DOI:
10.1039/C5RA12148E
(Paper)
RSC Adv., 2015,
5, 77332-77340
N-(3-Aminoalkyl)proline derivatives with potent antigycation activity†
Received
23rd June 2015
, Accepted 4th September 2015
First published on 4th September 2015
Abstract
The importance of amino acids in the therapy of conditions such as renal failure, neurological disorders and congenital defects has been documented. Some amino acids such as lysine and glycine have also been reported to have antiglycating activity. Herein we report the synthesis of a new series of N-(3-aminoalkyl)proline derivatives which are non-natural in nature. The compounds were unambiguously characterized by NMR, mass and IR spectroscopy. Their in vitro antiglycation activity was studied by circular dichroism and fluorescence spectrometry. The mechanism of action was also studied and found to take place by inhibition of Amadori product formation. The inhibition of AGE formation was further confirmed by western blot and LC-MS/MS analyses and the IC50 values of the potent compounds were determined. Compounds containing hydroxyl substituents at C4 were found to have superior antiglycation properties than those containing azide substituents at the same position. The compounds were additionally found to possess good anti-oxidant properties, which could lead to further reduction in AGE formation. Moreover, the title compounds were found to have low cytotoxicity in mammalian cells, another important attribute. Thus, the title compounds represent a novel promising class of antiglycating agents.
Introduction
Advanced Glycation End products (AGEs) are formed due to non-enzymatic reactions between proteins and reducing sugars. They are involved in the pathogenesis of diabetes and its complications. Thus, reducing AGE levels1 and inhibition of protein glycation is crucial in the prevention of the above complications. Some molecules such as aminoguanidine that reduce AGE levels, but have toxic side-effects have not been approved by the FDA, while other FDA-approved drugs have been shown to display anti-glycation activity1–5 in addition to their originally intended activities. These offer the possibility of repositioning these drugs for the treatment of diabetes and its complications. Reports from this laboratory have also been made for the use of N-(aminoalkyl)proline- and 4-hydroxy-N-(aminoalkyl)proline-derived compounds towards the synthesis of peptide nucleic acids6 and cell-penetrating oligomers,7 where these compounds were used as analogues of amino acids such as lysine and arginine.7b Since amino acids such as glycine and lysine have been reported to exert antiglycating activity,8 we surmised that the use of non-natural analogues such as the title compounds, would have advantages in terms of stability in vivo.
In this study, we report the synthesis and anti-glycation activity of selected N-(3-aminoalkyl)proline derivatives and their mode of action by various physicochemical assays such as circular dichroism (CD), fluorescence spectroscopy, MALDI-TOF and LC-MS/MS assays. We also show that these compounds are capable of exerting good anti-oxidant properties and display low cytotoxicity, thus enhancing their value as potential anti-glycation agents.
Results and discussion
Synthesis of title compounds
The title compounds were synthesized using a simple strategy outlined in Scheme 1. Accordingly, 4(S)-hydroxy-2(R)-proline methylester was N-alkylated by treating it with 3-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propyl methanesulfonate in CH2Cl2 in the presence of triethylamine to yield compound 1 which was subjected to acidolytic removal of the Boc protecting group to afford compound 2 in 62% yield. Compound 3 was obtained from 1 upon saponification with lithium hydroxide and subsequent purification by column chromatography on neutral alumina.
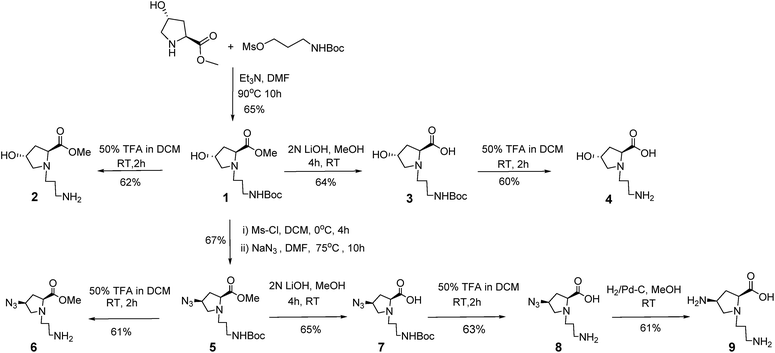 |
| | Scheme 1 Synthesis of the title compounds. | |
The removal of the Boc protecting group in 3 resulted in compound 4, which was obtained in 60% yield. Mesylation of the 4-OH group in compound 1 yielded the 4-O-mesyl derivative, which was further converted to its azide counterpart 5 in 67% yield over two steps after purification by column chromatography. Compound 6 was obtained by acidolytic removal of the Boc protecting group in 5, and purified by column chromatography. Compound 5, upon saponification with lithium hydroxide yielded 7 in 65% yield after column purification. Compound 7 was further subjected to removal of the Boc protecting group by treating it with TFA in CH2Cl2 to yield compound 8 in 63%. Reduction of the azide function in 8 by hydrogenation in the presence of Pd–C further gave compound 9 in 61% yield. All the compounds were unambiguously characterized by appropriate spectroscopic techniques.
