Controlled electrodeposition of nanostructured Pd thin films from protic ionic liquids for electrocatalytic oxygen reduction reactions†
Majid Asnavandi,
Bryan H. R. Suryanto and
Chuan Zhao*
School of Chemistry, The University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW 2052, Australia. E-mail: chuan.zhao@unsw.edu.au; Fax: +61 2 9385 6141; Tel: +61 2 9385 4645
First published on 26th August 2015
Abstract
Palladium (Pd) has been widely used as electrocatalysts for a number of important electrochemical reactions. Herein, we report a facile electrodeposition method for fabrication of nanostructured Pd thin films from protic ionic liquids. The electrochemical behavior and electrodeposition of Pd were studied in a protic ionic liquid, ethylammonium nitrate (EAN), compared with aqueous solution and aprotic ionic liquids, 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride-tetrafluoroborate (EMIM-Cl-BF4), using cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry. The electrodeposition of Pd in protic ionic liquids is found to proceed via an instantaneous nucleation and diffusion-controlled 3D growth mechanism, and accompanied with hydrogen co-evolution at more negative deposition potentials. By controlling the electrodeposition media, electrodeposition potential and time, we show that Pd thin films can be electrodeposited from protic ionic liquids with finely tuned nanostructures and large surface area. The prepared Pd thin films were employed as electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reactions in alkaline media with an onset potential of 0.95 V (RHE). It was found that Pd films prepared from protic ionic liquids exhibit larger electrochemically active surface area and higher catalytic activity for oxygen reduction reactions than aqueous and aprotic ionic liquid electrolytes under similar electrodeposition conditions.
Introduction
The oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) is a key reaction to many energy conversion and storage technologies such as fuel cells and metal-air batteries.1 Nevertheless the reaction requires 4 electron transfer for a complete reduction of O2 to H2O and is sluggish.2 Pt-based catalysts have been established as benchmark catalysts for ORR and have demonstrated a low overpotential and fast four electron transfer process.3 Nevertheless, Pt-based catalysts are less-resistant towards dissolution and poisoning agents such as CO. Moreover, their prohibitive prices have rendered them less attractive, and not suitable for large scale applicaitons.4,5 Recently, Pd have gained significant interest as an alternative catalyst for ORR for its high ORR activity, relatively lower cost and good stability in alkaline media. The activity of electrocatalyst for ORR has been shown to be strongly depending on the nanoparticle size and shape. Therefore, high level control over nanostructure of the electrocatalyst is necessary to optimise their electrocatalytic activity.6Electrodeposition is a facile and straightforward method to prepare thin films and coatings of various metals on substrate electrodes for electrocatalytic applications. Various media have been used for electrodeposition including aqueous, organic solvents, ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. In particular, ionic liquids (IL) have been receiving significant interests for electrodeposition of metals and alloys,7,8 including Pd for chemical and electrochemical applications.9,10 ILs have favourable properties that cannot be obtained from conventional electrolytes such as high electrical conductivity, thermal stability, non-volatility and wide potential window which allows electrodeposition of active metals such as aluminium and zinc.11,12 Besides, ILs have been known to be much safer than organic solvents since they are nonflammable.13 From an electrocatalysis perspective, ILs have been reported as great media for electrodeposition of nanocrystalline metals with enhanced catalytic activity. The low interfacial tension in ILs makes them easy to adapt to other phases and results in high nucleation rates and generally smaller nanoparticles, which is advantageous for achieving larger surface area to bulk ratio to facilitate fast electron transfer in electrocatalysis applications.8
There are two main categories of ILs which are aprotic (AILs) and protic ionic liquids (PILs).14 AILs have been extensively used for the electrodeposition of metal nanoparticles.11,13,15,16 Previously, AILs have been applied for electrodeposition of Pd including 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium dicyanamide (BMP-DCA),13 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride-tetrafluoroborate (BMIM-Cl-BF4),17 and 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide (BMP-TFSI).18 However, the synthesis of AILs comes with a much higher cost and complexity, and the solubility of metal cations is generally low in AILs. In contrast, PILs can be synthesised by simple proton transfer between Bronsted acid to Bronsted bases.19 Therefore, the cost of PILs are generally much lower compared to AILs due to the ubiquity of starting materials and the simple synthetic procedure. Moreover, the fluidity and attendant conductivity of PILs tend to be higher than AILs.19 Previous reports also show that wider range of metal salts have much higher solubility in PILs than in AILs.7 Recently we have synthesized and characterised a range of novel PILs,20 and demonstrated the applications of these PILs as versatile electrolytes for electrodeposition of micro-, nanostructures of metals such as Ag, Cu and Co.7,14,21
In this work we report the electrodeposition of nanostructured Pd thin films, for the first time, from a protic ionic liquid. The electrochemical behaviour of Pd in a typical PIL, ethylammonium nitrate (EAN) has been studied and compared with aqueous electrolytes and an aprotic ionic liquid, 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride-tetrafluoroborate (EMIM-Cl-BF4). Then, nanostructured Pd thin films are fabricated via potentiostatic electrodeposition on glassy carbon substrates and characterized by chronoamperometry and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The effect of time and reduction potential on the morphology of deposited thin films is studied. The electrocatalytic activity of Pd films electrodeposited from different electrolytes has been investigated for oxygen reduction reactions.
