Nanoscale high-entropy alloys for solar and thermal applications
Xinyang
Li†
,
Yalong
Zou†
,
Haijiao
Lu
 * and
Lianzhou
Wang
* and
Lianzhou
Wang

Nanomaterials Centre, School of Chemical Engineering, and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, QLD 4072, Australia. E-mail: haijiao.lu@uq.edu.au
First published on 28th January 2025
Abstract
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) represent a novel class of materials that challenge traditional alloy design principles by incorporating five or more principal elements in near-equiatomic ratios. This unique composition results in enhanced mechanical properties, thermal stability, and corrosion resistance. Recent research highlights the significant potential of HEAs in catalysis, particularly in solar- and thermo-related applications. Their high configurational entropy not only stabilizes single-phase structures but also facilitates unique electronic and catalytic behaviors. The tunability of HEAs allows for the optimization of their physical and chemical properties, enabling improved reaction rates and selectivity in various catalytic processes. This review provides a thorough overview of HEAs, covering their evolution, synthesis methods, characterization techniques, and computational modeling approaches. We critically assess the fundamental properties and underlying mechanisms driving their exceptional catalytic performance, and explore their current and potential applications in catalysis. By identifying key challenges and promising directions, we aim to guide future research toward unlocking the full potential of HEAs in catalytic systems.
Introduction
The concept of high-entropy alloys (HEAs) emerged in the late 1990s and early 2000s, signaling a departure from traditional alloy design principles.1–4 Inoue identified three essential requirements for amorphous alloy formation, one of which requires the inclusion of three or more elements.1 Building on this foundation, Greer introduced the “confusion principle”, positing that the high mixing entropy in multi-component alloys fosters the development of single-phase amorphous structures.2 A pivotal breakthrough occurred in 2004 with the discovery of the FeCrMnNiCo alloy by Cantor and colleagues, which exhibits a single face-centered cubic (FCC) structure through equimolar mixing of multiple elements.3 Simultaneously, Yeh and co-workers formally articulated the HEA concept, advocating for the use of multiple principal elements in near-equiatomic proportions to achieve a high mixing entropy solid solution.4 These foundational studies established the theoretical basis for HEAs, underscoring the significance of entropy-driven stabilization.Initial research on HEAs predominantly focused on their phase structures and mechanical properties, particularly for applications in extreme environments. Gludovatz and colleagues demonstrated that an HEA composed of Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni exhibited no ductile-to-brittle transition at low temperatures, with a fracture toughness exceeding 200 MPa m1/2.5 In parallel, Senkov and colleagues concentrated on heat-resistant HEAs, developing compositions such as Ta25Nb25W25Mo25 and Ta20Nb20W20Mo20V20, which exhibited remarkable yield strength at temperatures above 800 °C, significantly outperforming conventional high-temperature alloys like Haynes 230 and Inconel 718.6
With the advancement of nanotechnology, research on HEAs has progressively shifted from the macroscale to the nanoscale. Confined within a single lattice, the incorporation of multiple principal elements presents new opportunities for designing advanced catalysts with optimized activity, selectivity, and stability.7–11 The multi-element composition and complex structure of HEAs offer unique catalytic potential. The high mixing entropy compensates for enthalpy differences arising from element incompatibility by increasing configurational entropy, effectively overcoming the miscibility gap observed in bulk phases. This results in more diverse geometric and electronic properties, exemplifying the “cocktail effect” frequently observed in complex systems.12,13
Furthermore, significant atomic size differences in HEAs often induce severe lattice distortions, creating local thermodynamic nonequilibrium states. This “lattice distortion effect” plays a pivotal role in lowering energy barriers for molecular adsorption, activation, and conversion, with strain induced by distortion being particularly important in multi-element complex systems. Distortion can effectively modulate the energy levels of intermediates, alter absorption band gaps, and optimize catalytic pathways, thus enhancing catalytic efficiency.8,14 Additionally, HEAs exhibit the potential for a “sluggish diffusion effect”, which slows diffusion kinetics and improves the chemical, thermal, and mechanical stability of the material.15,16
Current research on HEAs at the nanoscale is predominantly focused on electrocatalysis, particularly for reactions such as water splitting10,17,18 and CO2 reduction.19–21 Recent studies have extended HEA applications into other energy-related fields, including batteries22–24 and nanowires.25,26 However, only a limited number of investigations have begun to explore HEAs in solar- and thermo-related catalysis.9,27,28 Given the significant potential advantages of HEAs, such as enhanced light absorption, improved thermal conversion efficiency, and stability at elevated temperatures, further research into their application in solar- and thermal-driven catalytic processes is of considerable importance. Due to their tunable catalytic properties, entropy-driven stabilization, and effective multi-element synergy, HEAs exhibit excellent photothermal conversion efficiency and the ability to dissociate C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bonds, making them highly promising for catalytic applications. The high-entropy structure of HEAs provides exceptional structural stability through kinetic sluggish diffusion effects and thermodynamic entropy stabilization, making them ideal candidates for high-temperature catalysis. Additionally, multi-element alloying enables HEAs to modulate their physical and chemical properties, offering the potential to sustain high hydrogen evolution activity while reducing dependence on precious metals. Transitioning from utilizing metals to “taming” metals, HEAs provide greater possibilities for surface and interfacial structure regulation compared to single-metal catalysts due to their diverse metallic combinations. Additionally, valuable insights and strategies derived from the structural design of catalytic materials can serve as important references for further advancements.29–35
O bonds, making them highly promising for catalytic applications. The high-entropy structure of HEAs provides exceptional structural stability through kinetic sluggish diffusion effects and thermodynamic entropy stabilization, making them ideal candidates for high-temperature catalysis. Additionally, multi-element alloying enables HEAs to modulate their physical and chemical properties, offering the potential to sustain high hydrogen evolution activity while reducing dependence on precious metals. Transitioning from utilizing metals to “taming” metals, HEAs provide greater possibilities for surface and interfacial structure regulation compared to single-metal catalysts due to their diverse metallic combinations. Additionally, valuable insights and strategies derived from the structural design of catalytic materials can serve as important references for further advancements.29–35
Herein, we briefly review the origins of HEAs, followed by an in-depth discussion of various synthesis methods and other innovative fabrication methods. The review then details a range of characterization techniques, which provide comprehensive insights into the microstructural features and catalytic properties of HEAs. Additionally, computational modeling approaches are introduced to explore the electronic structure and catalytic behavior of HEAs, particularly within the domains of solar- and thermo-related catalysis. Overall, this review aims to provide a thorough examination of HEAs, encompassing fundamental properties, synthesis strategies, and characterization methods, while also highlighting key research directions for designing efficient solar- and thermo-catalytic materials.
Principles and design strategies of HEAs
Definition and principle
In the research field of catalysis, the role of entropy, particularly configurational entropy arising from multi-component mixing, has not yet received sufficient attention, with most studies predominantly focused on enthalpic parameters. In thermodynamics, entropy is a fundamental parameter that quantifies the degree of disorder within a system. The entropy S of a system is defined by the following equation:36S = k![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) In In![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ω Ω | (1) |
In solid materials, entropy primarily arises from quantum states induced by lattice vibrations. The total entropy encompasses contributions from atomic arrangement (configurational entropy), atomic vibrations (vibrational entropy), electron configurations, and magnetic moments. In the context of solid solutions, when the enthalpy of mixing is negligible, the increase in entropy resulting from the mixing of different atomic species is referred to as configurational entropy. In HEAs composed of multiple principal elements, configurational entropy plays a predominant role, often dictating the total entropy of the system.
HEAs are characterized by the inclusion of multiple components in significant molar fractions. In a random solid solution, the mixing entropy of HEAs is considerably higher than that of traditional alloys, often exceeding the melting entropy of most metals, which typically remains below R (where R is the gas constant, 8.314 J mol−1 K−1). Based on this, alloy materials can be classified into the following categories: low-entropy alloys (less than 1R), representing traditional alloys; medium-entropy alloys (1R ≤ S ≤ 1.5R); and high-entropy alloys (greater than or equal to 1.5R) (Fig. 1a).4,38 In more recent studies, as the understanding of entropy in alloys has evolved, these definitions have become less rigid, with high entropy now being considered more as a relative concept achieved through the mixing of multiple elements.
 | ||
| Fig. 1 (a) Basic definition of high-entropy alloys, in which ΔGmix, ΔHmix, ΔSmix and T are the Gibbs free energy of mixing, the enthalpy of mixing, the entropy of mixing and the temperature, respectively. Reproduced from ref. 38 with permission from Nature, Copyright 2024. (b) Schematic comparison of phase-separated heterostructures synthesized by conventional slow reduction (slow kinetics) versus solid-solution HEA-NPs produced by the fast-kinetics CTS method. Reproduced from ref. 39 with permission from John Wiley and Sons, Copyright 2024. (c) The frequency of element usage in 408 multi-principal element alloys (MPEAs). Reproduced from ref. 7 with permission from Elsevier, Copyright 2017. (d) Transition metal elements and their significantly varied physicochemical properties in extreme alloying through high-temperature, high-entropy synthesis. Reproduced from ref. 40 with permission from Elsevier, Copyright 2021. | ||
It is generally assumed that a single solid solution structure is established in multi-component HEAs, allowing for the calculation of mixing entropy using the following formula (Fig. 1b):36
 | (2) |
Element selection
The selection of these elements is a critical step in the design of HEAs. In a comprehensive study, over 400 HEA samples were analyzed to determine the most frequently utilized elements. The results showed that Cr, Fe, Co, Ni, and Al were present in more than 50% of the alloys. To further emphasize the significance of element selection,7Fig. 1c lists the elements that appeared more than 100 times across these samples, offering insights into their prevalence and potential roles: Fe (348), Ni (341), Co (301), Cr (301), Al (274), Cu (186), Ti (121), and Mn (101).A visual inspection indicates that many of these elements are well suited for catalytic applications. In both photocatalytic and thermocatalytic reactions, researchers tend to follow a similar trend in element selection. By harnessing the synergistic effects inherent in high-entropy alloys, it is often possible to achieve performance enhancements where the combined effect exceeds the sum of the individual contributions. However, it is important to recognize that much of the current research focuses on maximizing the number of elements and optimizing the overall performance. Systematic studies that emphasize controlling variables within simplified systems and quantitatively assessing the impact of individual component additions remain relatively limited.
