to the lattice volume (pressure) and spin flipping is observed both experimentally and computationally upon increases (ca. 0.1 Å) in the Cu⋯Cu distance. Surprisingly, HKUST-1 shows a decrease (pinching) in Cu⋯Cu distance with an increase in cell volume, as shown in blue, Fig. 3b. A crystal subject to hydrostatic pressure will result in a greater Cu⋯Cu separation, or puckering. An estimate of these pressures is shown in Fig. 3.
Under high external pressure, the electronic structure is altered to a non-zero spin configuration. As the Cu⋯Cu distance is increased, the FM arrangement is favoured, with each paddlewheel converting to a spin triplet. Under expansion (e.g. at higher T) the metals are brought together, which subsequently destabilises both the occupied dz2 and partially occupied dx2−y2 orbitals, but the AFM state remains. Changes in effective mechanical pressure can also be induced by low loading levels of gaseous absorbates, which puckers the Cu⋯Cu motif, Fig. 3c.45–47
Complex magnetic behaviour was observed by the inclusion of a di-tert-butyl nitroxide radical, which both coordinated and coupled to the Cu ions.48 It is not surprising HKUST-1 interacts strongly with free radicals. As we will discuss in the catalysis section, this experiment provides a promising avenue for radical heterogeneous catalysis. The coordination process increases electron density around the Cu2+ dz2 orbitals: the destabilisation does not alter the AFM arrangement, but rather causes a gradual crystallographic expansion due to the increase in dz2 repulsion. The magnetic configuration not only affects the local Cu⋯Cu electronic structure, but also the solid-state workfunction.
Experimentally, workfunctions (or ionisation potentials) of MOFs are challenging to measure. MOFs are commonly unstable in polar solvents (posing problems for cyclic voltammetry measurements) and despite recent attempts at understanding surface terminations in MOFs,49–51 the exact topology is unknown (posing problems for photoemission characterisation). There are however four recent reports detailing an effective workfunction for HKUST-1,52–55 all of which suggest variable ionisation potentials depending on the spin state. Using a recent method for recovering the absolute electron energies of porous crystals,41 the predicted workfunctions of the various spin states of HKUST-1 may be aligned relative to vacuum, Fig. 4b. We compute the workfunctions of the AFM, FM and δ-bond state to be 7.0, 7.0 and 5.7 eV, which is in close agreement with ionisation potential measurements performed by Lee and co-workers (5.43 eV).54 The characteristic aquamarine hue, closely associated with the Cu⋯Cu motif, does not correlate with the electronic band gap of any of the spin states, it is rather attributed to optical transitions around 1.3 eV which can be associated with ligand field transitions and ligand-to-metal charge transfer.
3 Ionic and electrical conductivity
One can envisage many methods of activating ion conductivity in hybrid frameworks. In the case of hydrated HKUST-1, exposure to a strong base – ammonia is one example – weakens the aqueous O–H bond, resulting in labile protons.56,57 This phenomenon was further demonstrated by Hupp and co-workers, who showed an increase in proton conductivity (Grotthus mechanism58) upon loading of methanol in the hydrated structure.59As outlined in a recent review by Shimizu and co-workers, there are several drawbacks with using MOFs as ionic conductors.60 Perhaps surprisingly, most reports of Cu-MOFs show stability in ammonia; the same in not true with respect to oxygen centred nucleophiles.61 The primarily concern is that proton hopping sites are inherently nucleophilic. A destabilisation of the nucleophilic-bound proton is required to increase the protonic conductivity; a chemical characteristic which is essentially a measurement of guest molecule acidity. Thus the increase in nucleophilicity generally results in macroscopic framework decomposition.62 Tominaka and Cheetham presented an alternative mode of ion conductivity in microcrystalline samples. The ionic conductivity of pressed-pelleted frameworks was observed to be extrinsic (i.e. the conduction occurred at the poly-crystalline grain boundaries, rather than through the proposed Grotthus mechanism that dominates single crystal samples).63 Besides H+ conductivity, a recent screening of MOFs for use as cathodes in Li–air batteries showed crystalline HKUST-1 has a particularly large discharge capacity of 4170 mA h g−1, in which both ion transport and storage capabilities are exploited.64
The ability to tune the electronic structure of MOFs, through modification of the inorganic and organic components, make them exciting candidates for electronic applications. Notably, Dincă and co-workers have shown several examples of conductive MOFs.65–68 Most metal–organic frameworks are wide band gap insulators with high resistivity.6,69,70 Their porosity results in electronic bands composed of highly localised orbitals, and an absence of band dispersion in reciprocal space, as shown for HKUST-1 in Fig. 4a. This suggests that the most likely mode of electronic conduction is through electron hopping, rather than band transport.71–73 In the first report of a solar cell containing HKUST-1 electron injection to TiO2 and hole transport to a redox electrolyte was achieved.54 Elsewhere, hybrid organic–inorganic perovskite structured materials have achieved notable recent success in photovoltaic applications,74–76 originating in part from the interplay between the organic and inorganic components.77–80 One distinction of the hybrid perovskites is that the extended inorganic network provides robust band, rather than hopping, conductivity.