Results and discussion
Electrochemical behaviour of Pd in aqueous, aprotic and protic ILs
The electrochemical behaviour of Pd(II) in PIL is first studied by cyclic voltammetry and compared with aqueous and AIL electrolytes. Fig. 1a shows the cyclic voltammogram (CV) of Pd from an aqueous solution. A pronounced cathodic peak at potential (Ep-c) of −0.93 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) as well as an anodic peak (Ep-a) at −0.32 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) in the reverse scan are ascribed to reductive deposition and oxidative stripping of Pd, respectively. Fig. 1b shows the electrochemical behaviour of Pd in the AIL (EMIM-Cl-BF4) which is in agreement with previous studies.22,23 In the AIL, Ep-c was observed at −1.18 V (Ag QRE) and the Ep-a at −0.22 V (Ag QRE). The current loop observed in the CVs indicates a nucleation and growth mechanism for Pd electrodeposition.7 In case of EAN, the voltammogram (Fig. 1c) exhibits two peaks which is due to the Pd reduction in two steps.24,25 The peak in potential of ca. −0.62 V (Ag QRE) is attributed to the reduction of Pd(II) to Pd(I) and the second peak is for Pd(I) reduction to metallic Pd. This process was confirmed by reversing the cathodic scan prior to the second peak (Fig. 1c, black broken line), where the stripping peak at −0.2 V was not detected. Similar two step reduction of Pd(II) to Pd has been reported in other ILs.25,26 Fig. 1 shows that the Pd electrodeposition in all three electrolytes is an electrochemically irreversible process, as also confirmed with the linear behaviour of the reduction peak potential (Ep) versus log![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) υ (υ is scan rate),7 which is shown in Fig. S1.†
υ (υ is scan rate),7 which is shown in Fig. S1.†
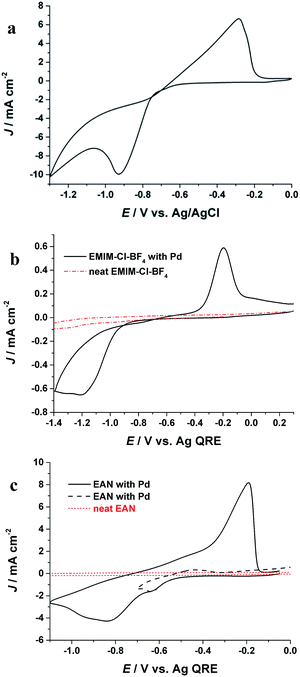 | ||
| Fig. 1 CVs of Pd electrodeposition in (a) aqueous solution containing 30 mM Pd and 0.1 M NH4OH, (b) EAN, (c) EMIM-Cl-BF4 at room temperature with a scan rate of 0.1 V s−1. | ||
The kinetic parameters of Pd2+ reduction are calculated using Nicholson and Shain analysis:27
| Ep − Ep/2 = −1.857RT/αnαF | (1) |
The linear dependence of reduction peak currents on the square root of scan rate, (Fig. S2b†), suggests that the reduction of Pd2+ in EAN and other electrolytes is a diffusion-controlled process.8 The diffusion coefficient can be determined using Schiffrin's equation:28–30
| Ip = 1.082nF3/2C∞Aυ1/2(D/πRT)1/2 | (2) |