Glycation inhibition studies
Circular dichroism (CD). CD is a powerful tool for investigating the structure and conformational changes of proteins, such as those occurring upon glycation,9 where an increase in the beta sheet conformation is observed. A decrease in the beta sheet conformation is therefore, indicative of antiglycation ability. Analysis of the CD spectra of BSA upon glycation in the presence of the title compounds (Fig. 1) revealed a decrease in the beta sheet percentage in comparison to glycated BSA, when no compound was present. In particular, the beta sheet conformation in the presence of compounds 2, 4, 6, 8 and 9 was 3%, 1.7%, 2.5%, 2% and 5.2% respectively, while that in glycated BSA was 18.7% and 5.7% in the presence of known anti-glycating agent, aminoguanidine (Amg). Thus, the title compounds are able to protect the conformation of BSA and inhibit beta sheet formation significantly, even in comparison to aminoguanidine.
 |
| | Fig. 1 CDPro analysis of (A) native BSA, (B) glycated BSA and (C–H) glycated BSA in the presence of 20 mM aminoguanidine and compounds 2, 4, 8, 6 and 9 respectively (Unrd = unordered). | |
In vitro glycation inhibition by fluorescence spectroscopy. The degree of glycation can be measured by measuring the fluorescence intensity at 440 nm, using an excitation wavelength of 370 nm,10 since most AGEs have a characteristic fluorescence with an excitation maximum approximately at 370 nm, and emission around 440 nm. A decrease in the fluorescence emission intensity is thus, indicative of inhibition of AGE formation. BSA was incubated with glucose in the presence and absence of title compounds and the fluorescence emission of the compounds was monitored after excitation at 370 nm (Fig. 2). The formation of AGEs was monitored after 14 days by measuring the fluorescence emission intensity at 440 nm. The fluorescence-based assay for AGEs was also used to determine the IC50 values of representative title compounds 2 and 6. Accordingly, these were found to be 19.2 mM and 29.5 mM respectively. In comparison, the IC50 value of aminoguanidine, considering the fluorescence excitation/emission as 370 nm/440 nm is reported to be 10 mM.11 However, this fluorescence-based method may be less specific12 because some fluorescent AGEs differ in their excitation–emission wavelengths.
 |
| | Fig. 2 AGE fluorescence spectra of BSA, glycated BSA, and glycated BSA treated with 20 mM title compounds and aminoguanidine. | |
Western blot assay. Western blot analyses of the glycation products of BSA in the presence and absence of the title compounds were carried out using both anti-AGE as well as anti-CML (anti-carboxymethyl lysine) antibodies, since CML is known to be the most abundant non-fluorescent AGE. In both the cases, compounds 2 and 4 were found to exhibit potent anti-glycation activity, which was even superior to aminoguanidine (Fig. 3). Ponceau staining of the gels was also carried out (ESI, Fig. S16†) to illustrate the protein (BSA) content in the samples.
 |
| | Fig. 3 Western blot analysis: anti-CML blot: lane (1–9) compound 9, 6, 8, 4, 2, aminoguanidine, glycated BSA, BSA, ladder; anti-AGE blot: lane (1–8) compound 9, 6, 8, 4, 2, aminoguanidine, glycated BSA, BSA. | |
From the above studies, compounds 2 and 4 emerged as the most promising title compounds with potent anti-glycation activity, which was found to be superior to known anti-glycating agent, aminoguanidine.
Probable mechanism of glycation inhibition. Circular dichroism, AGE fluorescence and western blotting suggested that at least some of the title compounds are capable of inhibiting AGE formation in proteins, using BSA as a representative protein. In order to probe the mechanism by which this occurs, a series of studies were undertaken, including MALDI-TOF-MS based insulin glycation assay, fructosamine assay, LC-MS/MS analysis of glycated peptide fragments formed after trypsin treatment and mass spectrometry of glucose adduct formation by the title compounds.
MALDI-TOF-MS based insulin glycation assay. Following a previously reported MALDI-TOF assay,2,5 insulin (m/z 5808) was glycated in presence of glucose to form Amadori modifications (m/z 5970). The intensity of glycated insulin was monitored in the presence or absence of inhibitors. Fig. 4 shows that all the title compounds were able to inhibit Amadori modification of insulin which is indicated by the decreased intensity of the glycated insulin peak, with compound 9 showing the highest inhibition.
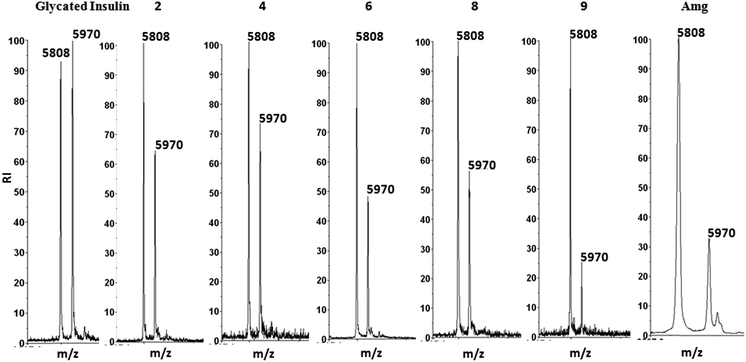 |
| | Fig. 4 MALDI-TOF assay for glycation inhibition for glycated insulin, insulin in presence of compounds 2, 4, 6, 8, 9 and aminoguanidine.5 | |
The ability of the title compounds to inhibit Amadori product formation was further studied by high resolution mass spectrometry (Q-Exactive, Orbitrap mass spectrometer). BSA was glycated in the absence or presence of the title compounds and the formation of Amadori product-modified peptides after digestion with trypsin was monitored by LC-MS/MS. Glycated BSA was found to have the highest number of Amadori-modified peptides (34), while all the title compounds had lower number of the same-29, 32, 28, 31 and 27 for compounds 2, 4, 6, 8 and 9 respectively (Fig. 5), while with aminoguanidine, the number was 24. The detailed analysis is delineated in the ESI, S19–S25.†
 |
| | Fig. 5 LC-MS/MS analysis depicting the number of AGE-modified peptides in glycated BSA and glycated BSA after treatment with aminoguanidine or title compounds. | |
Fructosamine assay. In the early stages of glycation, unstable Schiff bases are formed and turned into Amadori products such as fructosamine,13 which is clinically used as an indicator for short-term control of blood sugar in diabetic patients. Reduction of fructosamine, therefore, is a therapeutic strategy to delay incident vascular complications.14 The fructosamine assay is a simple colorimetric test that measures glycated serum protein concentrations. Colour change is based on the reduction of nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) to monoformazan (MF) by Amadori rearrangement products.15 The fructosamine levels in presence of the title compounds were found to be significantly lower than that in glycated BSA (Fig. 6). Specifically, the fructosamine levels were 539, 551, 476, 592 and 526 μmol L−1 in the presence of compounds 2, 4, 6, 8 and 9 respectively, which were even lower than that in the presence of aminoguanidine (735 μmol L−1), while the fructosamine level in glycated BSA was 976 μmol L−1. This data is thus, in accordance with that obtained from the MALDI-TOF assay, which suggested that the title compounds inhibited Amadori product formation.
