Nature of the multicomponent crystal of salicylic acid and 1,2-phenylenediamine†
Abstract
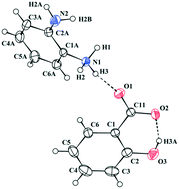
The synthesis and characterization of the multicomponent crystal formed by salicylic acid and 1,2-phenylenediamine (a diarylamine) are reported. The crystals are in the salt rather than cocrystal form, as witnessed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, solid-state NMR, and infrared spectroscopy. 1H double-quantum-single-quantum NMR was pivotal in confirming the proton transfer from the salicylic acid to the amine group of the basic coformer 1,2-phenylenediamine. DFT calculations were used for the geometry optimization of the hydrogen atom positions, and for calculating the NMR chemical shifts of the two possible salt/cocrystal X-ray diffraction models.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...