The diffusion coefficients of Pd have been calculated from the Schiffrin equations and the data are summarised in Table 1. The diffusion coefficients obtained in the aqueous and AIL are in agreement with previous studies.17,23,24,31 Furthermore, Gokhshtein equation (eqn (3))27 is also used for determination of kinetic constant of the reduction reactions (K0) which is shown in Fig. S3.†
jp = −0.227nFC∞AK0![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) exp(−αnαF(Ep − E0)/RT) exp(−αnαF(Ep − E0)/RT)
| (3) |
| Electrolyte | α | D/cm2 s−1 | K/cm s−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltammetric analysis | Chronoamperometric analysis (Cottrell equation) | |||
| Aqueous | 0.73 | 3.03 × 10−6 | 2.88 × 10−6 | 2.43 × 10−5 |
| EMIM-Cl-BF4 | 0.85 | 1.63 × 10−8 | 1.98 × 10−8 | 4.45 × 10−8 |
| EAN | 0.90 | 2.16 × 10−7 | 2.63 × 10−7 | 8.16 × 10−8 |
Investigation of Pd electrodeposition processes from aqueous, AIL and PIL
The electrodeposition processes of Pd from aqueous solutions, AIL and PIL ionic liquids at different potential have been studied by chronoamperometry. The diffusion coefficients of Pd2+ in different electrolytes were also determined using Cottrell equation35 (eqn (4)) which are quite comparable with that determined from Schiffrin equation.
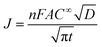 | (4) |
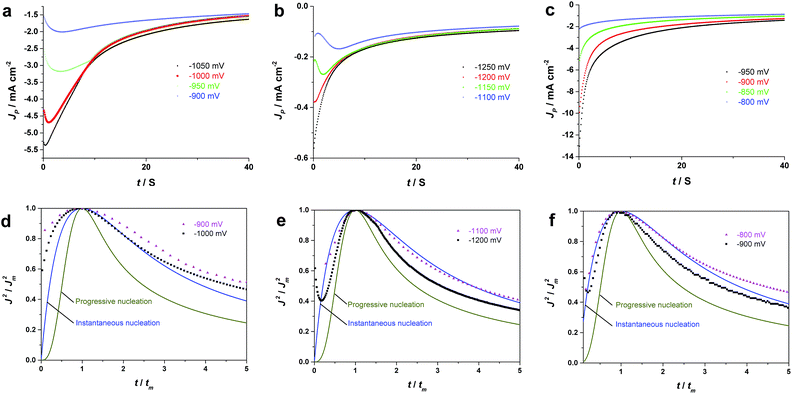
By comparing the chronoamperometric curves obtained at different potentials in each electrolyte, it is observed that all of the j–t transients of Fig. 2 were decreasing at different rates and eventually merge into a common current–time profile. In three electrolytes, all transients exhibit current maxima at initial times which shift to shorter times as the potential stepped into more negative values. The initially current increases are due to the nucleation and growth process as indicated by the current cross-over in the CVs.36 In other words, the characteristic shape of the chronoamperometric curves confirms the occurrence of nucleation and growth processes in the electrolytes which are in agreement with the nucleation loop observed in the cyclic voltammogram of Fig. 1.37 For EAN (Fig. 2c), the current maxima is only observed at more positive deposition potentials (e.g. −0.9 V). The significantly different diffusion-limited current values obtained at more negative deposition potentials (e.g. −1.1 V) indicate the presence of a parasitic reaction, which is most likely the hydrogen evolution in this case,21 as also evidenced by the visual detection of small gas bubbles on the electrode surface during the deposition process.