 |
| | Fig. 6 Fructosamine levels of BSA, glycated BSA and glycated BSA in presence of aminoguanidine or title compounds. | |
Adduct formation of title compounds with glucose. The title compounds were incubated in the presence of glucose and the reaction mixture was subjected to LC-MS analysis. All the compounds were found to form adducts with glucose. These are probably Schiff base type of adducts formed by the reaction of the free amino group in the title compounds with the aldehyde group of the sugar (Fig. 7, for a representative title compound, 2. The adduct formation with other title compounds is depicted in the ESI, page S17 and S18†). The formation of adduct with glucose could thus, be one of the ways by which the title compounds inhibit glycation.
 |
| | Fig. 7 (A) LC-MS spectrum of compound 2-glucose adduct and (B) probable mechanism of compound 2-glucose adduct formation. | |
Cytotoxicity assay. The cytotoxicity of the title compounds was evaluated in L6 rat muscle cells by measuring the cell viability using the standard MTT assay. It is a colorimetric assay that is based on the reduction of the tetrazolium dye, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide to a purple formazan derivative, that is achieved by enzymes present in viable cells. A decreased colour intensity is therefore indicative of low cell viability as a result of increased cytotoxicity. As seen in Fig. 8, all the title compounds were non-toxic at almost all concentrations tested, except at 40 mM concentration, where a slight decrease in cell viability was observed, this being more pronounced in compounds 6 and 8. However, this concentration is double that used for the glycation inhibition studies described herein.
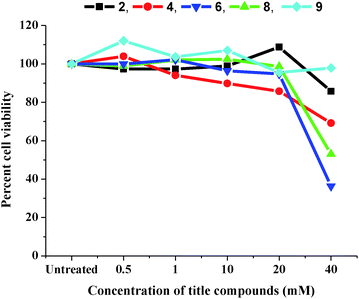 |
| | Fig. 8 MTT assay depicting viability of L6 rat muscle cells in presence of title compounds. | |
Anti-oxidant properties of title compounds. AGEs, along with advanced lipoxidation products, have also been implicated in the generation of free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS), that are known to be involved in a variety of cellular processes ranging from apoptosis and necrosis to carcinogenesis.16 It therefore follows that any candidate, that is capable of inhibiting AGE formation and additionally possess anti-oxidant properties, would have increased therapeutic value. Keeping this in mind, the title compounds were evaluated for their ability to reduce the concentration of intracellular ROS, using ascorbic acid as a control anti-oxidant, in a fluorescence-based assay. The anti-oxidant activity of a compound is evidenced by a decrease in the fluorescence intensity. Fig. 9 shows a comparative study of the title compounds for anti-oxidant activity, wherein, it was found that compounds 2 and 4 exhibited higher anti-oxidant activity than other compounds, including ascorbic acid. More specifically, the percent fluorescence values were 57, 56, 83, 62 and 70 for compounds 2, 4, 6, 8 and ascorbic acid respectively. Compound 9 did not show anti-oxidant activity as observed for other compounds.
 |
| | Fig. 9 Anti-oxidant properties of title compounds in comparison to ascorbic acid. | |
Experimental
Synthetic procedures
Methyl(2S,4R)-1-(3-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propyl)-4-hydroxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylate (1). Methyl(2S,4R)-4-hydroxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylate (1.00 g, 6.8 mmol) was dissolved in dry DMF; to it dry Et3N (3.6 mL, 20.0 mmol) was added and stirred for 5 min at RT. Then to the above solution, 3-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propyl methanesulfonate (2.09 g, 8.0 mmol) was added drop-wise with continuous stirring. The reaction mixture was heated at 90 °C for 10 h. The reaction was monitored by TLC and after completion of the reaction, DMF was removed under vacuum and the compound was extracted from water with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was concentrated to get the crude compound, which was purified by column chromatography to get yellow coloured gum (1.3 g, 65%). [α]D = −48.31 (c = 0.135 in MeOH); 1H NMR (200 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 1.44 (s, 9H), 1.59–1.69 (m, 2H), 2.08–2.17 (m, 2H), 2.38–2.56 (m, 2H), 2.69–2.83 (m, 1H), 3.08 (br s, 1H), 3.19 (br m, 2H), 3.36–3.34 (dd, J = 5.4, 10.1 Hz, 1H), 3.50–3.58 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 3.72 (s, 3H), 4.43–4.46 (m, 1H), 5.38 (br s, 1H) ppm. 13C NMR (50 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 28.0, 28.4, 39.3, 51.8, 60.9, 64.4, 70.0, 78.9, 156.3, 174.4 ppm; 13C DEPT (50 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 28.0 (CH2), 28.4, 38.5 (CH2), 39.3 (CH2), 51.8 (CH2), 51.8, 60.9 (CH2), 64.4, 70.0 ppm. HRMS: calculated mass for C14H26N2O5: 302.1842, observed mass (M + H): 303.1915, (M + Na): 325.1713.