Conventional semiconductors may be chemically doped to introduce an excess of electrons (donor states) or holes (acceptor states). The defect chemistry of MOFs is complex – many are kinetic products rather than in thermodynamic equilibrium – and there is no general approach to increase conductivity.81–83 One promising method to increase conductivity could be through increasing the MOF density. Assuming a fixed topology, this may be achieved through two approaches: (i) pre-synthetic ligand choice84 or (ii) loading of the MOF with electron hopping sites.85 In the latter approach, under-coordinated metal sites can be harnessed to transiently coordinate redox-active molecules. This principle was the basis of the seminal work of Allendorf and co-workers who demonstrated substantial electrical conductivity increase upon loading of HKUST-1 with tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ).55
The increase in conductivity of TCNQ@HKUST-1 can be understood from basic principles of semiconductor physics.86 TCNQ is widely used as an electron acceptor in organic electronics. The electronic workfunction of HKUST-1 (AFM configuration) is calculated to be 7.0 eV with a band gap of 3.5 eV, Fig. 4b. Single-molecule TCNQ is predicted to have an ionisation potential of 7.3 eV with an electronic gap of 1.8 eV (at the same level of theory). Solid-state calculations of the mixed system confirm that the addition of TCNQ to coordinatively-unsaturated Cu in HKUST-1 sites provides electronic stabilisation to the framework, increasing the work function to 7.2 eV. This stabilisation originates from back-bonding capability of TCNQ which subsequently lowers the valence band maximum (VBM, dominated by cupric oxide, Fig. 4c). The lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) of TCNQ becomes a mid gap state, consistent with its behaviour as an electron acceptor, Fig. 4d.
The inclusion of TCNQ provides a sub-framework connection – by the formation of a charge transfer salt – between the Cu paddlewheels. A similar principle of internal cross-linking modifications was demonstrated by Cohen and co-workers,87 but little attention has been paid to the electronic structure of the linking motifs. There is certainly scope for exploring both the inclusion of other molecules into the pores of HKUST-1 that form similar electrical contacts, with varying donor and acceptor levels.
4 Heterogeneous catalysis
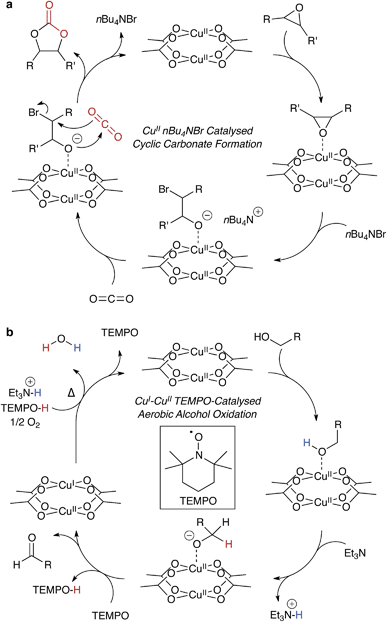
Many hybrid frameworks have shown success as heterogeneous catalysts, in part owing to the large internal surface areas. There are reports ranging from polymerisations88,89 to C–H bond activation90 and CO2 reduction.91 These catalytic frameworks generally contain motifs analogous to traditional molecular catalysts, featuring the same compositional diversity, with the advantage of regular ordering and potential ease of catalyst recovery.Many organic transformations do not require a redox active catalyst, but rather a combination of electron rich and deficient reagents, and an electrophilic centre, such as Cu2+. In principle, this type of catalysis would be ill-suited to MOFs because strongly nucleophilic reagents may result in framework decomposition. However, in reactions that are both gaseous and chemically moderate – such as the epoxide ring opening92,93 reaction shown in Fig. 5a – the porosity of MOFs comes as a benefit, with the presence of a regular array of metal centres to facilitate the stabilisation of reaction intermediates.
