A sensitive enzyme-free lactic acid sensor based on NiO nanoparticles for practical applications†
Abstract
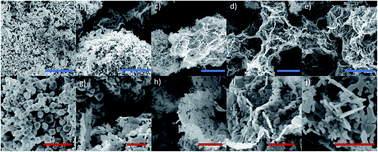
A facile and efficient electrochemical sensing platform has been successfully exploited for the first time for the determination of lactic acid using a nickel oxide (NiO) nanoparticle-modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE). Nickel oxide nanoparticles were prepared by a chemical growth method using different quantities of arginine as a soft template. The structural and morphological properties of NiO nanoparticles were characterized by Raman spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Cyclic voltammetry (CV) was used to study the electrochemical properties of various samples. The modified electrode is highly sensitive and presents a linear response over a wide range (0.005–5 mM) of lactic acid concentrations in 0.1 M NaOH. The detection limit for the sensor was found to be 5.7 μM, and it exhibits good stability. Furthermore, the sensor shows excellent selectivity in the presence of common interfering species. The lactic acid sensor showed good viability for lactic acid analysis in real samples (milk, yogurt and red wine) and demonstrated significant advancement in sensor technology for practical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...