Methyl(2S,4R)-1-(3-aminopropyl)-4-hydroxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylate (2). To compound 1 (0.10 g, 0.33 mmol), a 50% solution of TFA in DCM (5 mL) was added with vigorous stirring at RT. After completion of the reaction, solvents were removed under vacuum and crude compound was purified by column chromatography. The resultant TFA salt of the compound was obtained in 62% yield (0.065 g). [α]D = −24.47 (c = 0.11 in MeOH). IR (neat) ν: 3352, 2946, 2833, 1749, 1683 cm−1. 1H NMR (200 MHz, D2O) δ: 2.09–2.21 (m, 2H), 2.33–2.41 (m, 1H), 2.49–2.60 (m, 1H), 3.05–3.13 (m, 2H), 3.28–3.41 (m, 2H), 3.54–3.60 (m, 1H), 3.86 (s, 3H), 3.91–3.99 (m, 1H), 4.66 (br m, 2H) ppm. 13C NMR (50 MHz, D2O) δ: 24.6, 38.0, 38.8, 52.7, 53.2, 60.2, 64.8, 69.2, 175.5 ppm. 13C DEPT (50 MHz, D2O) δ: 34.6 (CH2), 38.0 (CH2), 38.8 (CH2), 52.7, 53.2 (CH2), 60.2 (CH2) 64.8, 69.2 ppm. HRMS: calculated mass for C9H18N2O3: 202.1317, observed mass (M + H): 203.1392.
(2S,4R)-1-(3-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl)amino)propyl)-4-hydroxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (3). Compound 1 (0.2 g, 0.66 mmol) was dissolved in methanol and to it, 2 N LiOH (3 mL) was added with vigorous stirring. The reaction was monitored by TLC and after completion of reaction, the reaction mixture was neutralised using Dowex H+ resin; the resin was subsequently filtered off. The filtrate was concentrated under vacuum and the compound was purified by column chromatography (0.12 g, 64%). [α]D = −35.06, (c = 0.09 in MeOH). 1H NMR (200 MHz, D2O) δ: 1.39 (s, 9H), 1.82–1.86 (m, 2H), 2.11–2.51 (m, 2H), 3.16 (br m, 2H), 3.23 (br s, 1H), 3.31 (br. m, 2H), 3.85–3.93 (dd, J = 4.2, 13.0 Hz, 1H), 4.14–4.23 (m, 1H), 4.59 (br s, 1H) ppm. 13C NMR (50 MHz, D2O) δ: 28.3, 30.1, 40.5, 58.0, 64.2, 71.1, 71.8, 83.6, 160.7, 175.6 ppm. 13C DEPT (50 MHz, D2O) δ: 28.3 (CH2), 30.1, 39.3 (CH2), 40.5 (CH2), 58.0 (CH2), 64.2 (CH2) 71.1, 71.8 ppm. HRMS: calculated mass for C13H24N2O5: 288.1685, observed mass (M + H): 289.1757.
(2S,4R)-1-(3-Aminopropyl)-4-hydroxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (4). Compound 3 (0.30 g, 1.04 mmol) was dissolved in a 50% solution of TFA in DCM (5 mL) with vigorous stirring at RT. The reaction was monitored by TLC and after the completion of reaction, solvents were removed under vacuum. Yield 0.19 g (60%). [α]D = −12.18 (c = 0.11 in MeOH). IR (neat) ν: 3375, 2948, 2834, 1684 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, D2O) δ: 2.12–2.13 (m, 2H), 2.25–2.32 (m, 1H), 2.52–2.56 (m, 1H), 3.06–3.10 (m, 2H), 3.27–3.38 (m, 2H), 3.52–3.54 (m, 1H), 3.94–3.97 (m, 1H), 4.51–4.55 (dd, J = 7.1, 11.3 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (br s, 1H) ppm. 13C NMR (50 MHz, D2O) δ: 23.4, 36.3, 38.0, 48.8, 54.5, 61.8, 69.3, 172.9 ppm. 13C DEPT (50 MHz, D2O) δ: 23.4 (CH2), 36.3 (CH2), 38.0 (CH2), 54.5 (CH2), 61.8 (CH2), 68.6, 69.3 ppm. HRMS: calculated mass for C8H16N2O3: 188.1161, observed mass (M + H): 189.1235.
Methyl(2S,4S)-4-azido-1-(3-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino) propyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate (5). To a solution of 1 (0.7 g, 2.30 mmol) in dry DCM, dry Et3N (0.9 mL, 6.90 mmol) was added and stirred for 5 min at RT. Ms-Cl (0.3 mL, 0.003 mol) was added dropwise at 0 °C, with continuous stirring. After completion of the reaction, DCM was evaporated under vacuum and the crude mesylated compound was used for further reaction without further purification. The mesylated compound was dissolved in dry DMF, to it NaN3 was added with continuous stirring (1.5 g, 23.1 mmol). The reaction was heated for 10 h at 75 °C. After completion of the reaction, DMF was removed under vacuum and the compound was purified by column chromatography (0.58 g, 67%). [α]D = −0.0686 (c = 0.1 in CHCl3). 1H NMR (200 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 1.44 (s, 9H), 1.65–1.68 (m, 2H), 2.02–2.15 (br m, 1H), 2.34–2.60 (m, 3H), 2.78–2.88 (m, 1H), 3.15–3.25 (br m, 4H), 3.77 (s, 3H), 3.96 (br s, 1H), 5.47 (br s, 1H) ppm. 13C NMR (50 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 27.8, 28.4, 35.4, 38.4, 51.7, 52.1, 58.0, 58.7, 64.8, 77.2, 78.6, 156.2, 173.3 ppm. 13C DEPT (50 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 27.7 (CH2), 28.4, 35.4 (CH2), 38.4 (CH2), 51.7 (CH2), 52.1, 58.0 (CH2), 58.7, 64.8 ppm. HRMS: calculated mass for C14H25N5O4: 327.1907, observed mass (M + H): 328.1979, (M + Na): 350.1797.