Ma and co-workers showed highly efficient CO2 conversion in HKUST-1, and quantitative catalytic turnover for their modified framework featuring an array of Cu2+ paddlewheels and single Cu2+ atoms.91 In their report (summarised in Fig. 5a), the phase transfer catalyst, n-tetrabutylammonium bromide, does not degrade the framework, and the reagents are the epoxide and CO2. In this case, Cu2+ coordinates the epoxide, weakening the C–O bond through the same mechanism that promotes proton conduction in the hydrated structure. This unconventional type of catalysis is exciting, and there is scope for chiral modifications of the framework and hence potential for asymmetric catalysis within designer porous materials.
Mixed-metal redox catalysis has also been demonstrated.94,95 In a recent report by Fischer and co-workers, the isostructural Ru-HKUST-1 was constructed with mixed RuII/III sites, which exhibited exceptional olefin hydrogenation turnover.96 The same Ru-HKUST-1 was reported in a study by Wade and Dincă, which also included several other interesting isostructural M-HKUST-1 analogues (M = Cr, Fe, Ni, Mo), all of which have multiple accessible oxidation states.97 The same principles of mixed-metal redox states can be applied to Cu-HKUST-1, forming reactive CuI/II paddlewheels. The radical stability of HKUST-1, as first demonstrated by Pöppl and co-workers,48 was recently revisited by Volkmer and co-workers, with the Cu⋯Cu paddlewheels showing mixed redox catalytic properties.98
Copper catalysis is important because it has cross-disciplinary relevance to both organic catalysis and biological systems. Many of these processes are involved in radical stabilisation,99 and this poses interesting challenges for heterogeneous development of HKUST-1 and derivatives for more complex reactions. One illuminating example is an extension to the work by Stahl and co-workers: the aerobic copper mediated radical oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes, an example is shown in Fig. 5b.100,101 This case has similar function to alcohol dehydrogenase with the inclusion of the radical initiator, TEMPO, which reduces the paddlewheel to a mixed oxidation state dimer. One possible limitation is the water by-product, so the reaction would have to be performed in conditions suitable for the liberation and reactivation of HKUST-1.
Screening porous frameworks for catalytic redox activity may be achieved with knowledge of only the energy of the bound electrons:102 the workfunctions from Fig. 4b. The frontier bands of HKUST-1 are cupric oxide centred, but the long-range electrostatic potential can result in substantial shifts with respect to corresponding molecular values, i.e. a cluster calculation of the cupric oxide paddlewheel may not reflect the electron energies of the periodic solid. In Fig. 6 we present a simple representation of four possible electronic processes that a reagent may have with the framework. If the reagent has unoccupied states lower in energy than the frameworks occupied states, there may spontaneous electron transfer from the valence band to the reagent LUMO (shown in green); this process will be limited by the instability of CuIII. A more probably case is the reduction of HKUST-1, if the reagent has filled states with low binding energy (shown in tangerine). The two other cases are where the guest molecule has mid-gap states that are empty (shown in red) or filled (shown in blue). The former is a simplification of the TCNQ example described in Fig. 4, whilst the latter relies on the unoccupied states of the framework.
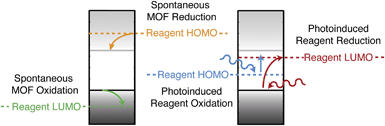 | ||
| Fig. 6 Examples of redox processes determined by the band energies of metal–organic framework and the molecular electron addition and removal energies of the reagents. A general scheme for computing the former quantities has been reported in ref. 41. | ||
Whilst the redox activity is linked to the absolute electron energies of the framework, these are not necessarily constant and can be influenced by changes in structure. Band modulation may prove to be an important tool for tailored catalysis. This modulation could be achieved physically by control of pressure, temperature or lattice strain.103 An alternative chemical route could be through modification of the organic ligand, thereby changing the structural topology or the electronic stability by electron donation or withdrawal.104 Two notable examples of this are the monoamination of the btc linker, first reported by Fröba and co-workers,105 and, separately, the aromatic ring catenation, first reported by Yaghi and co-workers.106 The latter case warranted a new name, MOF-14, as the pores were so large that interpenetration was observed. The non-interpenetrated structure should be accessible through solvent selection.
5 Gas storage, sensing and separation
Gaseous molecules have the potential to interact strongly with open metal sites, as defined by the electrostatic interaction between framework and absorbate. A stronger interaction is found for more polar and polarisable absorbates.107,108HKUST-1 has the highest density of Cu⋯Cu motifs of any known MOF. The exposed coordination sites provide a high metal-to-unit cell ratio, making HKUST-1 an excellent material for gas uptake, sensing, and separation.109 However, the space inside the pore (open pore volume space) is inactive. This factor is why no MOF currently achieves the physical requirements to be a useful alternative to compressed gas storage.110 Thus, we focus on the potential for gas sensing and separations achieved with HKUST-1.
