Themed collection Neurochemistry of lead and manganese

Neurochemistry of lead and manganese
Rachel Austin, Jennifer Freeman and Tomás Guilarte introduce this themed issue of Metallomics, on the neurochemistry of lead and manganese.

Metallomics, 2016,8, 561-562
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6MT90017H
Defining potential roles of Pb2+ in neurotoxicity from a calciomics approach
Metal ions play crucial roles in numerous biological processes, facilitating biochemical reactions by binding to various proteins.

Metallomics, 2016,8, 563-578
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6MT00038J
Lead neurotoxicity: exploring the potential impact of lead substitution in zinc-finger proteins on mental health
This critical review focuses on one possible link between the cellular biology of lead and its neurotoxic effects: the link between Pb2+ substitution for Zn2+ in zinc-finger proteins and mental illness in adulthood.
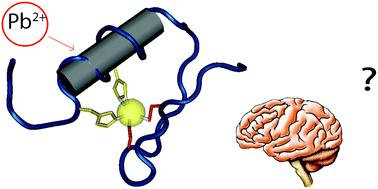
Metallomics, 2016,8, 579-588
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5MT00300H
Mutation in HFE gene decreases manganese accumulation and oxidative stress in the brain after olfactory manganese exposure
HFE H67D mutation up-regulates ferroportin, a metal exporter for manganese (Mn) and iron, and reduces Mn accumulation in the striatum after olfactory exposure to Mn, which consequently decreases Mn-induced oxidative stress in the brain.

Metallomics, 2016,8, 618-627
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6MT00080K
Lead and manganese levels in serum and erythrocytes in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment: results from the Australian Imaging, Biomarkers and Lifestyle Flagship Study of Ageing
A report on lead and manganese in serum and erythrocytes in one of the world's largest Alzheimer's disease cohorts.

Metallomics, 2016,8, 628-632
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6MT00019C
Tyrosine hydroxylase regulation in adult rat striatum following short-term neonatal exposure to manganese
Mn induces short- and long-term alterations on striatal tyrosine hydroxylase levels and phosphorylation in rats.

Metallomics, 2016,8, 597-604
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5MT00265F
Embryonic exposure to 10 μg L−1 lead results in female-specific expression changes in genes associated with nervous system development and function and Alzheimer's disease in aged adult zebrafish brain
Embryonic exposure to Pb at levels as low as 10 μg L−1 disturb global gene expression patterns in a sex-specific manner.

Metallomics, 2016,8, 589-596
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5MT00267B
Thermodynamics of Pb(II) and Zn(II) binding to MT-3, a neurologically important metallothionein
The first quantification of Pb(II) binding to MT-3 using ITC shows that lead binds more tightly than zinc to this brain-specific metallothionein.

Metallomics, 2016,8, 605-617
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5MT00209E
About this collection
This themed issue, Guest Edited by Professor Rachel Austin, Professor Jennifer Freeman and Professor Tomas Guilarte, highlights the molecular mechanisms by which lead and manganese impact the central nervous system.