Phase formation considerations
The selection of elements for HEAs is followed by a critical evaluation of phase formation, which directly influences the homogeneity and stability of the resultant alloy. From a phase compatibility perspective, elements with similar crystal structures are more likely to form stable phases when combined in high concentrations; for instance, both Cu and Ni exhibit an FCC structure. However, the actual phase formation is influenced by multiple factors.The development of either a single-phase or multi-phase structure largely depends on parameters such as differences in electronegativity, valence electron concentration (VEC), atomic size mismatch, mixing entropy, and mixing enthalpy. Mixing entropy can be analogized to a furnace: a greater diversity of components enhances the mixing effect, thereby promoting the stability of the solid solution phase. In contrast, mixing enthalpy can be likened to the heat generated during cooking; negative enthalpy values suggest that the components are more likely to coalesce.
Atomic radius differences act as a critical factor in determining phase formation, where smaller size discrepancies facilitate the integration of elements into a complete solid solution phase. Differences in electronegativity can be viewed as a measure of compatibility between elements—the smaller the difference, the more effectively the elements collaborate. Thermodynamic parameters, including mixing entropy, mixing enthalpy, and melting point, work in concert to determine the ease of forming solid solutions. The volume mismatch factor further characterizes the degree to which component volumes align, with reduced volume differences enhancing the likelihood of stable solid solution formation.
Furthermore, Yao and colleagues provided a quantitative summary of the relationships between atomic size, valence, and electronegativity, offering deeper insights into the complex interplay of these factors in determining phase stability in HEAs (Fig. 1d).40
FCC28,36,41,42 and BCC5,6,9–11 single-phase alloys are currently the two most extensively studied structures.43,44 Among these, the FCC structure is particularly prevalent in high-entropy alloy nanoparticles (such as truncated octahedra) due to its thermodynamic stability and high packing density, making it easier to form in multi-element systems. This structure offers more low-coordination sites, promoting catalytic reactions. A classic example is the Cantor alloy (CoCrFeMnNi), which has a stable single-phase FCC structure.3 Its stability is attributed to the relative uniformity of its constituent elements in terms of electronegativity, atomic radius, and VEC, resulting in a low tendency for phase separation. This makes it a representative of single-phase FCC structures in HEAs, and many catalytic designs are based on the selection of elements from this alloy.
Overall, HEAs exhibit the capacity to form a variety of phase structures, with the formation of solid solutions being the preferred outcome from a stability standpoint. Both single-phase and multi-phase solid solutions are generally favored, while the emergence of amorphous phases is occasionally permissible. In contrast, phase separation is typically avoided. As advancements in preparation techniques continue to evolve, the occurrence of mixed polycrystalline structures has been observed, alongside the coexistence of crystalline solid solutions and amorphous phases. The implications of these complex structures on catalytic performance warrant further investigation. Understanding the relationship between phase composition and catalytic efficacy is crucial for optimizing the application of HEAs in various catalytic processes.
Synthesis methods of HEAs at the nanoscale
While there have been comprehensive reviews on the synthesis of HEAs,45 few studies focus exclusively on the nanoscale synthesis of HEAs. The synthesis of HEAs demonstrates notable distinctions between traditional methods and nanoscale approaches. Conventional techniques, such as melting and casting, are adept at producing bulk materials characterized by uniform composition and superior mechanical properties, rendering them widely applicable in industrial contexts. However, these methods typically result in relatively large grain sizes, which constrain precision at the nanoscale. Consequently, traditional approaches are more suitable for the fabrication of stable and durable bulk structures, rather than for applications requiring nanoscale control and refinement.Powder metallurgy and mechanical alloying have become critical methods for synthesizing small-scale HEAs.27 Unlike conventional melting and casting processes primarily used for bulk alloy production, these techniques are particularly suited for the synthesis of fine particles. Known for their cost-effectiveness and ability to avoid rapid annealing steps, powder metallurgy and mechanical alloying have shown promising results in the fabrication of miniature high-entropy alloy catalysts. However, the potential of these methods to achieve true nanoscale synthesis remains a topic of ongoing debate.7,8
Methods dedicated to synthesizing purely nanoscale HEAs can be broadly categorized into four main approaches: thermally-assisted methods, chemical reaction/solution-based methods, vacuum physical deposition techniques, and other innovative technologies.
Thermal-assisted methods
Carbon thermal shock (CTS) synthesis and fast-moving bed pyrolysis employ high-temperature processes to generate solid-phase HEA nanoparticles (NPs) with dimensions ranging from a few nanometers to several tens of nanometers, as illustrated in Fig. 2a.29 CTS technology enables the synthesis of nanoscale particles from typically immiscible components by applying a thermal shock to metal salt precursors on a carbon support at approximately 200 K. By controlling CTS parameters, such as substrate choice, temperature, shock duration, and heating or cooling rates, diverse nanostructures can be formed, though the use of carbon as the substrate remains necessary. Notably, carbothermal shock synthesis is characterized by its high uniformity and productivity, making it suitable for large-scale applications. However, its applicability is constrained by the requirement of carbon as a substrate. Conversely, Joule heating synthesis has shown promise for the synthesis of HEA NPs. The Joule heating synthesis method generates a crystalline metal oxide coating on the substrate, which stabilizes the metal precursors and prevents nanoparticle agglomeration. Rapid Joule heating decomposes the metal precursors, forming high-entropy alloy nanoparticles (HEA-NPs) that are embedded within the oxide layer, resulting in particles with uniform size and well-dispersed distribution.49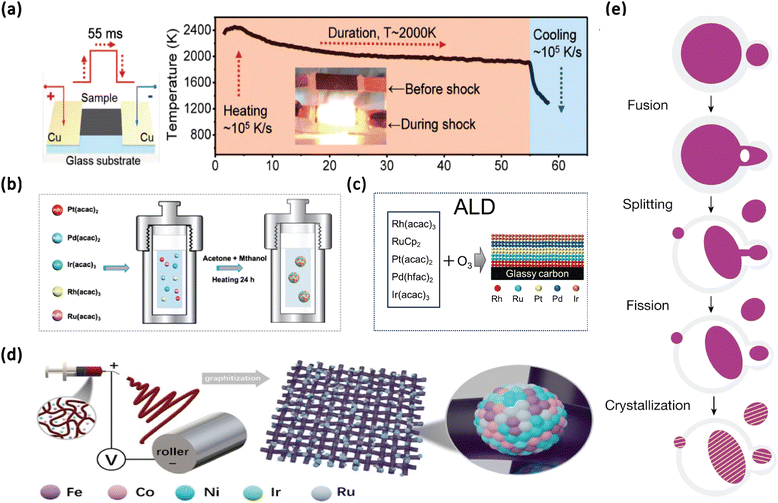 | ||
| Fig. 2 (a) Schematic illustration of the CTS process for the preparation of HEA NPs. Reproduced from ref. 39 with permission from John Wiley and Sons, Copyright 2024. (b) Schematic illustration of the solvothermal synthesis of PtPdIrRhRu HEAs. Reproduced from ref. 8 with permission from the American Chemical Society, Copyright 2020. (c) Schematic of synthesizing RhRuPtPdIr HEA/GC by the ALD method. Reproduced from ref. 46 with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry, Copyright 2024. (d) Typical synthesis procedure for FeCoNiIrRu/CNFs combining electrospinning and graphitization processes. Reproduced from ref. 47 with permission from Elsevier, Copyright 2022. (e) Schematic illustration of liquid metal-assisted synthesis of HEA NPs. Reproduced from ref. 48 with permission from Nature, Copyright 2023. | ||
Chemical reaction/solution methods
Solution synthesis and electrochemical synthesis are conducted at lower temperatures and pressures, resulting in the production of liquid-phase HEA NPs, as depicted in Fig. 2b.8 The solvent-based synthesis relies on uniformly mixing metal precursors in solution, followed by nanoparticle formation through reduction or pyrolysis processes. When the metal elements are mutually soluble, it is easier to form a homogeneous solid-solution structure, resulting in compositionally uniform HEA NPs. Notably, electrochemical synthesis shows priority due to its higher yields under ambient conditions. However, both methods generally provide moderate uniformity and control, potentially limiting their applications in synthesis requiring precise structural characteristics.Vacuum physical deposition methods
Atomic layer deposition (ALD) and molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) are distinguished by their capability to achieve atomic-level control and uniformity in the production of vapor-phase HEA nanostructures, as illustrated in Fig. 2c.46 In the ALD process, gaseous precursor chemicals are sequentially introduced into the reaction chamber, where they undergo surface reactions with the substrate. Each reaction results in the formation of a monolayer-thick film on the surface, while unreacted precursors are removed. By repeating this cycle, the thickness and composition of the film can be precisely controlled at the atomic level. MBE involves using an existing substrate and a heating source to convert pure elements or compounds into molecular or atomic beams. These beams are directed towards the heated substrate surface. On the substrate, the atoms or molecules from the beams condense and grow in a manner that is crystallographically matched, resulting in the formation of epitaxial films. These techniques are well suited for the fabrication of ultrathin films and nanostructures. However, their low production rates and high associated costs pose significant challenges to scalability, rendering them more suitable for small-scale, high-precision research applications.Other methods
Laser scanning ablation and electrospinning present distinct advantages for the synthesis of nanoparticles. Laser scanning ablation is characterized by its excellent control and productivity, making it particularly effective for rapid nanoparticle synthesis.56 Conversely, while electrospinning generates nanofibers, it typically exhibits lower production rates and is therefore more suited for experimental applications, as depicted in Fig. 2d.47 Liquid metal-assisted synthesis exemplified by the work in Fig. 2e utilizes gallium to facilitate the integration of multiple metals into HEAs. This method effectively addresses elemental incompatibilities under mild conditions while achieving high productivity at lower temperatures.48In summary, each method for the nanoscale synthesis of HEAs offers distinct advantages that align with specific research and production goals, as depicted in Table 1. Thermal-assisted techniques dominate in large-scale applications due to their cost-effectiveness and high throughput, positioning them as efficient choices for HEA synthesis, but these methods depend on high-temperature conditions, which increases energy consumption, and all but the fast moving beds have fast annealing as a process, which may damage the internal structure of the HEA and thus reduce the catalytic efficiency. Moreover, chemical solution-based methods are good options for achieving high-yield synthesis under milder reaction conditions with a relatively low cost, but due to insufficient thermodynamic drive, the lattice mismatch between metal elements is large, and multiphase structures tend to appear. Additionally, all thermal-assisted and chemical solution-based methods do not provide a solution for surface and structure precision control, but vacuum deposition methods fill this gap; they provide unparalleled precision in compositional and structural control, making them particularly favorable for applications requiring exact tailoring of HEA characteristics, but their disadvantages are obvious, such as time-consuming processes and high cost of equipment and materials. Compared to thermal-assisted and solvent-based synthesis methods, these approaches are more suited for exploring extreme performance in research than for industrial production. Emerging approaches, such as laser scanning and liquid metal-assisted synthesis, introduce novel routes that promote efficient synthesis under moderate conditions, expanding the range of accessible HEA fabrication techniques. Future research directions should emphasize the development of synthesis pathways that enable faster, more efficient production of HEA catalysts under mild conditions. These advancements are expected to improve both synthesis efficiency and structural integrity, thus enhancing the overall catalytic performance and applicability of HEAs.