MOFs can be used to sense molecules in many ways. Besides the visible colour shift observed for HKUST-1 (which is even notable in the dehydration process),55 optical and structural techniques can be used to detect absorbate induced changes in the framework.28 Most MOFs contract upon low loading of guest molecules.111 This contraction may be observable in optical spectroscopy, but also clearly shown with X-ray diffraction.45 The contraction is absorbate specific, and with the knowledge of band positions changing relative to pressure, one can envisage an electrical device based on change in resistance upon change in pressure. Also, if the change in pressure is substantial, one could observe a change the spin state: magnetoelastic sensing.
Generally, the more polar the guest molecules, the stronger the interaction with the framework. This fundamental physical concept reconciles the multitude of literature showing, for instance, selective retention of CO2 over CH4: CO2 has a much larger quadrupole moment than CH4.112 The single report that challenges this principle show retention of the less polarisable p-xylene over o/m-xylene, but in this case it was determined that the retention was attributed to o- and m-xylene accessing otherwise inaccessible pores.113
HKUST-1 features three distinct internal pores, two of comparable size (aperture = 14 Å) and a smaller pore (aperture = 10 Å). Of the two larger pores, one has Cu⋯Cu directed into the pores (shown coordinating TCNQ in Fig. 4c), making this ideal for gas interactions. The smallest pore could be used to retain smaller molecules. Increasing the density of both open-metal site, and the framework itself, are methods of increasing the selective retention and initial gas uptake volumes, but this comes with the cost of a reduced pore aperture.
6 Conclusions and outlook
Considering the body of research built up over the past 15 years, it is evident that HKUST-1 is a unique metal–organic framework. The electronic characteristics that underpin the performance of the material originate from the synergy of the structural organic linker, btc, and the magnetically coupled Cu⋯Cu paddlewheel motif. Drawing from the current state of understanding – and informed by first-principles materials modelling – we can infer a set of design principles to be used as a roadmap to other high-performance applications of HKUST-1, and importantly, the design of novel functional frameworks.Magnetic paddlewheels
The electronic structure of the cupric acetate-derived paddlewheel motif is complex and open to changes in chemical coordination and spin. Considering magnetic modulation, the design of organic linkers that permit superexchange interactions between adjacent paddlewheels is of particular interest. The primary challenge is to modify the organic motifs such that desirable orbital symmetry is obtained, without dramatic alteration to the overall MOF structure. One potential class of ligands could be the extended linear polyalkynes, which satisfy the preliminary criteria.114 Alternatively, the control of spin arrangements provides scope for three-dimensional arrays of quantum data storage, although chemical modification of the framework may be necessary to prolong the spin lifetimes.115 Furthermore, the observation of spin flipping may eventuate in magnetoelastic chemical sensing.Conductive paddlewheels
Currently, HKUST-1 features the most dense array of Cu⋯Cu motifs of any framework, with the smallest distance between adjacent Cu⋯Cu motifs. It should be possible to further reducing the porosity with ligand design, whereby modulating the inter-paddlewheel distances. This could result in an increase in the orbital overlap and potentially intra-framework electron transport. The gauntlet has been thrown down to the experimentalists to realise this challenge. Increasing the size of the ligand simply decreases the Cu⋯Cu density. While not optimal for conductivity, such an approach can be of interest for applications such as gas storage.116‘Rewiring’ the framework
Another method for increasing conductivity is modifications to the guest electron acceptor and donor sites. Electronic control of these guests would allow access to both the valence and conduction bands. Coordination control could provide a means to direct conductivity along specific crystallographic directions. Currently only TCNQ has been shown to increase conductivity in HKUST-1. This is not because it is unique, but rather because of its dimensions and that the electron energies coincide with HKUST-1. The same principles may be extended to any pair of materials.Porous catalysis
There are many opportunities for novel catalysis inside MOFs. In the case of HKUST-1, there is the potential for organic synthesis that is bio-relevant. The well-defined oxidation and spin states of the Cu⋯Cu motifs is desirable and there is scope for chiral catalysis in modified HKUST-1 analogues. Any material with open-metal sites can potentially be used to coordinate electron-rich motifs, thus paving way for heterogeneous catalysis in chemically robust frameworks.Chemical capture
Under-coordinated metal sites are ideal for increasing the local electric fields within a MOF pore. The Cu⋯Cu motif is particularly well-suited. The same forces that attract water and result in decomposition can be used to capture highly polar molecules like those found in nerve agents and chemical weapons. Thus, the application of MOFs for capture of polar molecules is an important variation on the usual approach that is storage of non-polar species like methane.117Acknowledgements
We thank M. D. Allendorf, A. A. Talin and M. E. Foster for constructive discussions on the electronic structure of HKUST-1, A. T. Murray for assistance with catalytic pathways, and K. T. Butler for insights into absolute electron energies. The research has been supported by the EPSRC (Grant nos EP/J017361/1 and EP/K004956/1), the ERC (Grant no. 277757) and the Royal Society. This work benefited from access to both the University of Bath's High Performance Computing Facility and ARCHER, the UK's national high-performance computing service, which is funded by the Office of Science and Technology through EPSRC's High End Computing Programme (EP/L000202).References
- A. K. Cheetham and C. N. R. Rao, Science, 2007, 318, 58 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. W. Brown, B. L. Henderson, M. D. Kiesz, A. C. Whalley, W. Morris, S. Grunder, H. Deng, H. Furukawa, J. I. Zink, J. F. Stoddart and O. M. Yaghi, Chem. Sci., 2013, 4, 2858 RSC.
