Surfactant-based promotion to gas hydrate formation for energy storage
Abstract
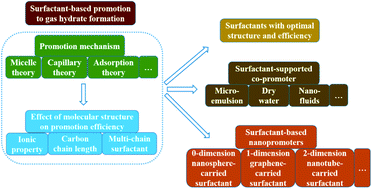
Gas hydrates have been endowed with great potential for natural gas storage and transportation; achieving the rapid hydrate formation and high storage capacity are critical to utilize this technology. Surfactants have been confirmed as the most efficient promoters for gas hydrate formation; however, the promotion mechanisms are un-unified, and foam generation during hydrate dissociation can seriously impact their applications. However, given that non-surfactant promoters, such as porous materials and metal nanoparticles, cannot produce obvious superiority over surfactants with regard to promotion efficiency, surfactants are still considered to be the most potential promoters for the industrial applications of hydrate technology. On this account, a review focused on the surfactant-promoted gas (particularly methane) hydrate formation during the past 2–3 decades has been presented in this study, with the aim of achieving a comprehensive evaluation on the current research status and effective guidance on research prospects. First, different promotion mechanisms of surfactants in gas hydrate formation were generalized and evaluated; thereafter, the effects of the molecular structures of surfactants on the promotion efficiency were analyzed; furthermore, surfactant-supported copromoters applied in gas hydrate formation were listed; finally, novel nanopromoters developed based on the promotion of surfactants during the recent years were summarized.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...