Methyl(2S,4S)-1-(3-aminopropyl)-4-azidopyrrolidine-2-carboxylate (6). To compound 5 (0.3 g, 0.91 mmol), a 50% solution of TFA in DCM (5 mL) was added with vigorous stirring at RT. The reaction was monitored by TLC and after the completion of reaction, solvents were removed under vacuum and the product was purified by column chromatography (0.19 g, 61%). [α]D = −8.83 (c = 0.105 in MeOH). IR (neat) ν: 3376, 2188, 1745, 1678 cm−1. 1H NMR (200 MHz, D2O) δ: 0.90–1.01 (m, 1H), 1.82–1.94 (m, 2H), 2.23–2.30 (m, 1H), 2.58–2.60 (m, 1H), 2.80–2.87 (m, 2H), 3.17–3.27 (m, 2H), 3.64 (s, 3H), 4.40–4.45 (m, 2H) ppm. 13C NMR (50 MHz, D2O) δ: 23.1, 33.7, 36.2, 52.9, 54.2, 58.6, 59.9, 65.7, 169.2 ppm. 13C DEPT (50 MHz, D2O) δ: 23.0 (CH2), 33.6 (CH2), 36.1 (CH2), 52.8 (CH2), 54.1, 58.5, 59.8 (CH2), 65.7 ppm. HRMS (ESI): calculated mass for C9H17N5O2: 227.1382, observed mass (M + H): 228.1457.
(2S,4S)-4-Azido-1-(3-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (7). Compound 5 (0.2 g, 0.61 mmol) was dissolved in methanol and to it 2 N LiOH (3 mL) was added with vigorous stirring. After completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was neutralised using Dowex H+ resin; the resin was subsequently filtered off. The filtrate was concentrated under vacuum and the compound was purified by column chromatography (0.125 g, 65%). [α]D = −4.54 (c = 0.11 in MeOH). 1H NMR (200 MHz, D2O) δ: 1.42 (s, 9H), 1.87–1.89 (br m, 2H), 2.34–2.41 (m, 1H), 2.68–2.79 (m, 1H), 3.06–3.39 (br m, 6H), 3.76–3.82 (m, 1H), 4.08–4.12 (m, 1H), 4.57 (br s, 1H) ppm. 13C NMR (50 MHz, D2O) δ: 25.7, 27.6, 34.3, 53.5, 59.0, 59.6, 67.2, 81.1, 158.2, 173.0 ppm. 13C DEPT (50 MHz, D2O) δ: 25.7 (CH2), 27.6, 34.3 (CH2), 36.8 (CH2), 53.5 (CH2), 59.0, 59.6 (CH2), 67.2 ppm. HRMS (ESI): calculated mass for C13H23N5O4: 313.1750, observed mass (M + H): 314.1817, (M + Na): 336.1635.
(2S,4S)-1-(3-Aminopropyl)-4-azidopyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (8). To compound 7 (0.3 g, 0.95 mmol), a 50% solution of TFA in DCM (5 mL) was added with vigorous stirring at RT. The reaction was monitored by TLC and after the completion of reaction, solvents were removed under vacuum. The crude compound was used without further purification (0.132 g, 63%). [α]D = −13.90 (c = 0.105 in MeOH). IR (neat) ν: 3377, 2953, 2122, 1683 cm−1. 1H NMR (200 MHz, D2O) δ: 2.08–2.16 (m, 2H), 2.38–2.46 (m, 1H), 2.70–2.85 (m, 1H), 3.04–3.11 (m, 2H), 3.37–3.41 (m, 2H), 3.80–3.86 (m, 1H), 4.25–4.29 (dd, J = 3.5, 10.8 Hz, 1H), 4.56–4.59 (m, 1H) ppm. 13C NMR (50 MHz, D2O) δ: 23.3, 34.1, 36.4, 52.8, 58.8, 60.0, 66.4, 162.7 ppm. 13C DEPT (50 MHz, D2O) δ: 23.3 (CH2), 34.1 (CH2), 36.3 (CH2), 52.8 (CH2), 58.8, 60.0 (CH2), 66.4 ppm. HRMS (ESI): calculated mass for C8H15N5O2: 213.1226, observed mass (M + H): 214.1299.
(2S,4S)-4-Amino-1-(3-aminopropyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (9). Compound 8 (0.2 g, 0.61 mmol) was dissolved in methanol, to it palladium on charcoal (0.02 g) was added and the reaction was allowed to proceed under H2 pressure (35–40 psi). After completion of reaction, the solvent was removed under vacuum and the crude compound (0.112 g, 61%) was purified by HPLC. [α]D = −13.9 (c = 0.1 in MeOH). 1H NMR (400 MHz, D2O) δ: 1.99–2.23 (m, 3H), 2.96–3.09 (m, 3H), 3.20–3.35 (m, 1H), 3.43–3.58 (m, 1H), 3.70–3.81 (m, 1H), 3.91–4.00 (m, 1H), 4.24–4.34 (m, 2H) ppm. 13C NMR (100 MHz, D2O) δ: 23.2, 32.7, 36.2, 47.2, 52.7, 55.8, 67.6, 163.0, 170.1 ppm. 13C DEPT (100 MHz, D2O) δ: 23.2 (CH2), 32.7 (CH2), 36.2 (CH2), 47.2, 52.7 (CH2), 55.8 (CH2), 67.6 ppm. HRMS (ESI): calculated mass for C8H17N3O2: 187.1321, observed mass (M + H): 188.1392.