- J. A. Mason, M. Veenstra and J. R. Long, Chem. Sci., 2014, 5, 32 RSC.
- F. Llabrés i Xamena, O. Casanova, R. Galiassotailleur, H. Garcia and A. Corma, J. Catal., 2008, 255, 220 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Dhakshinamoorthy, M. Alvaro and H. Garcia, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 11275 RSC.
- V. Stavila, A. A. Talin and M. D. Allendorf, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 5994 RSC.
- S. Jin, H.-J. Son, O. K. Farha, G. P. Wiederrecht and J. T. Hupp, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 955 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. H. Hendon, D. Tiana and A. Walsh, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14, 13120 RSC.
- C. H. Hendon, D. Tiana, T. P. Vaid and A. Walsh, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2013, 1, 95 RSC.
- D. Tiana, C. H. Hendon, A. Walsh and T. P. Vaid, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014, 16, 14463 RSC.
- R. Banerjee, A. Phan, B. Wang, C. Knobler, H. Furukawa, M. O'Keeffe and O. M. Yaghi, Science, 2008, 319, 939 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Furukawa, K. E. Cordova, M. O'Keeffe and O. M. Yaghi, Science, 2013, 341, 1230444 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Dzubak, L. Lin, J. Kim, J. Swisher, R. Poloni, S. N. Maximoff, B. Smit and L. Gagliardi, Nat. Chem., 2012, 4, 810 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Lee, W. C. Isley, A. L. Dzubak, P. Verma, S. J. Stoneburner, L.-C. Lin, J. D. Howe, E. D. Bloch, D. A. Reed, M. R. Hudson, C. M. Brown, J. R. Long, J. B. Neaton, B. Smit, C. J. Cramer, D. G. Truhlar and L. Gagliardi, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 698 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Lin, J. Jia, X. Zhao, K. M. Thomas, A. J. Blake, G. S. Walker, N. R. Champness, P. Hubberstey and M. Schröder, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2006, 45, 7358 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Chavan, J. G. Vitillo, D. Gianolio, O. Zavorotynska, B. Civalleri, S. Jakobsen, M. H. Nilsen, L. Valenzano, C. Lamberti, K. P. Lillerud and S. Bordiga, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14, 1614 RSC.
- H. Kim, J. Park and Y. Jung, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15, 19644 RSC.
- S. Lucena, P. Mileo, P. Silvino and C. Cavalcante Jr, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 19282 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Kieslich, S. Sun and T. Cheetham, Chem. Sci., 2014, 5, 4712 RSC.
- S. S. Chui, S. M. Lo, J. P. H. Charmant, A. G. Orpen and I. D. Williams, Science, 1999, 283, 1148 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Peng, G. Srinivas, C. E. Wilmer, I. Eryazici, R. Q. Snurr, J. T. Hupp, T. Yildirim and O. K. Farha, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 2992 RSC.
- S. Ma, D. Sun, J. M. Simmons, C. D. Collier, D. Yuan and H.-C. Zhou, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 1012 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Yan, A. J. Blake, W. Lewis, S. A. Barnett, A. Dailly, N. R. Champness and M. Schröder, Chem.–Eur. J., 2011, 17, 11162 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. K. Farha, C. E. Wilmer, I. Eryazici, B. G. Hauser, P. A. Parilla, K. O'Neill, A. A. Sarjeant, S. T. Nguyen, R. Q. Snurr and J. T. Hupp, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 9860 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Li, J. G. Bell, S. F. Tang, X. Lv, C. Wang, Y. Xing, X. Zhao and K. M. Thomas, Chem. Mater., 2014, 26, 4679 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Peng, V. Krungleviciute, I. Eryazici, J. T. Hupp, O. K. Farha and T. Yildirim, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 11887 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Yan, S. Yang, A. J. Blake and M. Schröder, Acc. Chem. Res., 2014, 47, 296 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. D. Allendorf, R. J. T. Houk, L. Andruszkiewicz, A. A. Talin, J. Pikarsky, A. Choudhury, K. A. Gall and P. J. Hesketh, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 14404 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. H. Hendon, K. E. Wittering, T.-H. Chen, W. Kaveevivitchai, I. Popov, K. T. Butler, C. C. Wilson, D. L. Cruickshank, O. Š. Miljanić and A. Walsh, Nano Lett., 2015, 15, 2149 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. K. Peterson, P. D. Southon, G. J. Halder, D. J. Price, J. J. Bevitt and C. J. Kepert, Chem. Mater., 2014, 26, 4712 CrossRef CAS.
