Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity of vitex honey against paracetamol induced liver damage in mice
Abstract
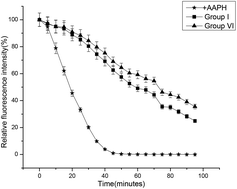
Fourteen vitex honeys from China were investigated to evaluate its antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity against paracetamol-induced liver damage. All honey samples exhibited high total phenolic content (344–520 mg GAE per kg), total flavonoid content (19–31 mg Rutin per kg), and strong antioxidant activity in DPPH radical scavenging, ferric reducing antioxidant power and Ferrous ion-chelating ability. Nine phenolic acids were detected in vitex honey samples, in which caffeic acid was the main compound. Honey from Heibei Zanhuang (S2) ranked the highest antioxidant activity was orally administered to mice (5 g kg−1, 20 g kg−1) for 70 days. In high-dose (20 g kg−1), vitex honey pretreatment resulting in significant increase in serum oxygen radical absorbance capacity (15.07%) and decrease in Cu2+-mediate lipoprotein oxidation (80.07%), and suppression in alanine aminotransferase (75.79%) and aspartate aminotransferase (74.52%), enhancement in the superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activities and reduction in malondialdehyde (36.15%) and 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (19.6%) formation compared with paracetamol-intoxicated group. The results demonstrated the hepatoprotection of vitex honey against paracetamol-induced liver damage might attribute to its antioxidant and/or perhaps pro-oxidative property.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...