Based on Scharifker and Hills model for diffusion-controlled growth of 3D hemispherical particles, the deposition transients for progressive and instantaneous nucleation can be expressed by the non-dimensional eqn (5) and (6),38 respectively:
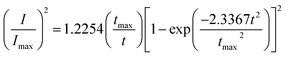 | (5) |
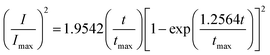 | (6) |
Fig. 2d–f, display the non-dimensional experimental plots obtained in different electrolytes versus those predicted for the limiting cases of instantaneous and progressive nucleation with diffusion-controlled growth. In all of the three electrolytes, experimental data fits closer to the theoretical curve derived from an instantaneous nucleation. The instantaneous nucleation of Pd in aqueous and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (BMIM-Cl) has previously been observed.24,25 The chronoamperometric data suggest that electrodeposition of Pd from EAN follows an instantaneous nucleation and diffusion-controlled 3D growth mechanism.
Physical characterisations of the electrodeposited Pd thin films
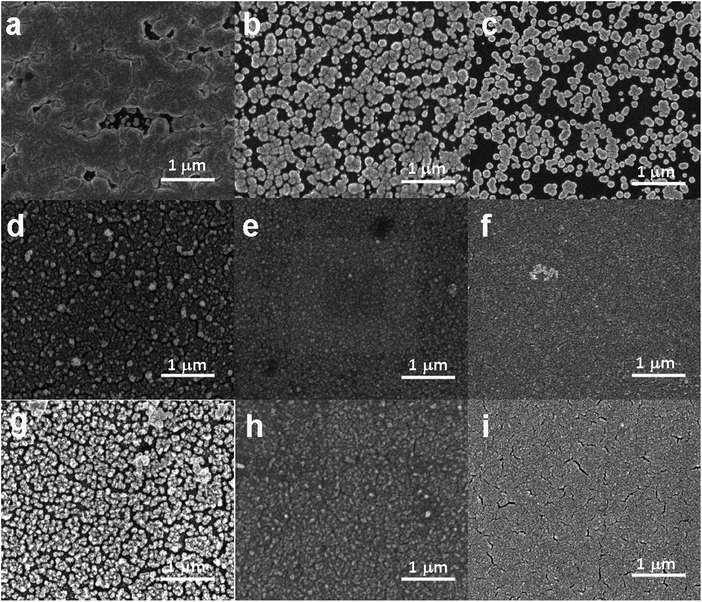
SEM was used to study the surface morphology of Pd thin films deposited from aqueous, AIL and PIL electrolytes. Fig. 3 shows the SEM images of Pd electrodeposited from aqueous solution, EMIM-Cl-BF4 and EAN obtained at different deposition potentials for 200 seconds. Based on SEM investigations, the Pd particles electrodeposited from aqueous solution show larger size than that from ILs. The granular morphology of the Pd thin films also confirms the instantaneous nucleation as predicted by Scharifker–Hills theoretical model.39 Based on the images, it can also be concluded that by applying more negative potentials, there are more nucleation sites,40 thus catalysts with fine grains and porous structure can be deposited. For EAN, with increasing electrodeposition time from 30 to 200 seconds, at a constant potential, the fine nanocrystallites agglomerate partially together and form a rough porous surface with each nanoparticle consisting of numerous sub-grains. These behaviour has been observed in previous studies and generally advantageous for offering larger surface areas and active sites for electrocatalysis.41,42Since catalytic activity of materials depends strongly on their surface area,5 we further measured the electrochemically active surface area (ECSA) of electrodeposited Pd thin films obtained from different electrolytes. The ECSA of each Pd electrocatalyst is determined by double layer capacitance (CDL) according to eqn (7):43
| ECSA = CDL/CS | (7) |
| Electrolytes | ECSA (cm2) |
|---|---|
| Aqueous | 0.24 |
| EMIM-Cl-BF4 | 0.34 |
| EAN | 0.42 |
Electrocatalytic oxygen reduction reactions
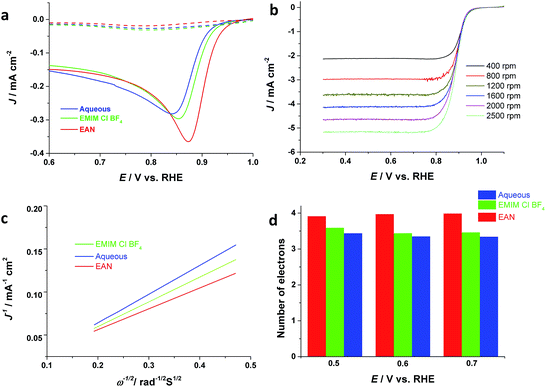
Finally, the electrocatalytic activity of the electrodeposited Pd films is investigated for oxygen reduction reactions, which is crucial to the development of fuel cells and metal-air batteries. Thus, Pd thin films are electrodeposited onto a GC electrode from aqueous, AIL saturated with oxygen or nitrogen, respectively. Fig. 4 depicts that the Pd film electrodeposited from EAN has the highest ORR catalytic activity compared to that from EMIM-Cl-BF4 and aqueous, in terms of both the ORR onset potential and current density. The onset potential of ORR for the Pd electrocatalysts obtained from EAN is ca. 0.95 V (RHE) with a half-wave potential of ca. 0.87 V. and PIL electrolytes, respectively, and their ORR catalytic activity in basic media have been investigated. Fig. 4a displays the linear sweep voltammograms (LSV) for ORR obtained in 1 M KOH. These values are comparable with commercial Pd/C and Pt/C,3,46,47 although the current density is lower than Pt/C.Furthermore, the RDE voltammetry has been applied for studying the ORR mechanism. Fig. 4b depicts RDE voltammograms obtained at Pd catalysts electrodeposited from EAN, for ORR at different rotating rates in oxygen-saturated 1 M KOH. Using Koutecky–Levich equation (eqn (8)),48 and the measured slopes in Fig. 4c, the apparent number of electrons transferred per oxygen molecule on the catalyst surface can be calculated.