Materials and methods
All the chemicals were procured from Sigma-Aldrich unless otherwise mentioned. TLC analyses were carried out on precoated silica gel 60 F254 (Merck). Column chromatographic separations were performed using neutral alumina or silica gel (60–120 mesh or 200–400 mesh, Merck) and using the solvent systems EtOAc/petroleum ether or MeOH/DCM. 1H and 13C NMR spectra were obtained using Bruker AC-200, AC-400 NMR spectrometers. The chemical shifts are reported in delta (δ) values and referred to internal standard TMS for 1H. High resolution mass spectra were recorded on a Thermo Fisher Scientific Q Exactive mass spectrometer. Specific rotations of samples were recorded on a Bellingham Stanley ADP220 Polarimeter, IR was recorded on Bruker Alpha spectrophotometer. Primary anti-AGE antibody, anti-CML antibody and secondary antibody conjugate were purchased from Merck Millipore (India).
Circular dichroism measurements. The CD spectra were measured as described earlier.5 The protein concentration was constant in all the samples (0.02 mg mL−1). CD spectra were acquired on a JASCO J-815 spectropolarimeter at room temperature. The spectra were collected as accumulations of three scans and were corrected for respective blanks. Results are expressed as molar ellipticity, [θ] (deg cm2 dmol−1). The CD spectra of the protein samples were analysed to calculate the secondary structure content using CDPro software that has three algorithms: CONTINLL, CDSSTR and SELCON3.17
In vitro glycation of bovine serum albumin (BSA). The BSA glycation reaction was performed as described earlier by Kańska and Boratyński18 with minor modification described recently by Kolekar et al.5 with or without title compounds (20 mM) and kept at 37 °C for 10–15 days. In vitro glycation was monitored by fluorescence spectroscopy, excitation at 370 nm and emission at 440 nm by using a spectrofluorometer (Thermo, Varioskan Flash Multimode Reader).
IC50 determination of representative title compounds. The percent inhibition of AGE formation was calculated using the formula: % inhibition = (1 − Fi/Fc) × 100, where Fi = fluorescence intensity of glycated BSA treated with inhibitor and Fc = fluorescence intensity of glycated BSA in the absence of any inhibitor. The apparent IC50 was determined by plotting the percent glycation inhibition vs. inhibitor concentration.
Western blot analysis using anti-AGE and anti-CML antibodies. BSA, glycated BSA or glycated BSA with 20 mM of aminoguanidine or 20 mM of compounds 2, 4, 6, 8, and were incubated at 37 °C for 10–15 days. 5 μg of each protein sample was separated by 12% SDS-PAGE and transferred onto a PVDF membrane. The membranes were blocked with 5% skimmed milk powder dissolved in PBS. The proteins were probed by anti-AGE and anti-CML antibodies at the antibody dilution of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2000 each. Secondary anti-rabbit antibody conjugated with HRP was used at a dilution of 1
2000 each. Secondary anti-rabbit antibody conjugated with HRP was used at a dilution of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5000 for both the blots. Immunoreactive bands were visualized using Western Bright Quantum western blotting detection kit (Advansta) and documented by Syngene Imaging System.
5000 for both the blots. Immunoreactive bands were visualized using Western Bright Quantum western blotting detection kit (Advansta) and documented by Syngene Imaging System.
MALDI-TOF-based insulin glycation assay. The reaction mixture (100 μL) comprising phosphate buffer (pH 7.4, 0.1 M) containing title compounds (20 mM), insulin (1.8 mg mL−1, 25 μL) and glucose (250 mM, 25 μL) was incubated at 37 °C. The reaction was monitored till the relative intensity of glycated insulin reached 100% as seen by MALDI-TOF-TOF analysis (AB SCIEX TOF/TOF™ 5800) (5 days). The reaction mixture was mixed with sinapinic acid (ratio 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5) and analysed by MALDI-TOF-TOF in linear mode using Anchor Chip 384 targets as described.1
5) and analysed by MALDI-TOF-TOF in linear mode using Anchor Chip 384 targets as described.1
Fructosamine assay. The fructosamine level was measured by the NBT Labkit (Chemelex, S.A.) protocol. 300 μL of 0.75 mM NBT was added to a 96-well microplate containing 30 μL of 0.50 μg BSA, glycated BSA, or glycated BSA with title compounds (20 mM). Glycated BSA with aminoguanidine (20 mM) was taken as a control. The reduction of NBT absorbance by fructosamine was measured at 520 nm immediately after additions (considered as Abs1) and after incubation at 37 °C for 15 min (considered as Abs2). The absorbance was monitored by using a UV spectrophometer (UV 1800, Shimadzu).
Adduct formation with glucose. To elucidate the AGE inhibition mechanism of the title compounds, 2, 4, 6, 8, 9 (20 mM each) were incubated with glucose (0.5 M) in phosphate buffer pH 7.4 at 37 °C for 6 days. The reaction was analysed by LC-MS on Q-Exactive Orbitrap to study and detect the glucose adduct formation with the title compounds.
MTT assay for cytotoxicity. L6 rat muscle cells were seeded at a cell density of 1 × 104 cells per well in a 96 well plate. After the cells adhered and attained their morphology, they were serum starved for 4 h and treated with various concentrations of the title compounds (2, 4, 6, 8, and 9) in triplicate for 16 h, while only serum starved cells served as control. After incubation, cells were given one wash with PBS and 100 μL fresh serum free media was added. 6 μL of 5 mg mL−1 MTT (dissolved in PBS) was added to each well and incubated in dark at 37 °C until violet formazan crystals were observed. Media from each well was discarded and crystals were dissolved in 100 μL DMSO. Absorbance was measured at 555 nm using Varioskan flash multimode plate reader. This assay was performed using the Vybrant MTT Proliferation Assay Kit from Invitrogen.