| Category | Method | Description | Equipment used | Synthesis temperature and pressure | Size | Uniformity | Controllability | Productivity | Phase | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT: room temperature; HP: high pressure. Controllability includes parameter control and reproducibility, and productivity covers the reaction time and potential batch capacity.a Can only use carbon as the substrate. | ||||||||||
| Thermal-assisted methods | Carbothermal shock synthesisa | Rapid thermal shock of metal salts on a carbon substrate to form HEA NPs | Current pulse device | ∼2000 K/1 atm | 3–25 nm | Good | Good | High | Solid phase | 36 |
| Microwave-assisted pyrolysis | Microwave heating of carbon-based materials followed by quenching to form HEA NPs | Microwave reactor | ∼1850 K/1 atm | 10–50 nm | Medium | Good | High | 50 | ||
| Fast moving bed pyrolysis | Rapid pyrolysis of metal precursors at high temperatures to create HEA NPs | Tube furnace | ∼923 K/1 atm Ar | 2–50 nm | Good | Medium | High | 51 | ||
| Joule heating synthesis | Joule heating triggers alloying of metal precursors into HEA NPs | Electric pulse equipment | ∼1073 K/1 atm | 10–100 nm | Medium | Medium | Medium | 49 | ||
| Arc-discharged plasma method | Arc discharge vaporizes metal precursors, leading to the formation of HEA NPs | Arc-discharge apparatus | ∼4000 K/vacuum Ar + H2 | 2–100 nm | Medium | Medium | High | 52 | ||
| Chemical reaction/solution methods | Solvent-thermal method | High-temperature, high-pressure solvent enables crystallization of HEA NPs | Hydrothermal reactor | ∼473 K/HP | 1–100 nm | Medium | Good | Low | Liquid phase | 53 |
| Electrosynthesis | Emulsified metal salt droplets are reduced on electrodes, forming HEA NPs | Three-stage electrolyzer | RT/1 atm | 10–100 nm | Medium | Good | High | 54 | ||
| Vacuum physical deposition methods continued | Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) | Layer-by-layer deposition forms uniform HEA nanostructures | ALD equipment | ∼423 K/vacuum | <10 nm | Excellent | Excellent | Low | Gas phase | 46 |
| Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE) | Ultra-precise molecular beam deposition forms HEA NPs with atomic accuracy | MBE equipment | ∼873 K/vacuum | <10 nm | Excellent | Excellent | Low | 55 | ||
| Others | Laser scanning ablation | Laser melts metals to rapidly form HEA NPs using an ultra-fast pulsed laser | Pulsed laser | ∼1000 K/1 atm | 1–10 nm | Good | Excellent | Medium | Solid phase | 56 |
| Electrospinning method | Electric field draws metal precursors into nanofibers, creating HEA NPs | Electro-spinning system | RT/vacuum | 10–100 nm | Medium | Good | Low | 47 | ||
| Liquid metal-assisted synthesis | Metal precursors mix in liquid metals to form HEA NPs | Liquid metal reactor | ∼923 K/1 atm | 10–100 nm | Good | Good | High | Liquid phase | 48 | |
Characterization techniques of high-entropy alloys
Characterized by complicated compositions, HEAs exhibit physical and catalytic properties that are significantly influenced by their microstructure and chemical state. Characterization is essential for understanding and optimizing these properties. By employing a range of techniques, researchers can gather critical information regarding crystal structure, elemental distribution, chemical environment, surface states, and microstructural features.57 These insights are vital for interpreting and predicting material behavior, encompassing phenomena such as local aggregation, surface reconstruction, and the formation of interfaces and vacancies across various applications.58HEA characterization techniques can be categorized into static and in situ characterization, as illustrated in Fig. 3. Static characterization encompasses various approaches, including diffraction, spectroscopy, microscopy, and mass spectrometry. Diffraction techniques are employed to ascertain phase structures, elucidating crystal types and lattice parameters. Spectroscopy methods focus on the chemical states of the materials, particularly regarding surface reactivity and the distribution of valence states. Microscopy techniques facilitate direct observation of nanoscale morphology and structural features, providing insights into elemental distribution, grain boundaries, and defects.49 Mass spectrometry (MS) is utilized to analyze the elemental composition and isotopic distribution of HEAs, which aids in the identification of different elements and potential impurities within the alloy.
Characterization requirements for HEAs vary significantly based on their target applications. The key parameters for catalytic applications include surface structure, active site distribution, and local density of states (LDOS), with emphasis on the analysis of surface chemical states and microstructural features. In contrast, thermocatalytic applications prioritize evaluating high-temperature stability and oxidation resistance. This necessitates a focus on phase stability and microstructural evolution, requiring detailed crystallographic and compositional analyses.
XRD serves as a fundamental tool for characterizing the crystal structure of HEAs. Powder XRD (PXRD) is particularly effective in revealing phase composition and crystal structure through the analysis of diffraction patterns. As the number of alloying elements increases, peak broadening in the diffraction patterns becomes more pronounced, often accompanied by phase transitions, such as from FCC to BCC structures. In BCC HEAs, additional impurity peaks are frequently observed. The presence of nanoscale grain sizes further exacerbates peak broadening, complicating the identification of potential impurities. PXRD is also utilized to determine lattice constants and assess crystallinity (Fig. 4a).25,65
 | ||
| Fig. 4 (a) XRD patterns of HEA NPs with different composition elements; (b) high-resolution TEM image, fast Fourier transform (FFT) image, and the corresponding atomic TEM-EDS maps of 21-HEA-NPs; and (c) STEM DF images and the corresponding EDS elemental maps of 21-HEA-NPs. Reproduced from ref. 25 with permission from Oxford University Press, Copyright 2022. (d) Synchrotron XRD pattern of Al1.3CoCrCuFeNi at room temperature; (e) a series of synchrotron XRD patterns of Al1.3CoCrCuFeNi from 100 to 800 °C. Reproduced from ref. 59 with permission from Nature, Copyright 2015. (f) EXAFS spectra in k-space for Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni absorbers in the FeO-high-entropy oxide (HEO). Reproduced from ref. 60 with permission from Science, Copyright 2023. (g) FT-EXAFS profiles of 15-HEA nanoparticles and comparison with their corresponding pure metal foils. Reproduced from ref. 40 with permission from Elsevier, Copyright 2021. (h) Normalized XANES spectra of HEAs at the Fe K-edge; (i) normalized EXAFS spectra of HEAs at the Fe K-edge. Reproduced from ref. 61 with permission from Elsevier, Copyright 2017. (j) XPS full spectrum of the surface of the ZrNbTaMoW HEA and HEO. Reproduced from ref. 27 with permission from Springer Nature, Copyright 2024. (k) HAADF-STEM of 3-PtRhMo NWs. Reproduced from ref. 62 with permission from Elsevier, Copyright 2023. (l) APT characterization of the passive film formed on the HEA after passivating treatment. Reproduced from ref. 63 with permission from Elsevier, Copyright 2019. (m) Mass activities of CrMnFeCoNi (CMFCN) HEAs with different BET areas in sulfuric acid aqueous solution; (n) ratios of the remaining mass after etching to the initial mass for the as-obtained samples and SEM images of different etching processes of CMFCN in sulfuric acid aqueous solution. Reproduced from ref. 64 with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry, Copyright 2020. | ||
High-resolution TEM (HR-TEM) complements PXRD by providing detailed insights into atomic arrangements and crystal plane characteristics. The presence of the (110), (101), and (211) crystal planes confirms the body-centered cubic (BCC) structure of 21-element HEA nanoparticles. Atomic-resolution TEM-energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (TEM-EDS) mapping demonstrated a uniform elemental distribution across the 21-element HEA nanoparticles. This homogeneity underscores the high-entropy effect, which stabilizes multi-element mixing and supports the nanoparticles’ consistent photothermal properties (Fig. 4b and c).25 To address the issue of peak broadening, synchrotron XRD, which offers high resolution, is particularly well suited for analyzing microstructural features and lattice distortion in complex alloys (Fig. 4d and e).49,59 Additionally, ND presents unique advantages in HEA research due to its sensitivity to light elements, such as lithium, as well as magnetic elements.51,66
For the characterization of elemental species, commonly used techniques include EDS and ICP-OES.67 Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) was utilized to analyze the bulk composition of multi-metal HEA NPs and to estimate their mixing entropy. Additionally, combining the element content data from ICP-OES with TEM-EDS mapping provided a means to assess the uniformity of elemental distribution within the particles, thereby evaluating alloy homogeneity. For example, in 21-element HEA nanoparticles, most elements displayed a uniform distribution, with only minor compositional fluctuations observed in Sn and In.25
XAS, which includes XANES and EXAFS, provides valuable information about the electronic state, local geometry, and valence state (Fig. 4f–i). In a study of AlFeCuCrMgx alloys, XANES revealed that Fe and Cr were primarily in the zero-valence state as expected for metals, while the Cu K-edge spectrum suggested the possible presence of oxide phases.61
EXAFS analyzes the oscillations beyond the absorption edge to extract local structural information, such as bond lengths and coordination numbers.68 For instance, EXAFS tests were used to investigate the bonding structure in 15-element HEA nanoparticles, finding that the metal bond distances were approximately 2 Å, confirming a uniform bonding structure with local fluctuations (Fig. 4g).32
XPS is used to analyze surface elemental composition and chemical states (Fig. 4j). For example, XPS analysis was employed to confirm the presence of Zr, Nb, Ta, Mo, and W in the HEA. Multiple valence states of Nb (Nb0, Nb4+, and Nb5+) were also detected, with changes in Nb valence states observed after oxidation in the HEO.27
Microstructural features such as local morphology, aggregation, and surface reconstruction are other important aspects in the characterization of HEAs, primarily analyzed using SEM and STEM. SEM utilizes reflected electron beams to image surface morphology, whereas STEM relies on transmitted electron beams, capturing data through detectors during penetration. STEM, especially with a HAADF detector, provides atomic-scale imaging with high contrast and resolution, enabling precise microstructural analysis. When combined with EDS, STEM generates detailed elemental distribution maps, overcoming the limitations of EDS alone. For example, HAADF-STEM can be used to visualize the uniform distribution of elements in HEA nanowires, demonstrating the effects of lattice distortion on electronic structure and catalytic performance (Fig. 4k).62
Additionally, 3D-APT enables the reconstruction of atomic distributions by using high voltage or laser assistance to field evaporate atoms from the sample surface. The ionized atoms are detected and identified based on their mass-to-charge ratios, while their positions are mapped in a three-dimensional space. This method is favorable for studying phase separation, precipitation, diffusion, and interfacial phenomena. For instance, STEM and APT analyses have shown that CoCrCuFeNiAl0.5 consists of coherent L12 and FCC nanophases,69 while APT has also been used to confirm the uniform distribution of elements in HEAs (Fig. 4l).57
For porous HEAs, the BET method measures the specific surface area and characterizes the pore structure, aiding in the understanding of adsorption behavior during catalytic reactions (Fig. 4m and n). When combined with SEM, BET provides both visual and quantitative insights into pore formation and size distribution. For example, SEM has been utilized to monitor the pore formation of CrMnFeCoNi HEAs over time, while BET measurements have confirmed the increase in the surface area. Both these changes contributed to improved catalytic performance.58 In addition, TPD offers a more direct and intuitive approach.28
While traditional techniques can effectively reveal the static structures of HEAs, in situ characterization techniques, unlike static observations of just the “starting” and “ending” points, are highly effective in interpreting the reaction processes. In situ environmental transmission electron microscopy (In situ ETEM) enables real-time observation of microstructural evolution under working conditions, such as high temperatures or reducing atmospheres. For example, ETEM has been employed to monitor the formation of GaFeMnNiCu HEA nanoparticles through liquid metal-assisted synthesis, confirming the method's feasibility and uncovering dynamic structural changes in the heating process.41 This technique significantly enhances the understanding of HEA behavior by tracking phase transitions, grain growth, and structural adjustments in real time.