| J−1 = JK−1 + (0.62nFD2/3Cυ−1/6ω1/2)−1 | (8) |
The Levich constant is calculated using a bulk oxygen solubility (C) of 1.2 × 10−6 mol cm−3, a diffusion coefficient (D) of 1.9 × 10−5 cm2 s−1 and a kinematic viscosity (υ) of 0.01 cm2 s−1 for KOH solution.49 RDE measurement revealed that oxygen is reduced at different potentials via four-electron reaction on Pd catalysts deposited from EAN. The electrons number of ORR at the Pd electrodeposited from aqueous solution is 3 at low overpotentials and increases as expected with the increase in overpotential (Fig. 4d).50 In comparison, the number of electrons obtained at Pd catalysts electrodeposited from ILs is close to four. Particularly, Pd deposited from the PIL shows 4 electrons pathway even at very low overpotentials values, suggesting PILs as a promising electrolyte media for electrodeposition of Pd nanostructures for ORR.
Conclusions
Electrodeposition of nanostructured Pd thin films from room temperature protic ionic liquids as green electrolytes has been reported. The electrochemical behaviour and kinetics of Pd is studied in a typical protic ionic liquid EAN and compared with an aprotic ionic liquid EMIM-Cl-BF4, and an aqueous electrolyte. The Pd electrodeposition from EAN is found to follow an instantaneous nucleation and diffusion-controlled 3D growth mechanism. The smaller and finer Pd nanoparticles have been achieved from ionic liquids and can be attributed to the low diffusion coefficient and interfacial tension in ionic liquids. Controlled electrodeposition from aqueous solution, EMIM-Cl-BF4, and EAN showed that surface morphology of Pd catalysts is strongly influenced by deposition potential and time. The Pd electrodeposited from EAN also showed higher electrocatalytic activity toward ORR, compared to aqueous and AIL electrolytes. The study highlights protic ionic liquid as novel electrolytes for electrodeposition of metallic nanoparticles with enhanced electrocatalytic activity for a number of important electrochemical reactions for energy storage and conversion.Experimental
High purity (>98%) 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (EMIM BF4), (>98%) ethylammonium nitrate (EAN) and (>98%) 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (EMIM Cl) were purchased from Io-Li-Tec (Germany). All ionic liquids were used as bench top condition without any further purification or drying process. EMIM-Cl-BF4 was prepared by mixing 0.4 M EMIM Cl into EMIM BF4. KF titration measurements show that under bench top conditions EAN and EMIM-Cl-BF4 contain 2.7 wt%, 2.2 wt% of water, respectively. PdCl2 (99.9%) and NH4OH (28%) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich and Ajax APS, respectively. All chemicals were used with no further purification.The electrochemical experiments were performed under normal bench-top laboratory condition with a CH760 Electrochemical Workstation (CH Instrument, Texas, USA) using a three-electrode cell arrangement. Glassy carbon (GC) with the surface area of 0.07 cm2 was used as the working electrode and a platinum wire was used as counter. For aqueous media a Ag/AgCl with 1 M KCl solution was used as the reference electrode while a silver wire separated with a glass frit from the ionic liquids was used as a quasi reference electrode (QRE) for ionic liquids. Before each experiment, the glassy carbon polished with 0.05 μm alumina slurry micro cloth polishing pad (Micropolish, Buehler), then thoroughly rinsed with ethanol and Milli-Q water and dry-wiped using a low-lint tissue. Argon was flowing during electrodeposition from the ionic liquids. All current densities in this paper were calculated by using the geometric surface area of the working electrode.
