Mechanisms and performance of calcium peroxide-enhanced Fe(ii) coagulation for treatment of Microcystis aeruginosa-laden water†
Abstract
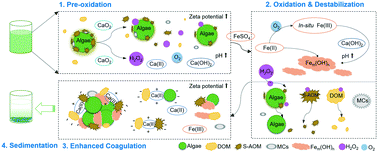
Pre-oxidation has been extensively studied as a pre-treatment for enhancement of algae-laden water coagulation. However, most current chemical oxidation technologies suffer from aggressive destruction of algae cells, which leads to cell lysis and undesirable release of algal metabolites. In this study, a novel calcium peroxide (CaO2) pre-oxidation process combined with ferrous sulfate (FeSO4) coagulation was explored to treat Microcystis aeruginosa-laden water, while minimizing the release of intracellular organic matter (IOM). This study aimed to investigate the removal efficiency of algae, microcystins (MCs) and dissolved organic matter (DOM), and explore the reaction mechanisms. Under the optimal conditions (0.5 mM CaO2), CaO2 enhanced coagulation resulted in algae, dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and MCs removal rates of 88.8%, 83.9% and 46.8%, respectively. Moreover, soluble microbial products and humic acid-like materials were effectively removed with increasing CaO2 dose. Notably, the photosynthetic activity of algal cells was significantly inhibited with slight damage of cell integrity, demonstrating the moderate oxidative capacity of CaO2. The H2O2 yield from CaO2 reached >50% over the entire treatment duration, which caused the inactivation of algal cells and improved DOM removal. Ca(OH)2 formed simultaneously, serving as a coagulant aid for enhanced formation of Fe-hydroxide and Fe-hydroxyl polymers (Fem(OH)n) from Fe(II) and in situ formed Fe(III), which promotes the aggregation of algae and organic matter to form larger flocs. This new treatment effectively mitigates the effects of algal blooms on water treatment, while minimizing the issues associated with current chemical oxidation technologies.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology Cover Art


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...