Moreover, through in situ TEM observations, the high-temperature oxidation process of HEAs was investigated, showing a significantly lower oxidation rate compared to single-metal (e.g., Co) and binary alloy (e.g., NiFe) nanoparticles of similar sizes. The oxidation kinetics of HEAs were found to follow a logarithmic law rather than the parabolic law predicted by Wagner's theory. During oxidation, transition metals (Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu) were observed to diffuse outward, while Pt remained at the core, preserving active catalytic centers and highlighting the potential of HEAs as durable catalysts.70
In addition, in situ neutron diffraction (In situ ND) or in situ X-ray diffraction (In situ XRD) techniques can be used to monitor the internal microstructural evolution of HEAs under mechanical loading in real time. For example, Frank et al. employed In situ ND to quantitatively track the phase transformation process of HEAs under increasing loads. They dynamically characterized the evolution of lattice strain, identified the relative contributions of deformation mechanisms (e.g., nano-twinning deformation and stacking faults), analyzed the dynamic rearrangement of crystal texture, and quantitatively described the distribution of different phases and their competitive relationships under deformation conditions.71 Although high-load conditions are rarely encountered during the catalytic process, they are present in some preparation methods, such as mechanical alloying. Theoretically, certain phase transformations can adjust the crystal structure and bandgap characteristics of photocatalytic materials. Lattice strain provides strain-induced surface activity, while texture evolution optimizes the arrangement and distribution of active sites. Understanding these mechanisms can guide the preparation process.
The reaction pathway of nitrate reduction to ammonia has been studied using in situ Raman spectroscopy, which provided real-time monitoring of intermediates on HEA catalyst surfaces. The stabilization of intermediates and the reconstruction of surface structures under reaction conditions were observed, contributing to enhanced selectivity for ammonia production.
Furthermore, in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy (In situ XAS) revealed the dynamic evolution of the oxidation states of different metal elements during the reaction, as well as adjustments in the atomic coordination number and bond lengths around HEA active sites. These findings offered valuable quantitative data on the synergistic effects between different metal elements in HEAs, elucidating their critical contributions to optimizing reaction pathways and stabilizing intermediates.
Through in-depth analyses of electronic states and bond length variations, the study also helped identify the most significant active sites within the HEA catalyst structure and their specific mechanisms of action.72 These discoveries suggest that integrating In situ XAS results with high-precision fabrication techniques, such as vacuum deposition, can more effectively regulate the surface structure and electronic properties of HEAs, thereby optimizing reaction selectivity.
Table 2 summarizes the commonly used characterization tools and their capabilities for analyzing high-entropy alloys (HEAs). Due to their complex composition and multifunctional properties (e.g., catalysis and heat resistance), HEAs rely heavily on advanced characterization techniques. Common techniques include XRD for analyzing crystal properties, EDS-STEM for compositional and morphological analysis, and XPS for evaluating chemical states, all of which play critical roles in HEA research. However, as the application scenarios of HEAs become increasingly complex, the importance of dynamic in situ characterization techniques has grown significantly. These dynamic in situ techniques are crucial for uncovering reaction mechanisms and studying the structural and performance changes of HEAs during synthesis and reaction processes.
| Method | Elemental component recognition | Phase structure measurement | Chemical measurement | Local structure display | Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The checkmark (√) indicates feasibility, the cross (×) denotes infeasibility, and the circle (○) suggests uncertainty or the inability to independently provide definitive characterization. | |||||
| PXRD | ○ | √ | × | × | Diffraction |
| HR-TEM | × | √ | × | √ | Microscopy |
| XAS | × | ○ | √ | √ | Spectroscopy |
| ICP | √ | × | × | × | Spectroscopy |
| EDS | √ | × | ○ | × | Spectroscopy |
| SEM | ○ | × | × | √ | Microscopy |
| STEM | ○ | × | × | √ | Microscopy |
| 3D-APT | √ | ○ | × | √ | Mass spectrometry |
| XPS | √ | × | √ | × | Spectroscopy |
| AFM | × | × | × | √ | Microscopy |
| BET | × | × | × | √ | Microscopy |
Simulation methods of HEAs in catalysis
Simulation plays a crucial role in elucidating the complex behaviors of HEAs and accelerating their development for catalytic applications. By utilizing computational techniques to model the interactions and properties of HEAs in various environments, researchers can efficiently screen potential candidates and predict performance metrics. This method enables exploration of numerous HEA configurations while providing essential insights into catalytic efficiency. Furthermore, simulation facilitates the generation of diverse HEA structures without the limitations associated with precise synthesis techniques, thereby expanding the potential for innovation and discovery in catalytic materials (Fig. 5).The first level of the proposed simulation strategy employs first-principles methods, primarily density functional theory (DFT). DFT analyzes multi-electron systems using electron density, solving the Kohn–Sham equations to provide insights into electronic distribution and atomic arrangements.73 This method reveals the influence of electron interactions on material properties and assesses the ground-state characteristics of multi-electron systems. By varying parameters, DFT can elucidate the four major effects of HEAs, as outlined in Table 3.
| Effect | Characteristic manifestation | Directly related DFT parameter(s) | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| In actual calculations, we often assume different active site types to ensure that multiple scenarios are considered.a Calculating the LDOS reveals electronic structure differences at various active sites, helping to understand how high entropy affects electron distribution and adsorption properties (direct calculation).b Quantifies energy changes during adsorption, showing how surface disorder under high entropy affects reaction pathways and adsorption behavior (indirect estimate, derived from energy differences).c Calculating migration energy barriers between elements evaluates the impact of hindered diffusion on different diffusion paths within the catalyst, revealing optimal paths (direct calculation). Usually negligible after forming a solid solution.d Analyzing DOS identifies electronic structure changes between elements, especially in the d-band, crucial for understanding how the cocktail effect enhances catalytic performance (direct calculation).e Quantifies the position of the d-band center relative to the Fermi level, revealing the relationship between the d-band electron density and the adsorption strength, and its contribution to catalytic activity (direct calculation).f Calculating surface energy changes before and after distortion reveals how lattice distortion regulates adsorption behavior (direct calculation).g Calculating geometric structure and bond length changes evaluates how lattice distortion affects active site geometry and modifies adsorption energy (direct calculation).h Quantifying the local stress and strain relationship due to lattice distortion helps in understanding its impact on the stability of catalytic sites and reaction rates (direct calculation). | |||
| High entropy effect | Disordered surface atom arrangement with an overall ordered lattice; local environmental complexity leads to various active sites and adsorption properties | Local density of states (LDOS)a | LDOS reflects the variation in the local electronic environment and ΔG measures changes in adsorption or reaction energies. |
| Gibbs free energy change (ΔG)b | |||
| Hindered diffusion effect | Reduced diffusion rates between elements in a multi-component solid solution, altering reaction kinetics and contributing to different active sites | Migration energy barrier (E_migration)c | E_migration quantifies the energy barrier for atomic diffusion, directly linking to reaction kinetics. |
| Cocktail effect | Non-linear enhancement of alloy properties due to interaction between the electronic structures of different elements, with the d-band center shifts closely related to catalytic activity | Density of States (DOS)d | DOS provides insights into the electronic structure, and the d_center determines catalytic activity trends. |
| d-band center position (d_center)e | |||
| Lattice distortion effect | Differences in atomic radii and lattice constants between elements cause lattice distortion, affecting local stress fields, surface energy, and catalytic reaction pathways | Surface energy variation (γ)f | γ evaluates changes in surface energy due to distortion, ΔR_site monitors active site geometry, and σ–ε captures lattice stress and strain effects. |
| Geometric adjustment of active sites (ΔR_site)g | |||
| Stress–strain relationship (σ–ε)h | |||
In practical scenarios for catalyst screening, it is unrealistic to compute every characteristic. The focus can be on identifying relevant reaction intermediates, assessing the catalyst's adsorption capacity for these intermediates, and calculating the changes in Gibbs free energy. This streamlined approach aligns with the first-level process, moving from left to right.
While DFT excels in local high-precision predictions, it encounters efficiency challenges in large-scale phase equilibrium assessments. The complexity of element arrangements and the variety of catalytic sites make it difficult to directly simulate catalytic performance in large unit cells, resulting in excessively long computation times. Conversely, smaller unit cells often fail to capture the full range of possibilities, exacerbating limitations of catalyst screening on a large scale and leading to significantly increased computational costs.
In recent years, the accumulation of large datasets from high-throughput simulations of HEAs has prompted researchers to explore machine learning (ML) techniques to expedite DFT processes.74 For instance, Gaussian process regression (GPR) and kernel ridge regression (KRR) models have been utilized to predict the adsorption energies of Cu–Mn–Ni–Zn HEAs.75 By training the models on a limited DFT dataset and screening 11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 920 datasets, the ML-accelerated approach achieved a computation time reduction of approximately 96.2% compared to traditional DFT methods. The predicted adsorption energies demonstrated high accuracy, with errors within 0.15 eV, closely aligning with the actual DFT results. Similar ML methodologies have also been successfully applied to reactions like electrocatalytic oxygen reduction and nitrate reduction to ammonia,76,77 effectively decreasing computational time while preserving predictive accuracy. Currently, these advancements are primarily achieved in electrocatalysis research.
