Hepatoprotective and urease inhibitory activities of garlic conjugated gold nanoparticles†
Abstract
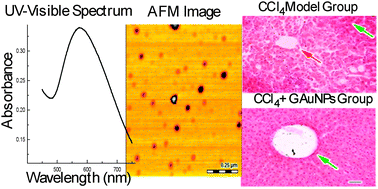
A robust synthetic method is reported for the synthesis of highly stable, poly disperse and spherical gold nanoparticles conjugated to an aqueous garlic extract (G-AuNPs). An ionic solution of gold was mixed and stirred with a dilute aqueous garlic extract at room temperature for 4 hours. The G-AuNPs were characterized by UV-Visible spectroscopy. The morphology and size of the G-AuNPs were determined by atomic force microscopy. FTIR spectroscopy revealed that secondary metabolites present in the garlic extract worked as capping agents around the gold nanoparticles. The G-AuNPs were quite stable even at higher temperature or with salt concentrations up to 10 mM or with various pH ranging from 4 to 11. Two different model systems were tested for evaluating the biological roles of G-AuNPs. They showed excellent hepatoprotective activity in a CCl4-induced acute hepatic injury model which was better than the positive control, silymarin. They also showed urease inhibitory activity with an IC50 value of 180.61 ± 1.06 μg mL−1. Therefore, the G-AuNPs can be useful in the treatment of diseases caused by injury or inflammation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...