Molecular mechanisms from insulin-mimetic effect of vitamin D: treatment alternative in Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
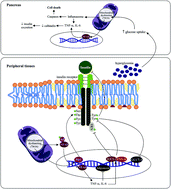
Diabetes mellitus is a complex and multifactorial disease with a global prevalence that exceeds 425 million people. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is characterized by a state of insulin resistance, which leads to metabolic alterations that aggravate the state of health of people. Vitamin D deficiency appears to play an important role in the triggering mechanisms of insulin resistance. In this review, an analysis is made of the biochemical mechanisms associated with the insulin-mimetic effect of vitamin D, its supplementation being a possible nutritional strategy for the T2DM treatment. The current scientific evidence is extensive regarding the dose of vitamin D used for an insulin-mimetic effect. However, clinical trials and systematic reviews show statistical differences on glucose, insulin, and glycated hemoglobin levels of patients with T2DM, associated with activation mechanisms of transcription factors related to genes of the glucide metabolism and the insulin receptor, and the regulation of intracellular Ca2+ insulin concentrations. Likewise, an indirect mechanism associated with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects has been shown that also leads to sensitivity to the insulin receptor. The use of a specific dose of vitamin D could be an effective alternative in the T2DM treatment, which would reduce the risk of complications derived from hyperglycemia.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...