For studying ORR catalytic activities of the deposited Pd catalysts from different electrolytes, voltammetry have been carried out in oxygen saturated 1 M KOH solution. A glassy carbon rotating disc electrode (RDE) with the diameter of 4 mm was also used for ORR kinetic measurements.
For characterization of deposited thin films, Pd was electrodeposited on the polished glassy carbon plates. Scanning electron microscopy (FEI Nova SEM 230) was used for morphology study.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to UNSW Mark Wainwright Analytical Center for providing access to their SEM facilities. The study was financed by Australian Research Council (DP110102569).Notes and references
- S. Yang, X. Feng, X. Wang and K. Müllen, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 5339–5343 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Daems, X. Sheng, I. F. J. Vankelecom and P. P. Pescarmona, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 4085 CAS.
- Y. Liang, Y. Li, H. Wang, J. Zhou, J. Wang, T. Regier and H. Dai, Nat. Mater., 2011, 10, 780–786 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Guo, S. Zhang and S. Sun, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 8526–8544 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Shao, F. Ding, J. Xiao, J. Zhang, W. Xu, S. Park and J. Zhang, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2013, 23, 987–1004 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. X. Wang, H. Inada, L. Wu, Y. Zhu, Y. Choi, P. Liu, W. P. Zhou and R. R. Adzic, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 17299–17302 Search PubMed.
- B. H. R. Suryanto, C. a. Gunawan, X. Lu and C. Zhao, Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 81, 98–105 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Zhao, D. R. MacFarlane and A. M. Bond, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 16195–16205 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C.-C. Tai, F.-Y. Su and I.-W. Sun, Electrochim. Acta, 2005, 50, 5504–5509 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Endres, D. MacFarlane and A. Abbott, Electrodeposition from ionic liquids, WILEY, Weinheim, 2008 Search PubMed.
- S. Zein El Abedin, P. Giridhar, P. Schwab and F. Endres, Electrochem. Commun., 2010, 12, 1084–1086 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Li, Y. Shen, Y. Zhang and Y. Liu, Chem. Commun., 2005, 360–362 RSC.
- H.-Y. Huang and P.-Y. Chen, Electrochim. Acta, 2011, 56, 2336–2343 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. A. Gunawan, B. H. R. Suryanto and C. Zhao, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2012, 159, D611–D615 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Giridhar, B. Weidenfeller, S. Zein El Abedin and F. Endres, ChemPhysChem, 2014, 1–9 Search PubMed.
- M. Marín-Sánchez, P. Ocón, A. Conde and I. García, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2014, 258, 871–877 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. Lanzinger, R. Böck, R. Freudenberger, T. Mehner, I. Scharf and T. Lampke, Trans. Inst. Met. Finish., 2013, 91, 133–140 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Bando, Y. Katayama and T. Miura, Electrochim. Acta, 2007, 53, 87–91 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Zhao, G. Burrell, A. A. J. Torriero, F. Separovic, N. F. Dunlop, D. R. MacFarlane and A. M. Bond, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2008, 112, 6923–6936 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Lu, G. Burrell, F. Separovic and C. Zhao, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2012, 116, 9160–9170 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. H. R. Suryanto, X. Lu, H. M. Chan and C. Zhao, RSC Adv., 2013, 3, 20936 RSC.