Flow cytometry analysis of intracellular reactive oxygen species in Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4743. Levels of intracellular ROS were measured in the presence of title compounds using ascorbic acid as control with 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (Molecular Probes). Cells were grown in SD medium with or without compounds for 3 days. Briefly, aliquots were taken after 3 days, cells were pelleted down and washed with PBS (137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4, 2 mM KH2PO4). Cells were incubated with the dye (10 μM) for 90 min at 30 °C. Cells were then washed twice in PBS and analyzed by flow cytometry analysis on BD Accuri C6 flow cytometer equipped with a 50 mW argon laser emitting at 488 nm. The green fluorescence was collected through a 488 nm blocking filter. Data acquired from a minimum of 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cells per sample at low flow rate were analyzed19 using BD accuri C6 software.
000 cells per sample at low flow rate were analyzed19 using BD accuri C6 software.
Orbitrap analysis, database search and PTM analysis. 100 μg of protein was reduced with 100 mM dithiotreitol (DTT) at 60 °C for 15 min, then alkylated with 200 mM iodoacetamide in dark at room temperature for 30 min. Proteins were digested by adding porcine trypsin in the ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 (final enzyme
50 (final enzyme![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) proteins) at 37 °C overnight. The digestion reaction was stopped by adding concentrated HCL and incubated for 10 min at 37 °C before vortexing and centrifugation and analysed on LC MS/MS (Q-Exactive Orbitrap, Thermo). The chromatographic separation was performed as described in our earlier report.5 The mass spectrometric data were processed using Proteome discoverer 1.4 (Version 1.4.0.288, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bremen, Germany). The data were searched against UniProt Bovine Serum Albumin (P02769) sequence database. Carbamidomethylation of cysteine (C) and oxidation at methionine (M) was considered as fixed and variable modification respectively. Additionally glycation modifications at lysine position were searched as dynamic variable modification included Amadori (+162.02 Da); Peptide and fragment mass tolerance were 10 ppm, 0.5 Da respectively with minimum of 2 missed cleavages and 1% false discovery rate (1% FDR). The identification of glycation modifications were selected based on the criteria described earlier.20
proteins) at 37 °C overnight. The digestion reaction was stopped by adding concentrated HCL and incubated for 10 min at 37 °C before vortexing and centrifugation and analysed on LC MS/MS (Q-Exactive Orbitrap, Thermo). The chromatographic separation was performed as described in our earlier report.5 The mass spectrometric data were processed using Proteome discoverer 1.4 (Version 1.4.0.288, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bremen, Germany). The data were searched against UniProt Bovine Serum Albumin (P02769) sequence database. Carbamidomethylation of cysteine (C) and oxidation at methionine (M) was considered as fixed and variable modification respectively. Additionally glycation modifications at lysine position were searched as dynamic variable modification included Amadori (+162.02 Da); Peptide and fragment mass tolerance were 10 ppm, 0.5 Da respectively with minimum of 2 missed cleavages and 1% false discovery rate (1% FDR). The identification of glycation modifications were selected based on the criteria described earlier.20
Conclusions
The studies reported herein represent an important contribution towards the search for new molecules that not only inhibit glycation and AGE formation, but are also effective at controlling the concentration of intracellular reactive oxygen species. Moreover, the title compounds are easily accessible synthetically through simple chemical transformations, that should be amenable to scale-up. The superior antiglycation properties of the title compounds have been demonstrated by circular dichroism, fluorescence spectroscopy, western blot assay and also mass spectrometry. Mass spectrometric analysis and the fructosamine assays suggest that the title compounds form adducts with glucose, indicating that they probably act by inhibiting the formation of Amadori products. The low cytotoxicity of the title compounds is yet another favourable attribute. On the whole, the compounds-methyl(2S,4R)-1-(3-aminopropyl)-4-hydroxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylate (2) and (2S,4R)-1-(3-aminopropyl)-4-hydroxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (4) exhibited the best activity in the present study. These results suggest the contribution of the C4-hydroxyl group towards the antiglycation activity of the title compounds, in addition to the free amino function. The hydroxyl group offers possibilities of hydrogen-bonding and/or metal ion chelation, which could influence the activity of the respective title compound. Further, C4 being a chiral centre, the role of stereochemistry on the observed activity also cannot be ruled out. Studies towards dissecting and discerning these effects are currently underway in our laboratory and will be reported in due course.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge research funding from CSIR project CSC0111. YMK thanks CSIR, India for post-doctoral Research Associateship. GSB thanks UGC, India for Research Fellowship. The assistance of Mrs S. S. Kunte is gratefully acknowledged for purification of compound 9.
References
- S. K. Kesavan, S. Bhat, S. B. Golegaonkar, M. G. Jagadeeshaprasad, A. B. Deshmukh, H. S. Patil, S. D. Bhosale, M. L. Shaikh, H. V. Thulasiram, R. Boppana and M. J. Kulkarni, Sci. Rep., 2013, 3, 2941 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. B. Golegaonkar, H. S. Bhonsle, R. Boppana and M. J. Kulkarni, Eur. J. Mass Spectrom., 2010, 16, 221 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. B. Bansode, A. K. Jana, K. B. Batkulwar, S. D. Warkad, R. S. Joshi, N. Sengupta and M. J. Kulkarni, PLoS One, 2014, 9, e105196 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. M. Joglekar, S. N. Panaskar, A. D. Chougale, M. J. Kulkarni and A. U. Arvindekar, Mol. BioSyst., 2013, 9, 2463 RSC.
- Y. M. Kolekar, V. Garikapati, S. B. Bansode, B. Santhakumari, H. V. Thulasiram and M. J. Kulkarni, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 25051 RSC.
