Xinjie Pei, Hua Zhang, Yang Zhou, Linjie Zhou and Jun Fu
Mater. Horiz., 2020,7, 1872-1882
DOI:
10.1039/D0MH00361A,
Communication
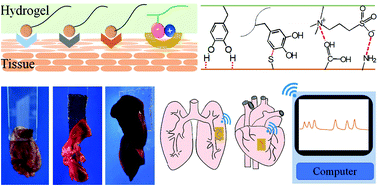
Skin-inspired sensors have great potential applications in wearable and implantable devices to monitor human motions. Robust tissue adhesion, fatigue resistance, and biocompatibility are desired for in situ signal capture and wireless transmission. Inspired by the mussel and zwitterionic adhesion mechanisms, we prepared novel stretchable, self-healing and polydopamine zwitterionic nanocomposite hydrogels that provide reversible and robust adhesion to tissues with a strength up to 19.4 kPa and a strain sensitivity of 4.3. The hydrogel sensors robustly adhere to organs like the heart, liver, and lungs to capture signals for remote monitoring and diagnostics through wireless transmission.