920 datasets, the ML-accelerated approach achieved a computation time reduction of approximately 96.2% compared to traditional DFT methods. The predicted adsorption energies demonstrated high accuracy, with errors within 0.15 eV, closely aligning with the actual DFT results. Similar ML methodologies have also been successfully applied to reactions like electrocatalytic oxygen reduction and nitrate reduction to ammonia,76,77 effectively decreasing computational time while preserving predictive accuracy. Currently, these advancements are primarily achieved in electrocatalysis research.
In complex environments, CALPHAD (CALculation of PHAse Diagrams) thermodynamic modeling is integrated at later stages of HEAs for thermocatalysis. This approach optimizes Gibbs free energy across compositions by incorporating DFT or experimental data. Comprehensive databases facilitate rapid phase diagram predictions and multi-phase equilibrium calculations, which are essential for intricate HEA systems. CALPHAD predicts phase evolution at varying temperature and pressures, optimizing the catalyst's phase composition for enhanced stability and selectivity.78,79 Additionally, it estimates element segregation in multi-component systems, providing insights into the distribution and stability of active elements. Coupling the Monte Carlo method with CALPHAD data and DFT interactions allows for investigations of microstructural evolution, phase transitions, and kinetic processes over extended timescales.80
Ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) enhances traditional CALPHAD models by providing insights into atomic-scale dynamics in complex environments. AIMD allows for real-time observation of atomic arrangements, diffusion, and phase transitions, making it particularly valuable for assessing phase stability in HEAs under varying temperature and pressure conditions.89 In catalysis, AIMD elucidates changes in surface electronic structures, such as shifts in the d-band center, which influence intermediate adsorption energies and optimize catalytic performance. Furthermore, AIMD captures synergistic effects in multi-component catalytic systems, offering explanations for surface reconstruction, local stress, and catalytic pathways and mechanisms.90–92
Overall, the development of HEA catalysts benefits from the integration of various simulation methods to balance accuracy and computational efficiency. DFT is effective for localized predictions but becomes computationally intensive for larger models. ML techniques can expedite this process, making them advantageous for initial screening. In complex environments, such as high-temperature catalysis, CALPHAD models, utilizing DFT or experimental data, enable phase diagram predictions and stability assessments. The Monte Carlo method effectively simulates microstructural evolution and phase dynamics over extended timescales. Additionally, AIMD provides insights into dynamic behavior under diverse environmental conditions, enhancing the understanding of catalytic processes at the atomic level.
HEAs in solar/thermal-related applications
Beyond their common applications in electrocatalysis, HEAs have recently emerged as promising candidates for solar- and thermal-related applications. Photocatalysis primarily involves photodecomposition reactions, while photothermal processes, particularly in solar-driven water evaporation and phase transitions, focus on enhancing solar energy utilization and photothermal conversion efficiency. HEAs’ ability to absorb light energy positions them as a promising class of photocatalysts for photocatalytic applications. Meanwhile, their efficient photothermal conversion potential makes them highly suitable for photothermal catalysis. Emerging studies are exploring HEAs in photothermal applications, specifically in CO2 hydrogenation reactions. Table 4 presents a concise overview of HEA systems that have been utilized in solar and thermal applications.| Catalysis materials | Phase structure | Catalytic reaction | Reaction conditions | Synthesis method | Particle size | Characterization for HEAs | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Ni40Fe30Co20Al10)90Ti10 A-HEA (as milled) | FCC + amorphous | Methyl blue (MB) degradation | RT and visible light | Others (mechanical alloying with or without annealing) | ∼15 nm | XRD, TEM, HRTEM, and XPS | Photocatalysis | 81 |
| (Ni40Fe30Co20Al10)90Ti10 H-HEA (homogenized) | FCC | 81 | ||||||
| NbTaZrMoW HEA | BCC | Methyl blue (MB) degradation | RT, UV light, and no external heating | Others (mechanical alloying) | 451.6 nm | XRD, SEM, EDS, and XPS | 27 | |
| Pt18Ni26Fe15Co14Cu27 HEA | FCC | Photocatalytic H2 production and benzyl alcohol oxidation | RT, 420 nm LED light, and no external heating | Solution method (low-temperature oil-phase synthesis) | 2 nm | XRD, TEM, AFM, XPS, and EIS | 82 | |
| MnFeCoNiCu HEA | FCC | Photocatalytic degradation of antibiotics (SMX, OFX, CFX) | RT, visible light, and no external heating | Others (induction melting, mechanical alloying) | 85 nm | XRD, SEM, EDS, TEM, XPS, BET, EPR, and AFM | 83 | |
| FeCoNiCuMn HEA | FCC | Photocatalytic CO2 reduction | RT, simulated sunlight, and AM1.5G | Solution method | 3.5 ± 0.2 nm | XRD, HAADF-STEM, TEM, EDS, XPS, ICP, AES, and XANES | 84 | |
| FeCoNiCuMn HEA/TiO2 | ||||||||
| NAO/HEA FeCoNiCrTi(Ti) | BCC | Tetracycline hydrochloride degradation | RT, simulated sunlight, and 300 W xenon lamp | Solution method | 15 μm | XRD, XPS, SEM, and TEM | 85 | |
| NAO/HEA FeCoNiCrMn(Mn) | FCC | |||||||
| NAO/HEA FeCoNiCrMo (Mo) | FCC | |||||||
| FeCoNiCrMn HEA | FCC | Solar steam generation | RT, sunlight, and no external heating | Thermal-assist method | 70–100 nm | XRD, XPS, SEM, and TEM | Photothermal conversion | 52 |
| FeCoNiTiVCrMnCu HEA@C | FCC + BCC | Solar steam generation | RT, sunlight, and no external heating | Thermal-assist method | ∼23.08 nm (core), ∼2.58 nm (shell) | XRD, TEM, STEM, EDS, XPS, and ICP-OES | 86 | |
| FeCoNiTiVCrMn HEA@C | FCC | |||||||
| FeCoNiTiVCr HEA @C | FCC | |||||||
| FeCoNiTiVCu HEA@C | FCC | |||||||
| FeCoNiTiVMnCu HEA@C | FCC + BCC | |||||||
| FeCoNiTiVMn HEA@C | FCC + BCC | |||||||
| FeCoNiCrMnCu HEA@C | FCC + BCC | |||||||
| MnNiZrRuCe HEA | FCC | CO2 methanation | 453–573 K, light intensity = 1.14 W cm−2, and 300 W Xe lamp | Others (co-precipitation method for HEH and heat treatment in H2/Ar at 360 °C) | ∼7.4 nm | XRD, TEM, EXAFS, SEM, HRTEM, and XPS | Photothermal catalysis | 87 |
| CoNiCuPdRu HEA/TiO2 | RWGS | 683 K, 3.0 W cm−2 light, and no external heating | Solution method | ∼2.6 nm | XRD, XPS, STEM, EDS, EXAFS, and XANES | 21 | ||
| PtPdRhRuCe HEA | FCC | NH3 oxidation | 973 K | Thermal-assist method | 5.30 ± 1.31 nm | XRD, HAADF-STEM, SEM, TEM, EDS, EXAFS, and ICP-MS | Thermal catalysis | 36 |
| PtPdRhCoCe HEA | 3.51 ± 0.62 nm | |||||||
| RuRhCoNi HEA | NH3 decomposition | 573–823 K | Thermal-assist method | 3–5 nm | XRD, SEM, TEM, EDS, EXAFS, and ICP | 41 | ||
| RuRhCoNiIr HEA | ||||||||
| CoMoFeNiCu HEA | 523–873 °C | Thermal-assist method | ∼22 nm | XRD, STEM, XPS, TEM, EDS, and ICP | 28 | |||
| AlNiCuPtPdAu HEA | CO oxidation | — | Others | 2–3 nm | EDS, HAADF-STEM, SEM, XPS, and HR-TEM | 42 | ||
| NiFeCoMnCu-HEAs/WC | Toluene steam reforming | 923 K | Solution method | ∼7–9 nm | XRD, SEM, TEM, XPS, EDS, and ICP-OES | 88 |
HEAs in solar-related catalysis
In photocatalysis, research has predominantly centered on HEOs and similar materials.87 However, from a theoretical perspective, HEAs also offer great potential in photocatalysis, due to their diverse metal compositions, unique electronic structures, and electrochemical properties. The interactions between different metal atoms modulate the surface Fermi level, influencing reactant adsorption and activation.93 The energy level differences between metals promote efficient electron–hole separation, which reduces recombination losses. HEAs also enhance charge separation, extend active species lifetimes, and enable selective regulation of photocatalytic pathways, such as CO2 reduction.94 Additionally, their complex composition improves thermodynamic stability and oxidation resistance, with metals like Ni and Cr forming self-repairing oxide layers to prolong catalyst life.95 Lattice distortion in HEAs can alter optical bandgaps, enhancing light absorption and photocatalytic efficiency.27 These features highlight HEAs’ promising applications in photocatalysis. However, the exploration of HEAs as photocatalysts is still limited,87,96–98 focusing mainly on low-energy reactions. Notably, advancements in photocatalytic CO2 reduction, water splitting, and ammonia decomposition remain sparse, highlighting substantial opportunities for further investigation in this field.Non-annealed high-entropy alloy (A-HEA) powders were synthesized through high-energy ball milling and subsequently annealed at 800 °C in a vacuum tube furnace to produce an annealed HEA (H-HEA) (Fig. 6a). Remarkably, the A-HEA displayed a unique mixed structure comprising FCC solid solution and amorphous phases, which significantly enhanced electron transport and photocatalytic performance, resembling characteristics of a homojunction unattainable with a single solid solution phase. Furthermore, the A-HEA demonstrated distinct stacking faults and nanotwin structures (Fig. 6b).81 This observation suggests that recent trends in rapid annealing techniques, such as carbothermal shock or Joule heating, may promote rapid crystallization or phase transformation, thereby eliminating phase mixing and defective structures like laminar dislocations and twins, which could degrade photocatalytic efficiency.