- M. OKeeffe, M. A. Peskov, S. J. Ramsden and O. M. Yaghi, Acc. Chem. Res., 2008, 41, 1782 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Nouar, J. F. Eubank, T. Bousquet, L. Wojtas, M. J. Zaworotko and M. Eddaoudi, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 1833 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Liu, B. Li, Y. Li, X. Li, F. Yang, G. Zeng, Y. Peng, Z. Zhang, G. Li, Z. Shi, S. Feng and D. Song, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 5031 RSC.
- Z. Liang, J. Du, L. Sun, J. Xu, Y. Mu, Y. Li, J. Yu and R. Xu, Inorg. Chem., 2013, 52, 10720 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Cai, X. Rao, Y. He, J. Yu, C. Wu, W. Zhou, T. Yildirim, B. Chen and G. Qian, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 1552 RSC.
- V. Guillerm, L. J. Weselinski, Y. Belmabkhout, A. J. Cairns, V. D'Elia, L. Wojtas, K. Adil and M. Eddaoudi, Nat. Chem., 2014, 6, 673 CAS.
- Y. He, B. Li, M. O'Keeffe and B. Chen, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 5618 RSC.
- W. Lu, Z. Wei, Z.-Y. Gu, T.-F. Liu, J. Park, J. Park, J. Tian, M. Zhang, Q. Zhang, T. Gentle III, M. Bosch and H.-C. Zhou, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 5561 RSC.
- P. K. Ross, M. D. Allendorf and E. I. Solomon, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111, 4009 CrossRef CAS.
- E. I. Solomon, B. L. Hemming and D. E. Root, Electronic Structures of Active Sites in Copper Proteins: Coupled Binuclear and Trinuclear Cluster Sites, Springer, Netherlands, 1993, pp. 3–5 Search PubMed.
- K. T. Butler, C. H. Hendon and A. Walsh, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 2703 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. X. Zhang, S. S.-Y. Chui and I. D. Williams, J. Appl. Phys., 2000, 87, 6007 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Pöppl, S. Kunz, D. Himsl and M. Hartmann, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 2678 Search PubMed.
- D. Tiana, C. H. Hendon and A. Walsh, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 13990 RSC.
- A. V. Neimark, F.-X. Coudert, A. Boutin and A. H. Fuchs, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2010, 1, 445 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Prestipino, L. Regli, J. Vitillo, F. Bonino, A. Damin, C. Lamberti, A. Zecchina, P. L. Solari, K. O. Kongshaug and S. Bordiga, Chem. Mater., 2006, 18, 1337 CrossRef CAS.
- C. M. Brown, Y. Liu, T. Yildirim, V. K. Peterson and C. J. Kepert, Nanotechnology, 2009, 20, 204025 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. Jee, K. Koch, L. Moschkowitz, D. Himsl, M. Hartman and A. Pöppl, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2011, 2, 357 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Zacher, R. Schmid, C. Wöll and R. A. Fischer, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 176 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Amirjalayer, M. Tafipolsky and R. Schmid, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2014, 5, 3206 CrossRef CAS.
- C. V. McGuire and R. S. Forgan, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 5199 RSC.
- R. Pohle, A. Tawil, P. Davydovskaya and M. Fleischer, Procedia Eng., 2011, 25, 108 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Davydovskaya, R. Pohle, A. Tawil and M. Fleischer, Sens. Actuators, B, 2013, 187, 142 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Lee, D. Shinde and S. Yoon, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118, 16328 CAS.
- A. A. Talin, A. Centrone, A. C. Ford, M. E. Foster, V. Stavila, P. Haney, R. A. Kinney, V. Szalai, F. El Gabaly, H. P. Yoon, F. Léonard and M. D. Allendorf, Science, 2014, 343, 66 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. W. Peterson, G. W. Wagner, A. Balboa, J. Mahle, T. Sewell and C. J. Karwacki, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 13906 CAS.