- M. D'Costa, V. A. Kumar and K. N. Ganesh, Org. Lett., 1999, 1, 1513 CrossRef.
-
(a) K. M. Patil, R. J. Naik, M. Vij, A. K. Yadav, V. A. Kumar, M. Ganguli and M. Fernandes, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2014, 24, 4198 CrossRef CAS PubMed;
(b) K. M. Patil, Ph. D. Dissertation, Pune University, India, 2014.
- S. Ramakrishnan and K. N. Sulochana, Exp. Eye Res., 1993, 57, 623 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Monacelli, D. Storace, C. D'Arrigo, R. Sanguineti, R. Borghi, D. Pacini, A. L. Furfaro, M. A. Pronzato, P. Odetti and N. Traverso, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2013, 14, 10694 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Nomoto, M. Yagi, U. Hamada, J. Naito and Y. Yonei, Anti-Aging Med., 2013, 10, 92 Search PubMed.
- L. Séro, L. Sanguinet, P. Blanchard, B. T. Dang, S. Morel, P. Richomme, D. Séraphin and S. Derbré, Molecules, 2013, 18, 14320 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. P. de la Maza, F. Garrido, N. Escalante, L. Leiva, G. Barrera, S. Schnitzler, M. Zanolli, J. Verdaguer, S. Hirsch, N. Jara and D. Bunout, J. Diabetes Mellitus, 2012, 2, 221 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Ardestani and R. Yazdanparast, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2007, 41, 572 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Meeprom, W. Sompong, C. B. Chan and S. Adisakwattana, Molecules, 2013, 18, 6439 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. R. Baker, D. V. Zyzak, S. R. Thorpe and J. W. Baynes, Clin. Chem., 1993, 39, 2460 CAS.
- L. Knels, M. Worm, M. Wendel, C. Roehlecke, E. Kniep and R. H. Funk, J. Neurochem., 2008, 106, 1876 CAS.
- N. Sreerama and R. W. Woody, Anal. Biochem., 2000, 287, 252 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- U. Kańska and J. Boratyński, Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp., 2002, 50, 61 Search PubMed.
- A. Mesquita, M. Weinberger, A. Silva, B. Sampaio-Marques, B. Almeida, C. Leão, V. Costa, F. Rodrigues, W. C. Burhans and P. Ludovico, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2010, 107, 15123 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. S. Bhonsle, A. M. Korwar, S. K. Kesavan, S. D. Bhosale, S. B. Bansode and M. J. Kulkarni, Eur. J. Mass Spectrom., 2012, 18, 475 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: NMR, mass spectra of 1–9, mass spectra of glucose adducts with 4, 6, 8 & 9, Orbitrap analysis, database search & PTM analysis, Ponceau staining of anti-AGE & anti-CML blots, AGE fluorescence spectra of glycated BSA treated with 1, 3, 5 & 7. See DOI: 10.1039/c5ra12148e |
|
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 |
Click here to see how this site uses Cookies. View our privacy policy here. 
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2000 each. Secondary anti-rabbit antibody conjugated with HRP was used at a dilution of 1
2000 each. Secondary anti-rabbit antibody conjugated with HRP was used at a dilution of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5000 for both the blots. Immunoreactive bands were visualized using Western Bright Quantum western blotting detection kit (Advansta) and documented by Syngene Imaging System.
5000 for both the blots. Immunoreactive bands were visualized using Western Bright Quantum western blotting detection kit (Advansta) and documented by Syngene Imaging System.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5) and analysed by MALDI-TOF-TOF in linear mode using Anchor Chip 384 targets as described.1
5) and analysed by MALDI-TOF-TOF in linear mode using Anchor Chip 384 targets as described.1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cells per sample at low flow rate were analyzed19 using BD accuri C6 software.
000 cells per sample at low flow rate were analyzed19 using BD accuri C6 software.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 (final enzyme
50 (final enzyme![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) proteins) at 37 °C overnight. The digestion reaction was stopped by adding concentrated HCL and incubated for 10 min at 37 °C before vortexing and centrifugation and analysed on LC MS/MS (Q-Exactive Orbitrap, Thermo). The chromatographic separation was performed as described in our earlier report.5 The mass spectrometric data were processed using Proteome discoverer 1.4 (Version 1.4.0.288, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bremen, Germany). The data were searched against UniProt Bovine Serum Albumin (P02769) sequence database. Carbamidomethylation of cysteine (C) and oxidation at methionine (M) was considered as fixed and variable modification respectively. Additionally glycation modifications at lysine position were searched as dynamic variable modification included Amadori (+162.02 Da); Peptide and fragment mass tolerance were 10 ppm, 0.5 Da respectively with minimum of 2 missed cleavages and 1% false discovery rate (1% FDR). The identification of glycation modifications were selected based on the criteria described earlier.20
proteins) at 37 °C overnight. The digestion reaction was stopped by adding concentrated HCL and incubated for 10 min at 37 °C before vortexing and centrifugation and analysed on LC MS/MS (Q-Exactive Orbitrap, Thermo). The chromatographic separation was performed as described in our earlier report.5 The mass spectrometric data were processed using Proteome discoverer 1.4 (Version 1.4.0.288, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bremen, Germany). The data were searched against UniProt Bovine Serum Albumin (P02769) sequence database. Carbamidomethylation of cysteine (C) and oxidation at methionine (M) was considered as fixed and variable modification respectively. Additionally glycation modifications at lysine position were searched as dynamic variable modification included Amadori (+162.02 Da); Peptide and fragment mass tolerance were 10 ppm, 0.5 Da respectively with minimum of 2 missed cleavages and 1% false discovery rate (1% FDR). The identification of glycation modifications were selected based on the criteria described earlier.20