 | ||
| Fig. 6 (a) Schematic diagram of phase interfaces for the A-HEA and H-HEA; (b) inverse fast Fourier transform image corresponding to the twin boundary of the AC-HEA. Reproduced from ref. 81 with permission from Elsevier, Copyright 2020. (c) CO2 photocatalytic reduction over pure TiO2 and a series of x-HEA/TiO2 catalysts. Reproduced from ref. 84 with permission from John Wiley and Sons, Copyright 2024. (d) FCC structures of different HEAs and the corresponding d band filling by different 3d metals. Reproduced from ref. 86 with permission from John Wiley and Sons, Copyright 2021. (e) Schematic illustration of HEA@C NPs. Reproduced from ref. 99 with permission from Elsevier, Copyright 2022. (f) Selectivity and yields of CO over mono- and HEA-loaded TiO2 catalysts; (g) comparison of the stability of the light-driven RWGS reaction with different catalysts; and (h) long-term stability test of HEA/TiO2 and mixed CoNiCuPdRu/TiO2 catalysts. Reproduced from ref. 21 with permission from John Wiley and Sons, Copyright 2024. (i) Nitrogen TPD profiles recorded at a temperature ramping rate of 10 °C min−1 of HEA-CoxMoy; (j) estimation of the nitrogen adsorption energies (ΔEN) for the HEA-CoxMoy catalysts; and (k) NH3 decomposition at different concentrations of HEA-Co55Mo15. Reproduced from ref. 28 with permission from Nature, Copyright 2019. | ||
Similarly, NbTaZrMoW HEAs and their oxides were designed for the photodegradation of methyl blue, leveraging elements commonly found in refractory alloys. Strikingly, HEAs demonstrated nearly double the photocatalytic efficiency of HEOs, challenging the prevailing assumption that oxides generally exhibit superior photocatalytic activity over metal alloys.27 Furthermore, partially oxidized HEAs outperformed both pure HEAs and HEOs. While the mechanism was not fully explained, it is likely that the coexistence of metal and oxide regions forms a heterojunction-like structure at the interface. This interface may retain lattice strain and defects, creating additional active sites, while the metallic regions enhance charge separation and transport, ultimately boosting photocatalytic performance.
In a related study, a Pt18Ni26Fe15Co14Cu27 HEA was integrated with protonated g-C3N4 (HCN) nanosheets, forming a Schottky junction at the interface.82 This configuration enabled a bifunctional photocatalytic system that facilitated simultaneous hydrogen evolution and benzyl alcohol oxidation. This work distinguishes itself from other HEA studies by avoiding agglomeration in nanoparticles below 2 nm, whereas other studies often observe agglomeration at this size.57 Under visible light irradiation (420 nm LED light), the photocatalytic hydrogen production rate of the HEA/HCN composite catalyst reached 4.825 mmol g−1 h−1 with an apparent quantum efficiency (AQY) of up to 20.12%. In the benzyl alcohol selective oxidation reaction, the benzaldehyde (BAD) generation rate reached 5.44 mmol g−1 h−1, which was 6.6 times higher than that of pure HCN, with a selectivity of 99% and a stability of more than 20 hours.
In the design of new photocatalysts, key criteria such as thermal stability, acid–base resilience, visible-light absorption, and environmental compatibility must be emphasized. The integration of an NiAl2O4 catalyst with HEAs was the first work of a Z-type heterojunction photocatalyst.85 NiAl2O4 was specifically engineered to leverage its superior properties, and it formed an effective junction with HEAs, significantly enhancing photocatalytic performance. In another work, the FeCoNiCuMn HEA–TiO2 heterostructure showed excellent photostability as a photocatalyst for CO2 reduction (Fig. 6c).84 At the interface with TiO2, the formation of a Schottky barrier led to a heterojunction, significantly enhancing the CO2 reduction efficiency. Despite these advances, HEAs were employed as ‘cocatalysts’, and their standalone photocatalytic performance remains unexplored, presenting a gap for future investigation.
In general, the integration of HEAs in photocatalysis remains in its nascent stages, yet the emerging insights are promising. Advances can be framed through both internal and external perspectives—focusing on the inherent structural complexity of HEAs and their external bonding interactions. Optimization of these factors is closely tied to material selection, both in HEA composition and the choice of junction-forming materials, alongside tailored synthesis methods. Heterojunctions are proving to be a pivotal strategy for enhancing photocatalytic activity, with non-annealed approaches preserving critical structural defects that boost performance. Nevertheless, the application of HEAs, especially in reactions like CO2 reduction, warrants deeper investigation to refine selectivity and improve catalytic yields. Notably, the influence of the HEA absorbance range and light-harvesting efficiency remains underexplored. Furthermore, it is a crucial consideration to determine whether HEAs serve best as primary catalysts, co-catalysts, or platforms for hybrid systems for the development of this research field.
HEAs in photothermal catalysis
A recent study demonstrated that seven-membered HEA NPs (FeCoNiTiVCrCu) achieved an average absorptivity exceeding 95% across the solar spectrum (250 to 2500 nm) and a water evaporation efficiency of 2.26 kg m−2 h−1. By engineering the 3d electronic band structure to optimize filling above and below the Fermi energy level, robust d–d interband transitions (IBTs) were successfully realized (Fig. 6d).86 To further enhance performance, the HEA core was encapsulated with a graphite shell, creating a synergistic effect between the two layers (Fig. 6e).99 Experimental results showed that the thermal conductivity of HEA@C NPs (FeCoNiTiVCrMnCu@C) was reduced by approximately 26.6% compared to their 7-element counterparts, achieving an energy utilization efficiency of 98.2% under one sun, thus validating the graphite shell's role in optimizing photothermal conversion.99 In contrast, FeCoNiCrMn alloys exhibited a maximum photothermal conversion efficiency of 93%.52 Although this is lower than that of FeCoNiTiVCrCu HEAs, the authors noted that the less metal-intensive 3d transition could be a contributing factor, suggesting that modulating elemental ratios in non-equivalent HEAs may yield improved photothermal conversion efficiencies.
In short, remarkable full-spectrum absorption at 250–2500 nm has been demonstrated in HEAs by strategically adding specific elements and enhancing 3d electronic band filling to facilitate d–d interband transitions. The introduction of non-equimolar elemental modulation, coupled with a graphite shell, effectively reduced thermal conductivity, fostering heat aggregation and resulting in an impressive photothermal conversion efficiency of 98%. These advancements not only underscore the exceptional light absorption and photothermal properties of HEAs but also pave the way for their application as photocatalysts and photothermal catalysts, representing a significant leap forward in photophysical water evaporation technologies.
Additionally, insights from photocatalytic studies indicate that HEAs possess abundant potential active sites due to their aberration effects.21 Therefore, HEAs are promising candidates for high-value-added reactions involving catalytic activity and chemical transformations, such as conventional CO2 hydrogenation and reduction.
Recent studies highlight the promising potential of HEAs in photothermal catalysis, especially in light-driven reverse water-gas shift (RWGS) reactions. For instance, a porous TiO2-supported CoNiCuPdRu HEA catalyst demonstrated exceptional performance, achieving a CO production rate of 1.23 mol gmetal−1 h−1 with over 99% selectivity and stable operation over ∼1000 hours. Acting as a “nano-heater”, this catalyst raised local temperatures to 410 °C without external heating, thus enhancing CO2 conversion and reducing activation energy.21
When metal catalysts (e.g., Pt, Pd, and Ru) are dispersed on specific oxide supports (e.g., TiO2, CeO2, and ZnO) and subjected to reduction or high-temperature treatments, strong chemical or electronic interactions may develop between the metal and the support. These interactions profoundly alter the physical and chemical properties of the metal surface, significantly influencing catalytic activity, selectivity, and resistance to deactivation.
In certain reducible supports, such as TiO2, CeO2, and ZnO, high-temperature reduction can induce the formation of oxygen vacancies (Ov). The electrons associated with these oxygen vacancies migrate to the metal particles, increasing the electron density of the metal. Conversely, some supports, such as Al2O3 and SiO2, can extract electrons from the metal through strong interfacial interactions, thereby reducing the metal's electron density.
Moreover, the strong interactions between the metal and the support often lead to the formation of interfacial chemical bonds, such as metal–oxygen (M–O) bonds. This bonding induces a redistribution of charge at the interface, typically involving electron transfer from materials with lower work functions to those with higher work functions.
For HEAs, in addition to the strong interactions between metal ions and supports, significant interactions also exist between the constituent metals. The enhanced selectivity and productivity of HEA-based catalysts may be attributed to the “cocktail effect”, where the synergistic interactions among the metals enhance the activation of carbon dioxide.
In addition, in situ characterization studies show that the “hysteresis diffusion effect” within HEAs confers structural stability, preventing sintering during reactions, while H2 pretreatment further stabilizes active sites by reducing CO poisoning. Although some studies do not fully explain the choice of elements in HEAs, likely selected for catalytic performance and anti-poisoning properties, future work could explore compositional adjustments to optimize catalytic efficiency.
In addition to the RWGS reaction, MnNiZrRuCe HEAs have been utilized for photothermal CO2 methanation via light-assisted thermocatalysis without a support, achieving 100% selectivity and a methanation rate of 82.9 mmol g−1 h−1, despite a moderate stability of 100 hours.87 This achievement suggests significant potential for further optimization. Furthermore, studies on photothermal catalyzed water decomposition and ammonia decomposition are limited, representing a valuable avenue for future research.
Overall, given the early development stage of HEAs for photothermal catalysis, it is essential to draw insights from other high-entropy materials. It may be an effective strategy to adapt findings from high-performance HEOs and similar materials to enhance the catalytic performance of HEAs in specific systems.
HEAs in thermocatalysis
HEAs, originally designed for refractory materials, harness the high entropy effect to ensure stability at elevated temperatures, while lattice distortions create abundant active sites. This dual functionality positions them as effective standalone catalytic platforms or supports for other stable substances, emphasizing their potential in thermocatalysis.In ammonia decomposition, conventional Co–Mo bimetallic alloys often exhibit limited catalytic activity due to a substantial mutual solubility gap, constraining their practical applications (Fig. 6i–k).28 In contrast, CoMoFeNiCu HEAs significantly enhance catalytic performance by optimizing the Co/Mo ratio, even surpassing Ru catalysts at 500 °C. This catalyst demonstrates exceptional thermal stability, exhibiting negligible performance degradation after 50 hours of continuous operation at such a high temperature, highlighting its robust catalytic capabilities.