- B. Jee, K. Eisinger, F. Gul-E-Noor, M. Bertmer, M. Hartmann, D. Himsl and A. Pöppl, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 16630 CAS.
- N. Agmon, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1995, 244, 456 CrossRef CAS.
- N. C. Jeong, B. Samanta, C. Y. Lee, O. K. Farha and J. T. Hupp, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 51 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Ramaswamy, N. E. Wong and G. K. H. Shimizu, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 5913 RSC.
- M. G. Campbell, D. Sheberla, S. F. Liu, T. M. Swager and M. Dincă, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 4349 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Mustafa, E. Breynaert, S. R. Bajpe, J. A. Martens and C. E. A. Kirschhock, Chem. Commun., 2011, 47, 8037 RSC.
- S. Tominaka and A. K. Cheetham, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 54382 RSC.
- D. Wu, Z. Guo, X. Yin, Q. Pang, B. Tu, L. Zhang, Y.-G. Wang and Q. Li, Adv. Mater., 2014, 26, 3258 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Narayan, T. Miyakai, S. Seki and M. Dinc, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 12932 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Sun, T. Miyakai, S. Seki and M. Dincă, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 8185 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Sheberla, L. Sun, M. A. Blood-Forsythe, S. Er, C. R. Wade, C. K. Brozek, A. Aspuru-Guzik and M. Dincă, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 8859 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. S. Park, E. R. Hontz, L. Sun, C. H. Hendon, A. Walsh, T. Van Voorhis and M. Dincă, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 1774 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. D. Allendorf, A. Schwartzberg, V. Stavila and A. A. Talin, Chem.–Eur. J., 2011, 17, 11372 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Falcaro, R. Ricco, C. M. Doherty, K. Liang, A. J. Hill and M. J. Styles, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 5513 RSC.
- P. Y. Yu and M. Cardona, Fundamentals of Semiconductors, Springer, Berlin, 3rd edn, 2005 Search PubMed.
- D. L. Turner, T. P. Vaid, P. W. Stephens, K. H. Stone, A. G. DiPasquale and A. L. Rheingold, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 14 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Loera-Serna, M. A. Oliver-Tolentino, M. de Lourdes López-Núñez, A. Santana-Cruz, A. Guzmán-Vargas, R. Cabrera-Sierra, H. I. Beltrán and J. Flores, J. Alloys Compd., 2012, 540, 113 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Kojima, K. Teshima, Y. Shirai and T. Miyasaka, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 6050 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J.-H. Im, C.-R. Lee, J.-W. Lee, S.-W. Park and N.-G. Park, Nanoscale, 2011, 3, 4088 RSC.
- M. M. Lee, J. Teuscher, T. Miyasaka, T. N. Murakami and H. J. Snaith, Science, 2012, 338, 643 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. M. Frost, K. T. Butler, F. Brivio, C. H. Hendon, M. Van Schilfgaarde and A. Walsh, Nano Lett., 2014, 14, 2584 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. M. Frost, K. T. Butler and A. Walsh, APL Mater., 2014, 2, 081506 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. H. Hendon, R. X. Yang, L. A. Burton and A. Walsh, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 9067 CAS.
- A. Walsh, D. O. Scanlon, S. Chen, X. G. Gong and S.-H. Wei, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 1791 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Walsh, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2010, 1, 1284 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Walsh, Proc. R. Soc. A, 2011, 467, 1970 CrossRef CAS.
- M. J. Cliffe, W. Wan, X. Zou, P. A. Chater, A. K. Kleppe, M. G. Tucker, H. Wilhelm, N. P. Funnell, F.-X. Coudert and A. L. Goodwin, Nat. Commun., 2014, 5, 4176 CAS.
- T.-H. Chen, I. Popov, W. Kaveevivitchai and O. Š. Miljanić, Chem. Mater., 2014, 26, 4322 CrossRef CAS.
- M. E. Foster, J. D. Azoulay, B. M. Wong and M. D. Allendorf, Chem. Sci., 2014, 5, 2081 RSC.
- S. Sze and M.-K. Lee, Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology, John Wiley & Sons, Singapore, 3rd edn, 2013 Search PubMed.
