Heterojunction photoanodes for solar water splitting using chemical-bath-deposited In2O3 micro-cubes and electro-sprayed Bi2WO6 textured nanopillars†
Abstract
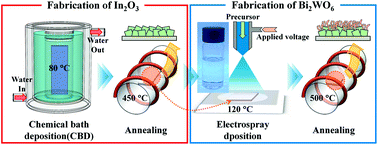
In2O3 micro-cubes were fabricated via chemical bath deposition (CDB) on an indium tin oxide (ITO) substrate, over which highly textured Bi2WO6 nanopillars were grown via a diffusion-and-aggregation phenomenon by electrostatic spraying deposition (ESD). The resulting heterojunction bilayer exhibited a photocurrent density value of 1.03 mA cm−2 under visible light of 100 mW cm−2 intensity. Widening the light absorptivity spectrum and reducing the charge recombination enhanced the performance of the heterojunction bilayer films for solar water splitting.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...