Simultaneous monitoring of 32S, 33S and 34S isotopes of H2S using cavity ring-down spectroscopy with a mid-infrared external-cavity quantum cascade laser
Abstract
The simultaneous monitoring of three stable isotopes of hydrogen sulphide (H2S), i.e. H232S, H233S, and H234S, within a single laser scan of 0.4 cm−1 has been achieved by means of a continuous-wave (cw) external-cavity quantum cascade laser (EC-QCL) coupled to high-resolution cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) near 7.5 μm. The measurement precisions of S32, S33, and S34 isotopes of H2S were found to be 1190 ppb, 13 ppb, and 124 ppb for the integration times of 264 s, 261 s, and 247 s, respectively. The mode-hop-free (MHF) tunability (1257 cm−1 to 1340 cm−1) of the EC-QCL was subsequently exploited to identify the interference-free 9 transition lines of H232S and H233S arising from the fundamental bending vibration (ν2) for the trace detection of H2S isotopes. A limiting sensitivity (1σ) of 20 ppb of total H2S concentration was achieved for an integration time of 250 s by targeting the rotational transition [i.e.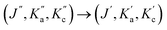 ] of (4, 4, 1) → (5, 5, 0), centred at ∼1292.857 cm−1. Finally, simultaneous monitoring of multiple trace species such as CH4, N2O, and H2S in a single laser scan of 0.05 cm−1 was demonstrated with high sensitivity and molecular specificity. The present study may lead to several potential future applications ranging from understanding of sulphur isotope geochemistry and fractionations to environmental sensing.
] of (4, 4, 1) → (5, 5, 0), centred at ∼1292.857 cm−1. Finally, simultaneous monitoring of multiple trace species such as CH4, N2O, and H2S in a single laser scan of 0.05 cm−1 was demonstrated with high sensitivity and molecular specificity. The present study may lead to several potential future applications ranging from understanding of sulphur isotope geochemistry and fractionations to environmental sensing.

- This article is part of the themed collection: JAAS Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...