- C. A. Allen and S. M. Cohen, Inorg. Chem., 2014, 53, 7014 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Uemura, R. Kitaura, Y. Ohta, M. Nagaoka and S. Kitagawa, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2006, 118, 4218 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. Distefano, H. Suzuki, M. Tsujimoto, S. Isoda, S. Bracco, A. Comotti, P. Sozzani, T. Uemura and S. Kitagawa, Nat. Chem., 2013, 5, 335 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. J. Xiao, E. D. Bloch, J. A. Mason, W. L. Queen, M. R. Hudson, N. Planas, J. Borycz, A. L. Dzubak, P. Verma, K. Lee, F. Bonino, V. Crocellà, J. Yano, S. Bordiga, D. G. Truhlar, L. Gagliardi, C. M. Brown and J. R. Long, Nat. Chem., 2014, 6, 590 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W.-Y. Gao, Y. Chen, Y. Niu, K. Williams, L. Cash, P. J. Perez, L. Wojtas, J. Cai, Y.-S. Chen and S. Ma, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 2615 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. R. Johnson, T. Nakata and Y. Kishi, Tetrahedron Lett., 1979, 20, 4343 CrossRef.
- D. Jiang, T. Mallat, F. Krumeich and A. Baiker, J. Catal., 2008, 257, 390 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. F. Leong, B. Chan, T. B. Faust and D. M. D'Alessandro, Chem. Sci., 2014, 5, 4724 RSC.
- A. F. Cozzolino, C. K. Brozek, R. D. Palmer, J. Yano, M. Li and M. Dincă, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 3334 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Kozachuk, I. Luz, F. X. Llabrés I Xamena, H. Noei, M. Kauer, H. B. Albada, E. D. Bloch, B. Marler, Y. Wang, M. Muhler and R. A. Fischer, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 7058 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. R. Wade and M. Dincă, Dalton Trans., 2012, 7931 RSC.
- M. Grzywa, C. Gessner, B. Bredenkoetter, D. Denysenko, J. Van Leusen, P. Kögerler, E. Klemm and D. Volkmer, Dalton Trans., 2014, 16846 RSC.
- C. H. Hendon, D. R. Carbery and A. Walsh, Chem. Sci., 2014, 5, 1390 RSC.
- J. M. Hoover, B. L. Ryland and S. S. Stahl, ACS Catal., 2013, 3, 2599 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. L. Ryland and S. S. Stahl, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 8824 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. B. Chambers, X. Wang, N. Elgrishi, C. H. Hendon, A. Walsh, J. Bonnefoy, J. Canivet, E. A. Quadrelli, D. Farrusseng, C. Mellot-Draznieks and M. Fontecave, ChemSusChem, 2015, 8, 603 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. T. Butler, C. H. Hendon and A. Walsh, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 22044 CAS.
- C. H. Hendon, D. Tiana, M. Fontecave, C. Sanchez, L. D'arras, C. Sassoye, L. Rozes, C. Mellot-Draznieks and A. Walsh, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 10942 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Peikert, F. Hoffmann and M. Fröba, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 11196 RSC.
- B. Chen, M. Eddaoudi, S. T. Hyde, M. O'Keeffe and O. M. Yaghi, Science, 2001, 291, 1021 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Meek, S. Teich-McGoldrick, J. J. Perry IV, J. A. Greathouse and M. D. Allendorf, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 116, 19765 CAS.
- Z. Hulvey, K. Lawler, Z. Qiao, J. Zhou, D. Fairen-Jimenez, R. Q. Snurr, S. V. Ushakov, A. Navrotsky, C. M. Brown and P. M. Forster, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117, 20116 CAS.
- Y. He, W. Zhou, G. Qian and B. Chen, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 5657 RSC.
- S.-J. Lee and Y.-S. Bae, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118, 19833 CAS.
- A. V. Neimark, F.-X. Coudert, C. Triguero, A. Boutin, A. H. Fuchs, I. Beurroies and R. Denoyel, Langmuir, 2011, 27, 4734 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. L. Hickey and C. N. Rowley, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2014, 118, 3678 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Vermoortele, M. Maes, P. Z. Moghadam, M. J. Lennox, F. Ragon, M. Boulhout, S. Biswas, K. G. M. Laurier, I. Beurroies, R. Denoyel, M. Roeffaers, N. Stock, T. Dren, C. Serre and D. E. De Vos, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 18526 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. H. Hendon, D. Tiana, A. T. Murray, D. R. Carbery and A. Walsh, Chem. Sci., 2013, 4, 4278 RSC.
- J. R. Weber, W. F. Koehl, J. B. Varley, A. Janotti, B. B. Buckley, C. G. Van de Walle and D. D. Awschalom, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2010, 107, 8513 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Duan, C. Wu, S. Xiang, W. Zhou, T. Yildirim, Y. Cui, Y. Yang, B. Chen and G. Qian, Inorg. Chem., 2015, 54, 4377 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. B. Decoste and G. W. Peterson, Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 5695 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 |