In catalytic pyrolysis of biomass, zeolite-structured catalysts are commonly employed. However, these catalysts, primarily composed of aluminosilicates, exhibit thermal stability only up to 800–900 °C, with structural integrity maintained at temperatures as high as 1000 °C. Beyond this threshold, the crystal structure deteriorates, leading to diminished catalytic performance or failure. Consequently, exploring the catalytic potential of high-entropy alloys at elevated temperatures presents a promising research avenue. Similarly, steam reforming processes, such as methane or tar reforming, operate at elevated temperatures (600 °C–900 °C), allowing for the optimization of catalytic performance through precise tuning of alloy compositions. Recent studies, including NiFeCoMnCu HEAs loaded on charcoal for biomass tar reforming, have achieved stable toluene conversions exceeding 95% at 650 °C for 48 hours.88
HEAs composed of non-precious metals present a promising strategy to improve resistance to poisoning from contaminants such as sulfur and chlorine.100,101 Previous studies have demonstrated that the careful selection of elemental compositions can yield favorable catalytic properties under mild conditions; however, the nanoscale stability of these materials warrants further investigation. Addressing this stability issue could pave the way for innovative strategies in source-based carbon reduction. The implementation of source-based carbon reduction techniques in high-temperature thermocatalysis not only enhances combustion efficiency but also minimizes the formation of unburned hydrocarbons, including soot and carbon monoxide. This approach allows for a more efficient conversion of fuel into thermal energy, thereby enabling greater energy output from the same fuel quantity.
Conclusion and future prospect
In conclusion, HEAs exhibit significant potential for applications in solar- and thermal-related catalysis. However, research in this field is still in its early stages and faces several significant challenges. These include the difficulty of achieving modulated synthesis through low-cost and mild-environmental approaches and the absence of detailed explanations of catalytic process mechanisms in photo-related catalytic applications. Additionally, there are limited reference data and challenges in integrating advanced techniques. To address these issues, future investigations should focus on optimizing synthetic methodologies, gaining a deeper understanding of structure–property relationships, and applying advanced characterization and simulation techniques. Moreover, future investigations should prioritize the following areas:1. Element and phase exploration: systematically assess solid–solution HEA systems to quantify the impacts of elemental variations on catalytic efficacy. This includes evaluating the necessity and economic implications of incorporating precious metals, alongside enhancing insights into the catalytic performance of hybrid phases, including mixed, amorphous, and crystalline structures.
2. Precision-tuned synthesis: develop rapid synthesis techniques that avoid annealing to maintain internal defects and active surface sites, thereby enhancing catalytic performance.
3. Mechanistic insights: in the screening and design of catalysts, machine learning will play an increasingly critical auxiliary role due to the extremely large compositional space and complex synergistic effects in high-entropy alloys and other complex material systems. Future developments may no longer be limited to the prediction of single features (e.g., adsorption energy) but will involve the integration of multidimensional data to achieve comprehensive screening and design from a global perspective. In this regard, we particularly recommend introducing Rough Set Machine Learning (RSML) methods. RSML can efficiently extract key variables critical to catalytic performance from multidimensional feature data, enabling feature reduction and significantly simplifying model complexity. Furthermore, this method excels in handling limited datasets without requiring prior probabilistic distributions, making it particularly suitable for addressing data sparsity and uncertainty challenges in high-entropy alloys and other complex systems. By leveraging rough set theory, intuitive “if-then” rules can be generated. These rules not only provide interpretability for machine learning predictions but also offer clear experimental guidance for the rational design of catalysts.
Regarding in situ characterization techniques, utilizing advanced in situ techniques to elucidate the microscopic mechanisms of catalytic reactions has become increasingly important for the development of HEA catalysts. Advanced in situ characterization can capture the dynamic changes of HEA catalysts under reaction conditions, identify active sites and reaction intermediates, and reveal the unique changes in high-entropy alloy catalysts during reactions. This approach marks a shift from ‘emphasizing performance while neglecting principles’ to ‘understanding processes to further optimize performance’. Thus, we should put more effort on the in situ characterization to explain the processes in HEAs for photocatalysis which is underdeveloped. Moreover, we must recognize the interdependence of in situ experimental techniques and computational approaches based on AI and machine learning. In situ characterization provides mechanistic insights, supplements high-quality and diverse datasets, and enhances interpretability, while machine learning accelerates the exploration process. Cross-disciplinary collaborations combining these approaches are highly promising and deserve greater attention.
4. Application expanding: broaden the scope of HEAs to encompass high-value solar- and thermo-catalytic reactions, including water decomposition, ammonia decomposition, and high-temperature combustion, addressing critical energy and environmental challenges while promoting carbon reduction.
5. Stability investigations: examine the structural stability and anti-poisoning capabilities of HEAs under challenging conditions, such as high temperature and pressure, to ensure sustained catalyst performance.
Through ongoing research and innovation, HEAs are expected to emerge as a new generation of high-performance solar- and thermo-catalytic materials, playing a pivotal role in advancing sustainable energy solutions and environmentally friendly technologies.
Data availability
Data availability is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support from the Australian Research Council through its DECRA (DE230100357), Discovery Project (DP230100621), and Laureate Fellowship (FL190100139) schemes, The University of Queensland through its Research Donation Generic Scheme, and the QUEX Institute through its Research Accelerator Grant. Y. Zou gratefully acknowledges the support from The University of Queensland Earmarked Scholarship.References
- A. Inoue, Acta Mater., 2000, 48, 279–306 CrossRef CAS.
- A. L. Greer, Nature, 1993, 366, 303 CrossRef.
- B. Cantor, I. Chang, P. Knight and A. Vincent, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2004, 375, 213–218 CrossRef.
- J. W. Yeh, S. K. Chen, S. J. Lin, J. Y. Gan, T. S. Chin, T. T. Shun, C. H. Tsau and S. Y. Chang, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, 6, 299–303 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Gludovatz, A. Hohenwarter, D. Catoor, E. H. Chang, E. P. George and R. O. Ritchie, Science, 2014, 345, 1153–1158 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Senkov, G. Wilks, D. Miracle, C. Chuang and P. Liaw, Intermetallics, 2010, 18, 1758–1765 CrossRef CAS.
- D. B. Miracle and O. N. Senkov, Acta Mater., 2017, 122, 448–511 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Xin, S. Li, Y. Qian, W. Zhu, H. Yuan, P. Jiang, R. Guo and L. Wang, ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 11280–11306 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Huang, G. Yang, S. Li, H. Wang, Y. Cao, F. Peng and H. Yu, J. Energy Chem., 2022, 68, 721–751 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Zhang, W. Yuan, X. Zhang, Y. Ke, Y. Wu, Y. Bai, S. Jiang and Y. Tang, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2024, 12, 18705–18732 RSC.
- Y. Wang and Y. Wang, Nano Energy, 2022, 104, 107958 CrossRef CAS.
- J.-W. Yeh, JOM, 2013, 65, 1759–1771 CrossRef CAS.
- M. G. Poletti and L. Battezzati, Acta Mater., 2014, 75, 297–306 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Khorshidi, J. Violet, J. Hashemi and A. A. Peterson, Nat. Catal., 2018, 1, 263–268 CrossRef.
- K.-Y. Tsai, M.-H. Tsai and J.-W. Yeh, Acta Mater., 2013, 61, 4887–4897 CrossRef CAS.
- K. A. Jackson, Kinetic processes: crystal growth, diffusion, and phase transitions in materials, John Wiley & Sons, 2010 Search PubMed.
- Z.-J. Zhang, N. Yu, Y.-L. Dong, G. Han, H. Hu, Y.-M. Chai and B. Dong, Chem. Eng. J., 2024, 498, 155736 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Ahmad, A. Nairan, Z. Feng, R. Zheng, Y. Bai, U. Khan and J. Gao, Small, 2024, 20, 2311929 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Nellaiappan, N. K. Katiyar, R. Kumar, A. Parui, K. D. Malviya, K. Pradeep, A. K. Singh, S. Sharma, C. S. Tiwary and K. Biswas, ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 3658–3663 CrossRef CAS.
- J. K. Pedersen, T. A. Batchelor, A. Bagger and J. Rossmeisl, ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 2169–2176 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Xiong, X. Ji, K. Mao, Y. Dong, L. Cai, A. Chen, Y. Chen, C. Hu, J. Ma and J. Wan, Adv. Mater., 2024, 36, 2409689 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Zhang, X. Hui, Y. Nie, R. Wang, C. Wang, Z. Zhang and L. Yin, Small, 2023, 19, 2206742 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Liu, Y. Wang, T. Jiang, S. Jin, M. Sajid, Z. Zhang, J. Xu, Y. Fan, X. Wang and J. Chen, ACS Nano, 2024, 18, 4229–4240 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Zheng, R. Lv, C. Luo, Y. Guo, M. Yang, K. Hu, K. Wang, L. Li, F. Wu and R. Chen, Adv. Energy Mater., 2024, 14, 2402042 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liao, Y. Li, R. Zhao, J. Zhang, L. Zhao, L. Ji, Z. Zhang, X. Liu, G. Qin and X. Zhang, Natl. Sci. Rev., 2022, 9, nwac041 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Zhan, Y. Xu, L. Bu, H. Zhu, Y. Feng, T. Yang, Y. Zhang, Z. Yang, B. Huang and Q. Shao, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 6261 CrossRef CAS.
- O. Zakir, O. Guler, R. Idouhli, A. Nayad, M. Khadiri, S. Guler, A. Abouelfida and B. Dikici, J. Mater. Sci., 2024, 59, 12050–12064 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Xie, Y. Yao, Z. Huang, Z. Liu, J. Zhang, T. Li, G. Wang, R. Shahbazian-Yassar, L. Hu and C. Wang, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 4011 CrossRef.
- V. H. Do, P. Prabhu, V. Jose, T. Yoshida, Y. Zhou, H. Miwa, T. Kaneko, T. Uruga, Y. Iwasawa and J. M. Lee, Adv. Mater., 2023, 35, 2208860 CrossRef CAS.
- N. L. Sui and J. M. Lee, Small, 2023, 19, 2205940 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Prabhu, V. Jose and J. M. Lee, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 1910768 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Prabhu and J.-M. Lee, Chem Catal., 2023, 3, 100621 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Wang, J. Chen, Y. Lin, X. Wang, J. Li, Y. Li, L. Gao, L. Zhang, D. Chao and X. Xiao, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, 2008422 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Wang, J. Li, K. Li, Y. Lin, J. Chen, L. Gao, V. Nicolosi, X. Xiao and J.-M. Lee, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50, 1354–1390 RSC.
- P. Prabhu, V. Jose and J.-M. Lee, Matter, 2020, 2, 526–553 CrossRef.
- Y. Yao, Z. Huang, P. Xie, S. D. Lacey, R. J. Jacob, H. Xie, F. Chen, A. Nie, T. Pu and M. Rehwoldt, Science, 2018, 359, 1489–1494 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Yan, P. K. Liaw and Y. Zhang, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2021, 52, 2111–2122 CrossRef CAS.