- L. Jou, J. Chang, T. Whang and I. Sun, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2010, 157, 443–449 CrossRef PubMed.
- S.-I. Hsiu, C.-C. Tai and I.-W. Sun, Electrochim. Acta, 2006, 51, 2607–2613 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Rezaei, M. Ghorbani and A. Dolati, Electrochim. Acta, 2010, 56, 483–490 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Jayakumar, K. A. Venkatesan, T. G. Srinivasan and P. R. Vasudeva Rao, Electrochim. Acta, 2009, 54, 6747–6755 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-Y. Huang and P.-Y. Chen, Talanta, 2010, 83, 379–385 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. S. Nicholson and I. Shain, Anal. Chem., 1964, 36, 706–723 CrossRef CAS.
- G. H. Lane, A. S. Best, D. R. MacFarlane, M. Forsyth, P. M. Bayley and A. F. Hollenkamp, Electrochim. Acta, 2010, 55, 8947–8952 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. E. Poling, J. M. Prausnitz and J. P. O'Connell, in Handbook of Electrochemistry, ed. C. G. Zoski, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1st edn, 2007 Search PubMed.
- D. J. Schiffrin, J. Electroanal. Chem., 1986, 201, 199–203 CrossRef CAS.
- F.-Y. Su, J.-F. Huang and I.-W. Sun, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2004, 151, C811–C815 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. A. Kestin, J. Sokolov and M. Wakeham, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 1978, 7, 941–948 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Litaeim and M. Dhahbi, J. Mol. Liq., 2010, 155, 42–50 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Rilo, J. Vila, M. García, L. M. Varela and O. Cabeza, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2010, 55, 5156–5163 CrossRef CAS.
- A. J. Bard and L. R. Faulkner, Electrochemical methods: Fundamentals and Applications, WILEY, New York, 2nd edn, 2001 Search PubMed.
- M. Rezaei, S. H. Tabaian and D. F. Haghshenas, Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 59, 360–366 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Rezaei, S. H. Tabaian and D. F. Haghshenas, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2012, 687, 95–101 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Scharifker and G. Hills, Electrochim. Acta, 1983, 28, 879–889 CrossRef CAS.
- N. D. Nikolić, E. R. Ivanović, G. Branković, U. Č. Lačnjevac, S. I. Stevanović, J. S. Stevanović and M. G. Pavlović, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, 46, 1760–1774 CrossRef.
- D. Grujicic and B. Pesic, Electrochim. Acta, 2005, 50, 4426–4443 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J.-K. Chang, C.-H. Huang, W.-T. Tsai, M.-J. Deng, I.-W. Sun and P.-Y. Chen, Electrochim. Acta, 2008, 53, 4447–4453 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Gannouni, I. Ben Assaker and R. Chtourou, Superlattices Microstruct., 2013, 61, 22–32 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. C. L. McCrory, S. Jung, J. C. Peters and T. F. Jaramillo, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 16977–16987 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J.-P. D. Joel Fournier, L. Brosard, J.-Y. TiIquin, R. Côté and H. M. Daniel Guay, J. Electroanal. Chem., 1996, 143, 919–926 Search PubMed.
- I. Najdovski, P. Selvakannan, A. P. O'Mullane and S. K. Bhargava, Chem.–Eur. J., 2011, 17, 10058–10063 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Xu, Z. Luo, Z. Fan, X. Zhang, C. Tan, H. Li, H. Zhang and C. Xue, Nanoscale, 2014, 6, 11738–11743 RSC.
- H. Wang, Y. Yang, Y. Liang, G. Zheng, Y. Li, Y. Cui and H. Dai, Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5, 7931–7935 CAS.
- S. Kondo, M. Nakamura, N. Maki and N. Hoshi, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 12625–12628 CAS.
- M. Vikkisk, I. Kruusenberg, U. Joost, E. Shulga, I. Kink and K. Tammeveski, Appl. Catal., B, 2014, 147, 369–376 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Kim, T. Momma and T. Osaka, J. Power Sources, 2009, 189, 909–915 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c5ra13898a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 |