- W.-L. Hsu, C.-W. Tsai, A.-C. Yeh and J.-W. Yeh, Nat. Rev. Chem., 2024, 8, 471–485 CrossRef.
- Q. Wang, J. Xie, Y. Qin, Y. Kong, S. Zhou, Q. Li, Q. Sun, B. Chen, P. Xie and Z. Wei, Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2024, 11, 2301020 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Yao, Z. Huang, L. A. Hughes, J. Gao, T. Li, D. Morris, S. E. Zeltmann, B. H. Savitzky, C. Ophus and Y. Z. Finfrock, Matter, 2021, 4, 2340–2353 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Yao, Z. Liu, P. Xie, Z. Huang, T. Li, D. Morris, Z. Finfrock, J. Zhou, M. Jiao and J. Gao, Sci. Adv., 2020, 6, eaaz0510 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-J. Qiu, G. Fang, Y. Wen, P. Liu, G. Xie, X. Liu and S. Sun, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 6499–6506 RSC.
- O. N. Senkov, D. B. Miracle, K. J. Chaput and J.-P. Couzinie, J. Mater. Res., 2018, 33, 3092–3128 CrossRef CAS.
- E. George, D. Raabe and R. Ritchie, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2019, 4, 515–534 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Luo, H. Han, L. Chen, D. Feng, L. Li, T. Zhai, Z. Chen, R. Gao, H. Wu and S. Liu, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 90, 885–917 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zou, L. Jing, J. Zhang, S. Luo, L. Wang, Y. Li, R. Goei, K. W. Tan and A. I. Y. Tok, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2024, 12, 5668–5678 RSC.
- H. Zhu, Z. Zhu, J. Hao, S. Sun, S. Lu, C. Wang, P. Ma, W. Dong and M. Du, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 431, 133251 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Cao, J. Liang, Z. Guo, K. Yang, G. Wang, H. Wang, X. Wan, Z. Li, Y. Bai and Y. Zhang, Nature, 2023, 619, 73–77 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Ahn, S. Park, D. Oh, Y. Lim, J. S. Nam, J. Kim, W. Jung and I.-D. Kim, ACS Nano, 2023, 17, 12188–12199 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Qiao, M. T. Saray, X. Wang, S. Xu, G. Chen, Z. Huang, C. Chen, G. Zhong, Q. Dong and M. Hong, ACS Nano, 2021, 15, 14928–14937 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Gao, S. Hao, Z. Huang, Y. Yuan, S. Han, L. Lei, X. Zhang, R. Shahbazian-Yassar and J. Lu, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 2016 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Feng, H. Yao, Z. Sun, Y. Liao, J. Wang, R. Zhao and Y. Li, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2024, 16, 41027–41035 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Bondesgaard, N. L. N. Broge, A. Mamakhel, M. Bremholm and B. B. Iversen, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29, 1905933 CrossRef CAS.
- M. W. Glasscott, A. D. Pendergast, S. Goines, A. R. Bishop, A. T. Hoang, C. Renault and J. E. Dick, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 2650 CrossRef.
- Y. Ling, J. Chen, A. He, G. Wang, X. Yu, M. Xu, Z. Han, J. Du and Q. Xu, J. Appl. Phys., 2022, 131, 233904 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Waag, Y. Li, A. R. Ziefuß, E. Bertin, M. Kamp, V. Duppel, G. Marzun, L. Kienle, S. Barcikowski and B. Gökce, RSC Adv., 2019, 9, 18547–18558 RSC.
- M. Li, F. Lin, S. Zhang, R. Zhao, L. Tao, L. Li, J. Li, L. Zeng, M. Luo and S. Guo, Sci. Adv., 2024, 10, eadn2877 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Sun and S. Dai, Sci. Adv., 2021, 7, eabg1600 CrossRef CAS.
- L. J. Santodonato, Y. Zhang, M. Feygenson, C. M. Parish, M. C. Gao, R. J. K. Weber, J. C. Neuefeind, Z. Tang and P. K. Liaw, Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 5964 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Pu, D. Moseley, Z. He, K. C. Pitike, M. E. Manley, J. Yan, V. R. Cooper, V. Mitchell, V. K. Peterson and B. Johannessen, Sci. Adv., 2023, 9, eadi8809 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Maulik, N. Patra, D. Bhattacharyya, S. Jha and V. Kumar, Solid State Commun., 2017, 252, 73–77 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Sun, W. Zhang, Q. Zhang, Y. Li, L. Gu and S. Guo, Matter, 2023, 6, 193–205 CrossRef CAS.
- K. F. Quiambao, S. J. McDonnell, D. K. Schreiber, A. Y. Gerard, K. M. Freedy, P. Lu, J. E. Saal, G. S. Frankel and J. R. Scully, Acta Mater., 2019, 164, 362–376 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Peng, Y. Xie, Z. Xie, Y. Wu, W. Zhu, S. Liang and L. Wang, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8, 18318–18326 RSC.
- D. Wu, K. Kusada, T. Yamamoto, T. Toriyama and H. Kitagawa, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 13833–13838 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Guo, W. Dmowski, J.-Y. Noh, P. Rack, P. K. Liaw and T. Egami, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2013, 44, 1994–1997 CrossRef CAS.
- J. W. Olesik, Anal. Chem., 1991, 63, 187–192 CrossRef.
- C. M. Rost, E. Sachet, T. Borman, A. Moballegh, E. C. Dickey, D. Hou, J. L. Jones, S. Curtarolo and J. Maria, Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 8485 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Xu, P. Liu, S. Guo, A. Hirata, T. Fujita, T. Nieh, C. Liu and M. Chen, Acta Mater., 2015, 84, 145–152 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Song, Y. Yang, M. Rabbani, T. T. Yang, K. He, X. Hu, Y. Yuan, P. Ghildiyal, V. P. Dravid and M. R. Zachariah, ACS Nano, 2020, 14, 15131–15143 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Frank, Y. Chen, S. Nene, S. Sinha, K. Liu, K. An and R. Mishra, Mater. Today Commun., 2020, 23, 100858 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Begildayeva, J. Theerthagiri, W. Limphirat, A. Min, S. Kheawhom and M. Y. Choi, Small, 2024, 20, 2400538 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Dhakal, Electronic Theses and Dissertations, 2017, p. 5407 Search PubMed.
- G. R. Schleder, A. C. Padilha, C. M. Acosta, M. Costa and A. Fazzio, JPhys Mater., 2019, 2, 032001 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Rittiruam, P. Khamloet, A. Ektarawong, C. Atthapak, T. Saelee, P. Khajondetchairit, B. Alling, S. Praserthdam and P. Praserthdam, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2024, 652, 159297 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wan, Z. Zhang, W. Yu, H. Niu, X. Wang and Y. Guo, Patterns, 2022, 3, 100553 CrossRef CAS.
- X. He, Langmuir, 2024, 40, 15503–15511 CAS.
- U. R. Kattner, Tecnol. Metal., Mater. Min., 2016, 13, 3 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Zhang and Y. Yang, MRS Bull., 2022, 47, 158–167 CrossRef.
- Z.-K. Liu, J. Phase Equilib. Diffus., 2009, 30, 517–534 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Wang, Y. Wang, N. Wang, S. Xu, Z. Han and Y. Wang, Mater. Lett., 2021, 283, 128817 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Sun, W. Wang, P. Lu, Q. Liu, L. Wang and H. Tang, Chin. J. Catal., 2023, 51, 90–100 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Das, M. Sanjay, S. Kumar, S. Sarkar, C. S. Tiwary and S. Chowdhury, Chem. Eng. J., 2023, 476, 146719 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Huang, J. Zhao, H. Guo, B. Weng, H. Zhang, R. A. Saha, M. Zhang, F. Lai, Y. Zhou and R. Z. Juan, Adv. Mater., 2024, 36, 2313209 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Yu, S. Wang, Y. Zhang, H. Gao, X. Zhou, D. Li, H. Yang, L. Fang, H. Zhang and A. Syed, Ceram. Int., 2024, 50, 29528–29546 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Li, Y. Liao, J. Zhang, E. Huang, L. Ji, Z. Zhang, R. Zhao, Z. Zhang, B. Yang and Y. Zhang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 27113–27118 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Yu, X. Ding, Y. Yao, W. Gao, C. Wang, C. Wu, C. Wu, B. Wang, L. Wang and Z. Zou, Adv. Mater., 2024, 2312942 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Zhang, Q. Yao, H. Pan, Y. Liu, Z. Shen, Z. Ge, L. Li, Y. Zhang, X. Li and Y. Wang, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 49, 690–698 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Marx and J. Hutter, Ab initio molecular dynamics: basic theory and advanced methods, Cambridge University Press, 2009 Search PubMed.
- Z. Wang, X. Tan, Z. Ye, S. Chen, G. Li, Q. Wang and S. Yuan, Green Chem., 2024, 26, 9569–9598 RSC.
- L. Li, B. Li, H. Guo, Y. Li, C. Sun, Z. Tian and L. Chen, Nanoscale, 2020, 12, 15880–15887 RSC.
- Z. Yao, G.-J. Xia, W. Cao, K.-H. Zeng and Y.-G. Wang, J. Catal., 2023, 418, 1–12 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Song, G. He and H. Fei, Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin., 2023, 9, 2212038 Search PubMed.
- Y. He, L. Yin, N. Yuan and G. Zhang, Chem. Eng. J., 2024, 481, 148754 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Lokesh and R. Srivastava, Energy Fuels, 2022, 36, 13417–13450 CrossRef CAS.
- J. S. Shaikh, M. Rittiruam, T. Saelee, V. Márquez, N. S. Shaikh, P. Khajondetchairit, S. C. Pathan, N. Jiraborvornpongsa, S. Praserthdam and P. Praserthdam, J. Alloys Compd., 2023, 969, 172232 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Liu, Z. Yang, Z. Xu, Y. He and Y. Lao, J. Alloys Compd., 2024, 1008, 176504 CrossRef CAS.
- S.-H. V. Oh, S.-H. Yoo and W. Jang, npj Comput. Mater., 2024, 10, 166 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liao, Y. Li, L. Ji, X. Liu, X. Zhao, H. Rong, D. Xu, G. Qin and X. Zhang, Acta Mater., 2022, 240, 118338 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Wang, L. Chen, R. Qin, R. Wang and L. Yu, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2023, 153, 110794 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Wang, S. Sun, S. Ren, Z. Chen, M. Wang, X. Li and L. Wang, Catal. Today, 2023, 418, 114046 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † These authors contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |






