 Open Access Article
Open Access ArticlePractical considerations to optimize aquatic testing of particulate material, with focus on nanomaterials†
Simon
Luederwald
 *a,
Jordan
Davies
b,
Teresa F.
Fernandes
*a,
Jordan
Davies
b,
Teresa F.
Fernandes
 c,
Antonia
Praetorius
c,
Antonia
Praetorius
 d,
Jacques-Aurélien
Sergent
d,
Jacques-Aurélien
Sergent
 e,
Kristi
Tatsi
f,
Joan
Tell
g,
Niels
Timmer
e,
Kristi
Tatsi
f,
Joan
Tell
g,
Niels
Timmer
 h and
Stephan
Wagner
h and
Stephan
Wagner
 i
i
aExperimental Ecology, BASF SE, Carl-Bosch-Strasse 38, 67056 Ludwigshafen am Rhein, Germany. E-mail: simon.luederwald@basf.com
bLyondellBasell, Delftseplein 27E, 3013 AA Rotterdam, Netherlands
cInstitute of Life and Earth Sciences, Heriot Watt University, The Avenue, Edinburgh EH14 4AS, UK
dInstitute for Biodiversity and Ecosystem Dynamics, University of Amsterdam, Science Park 904, 1098 XH Amsterdam, Netherlands
eToxicological and Environmental Risk Assessment Unit, Solvay SA, 1120 Brussels, Belgium
fCorteva Agriscience UK Ltd., 101 Park Square, Milton Park, Abingdon, Oxfordshire, OX14 4RY, UK
gMerck Sharp & Dohme LLC, 2000 Galloping Hill Road, Kenilworth, NJ, USA
hCharles River Laboratories Den Bosch BV, Hambakenwetering 7, 's-Hertogenbosch, Netherlands
iHochschule Fresenius, Institute for Analytical Research, Limburger Str. 2, 65510 Idstein, Germany
First published on 26th April 2024
Abstract
Aquatic testing of particulate materials (PMs), e.g., nanomaterials (NMs) and microplastics (MPs), poses inherent challenges potentially hindering the application of existing test guidelines (TGs). Those TGs are primarily designed for hazard assessment of the dissolvable form of a material, whereas the guidance document on aquatic and sediment toxicological testing of NM (OECD Guidance Document 317) encourages the inclusion of potential colloidal fractions in the assessment. A prerequisite for the testing of PMs is the preparation of stable dispersions. However, testing difficulties may result from the fact that nano-scale PMs are inherently unstable when dispersed in test media, leading to the need for differentiation of potential chemical vs. physical effects caused by the tested material. Aquatic testing of unstable PMs will likely result in inconsistent and non-uniform uptake and exposure scenarios and thus effects observed in the respective test systems. Maintaining stable exposure conditions is often very challenging given the constantly changing size of the PM and its agglomerates, requiring observed endpoints to be based on measured concentrations and particle size distributions present in the water phase, while neglecting agglomerated and settled particulates. In this paper we describe the current state of PM-testing, demonstrate PM-specific challenges in aquatic testing (e.g., test duration, physical effects, instability, biodegradation, bioaccumulation) with a focus on NMs, considering a set of most relevant TGs, and provide proposed testing considerations to optimize aquatic testing of PMs.
Environmental significanceAquatic testing of particulate materials (PMs), especially nanomaterials (NMs) and microplastics (MPs) requires special attention. Following standard approaches embedded in existing OECD test guidelines and available OECD guidance documents leads to various challenges, that can result in non-uniform and non-comparable results, implying a misuse of resources, which is not in accordance with the 3R-principle, and ultimately to acceptance issues with authorities. As part of this work, the manuscript i.) identifies the current state of the aquatic toxicity testing of PMs, considering the regulatory and technical state of play, ii.) presents potential emerging challenges while following existing PM testing approaches, and iii.) proposes options to assist in study design such that the most appropriate tests and procedures are conducted for the intended purpose. |
1. Introduction
There is a rapidly growing and expanding market for particulate materials (PMs), which in the context of this article are considered as (engineered) nanomaterials (NMs) and microplastics (MPs). Hence, there is a need to better understand the adequacy of available test guidelines (TGs) from the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), or other similar standards like US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Office of Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances (OPPTS), American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) or International Organization for Standardization (ISO), to determine endpoints, e.g., related to the (eco)toxicity, degradation and bioaccumulation of PMs, compared with their non-particulate/non-nano counterparts. NMs are defined as “chemical substances or materials containing particles with sizes between 1 to 100 nm in at least one dimension”.1 Based on their high surface to volume ratios NMs possess different characteristics, relative to micron-sized substances or PMs of larger (e.g., in the lower mm range) sizes.1 MPs are considered as solid plastic particles composed of polymers and functional additives, typically smaller than 5 mm.2OECD TGs for the aquatic toxicity testing of chemicals are embedded amongst others in ‘Section 2 – Effects on Biotic Systems’ of the OECD TGs, and are designed to be applicable to various chemicals, such as mono- or multi-constituent substances, mixtures of chemicals, pesticide formulations, and cosmetic products.3 For substances and mixtures classified as ‘difficult to test’ there is additional guidance provided in the OECD Guidance Document (GD) 23.4 However, OECD GD 23 does not specifically address the testing difficulties associated with PMs. The scope is primarily focussed on aquatic testing of the dissolved fraction of a chemical and is not applicable to aquatic tests including undissolved particulates, with two exceptions: (i) when specific regulatory relevance exists, and (ii) when the test substance forms an aqueous stable dispersion or emulsion.4 Assessing potential effects of PMs on the aquatic environment, however, requires the consideration of the insoluble particulates and, even more importantly, not neglecting their fate in the receiving compartment.
Once in the aquatic environment NMs, and PMs in general, are subjected to physical, chemical, and biological transformation processes, e.g., agglomeration, sedimentation, dissolution, oxidation/reduction, sulfidation, and interactions with biological surfaces, etc.5,6 Such processes will inevitably change the ecotoxicological and bioaccumulation potential of the PMs over time; therefore, proposing relevant hazard properties for robust risk assessment and risk management can be complex. This can potentially cause acceptance issues with authorities. Therefore, more guidance is needed for aquatic toxicity testing of PMs, along with proper evaluation of observed results. In the current paper we:
i. identify the current state of the aquatic toxicity testing of PMs, considering the regulatory and technical state of play.
ii. present potential emerging challenges in following the existing PM testing approaches, based on mostly NM literature which can also be applicable to Advanced Materials and more broadly to MPs,
iii. propose options to assist in study design such that the most appropriate tests and procedures are conducted for the intended assessment purpose.
2. Current status of particulate material testing approaches
2.1. Regulatory state of play and impact on different sectors
| Regulatory framework | Definitione | Approval procedure | Safety assessment | Labelling | Guidance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Not a formal definition in the legal text although the European Commission aligns this with the definition in the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR). b Safety assessment as part of standard REACH exposure and risk assessments. c Not a specific guidance but a statement has been included in the guidance documents related to nanomaterials. d Since the publication of Rauscher et al., 2017,10 EFSA have provided guidance to cover food contact materials. e A Commission Recommendation of 10 June 2022 (ref. 12) on the definition of nanomaterial sets out definitions for ‘nanomaterial’ and associated terms. It is understood that the nanomaterial definition therein is to eventually be implemented into each relevant regulatory framework in the EU. | |||||
| REACH (chemicals) regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 | xa | xb | x | ||
| Biocidal products regulation (EU) No. 528/2012 | x | x | x | x | xc |
| Cosmetic products regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009 | x | x | x | x | x |
| Novel food regulation (EU) No. 2015/2283 | x | x | x | x | x |
| Food additives regulation (EC) No. 1333/2008 | x | x | x | ||
| Plastic food contact materials regulation (EU) No. 10/2011 | x | x | |||
| Active and intelligent food contact materials regulation (EC) No. 450/2009 | x | x | xd | ||
| Provision of food information to consumers regulation (EU) No. 1169/2011 | x | x | |||
| Country/regulation | Topic | Specific parameters addressed |
|---|---|---|
| Health Canada Working definition in 2008/11 | Policy Statement on Health Canada's Working Definition for Nanomaterial | Size and nanoscale properties/phenomena criteria |
| NICNAS (Australia) Working definition 2010/10 | Guide to categorising your chemical importation and manufacture | Size and unique properties criteria |
| US EPA definition 2017 | Questions About Nanotechnology | Unique properties |
| US FDA 2014/06 | Considering Whether an FDA-Regulated Product Involves the Application of Nanotechnology Guidance for Industry | Size, partial inclusion of specific dimension related properties or phenomena |
In general, for most EU regulatory frameworks, testing (including PM testing) follows standard guidelines, e.g., OECD, to ensure uniformity and reproducibility using the MAD (Mutual Acceptance of Data) concept. For REACH purposes (as a result of the requirements in the implementing regulation on NMs ((EU) No. 2018/1881)) updated guidance is now available for NM testing as the following appendices to REACH guidance on information requirements and chemical safety assessment: Appendix for nanoforms applicable to the Guidance on Registration and Substance Identification;13 Appendices R7-1 and R7-2 for nanomaterials applicable to Endpoint specific guidance Chapters R7a, R7b and R7c;14–16 Appendix R10-2 Recommendations for nanomaterials applicable to Chapter R.10 Characterisation of dose [concentration] – response for environment;17 Appendix R14-4 Recommendations for nanomaterials applicable to Chapter Occupational exposure estimation;18 Appendix R.6-1 for nanoforms applicable to the Guidance on QSARs and Grouping of Chemicals.19
The REACH guidance provided by the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) aligns with general approaches in recent OECD guidelines discussing such materials.16 Relating to novel food and feed additives, and food contact material regulations, European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has produced guidance on technical requirements to establish the presence of small particles in the food and feed chain.20 This guidance relates to physical–chemical testing and the risk assessment of nanomaterials relevant to human and animal health, including potential testing strategies.21 EFSA has also produced a scientific opinion on environmental risk assessment of nanomaterials.22 For BPR (Biocidal Products Regulation), no test specific guidance is available for nanomaterials. However, general ECHA guidance23 states that if test methods are applied to nanomaterials, their scientific appropriateness needs to be justified and any technical adaptations need to be explained.
Restrictions are normally applied to limit or ban the manufacture, placing on the market (including imports) or use of a substance, and can impose additional requirements such as technical measures or specific labels. ECHA's definition of MPs is very broad. Plastic is not defined as such, and ECHA uses the REACH definition of polymers (REACH Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006; Art 3.5). The use of synthetic polymers in medicinal products for human and veterinary use is derogated from this restriction, but intricate labelling and reporting is required.
ECHA's proposed definition of MPs comprises all solid polymers at ambient conditions with a particle size smaller than 5 mm in all dimensions. This would include nanoplastics (although these are covered within the general NM framework) as no lower size limit is currently proposed for reasons of practicality and enforceability. Not subject to the restriction are naturally occurring, not chemically modified polymers, and (bio)degradable and soluble polymers according to interim criteria set out in the Annex XV restriction report.24 ECHA's broad definition of MPs puts a significant number of essential constituents in the formulation of medicinal products (excipients) used in the pharmaceutical industry and listed in the European Pharmacopeia into the scope of the restriction (e.g., cellulose acetate, hydroxypropylcellulose, etc.).
The European Pharmacopoeia includes an adopted list of excipients which are approved and safe for use in drug products; these are polymers in many cases. Excipients listed in pharmacopoeia show a good safety profile with regard to human or animal health and are comprehensively tested in accordance with the required safety studies for approval of drug products. However, in general, data are often lacking on biodegradation, solubility etc. and overall environmental impacts of such materials.
In addition to pharmaceutical excipients, the ECHA MP restriction proposal is also expected to significantly impact the agrochemical industry (e.g., controlled-release fertilizer and polymers used in formulations for biocides and plant-protection products), the cosmetics industry (e.g., fragrance encapsulation and polymers used in personal care products), the detergents and maintenance industry, and numerous other industries. The most relevant aspect for MPs that fall under this restriction would be biodegradability, as there is a derogation for any MP that satisfies specific biodegradability criteria; products and raw materials containing intentionally added MPs that do not biodegrade cannot be placed on the market in the EU.24 Since biodegradable polymers are exempt from the forthcoming MP restriction proposal, there is an urgent need for adequate biodegradability testing of MPs.
2.2. Technical state of play
The OECD Working Party on Manufactured Nanomaterials (WPMN) is developing new guidelines for the evaluation of NMs or revisiting the existing documents for their applicability. This work is also, more recently, supported by Horizon 2020 funded projects such as NANOMET focusing only on the physico chemical characterization (https://www.oecd.org/chemicalsafety/nanomet/) and NanoHarmony dealing with physico-chemical characterization and (eco-)toxicity evaluation (https://www.nanoharmony.eu). The NanoHarmony project particularly aims to work on bioaccumulation (TG305 and associated Guidance Document), toxicokinetics (new test guideline), intestinal fate (new Guidance document), ecotoxicology, quantification of NMs in biological samples, solubility and dissolution rate (Guidance document 318), surface chemistry characterization (new guidance document), and dustiness measurement (new test guideline). All these endpoints and approaches are relevant in the EU for the newly adopted annexes for REACH with specific requirements for nanoforms ((EU) No. 2018/1881). Some of these tasks, aiming at accelerating the validation and acceptance of the updated OECD guidelines, have already been finalized, among them the OECD guidance document (GD) 317 ‘Guidance Document on Aquatic and Sediment Toxicological Testing of Nanomaterials’ and TG 318 ‘Dispersion Stability of Nanomaterials in Simulated Environmental Media’ are of relevance for aquatic testing of PMs.3,25 While the OECD guidelines developed are specific to NMs, several concepts would be applicable to MPs with additional considerations as discussed in Petersen et al. (2022).26The GD 317 (ref. 3) aims at addressing the issue of a current gap in existing OECD GDs and TGs which relates to PMs requiring extensive consideration of undissolved particulates present in test solutions. The GD 317 is split into three main sections: (i) preparation of NM dispersions, (ii) conduct of tests, and (iii) data analysis and reporting, to facilitate quality and reliability of ecotoxicity data of NMs. While GD 317 states hazard testing of the whole NM sample (including suspended, settled, and dissolved fractions) as the recommended standard approach, the exclusion of settled material (i.e., hazard testing of suspended and dissolved fractions), or solely testing the dissolved fraction, might be accepted if the goal is to determine the contribution of dissolved or settled fractions on the overall hazard of the NM.
OECD TG 318 addresses the testing of dispersion stability of NMs, and how to use such data for further environmental testing and assessment strategies.25 The objective of this TG is to provide details on the ability of a NM to achieve a state of colloidal dispersion and how this dispersion can be preserved under environmentally relevant but also varying conditions. Therefore, a dispersion of the NM is prepared by means of a calibrated sonication method, followed by mass concentration analyses of the particles, while the NM experiences homoagglomeration and sedimentation in aquatic media of different composition.25 Petersen et al. (2022)26 note, however, that sonication may not be appropriate when testing MPs due to intrinsic limitations for MPs which are the disintegration of the particles or changes to the surface of the particles. The project NANoREG (‘A common European approach to the regulatory testing of nanomaterials’) also has developed, tested, and validated protocols for the preparation of NM dispersions suggesting the use of additives such as natural organic matter (Suwannee River natural organic matter (NOM)) and ethanol to increase the dispersibility of NMs.27 Those additions might, however, change properties of the particulate matter under consideration (NMs, MPs), as well as their fate and behavior, and ultimately their ecotoxicological potential under testing conditions (see also section 3.4.).
Further guidance is provided in the OECD GD 318 (‘Guidance Document for the Testing of Dissolution and Dispersion Stability of Nanomaterials, and the Use of the Data for Further Environmental Testing and Assessment’),28 in a best case allowing a judgement as to whether the PM to be tested is actually tested as suspended particle, as dissolved substance, or even both, most likely depending on the applied experimental conditions, such as exposure time, test medium ionic strength and pH, for example.
The ongoing work at the OECD level on NMs is summarized in their current workplan (Work plan for the Test Guidelines Programme (TGP) (https://oecd.org)), with additional TGs finalized in 2022 relating to particle size and size distribution (OECD TG 125 (ref. 29)) and determination of the volume specific surface area of manufactured nanomaterials (OECD TG 124 (ref. 30)).
3. Challenges in following current particulate material testing approaches
Until the publication of OECD GD 317 (ref. 3) in 2017, NM-/PM-specific hazard testing addressing the handling of undissolved test substances had not been covered by existing TGs and GDs. The OECD GD 23 on aquatic toxicity testing of ‘difficult to test’ substances essentially recommends the removal of undissolved or settled material from test solutions prior to testing, in order to describe effects of the dissolved test substance only.4 Contrastingly, a prerequisite for testing PMs is the preparation of stable dispersions, also containing the undissolved fraction of the test substance. PMs/NMs released into the environment or applied to standardized test media proposed in OECD TGs, are known to be subjected to transformation processes such as dissolution, homo- and/or hetero-agglomeration5 and surface transformations (e.g., due to oxidation/sulfidation, corona formation/biofouling or other ageing/weathering processes), which will ultimately alter their fate and ecotoxicological potential. In addition, such transformation and fate processes will inevitably inhibit the achievement of a constant and accurately quantifiable exposure during aquatic testing, potentially reducing the validity and reproducibility of the assay. In the following sections, the properties of PMs which can lead to the key challenges that may arise in adhering to the current TGs are explored and suggestions on how to overcome or account for these challenges in environmental fate and ecotoxicology testing are presented.3.1. Environmental fate and exposure considerations
Critical to any testing strategy is an exposure-driven, risk-based approach. Assessing chemical safety based on hazard alone, with little consideration for fate and exposure, can result in misuse of resources and may not be in accordance with e.g., the 3Rs (replacement, reduction, refinement) principle, with the potential use of test animals without properly evaluating necessity (i.e., reduction by choosing the right strategy). A logical deduction would then be to tailor the approach for PMs to be more in line with existing tiered test strategies. Stability and persistence in the environment could be determined alongside in vitro test batteries before in vivo toxicity testing in animals, particularly vertebrates, is considered. Ideally, there would be clearly defined criteria with respect to stability, persistence, and in vitro parameters, which could be used to waive animal testing if they are met unequivocally. Once animal testing is deemed necessary, fate and environmental exposure should be determined to appropriately decide on testing needs.It has already been recognized for environmental fate and transport models, which are crucial in providing exposure estimates to inform risk assessment and chemical prioritization, that existing approaches for chemicals cannot be directly applied to undissolved PM. Established multimedia mass-balance models for organic chemicals,31 based on the fugacity approach and reliant on partition-coefficients as input parameters, do not adequately represent the kinetically driven behaviour of nano- and micro-sized particles.32–34 Several new modelling approaches have been developed over the past decade,35–37 drawing from established concepts of colloid science (e.g., to describe particle aggregation and sedimentation) and from the ever-growing literature on specific processes including (but not limited to) dissolution, corona formation/biofouling, degradation, and fragmentation. First particle-specific versions of multimedia environmental fate models used in regulatory contexts have been developed, such as SimpleBox4nano,38 the NM-version of SimpleBox, and the ‘regional distribution module’ in the European Union System for the Evaluation of Substances (EUSES).
3.2. Test duration
During the aquatic test period PMs are prone to various changes, such as dissolution and agglomeration,39 impacting their fate, bioavailability, and ultimately their potential ecotoxicological impact.40 In the case of unstable PM dispersions, the duration of an experiment will affect the agglomeration state and consequently the particles size(s) that the test organisms will be exposed to ref. 41. PM stability can be evaluated according to OECD TG 318 (ref. 25) in parallel to performing toxicity testing, in order to control the degree of agglomeration likely present in a test system at a given timepoint. This also highlights the need for following standardized dispersion protocols and preparing fresh dispersions for each experiment.Previous publications assessing the risk of PMs for aquatic ecosystems indicated a negative impact on inhabiting invertebrates as a result of prolonged exposure periods, leading to physical implications, e.g., through bioaccumulation or coating of the organisms' outer surface with the PM (TiO2 (ref. 42 and 43)). In the latter study, extending the standardized study duration for an OECD TG 202 (Daphnia Acute Immobilization Test, without feeding of the test organism) test from 48 h to 96 h revealed a distinctively increased effect, i.e., 0% (48 h) vs. 100% (96 h) immobility of the test organism, when applying the NM in the low concentration range.43 Likewise, Eltemsah and Bøhn (2019)44 observed elevated immobility in D. magna when exposed to MP, when prolonging the exposure period from 48 h to 120 h,44 potentially triggered by physical rather than strictly chemical interference with the test organism, e.g., by clogging its filtering apparatus or gut with plastic particles.
It needs to be mentioned though, that extending the standardized study duration in studies where no feeding takes place might cause adverse effects in the test organism despite the presence or absence of the PM, e.g., due to a reduced physiological fitness, e.g., caused by starvation. Thereby, reference toxicant testing also adapted to extended exposure durations should be considered a prerequisite to resolve this potential issue. A 21-day Daphnia chronic NM-exposure, generally following the OECD TG 211 (ref. 45) without specific adaptations for the testing of NMs, showed a significantly decreased number of offspring relative to the control, at concentrations as low as 0.1 mg L−1.42,46 Observations by Ellis et al. (2020)47 indicated that exposure to PMs in the nano- and microscale can lead to a delayed maturity and consequently reproduction in D. magna, which is currently not captured by a 21-day exposure period.47 Extending the exposure period towards PMs to 28–30 days might allow to get a better picture of potential long-term effects in D. magna, since the first and subsequent broods can be delayed due to NM exposure.47 Extension of the test duration would allow evaluation of five broods, which is more comparable with evaluation under standardized non-NM test conditions.
Standard short-term toxicity tests with exposure periods no longer than 48 h, for example, might not reasonably describe potential NM-specific toxicity towards aquatic biota. Where testing approaches for conventional chemicals are mostly comprising exposure via the water phase, there is evidence in aquatic NM testing highlighting the importance of sediment testing, especially for non-stable NM-suspensions.39 Considering animal welfare and the 3Rs principle, testing decisions need to be well informed and justified in two ways, (i) performance of chronic testing without proper substantiation, as well as (ii) performing acute toxicity testing when it is to be expected that only chronic effects will occur. Development of TGs for aquatic toxicity testing of PM was previously focused on short-term effects, and further development and/or adaptation of chronic test methods is required to ensure appropriate methods are applied.
3.3. Physical effects
Among the testing difficulties for PM is the differentiation of potential chemical vs. physical effects caused by the tested material. There are studies pointing out the size-dependent impact of NMs, for example to green algae.48 Algae were more sensitive to smaller particles, as more of those were attached onto the surface of algal cells, compared to initially bigger particles. He et al. (2019)48 also reported hetero-agglomeration between the NM and the algal cells, resulting in enhanced generation of reactive oxygen species in algal cells with increasing NM-concentration.Likewise, another study reported physical effects of nanoscale-TiO2, such as cell wall damage of TiO2-entrapped algae.49 The authors also reported a reduced chlorophyll a content in algae in the presence of nTiO2, indirectly indicating potential shading effects, which could be triggered by NM-adsorption or -coating, leading to a reduced illumination of the algae, ultimately inhibiting growth.49,50
Furthermore, it has been shown, that the presence of PMs such as MP exhibit a high potential for ingestion, e.g., as shown in marine fish larvae or Daphnia, finally resulting in gut passage or potential accumulation in the animals' gastrointestinal tract.51,52 For NMs, additional sub-lethal effects arising from physical effects have been reported as changes in feeding and depuration and impaired mobility in crustaceans and excess mucous production in fish.50
OECD GD 317 (ref. 3) states ‘If a distinction between chemical and physical effects can be made, this should be reported’, and furthermore ‘Robust prescriptive and interpretative guidance is beyond scope of this GD due to lack of precedent for how NM-specific attributes (e.g., agglomeration vs. single particle exposures, suspended particles vs. settled particles, physical vs. chemical toxicity) will be handled in an ecological hazard assessment and risk assessment’.
Applying a conventional experimental setup for aquatic ecotoxicity-testing for NMs, and in a broader view to PM, the distinction between physical and chemical effects is simply not possible via a single experiment, due to difficulties in following up throughout the assay the amount of dissolved fraction of the test substance under testing conditions. In any case, a pragmatic approach needs to be followed in regulatory testing regarding dissolution of test substance and comparison across dissolved/particle fraction effects. An approach to tackle the identification of physical effects associated with NM-exposure has been proposed and some publications are already available on this aspect (e.g., Yue et al., 2015 (ref. 53)). The interest of such methods is to be able to distinguish physical effects from toxic effects, although in practical terms, as indicated above, that is often not a simple task.
3.4. Instability
PMs, here referring to NMs, are inherently unstable when dispersed in testing media (or in environmental media).33 They can remain in dispersion throughout another phase for a long time by forming kinetically stable colloidal suspensions (e.g., through electrostatic and/or steric stabilization effects), but this kinetic stability is contingent on a set of favorable conditions (e.g., related to dispersibility, pH, salinity, presence of steric stabilizing agents such as natural organic matter (NOM) or surface coatings on the particles). The big influence of solution conditions on particle stability results in large variations in particle dispersal state in different test media. As a result, test organisms are not being exposed to the same forms (and number concentrations) of a given test material, which represents a particular challenge for producing comparable test results. Using NOM in terms of test media manipulations, for instance, may be considered on a case-by-case basis as an acceptable stabilizing agent for NM,3 or PM in general. However, a review by Arvidsson et al. (2020)54 found that in 80% of 66 investigated studies, the presence of NOM showed a reduction in NM ecotoxicity.54 Thereby, the quantity and quality of the applied NOM do correlate with the ecotoxicological potential of NMs.55 Since dissolved organic materials can be found in almost every aquatic ecosystem ranging in concentrations of 0.1–10 mg L−1,56 reduced NM ecotoxicity due to the presence of NOM may represent a more realistic estimation of the actual toxic potential of a NM when comparing observed effects of a NM in the absence of NOM. Moreover, NOM might also act as a source of energy for aquatic organisms such as D. magna, potentially increasing energy reserves in the organism, resulting in a generally higher fitness and tolerance towards stressors.40,61,62 Consequently, risk exerted from stably dispersed relative to agglomerated particles (NOM presence vs. NOM absence), might skew the interpretation of the actual risk of a certain NM towards the environment.NOM coronas, an interfacial area between NMs and the surrounding environment, have been reported to predominantly alleviate the NM toxicity due to several reasons, (i) hampering physical interaction between the NM and the test organism, e.g., Lin et al. (2012),57 (ii) capturing harmful reactive oxygen species, e.g., Lüderwald et al. (2019),58 and (iii) complexation and reduction of bioavailable ions, dissolved from the NM e.g., Li et al. (2011).59 NOM coronas are a coating which may include proteins and other organic molecules.60 NOMs can help to increase distribution, dispersibility and homogeneity of test dispersions,27 but it is important to remember that standard tests do not aim to reproduce environmental conditions and use of NOMs will lead to challenges in standardisation of studies and comparability of results. Contrastingly, a review by Nasser et al. (2020)131 is highlighting the importance of including biomolecules in standard testing protocols for NM-testing allowing the adsorption of an ecological corona onto the NM, ultimately ensuring real and more environmentally relevant exposure and effect scenario. There are, however, still uncertainties related to a standardized use of NOM as stabilizing agent, mainly due seasonal and regional variability in quality, and furthermore due to a lack of comprehensive characterization.
3.5. Reactivity
Reactivity is a physical–chemical property of PMs, and it varies between PMs. With their high surface to volume ratio, reactivity of NMs especially is in part unique, and surface area correlates for instance with reactivity also of PMs in general. Reactivity is often related to surface processes63e.g., release of ions leading to the formation of the toxic species like dissolved metal ions or radicals like reactive oxygen species (ROS). Hence reactivity might be key in predicting the toxic action of metal or metal oxide PMs and it is considered as a rationale for toxicity of a PM. The inherent reactivity can be described by the redox potential of the particle, as a measure of the tendency to release or acquire electrons, the radical formation potential, and the photocatalytic activity. Formation of free radicals often causes formation of ROS and is usually associated with oxidative stress as well as toxicity (or adverse biological effects). Photocatalytic activity creates electron–hole pairs under irradiation of light resulting in the generation of ROS.64 Reactivity is controlled by particle properties and solution chemistry. Particle properties controlling reactivity of PMs are particle size, particle shape, surface area, crystallinity as well as surface chemistry including coatings. These may also be modulated by the chemistry of the dispersion agent including pH, ionic strength, and presence of organic ligands. Therefore, reactivity can only be determined for well-defined conditions and is not directly transferable between materials and solution conditions. If conditions are unstable during a test, reactivity may increase or decrease, leading to a higher variability in results. This approach requires robust measures for the reactivity.The redox potential, as the inherent reactivity of a PM dispersion, may not be measured, as the available methods like potentiometry are sensitive to coexisting redox active species. There is also no method to determine the formation potential of free radicals. Therefore, reactivity is determined indirectly by measuring the oxidative activity of NMs using the potassium iodide test for hydroxyl radicals. Photocatalytic activity can be determined by monitoring nicotine adenine dinucleotide hydrate (NADH) oxidation according to ISO 20814:2019. TGs for reactivity address also the response to ROS formation including both chemical and toxicological effects.65
3.6. Size, shape, coatings and heterogenicity of the materials
Particle size and shape are crucial properties affecting fate and behavior of PMs. Particle size and shape will affect potential uptake by, and translocation within, organisms and will influence the agglomeration behavior and hence the stability of PMs and their settling behavior.66–69 The literature on particle size dependent toxicity is not conclusive but size-unique effects are most likely to occur below 30 nm scale.70 Pure chemical substances are classified unambiguously by their substance identity (e.g., Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) number), whereas particles need to be described by means of their chemical as well as their physical characteristics. The physical properties of PMs, such as size and shape, add an additional degree of complexity to their behavior and consequently to their assessment. To complicate matters further, these properties are not represented by single values but by a distribution of values. Within a given PM, heterogeneous particle populations with contrasting material properties are common, creating particular challenges for selecting adequate reference materials. Another specificity of NMs is the fraction of atoms that is available to the surrounding microenvironment. This percentage increases very rapidly when the diameter of the particle falls below a size of 20 nm as the surface area-to-volume ratio increases (Fig. 1).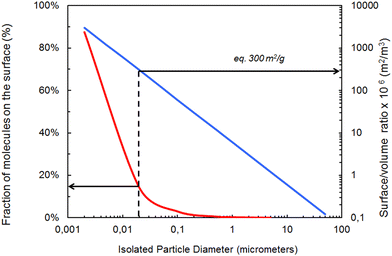 | ||
| Fig. 1 Relationship between fraction of molecules on the surface, isolated particle diameter and surface/volume ratio for spheroidal materials, adapted, with permission, from Witschger & Fabriès (2005).76 Footnotes to figure: the blue line represents the correlation between isolated particles supposed to be spherical and their surface/volume ratio. The red curve represents the correlation between the diameter of these particles and the fraction of atoms at the surface. | ||
The term ‘particle coating’ mostly relates to organic molecules adhering to the surface of inorganic particles. Particle coatings are often used to increase stability of particle dispersions, changing surface charge, or introducing steric hindrance between particles. Characterization of such coating substances is required by REACH (Appendix for nanoforms applicable to the Guidance on Registration and Substance Identification13). Once inorganic particles enter the environment or are present in biota, natural processes can also form organic coatings, usually referred to as corona.71 Method development and harmonization is currently done at the OECD level (OECD WNT project 1.6, Work plan for the Test Guidelines Programme (TGP) (https://oecd.org)). NM coatings do not only affect particle aggregation of the materials but also greatly affect environmental fate and toxicity. The effect of NM coatings on biological up-take, pharmacokinetics, and toxicity potential has been demonstrated in numerous studies (e.g. Louie et al., 2016 (ref. 72)). Aggregation in surface waters and transport in porous media may be affected by organic coatings.73
In systems with heterogeneous components like natural macromolecules, such as NOM, interactions are more complex, and prediction may not be successful.56 Therefore, characterization of these complex systems is a requirement for understanding the interaction of organic molecules with the particle surface and its consequences for particle fate.56,74,75
3.7. Biodegradation testing
The environmental fate (biodegradation specifically) of PMs is important in understanding their potential for persistence across different environmental compartments. Biodegradability should be considered as an intrinsic chemical property; a molecule or chemical bond is either biodegradable or not, and the circumstances or suitability of the chosen test setup do not change this property.77 Misclassification of biodegradability either way (i.e., false positive as well as false negative) may waste resources and does not contribute to environmental protection. This is especially relevant for PM, where purely physical effects can impact the accurate assessment of biodegradability. Therefore, adequately adapted testing protocols are required to deal with the complexities and specific properties of PMs, especially since biodegradable polymers are exempt from the forthcoming ECHA MP restriction proposal.24Standard ready biodegradability studies (OECD TGs 301 and 310) use various methods to quantify and evaluate biodegradability and are very stringent.78,79 Definitions of degradability can be found in Table S1.† A readily biodegradable classification requires strict criteria to be met and chemicals classed as readily biodegradable are considered to degrade rapidly and completely in the environment. Less stringent biodegradation tests are also available (e.g., OECD TG 302) which assess inherent and/or ultimate biodegradability.80–82 Inherently biodegradable chemicals are likely to ultimately degrade in the environment given adequate time. Primary biodegradation, i.e., structural change of a chemical resulting in loss of the original chemical identity or properties, can be especially relevant for chemicals with toxic effects, since the resulting transformation product(s) may no longer have these toxic effects. However, this potentially mitigating effect of primary biodegradation may be less likely for PM, since the overall properties of PMs are not expected to be impacted as strongly by the removal of a small number of functional groups.
Behaviour of PMs, here referring to NMs, is impacted by their intrinsic properties, including particle size, physicochemical properties, transformation potential, and extrinsic properties such as solubility/dissolution, aggregation/sedimentation, etc., all of which can influence persistency.6 For most (non-porous) PMs, biodegradation will predominantly start at the particle's surface and the rate of biodegradation can be limited significantly for larger particles (especially compared to dissolved and fully accessible counterparts), making it difficult to meet the general criteria for ready biodegradability for PMs. However, this does not mean that biodegradation cannot occur in such studies or under realistic environmental conditions.
Some work is available which makes use of standard ready biodegradation screening test guidelines to consider varying types of particulate material, e.g., Albright 3rd & Chai (2021).83 These authors examined a number of published polymer degradation studies and found that aspects of study design (e.g., physical form of tested material, selection of test systems, etc.) were critical in determining the outcomes of such studies.83 Nabeoka et al. (2021)84 investigated using OECD TG 301F78 with several purportedly biodegradable plastics. Non-specific bacteria were utilised, and the effects of prolongation (up to 90 days) considered, with cellulose (<50 μm) as a reference material. Particle sizes of 250 and 500 μm were used for each tested material. Varying degrees of degradation were observed with some substances meeting the ready biodegradability criteria, highlighting the fact that it is not impossible for PMs to meet the criteria for ready biodegradability.
Potential degradation of polymers has also been investigated using OECD TG 301B78 with modifications,85 assessing biodegradability of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) foam, beeswax, jojoba wax, and other non-soluble PMs. Modifications included extension to 80 days and gravimetric analysis of the dosed test materials and filtrate (including mass), used to determine residual test material. Considerations were also made to the accurate dosing of test material to minimise common issues with test material losses to the test vessel walls which can limit bioavailability. Effect of particle size was considered for PHBV (125, 250, 500 μm). The results showed that most particles reached maximum mineralisation in 80 days. Smaller particles degraded slightly faster although impact was limited since differences in particle size were small.
Although the results varied amongst substances tested, these studies help demonstrate adaptations are warranted to ensure test designs are adequate to assess PM. Given the evidence that extended test durations may lead to increased rates of biodegradation/mineralisation, this is worthwhile investigating further.
Traditionally, substances considered in biodegradation testing are organic. However, materials comprising allotropes of carbon (carbon nanotubes, graphite, carbon black etc.) can often sit between definitions, as may other PMs. These materials are highly important commercially, and with their high production volumes, understanding their persistence and fate is critical. Chen et al. (2017)86 reviewed biodegradation potential in the environment of these substance types, while Goodwin Jr et al. (2018)87 demonstrated that supplementing polymer matrices with carbon nanotubes might increase their environmental persistence. Microbial species that can adapt to degrade such substances were described, although the metabolic pathways of degradation are uncertain. Laux et al. (2018)88 also reviewed the literature in relation to carbon nanotube environmental fate and found numerous challenges in relation to analytical determination, isolation, standard preparation procedures etc. which would all impact standard testing. Interestingly, the REACH dossier for carbon black shows environmental fate endpoints were waived based on the exemption for inorganic materials.89 Carbon black is a major constituent of e.g., tyre and road wear particles,90 which means its environmental fate and persistence are highly relevant as this material is expected to have a high potential for release into the environment. More research is required to develop strategies to overcome potential limitations of testing in relation to these substances, like carbon black. Once better understood, these insights need to be incorporated into test designs to allow for more reliable testing of carbon NMs.
Generally, the OECD TG 301/302/310 tests are a cost-effective way to screen for potentially persistent chemicals. However, limitations arise when testing particulates, which are generally poorly soluble, including the requirement for high test concentrations, limited microbial diversity, conservative pass rates, relatively short study duration, etc. Some of these issues have been adequately dealt with in several ISO Standards that have been developed specifically to test the biodegradation of polymers.91–94 However, one potential drawback of this is the perceived compartment-specificity of these ISO Standards. As described above, numerous attempts are being made to modify standardized methods to better suit PMs, but regulatory guidance is important to ensure a level playing field, prevent misuse of resources, and to guide future research in the desirable direction. Optimization of test setup is essential for current and future testing of particulate materials.
3.8. Bioaccumulation testing
Understanding the bioaccumulation potential of chemicals and materials including PMs is a key element of environmental risk assessment under the REACH Regulation ((EC) No. 1907/2006) and BPR ((EU) No. 528/2012). Persistent, bioaccumulative and toxic (PBT) and very persistent, very bioaccumulative (vPvB) assessments are conducted under both regulations, and once a substance is established as persistent (P) or very persistent (vP), bioaccumulation potential must be evaluated. Although according to the REACH Annex XIII (the annex excludes organic substances, including organo-metals) several metal-based PMs would be excluded from the PBT/vPvB assessment requirements, they would still require the bioaccumulation risk assessment under the standard information requirements (Annex IX) for MP. The key criterion of concern in the EU is biodegradation; therefore, only NMs are considered further in the section with a focus on evaluating the aquatic bioaccumulation potential, but reference is made to MPs where applicable.According to ECHA R 7-2 appendix to R7c16 the OECD TG 305 (ref. 95) is partially applicable for NMs since only the dietary exposure route should be followed (with the main endpoint being a biomagnification factor or BMF), unless the NMs undergo dissolution in which case the aqueous route is applicable (with the main endpoint being a bioconcentration factor or BCF). Unlike for solutes, a BCF cannot be calculated for insoluble PMs since no equilibrium will be reached between organism and water phase, as discussed for NMs by Handy et al., 2012.96 In the absence of steady state, for NMs, the bioaccumulation potential can be estimated kinetically providing the uptake and depuration rates are evaluated.16 In fish, the dietary route is expected to be most applicable for particle uptake, however, Roch et al. (2020)97 reported that aqueous route can be a possible source of MP intake for marine fish that actively drink the water.98 When considering the dietary route of exposure, it must be recognised that it is technically challenging to verify PM size and distribution to confirm the dosed material represents the manufactured PMs. The concentration can be confirmed by analysing the total main component (e.g., metal for metal/metal oxide NMs) concentrations, to confirm the dose and using specialised techniques to measure concentration of intact particles (single particle ICP-MS). Since there are several options for dosing the feed in the OECD TG 305,95e.g., either by directly mixing particles into the feed or by mixing a stock solution with the feed, a standardised approach would be beneficial, since the method of dosing can impact on dissolution, aggregation, and other physical–chemical properties.99,100
Bioaccumulation testing in fish of all the various PMs (with varying shapes, size, chemistries, functions) that are placed on the market would lead to an impractical workload, not to mention the number of fish that would need to be used for the testing. Before testing is considered, relevant grouping and read-across strategies should be evaluated to minimise the need to test each PM individually, extensive guidance on this is provided by the EU Horizon 2020 funded Gracious project (https://www.h2020gracious.eu). If it is deemed necessary to generate data, a tiered strategy for bioaccumulation testing would be the most appropriate approach which is in line with the principles of 3Rs. Handy et al. (2018; 2021 and 2022)101–103 have proposed a tiered bioaccumulation testing strategy for NMs using fish and more recently also considering read across from earthworms102 and in vitro fish alternatives.103 The authors outline a tiered approach where in the first-tier existing data would be reviewed alongside the analysis of chemical triggers: dissolution and settling rate, as opposed to the n-octanol–water partition coefficient (log![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Kow) which is not applicable for NMs.33,102 In the second tier, NM-specific in silico models and validated screening tools would be evaluated alongside analysis of existing bioaccumulation data sets, invertebrate tests (discussed below), fish cell line tests and read-across. In the same tier, the authors also suggest data from an earthworm bioaccumulation study (OECD TG 317 (ref. 104)) may be indicative of bioaccumulation potential in fish in the case of metal based NMs.102 In the third tier, in chemico (digestibility assays that simulates the digestive processes of the fish gut) and ex vivo (ex vivo fish gut sac testing, see further in Handy et al. (2018)101) testing is proposed. Finally, if at all tiers hazard from bioaccumulation was identified, the fourth tier would be initiated which involves the in vivo dietary bioaccumulation test. Such alternative approaches in tiers 2 to 3 as proposed by Handy et al. (2018,101 2021,102 2022 (ref. 103)) would require further research and/or ring-testing to gain regulatory acceptance.
Kow) which is not applicable for NMs.33,102 In the second tier, NM-specific in silico models and validated screening tools would be evaluated alongside analysis of existing bioaccumulation data sets, invertebrate tests (discussed below), fish cell line tests and read-across. In the same tier, the authors also suggest data from an earthworm bioaccumulation study (OECD TG 317 (ref. 104)) may be indicative of bioaccumulation potential in fish in the case of metal based NMs.102 In the third tier, in chemico (digestibility assays that simulates the digestive processes of the fish gut) and ex vivo (ex vivo fish gut sac testing, see further in Handy et al. (2018)101) testing is proposed. Finally, if at all tiers hazard from bioaccumulation was identified, the fourth tier would be initiated which involves the in vivo dietary bioaccumulation test. Such alternative approaches in tiers 2 to 3 as proposed by Handy et al. (2018,101 2021,102 2022 (ref. 103)) would require further research and/or ring-testing to gain regulatory acceptance.
However, until a widely acceptable tiered strategy exists, information from a variety of sources comprised in a weight of evidence approach may be utilised to evaluate the bioaccumulation of PMs. As for other tests, it is important to consider testing with invertebrates before testing with vertebrates. There have been research projects and multiple studies in fresh-water crustaceans (e.g., the benthic amphipod Hyalella azteca for which test-methods have been developed for difficult to tests substances (including NMs) as reported in Schlechtriem et al., 2022 (ref. 105)) and sediment-dwelling invertebrates (e.g., O'Rourke et al., 2015;106 Little and Fernandes, 2019;107 Little et al., 2021 (ref. 108)). Testing with sediment-dwelling oligochaetes is described in OECD TG 315 (ref. 109) and there is no reason why such an approach cannot be used with PMs, with again some design considerations, such as how to apply the PM to the system; for example, should PM be applied via the water or thoroughly mixed with the sediment. Different approaches would likely lead to different results, for example direct application to sediment versus waterborne exposure, depending on the physical–chemical properties of the PM to be tested. At the moment discussions are ongoing amongst stakeholder groups regarding the potential use of other invertebrate test organisms such as the mollusc Lymnaea stagnalis and a variety of crustaceans (e.g., the amphipod Orchestia gammarellus). When established, either via in chemico, in vitro or ex/in vivo methods, data on bioaccumulation of PMs would also aid decision making for ecotoxicology testing of PMs.
3.9. Aquatic ecotoxicity testing
Establishing the hazard profile of chemicals including PMs underpins the environmental risk assessment framework and, in several countries globally, it can be the only data requirement (without the need of exposure and consequent risk assessment). As discussed in section 2.2 of this paper, work has been performed at the OECD level to assess ways in which the OECD TGs used to establish the hazard profiles of chemicals could be improved or adapted for PMs. Further work on this has also been evaluated in the different workshops (e.g., a workshop on adapting OECD aquatic toxicity tests for use with NMs summarized in Petersen et al., 2015 (ref. 70)), EU wide projects (e.g., EnvNano on revising REACH guidance for aquatic ecotoxicity endpoints110) and in literature. The following sections summarize examples on how physical, chemical, and environmental fate properties of PMs can be considered in ecotoxicology testing.Connolly et al. (2023 (ref. 111)) suggested that 2D graphene NM can lead to issues in algal growth inhibition assays (OECD 201 (ref. 112)). This can be due to a number of factors including increased shading (graphene is colored and light absorbing), interference with experimental readouts (graphene can aggregate with algae) and also lead to a depletion of essential nutrients (essential minerals can absorb to graphene).
The possibility of non-toxicological effect mechanisms, e.g., physical effects, as discussed in section 3.3, also needs to be considered when conducting ecotoxicological studies. Considering Daphnia testing, the attachment of particles to the organism43 can impact mobility113,114 and in standard testing both immobility and lethality could be considered as necessary endpoints.115 Biological surface coating of Daphnia may affect carapace shedding,43,132 which may impair growth and mobility. Shedding behavior (e.g., timing) of Daphnia, number of carapace-shedding events, but also a visual assessment of particle binding onto the organisms' surface could be easily included in the standard testing of NMs. However, the practical aspects of distinguishing the two endpoints would need to be clearly defined (e.g., would the presence of heart rate be evaluated in daphnids who appear immobile). Skjolding et al. (2016)50 have recommended physical effects to either be accounted for when reporting endpoints or minimised as far as possible in the experimental phase to present the real particle toxicological effects from being overshadowed. Sørensen et al. (2014)116 and Sørensen et al. (2015)117 suggested ways of avoiding physical effects such as including mesh bottoms in Daphnia testing and by avoiding shading effects in algal testing by using a double-vial setup. Recently, Hund-Rinke et al. (2020)118 have proposed that physical attachment efficiency of particles can be predictive of the toxicity which would be useful tool in grouping and read-across for regulatory purposes.
Hund-Rinke et al. (2016)119 reported progress from the MARINA (MAnaging RIsks of NAnoparticles) project, where eight OECD TGs were adapted for the testing of NMs. A similar recommendation to metals was concluded for metal-based NMs for algae testing (OECD TG 201), a chelating agent EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) free media was recommended (since EDTA can bind to the metal NM reducing its bioavailability and subsequent toxicity, Hund-Rinke et al., 2016 (ref. 119)). For acute Daphnia testing (OECD TG 202 (ref. 120)), potential sedimentation of NMs triggering reduced exposure towards the test organism can be reduced by testing at pH values where the NM-dispersion is more stable while simultaneously applying a test medium with a lower ionic strength,119 however, its impact on animal health would need to be carefully evaluated. It is known daphnids prefer hard water with low to no changes to pH therefore, any change to test media would require testing. Although wider consensus has not yet been reached whether altering test media is appropriate for NM testing due to impact on animal health and decrease in comparability with historic data sets, if alterations are applied, e.g., to increase NM stability, a reference toxicant control in the altered media must be included.70
For the fish early-life stage toxicity test (OECD TG 210 (ref. 121)), sedimentation of the tested NM could be avoided by modifications of the exposure chamber, along with an increased test dispersion exchange (e.g., every 24 h or applying a flow-through system). Slight stirring of the test dispersion might keep the NM in dispersion enhancing a stable exposure of the organism (e.g., zebrafish; Hund-Rinke et al., 2016 (ref. 119)). Prototypes of adapted exposure chambers were already reported by Boyle et al. (2014).122
For sediment-water toxicity testing (OECD TG 225 (sediment-water Lumbriculus toxicity test using spiked sediment)123), potentially reduced bioavailability of the NM due to sorption to organic matter was identified.124 Reduction of organic matter content in the sediment (e.g., reducing peat from 5% to 2%) will most likely favor an increased bioavailability of the NM as is known for non-particulate organic chemicals in the OECD TG 225 test. While a generalization to all sediment organisms cannot be made since the impact of organic matter content on bioavailability in sediment can depend on the organism and their ecology.125 Furthermore, the adapted composition of the sediment is suggested to better reflect the environmental behavior of the NMs, however, as with any alteration to standard test media its impact on organism health should carefully monitored.
Finally, when evaluating ecotoxicology data generated from PM studies, dosimetry needs to be considered. Various options are presented in the OECD GD 317.3
4. Summary and recommendations for a strategy for aquatic testing of particulate material
As set out in section 3, there are a number of challenges in following current PM testing approaches. For aquatic testing of particulate materials, physical chemical properties need to be clearly established prior to initiating any further testing. The key considerations for test design development include chemical composition (metal vs. organic), size, dissolution potential, and stability information. The next points to evaluate are the environmental fate profile and exposure considerations, in order to choose the most appropriate method of dosing and experimental set-up, e.g., if PMs tend to be bound to sediment, biodegradation in sediment systems would be a priority and bioaccumulation in and ecotoxicology testing of sediment dwelling organisms would be the first choice.For biodegradation studies, bioavailability (as impacted by e.g., floating, sinking, poor solubility, hetero-agglomeration) and the unfavorable surface-to-volume ratio need to be evaluated and the study design optimized, if possible.
For evaluation of bioaccumulation potential, a tiered approach may be most appropriate, consisting of initial evaluation of physical–chemical properties (as for any ecotoxicology test with PMs), followed by various options of in vitro (fish cell line) testing, invertebrate testing (especially, if based on environmental fate information, the PMs are more likely found in sediment or soil), in chemico (digestibility assays) and ex vivo (fish gut sac) testing, culminating with an in vivo fish test only if necessary and if the aquatic compartment is the main environmental sink for the PMs. While such a tiered approach gains regulatory acceptance, information from multiple sources could be utilized to apply a weight of evidence approach.
Regarding aquatic ecotoxicity testing, Table 3 (below) lists some key aquatic ecotoxicology OECD TGs along with the testing considerations present in OECD GD 317 as well as specific recommendations/suggestions beyond those in the guidance, including recommendations for further research.
| Organism (exposure) | Exposure duration | Test guideline | OECD GD 317 specific considerations | OECD GD 317 general considerations | Additional considerations/strategies for test designs and possible future research areas |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algae (water) | Chronic | OECD 201: Freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria, Growth Inhibition Test | - Shading effects | - Lighting considerations | Analytical requirements for inorganic PM (consider use of specialist techniques e.g., Raman spectroscopy, single particle ICP-MS etc.) |
| - Coloured test items | - Comparative control requirements | ||||
| - Prolonged agitation of test medium | - Solubility considerations | Consider conducting an OECD 221 (Lemna sp. Growth Inhibition Test) instead of an OECD 201, depending on regulatory requirements. OECD 221 allows a daily test dispersion renewal or flow-through setup, consequently improving exposure conditions, especially for unstable PMs | |||
| - Effects of/on media | |||||
| - Quantifying biomass | - Analytical requirements | ||||
| - Potential artefacts generated by PM interfering with biomass assessments | - Dispersion stability | ||||
| - Feeding considerations | - PM sedimentation leading to reduced exposure (at least for waterborne exposure), as well as inaccurately measured exposure concentrations | Reduction of dispersion challenges by PM-conditioning, e.g., addition of NOM while testing | |||
| - For aquatic exposure (excluding algae) consider frequent renewal of test media e.g., daily or every 2–3 days. Establish the appropriate renewal frequency during a small-scale pre-test | |||||
| Lemna (water) | Chronic | OECD 221: Lemna sp. Growth Inhibition Test | - Alternatively used for coloured particulates exerting shading effects | Reduction of dispersion challenges by PM-conditioning, e.g., addition of NOM while testing | |
| - Adsorption of particles, agglomerates onto plant roots | |||||
| - Potential exposure of roots via particle bottom layer | |||||
| Invertebrate (water) | Acute | OECD 202: Daphnia sp. Acute Immobilisation Test | - Bottom layer of agglomerates might induce additional physical effects, e.g., coating/clogging of the filter apparatus etc. | - Solubility considerations | Prolongation of test duration, if deemed appropriate, may support distinguishing physical rather than strictly chemical interference with the test organism, e.g., by clogging its filtering apparatus or gut with particles |
| - Dispersion stability | |||||
| Reference toxicant testing should also be adapted to extended exposure durations as prerequisite to resolve potential issues associated with reduced physiological fitness, e.g., caused by starvation | |||||
| Reduction of dispersion challenges by PM-conditioning, e.g., addition of NOM while testing | |||||
| Fish (water) | Acute | OECD 203: Fish, Acute Toxicity Test | - Bottom layer of agglomerates might induce additional physical effects, e.g., coating/clogging of the filter apparatus etc. | - Solubility considerations | Adjust the setup to daily test dispersion renewal or flow-through whenever possible to maintain stable exposure conditions |
| - Dispersion stability | |||||
| Reduction of dispersion challenges by PM-conditioning, e.g., addition of NOM while testing | |||||
| Invertebrate (water) | Chronic | OECD 211: Daphnia magna Reproduction Test | - Bottom layer of agglomerates might induce additional physical effects, e.g., coating/clogging of the filter apparatus etc. | Adjust the setup to daily test dispersion renewal or flow-through whenever possible to maintain stable exposure conditions | |
| Reduction of dispersion challenges by PM-conditioning, e.g., addition of NOM while testing | |||||
| Fish (water) | Chronic | OECD 210: Fish, Early-life Stage Toxicity Test | - Feeding considerations | Physical effect could be relevant (abrasivity for inorganics or crystalline forms) | |
| - If conducted as flow-through (FT) test then evaluation needs to be made that FT system is not impacted by clogging of the PMs | Consider gentle stirring of the test dispersions to keep the PM in dispersion rather than agglomerated to avoid sedimentation | ||||
| Make use of abiotic replicates for concentration control analyses. Improves the interpretation of PM fate is dispersion but also facilitates the interpretations how other particulates, e.g., food or excretions on influences dispersion stability | |||||
| Reduction of dispersion challenges by PM-conditioning, e.g., addition of NOM while testing | |||||
| Invertebrate (sediment) | Chronic | OECD 225: Sediment-Water Lumbriculus Toxicity Test Using Spiked Sediment | - Reductions in bioavailability due to sorption to organic matter | Physical effect could be relevant (abrasivity for inorganics or crystalline forms) | |
| - Spiking homogeneity issues; most appropriate compartment to spike | Future research: development of novel exposure chambers for invertebrates and aquatic plants to enable continuous mixing of test media, i.e., suspension of PMs to ensure exposure is maintained (similar to those developed for the fish early life stage OECD TG 210 study); establishment of PM specific reference toxicant | ||||
| - Feeding considerations | |||||
| Invertebrate (sediment) | Chronic | OECD 225: Sediment-Water Lumbriculus Toxicity Test Using Spiked Sediment | - Reductions in bioavailability due to sorption to organic matter | ||
| - Spiking homogeneity issues; most appropriate compartment to spike | |||||
| - Feeding considerations |
As highlighted above, the evaluation of all available information for PMs is important when devising a test strategy, and there are some key properties of PMs that should be considered to ensure the test systems are set up in the most appropriate manner. Fig. 2 builds on the challenges discussed in section 3 and sets out the key properties of PM to consider in test design development. Against these key properties are listed the associated physico-chemical properties and resulting consequences and considerations/recommendations in conducting fate, biodegradation, bioaccumulation and ecotoxicity testing of PM that should be considered for the test design and set up.
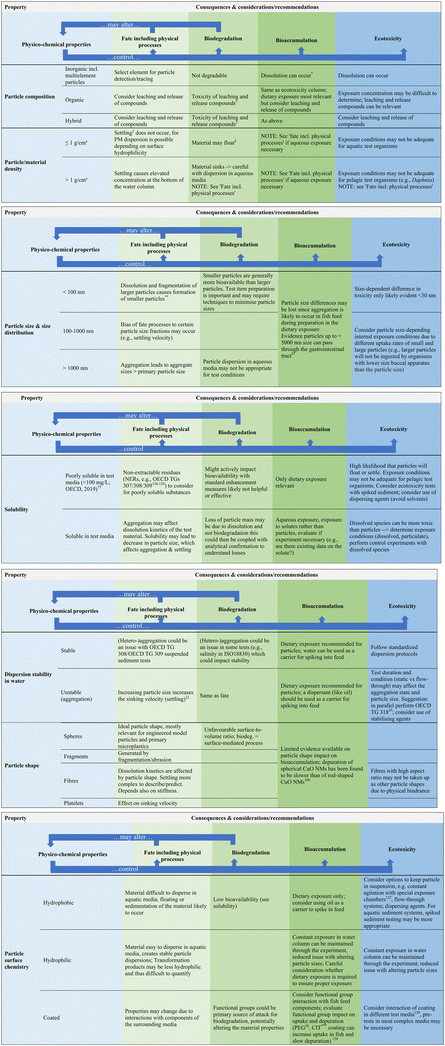 | ||
| Fig. 2 Proposed considerations and recommendations when devising a testing strategy to optimize testing for PM. Footnotes to figure: regarding bioaccumulation testing and in line with ECHA guidance: unless dissolution occurs, only dietary exposure route is relevant. Therefore, unless explicitly stated, the recommendations are based on a dietary exposure route; Standard OECD and ISO test guidelines are considered (Table S2†) but others may be relevant; properties of particle itself considered and not surrounding media.25,97,100,122,126–130 | ||
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare. The coauthors of this manuscript consist of members of an ECETOC Expert Group (comprising members from industry, CROs and academia). The views expressed in this article are solely those of the coauthors and may not represent those of the sponsoring organisations. Expert Group members from industry are employed by companies producing a range of chemicals. The issues of aquatic testing of particulate matter impact substances of interest to these companies. This manuscript was subjected to the usual internal peer-review process required by the companies, and only few minor, mostly editorial changes were requested. This manuscript was also reviewed by the ECETOC Scientific Committee consisting of representatives of academia and industry (http://www.ecetoc.org/about-ecetoc/scientific-committee/). This review yielded few and only minor comments.Acknowledgements
This work was conducted as part of the European Centre for Ecotoxicology and Toxicology of Chemicals (ECETOC) Expert Group ‘Strategies to overcome challenges in aquatic testing of particulate material’ (2020–2022). The authors' time to contribute to this review was supported by their organisations. This work was conducted as part of the European Centre for Ecotoxicology and Toxicology of Chemicals (ECETOC; https://www.ecetoc.org) Expert Group ‘Strategies to overcome challenges in aquatic testing of particulate material’. The authors would like to thank the ECETOC Scientific Committee, as well as the three external reviewers, including Dr. Susana Loureiro (Universidade de Aveiro), for their critical comments and valuable feedback during the preparation of this manuscript. We thank ECETOC Scientific Committee members Ben van Ravenzwaay (Wageningen University and Research) and Kees van Leeuwen (KWR Watercycle Research Institute) for stewarding this ECETOC Task Force, providing guidance, review and technical oversight. We thank the ECETOC secretariat for organisational and technical assistance to the Task Force. The authors also thank the two reviewers selected by the Editor that were anonymous to the authors. The comprehensive and helpful comments served to improve the manuscript.Notes and references
- ECHA, Nanomaterials. Retrieved 24 February 2021 from https://echa.europa.eu/regulations/nanomaterials, 2022.
- ECHA, Microplastics. Retrieved 24 February 2021 from https://echa.europa.eu/hot-topics/microplastics, 2022.
- OECD, Guidance document on aquatic and sediment toxicological testing of nanomaterials. Series on Testing and Assessment No. 317. ENV/JM/MONO(2020)8, 20 July 2020, OECD Series on Testing and Assessment, 2020 Search PubMed.
- OECD, Guidance Document on Aquatic Toxicity Testing of Difficult Substances and Mixtures. 16 May 2019, OECD Series on Testing and Assessment, 2019 Search PubMed.
- M. Bundschuh, J. Filser, S. Lüderwald, M. S. McKee, G. Metreveli, G. E. Schaumann, R. Schulz and S. Wagner, Nanoparticles in the environment: where do we come from, where do we go to?, Environ. Sci. Eur., 2018, 30, 6 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. R. Lead, G. E. Batley, P. J. J. Alvarez, M. N. Croteau, R. D. Handy, M. J. McLaughlin, J. D. Judy and K. Schirmer, Nanomaterials in the environment: Behavior, fate, bioavailability, and effects-An updated review, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2018, 37, 2029–2063 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- European Commission, Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/1881 of 3 December 2018 amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards Annexes I, III, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X, XI, and XII to address nanoforms of substances, http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2018/1881/oj, 2018.
- A. Pavlicek, F. Part, G. Rose, A. Praetorius, M. Miernicki, A. Gazsó and M. Huber-Humer, A European nano-registry as a reliable database for quantitative risk assessment of nanomaterials? A comparison of national approaches, NanoImpact, 2021, 21, 100276 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Ministry of ecology sustainable development transport and housing, Decree no. 2012–232 of 17 February 2013 on the annual declaration on substances at nanoscale in application of article R. 523-4 of the Environment code (2012), OFFICIAL JOURNAL OF THE FRENCH REPUBLIC Text 4/44, 2012.
- H. Rauscher, K. Rasmussen and B. Sokull-Klüttgen, Regulatory Aspects of Nanomaterials in the EU, Chem. Ing. Tech., 2017, 89, 224–231 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Miernicki, T. Hofmann, I. Eisenberger, F. von der Kammer and A. Praetorius, Legal and practical challenges in classifying nanomaterials according to regulatory definitions, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2019, 14, 208–216 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- European Commission, COMMISSION RECOMMENDATION of 10.6.2022 on the definition of nanomaterial (Text with EEA relevance) {SWD(2022) 150 final} Brussels, 10.6.2022. C(2022) 3689 final, https://ec.europa.eu/environment/chemicals/nanotech/pdf/C_2022_3689_1_EN_ACT_part1_v6.pdf, 2022.
- ECHA, Appendix for nanoforms applicable to the Guidance on Registration and Substance Identification. Version 2.0. January 2022, https://echa.europa.eu/documents/10162/13655/how_to_register_nano_en.pdf/f8c046ec-f60b-4349-492b-e915fd9e3ca0, 2022, DOI:10.2823/40.
- ECHA, Guidance on information requirements and chemical safety assessment. Appendix R7-1 for nanomaterials applicable to Chapter R7a Endpoint specific guidance. Version 4.0. December 2022, https://echa.europa.eu/documents/10162/17224/appendix_r7a_nanomaterials_en.pdf/1bef8a8a-6ffa-406a-88cd-fd800ab163ae?t=1671617922346, 2022, DOI:10.2823/496606.
- ECHA, Guidance on information requirements and chemical safety assessment. Appendix R7-1 for nanomaterials applicable to Chapter R7b Endpoint specific guidance. Version 2.0. May 2017, https://echa.europa.eu/documents/10162/17224/appendix_r7b_nanomaterials_en.pdf/6eca425a-ede1-4c9e-8151-af77973caf32?t=1495464497320, 2017, DOI:10.2823/72973.
- ECHA, Guidance on information requirements and chemical safety assessment. Appendix R7-2 for nanomaterials applicable to Chapter R7c Endpoint specific guidance. Version 3.0 October 2021, https://echa.europa.eu/documents/10162/17224/appendix_r7c_nanomaterials_en.pdf/c2d8e0ce-2ab4-4035-a05f-e2dec924d87a?t=1633348200288, 2021, DOI:10.2823/783979.
- ECHA, Guidance on information requirements and chemical safety assessment. Appendix R10-2 Recommendations for nanomaterials applicable to Chapter R.10 Characterisation of dose [concentration] - response for environment. May 2012, https://echa.europa.eu/documents/10162/17235/appendix_r10_05-2012_en.pdf/d5bc0038-0b76-4045-b101-b4cdfd47c7c6?t=1337944934120, 2012.
- ECHA, Guidance on information requirements and chemical safety assessment. Appendix R14-4 Recommendations for nanomaterials applicable to Chapter R.14 Occupational exposure estimation. May 2012, https://echa.europa.eu/documents/10162/17235/appendix_r14_05-2012_en.pdf/7b2ee1ff-3dc7-4eab-bdc8-6afd8ddf5c8d?t=1337944949217, 2012.
- ECHA, Guidance on information requirements and chemical safety assessment. Appendix R.6-1 for nanoforms applicable to the Guidance on QSARs and Grouping of Chemicals. Version 2.0. December 2019, https://echa.europa.eu/documents/10162/<?ccdc_no 2324906?><?ccdc_no 2324906?>2324906<?ccdc END?><?ccdc END?>/appendix_r6_nanomaterials_en.pdf/71ad76f0-ab4c-fb04-acba-074cf045eaaa?t=1575294955659, 2019, DOI:10.2823/273911.
- Efsa Scientific Committee, S. More, V. Bampidis, D. Benford, C. Bragard, T. Halldorsson, A. Hernandez-Jerez, S. H. Bennekou, K. Koutsoumanis, C. Lambre, K. Machera, H. Naegeli, S. Nielsen, J. Schlatter, D. Schrenk, V. Silano Deceased, D. Turck, M. Younes, J. Castenmiller, Q. Chaudhry, F. Cubadda, R. Franz, D. Gott, J. Mast, A. Mortensen, A. G. Oomen, S. Weigel, E. Barthelemy, A. Rincon, J. Tarazona and R. Schoonjans, Guidance on technical requirements for regulated food and feed product applications to establish the presence of small particles including nanoparticles, EFSA J., 2021, 19, e06769 Search PubMed.
- Efsa Scientific Committee, S. More, V. Bampidis, D. Benford, C. Bragard, T. Halldorsson, A. Hernandez-Jerez, S. Hougaard Bennekou, K. Koutsoumanis, C. Lambre, K. Machera, H. Naegeli, S. Nielsen, J. Schlatter, D. Schrenk, V. Silano Deceased, D. Turck, M. Younes, J. Castenmiller, Q. Chaudhry, F. Cubadda, R. Franz, D. Gott, J. Mast, A. Mortensen, A. G. Oomen, S. Weigel, E. Barthelemy, A. Rincon, J. Tarazona and R. Schoonjans, Guidance on risk assessment of nanomaterials to be applied in the food and feed chain: human and animal health, EFSA J., 2021, 19, e06768 Search PubMed.
- J. T. K. Quik, J. A. J. Meesters, W. J. G. M. Peijnenburg, W. Brand and E. A. J. Bleeker, Environmental Risk Assessment (ERA) of the application of nanoscience and nanotechnology in the food and feed chain, EFSA Supporting Publications, 2020, vol. 17, p. 1948E Search PubMed.
- ECHA, Guidance on the Biocidal Products Regulation, https://echa.europa.eu/documents/10162/23036412/bpr_guidance_vol_iv_part_a_en.pdf/4a70aa9e-7491-7fc5-0734-6777ade10b02, 2022.
- ECHA, Restricting the use of intentionally added microplastic particles to consumer or professional use products of any kind, https://echa.europa.eu/registry-of-restriction-intentions/-/dislist/details/0b0236e18244cd73, 2018.
- OECD, Test No. 318 Dispersion Stability of Nanomaterials in Simulated Environmental Media. Adopted: 9 October 2017, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 3, 2017 Search PubMed.
- E. J. Petersen, A. J. Kennedy, T. Hüffer and F. von der Kammer, Solving Familiar Problems: Leveraging Environmental Testing Methods for Nanomaterials to Evaluate Microplastics and Nanoplastics, Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(8), 1332 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Booth and K. A. Jensen, Protocol for producing reproducible dispersions of manufactured nanomaterials in environmental exposure media Preparation and physicochemical characterisation of manufactured nanomaterials (MNMs) in environmental fate and ecotoxicity exposure media. Version 6, 2015.
- OECD, Guidance document for the testing of dissolution and dispersion stability of nanomaterials and the use of the data for further environmental testing and assessment strategies. Series on Testing and Assessment. No. 318. ENV/JM/MONO(2020)9. 28 July 2021, OECD Series on Testing and Assessment, 2021 Search PubMed.
- OECD, Test No. 125: Nanomaterial Particle Size and Size Distribution of Nanomaterials, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 1, OECD Publishing, Paris, 2022 Search PubMed.
- OECD, Test No. 124: Determination of the Volume Specific Surface Area of Manufactured Nanomaterials, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 1, OECD Publishing, Paris, 2022 Search PubMed.
- D. Mackay, S. Paterson and W. Y. Shiu, Generic models for evaluating the regional fate of chemicals, Chemosphere, 1992, 24, 695–717 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Praetorius, M. Scheringer and K. Hungerbühler, Development of Environmental Fate Models for Engineered Nanoparticles—A Case Study of TiO2 Nanoparticles in the Rhine River, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2012, 46, 6705–6713 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Praetorius, N. Tufenkji, K.-U. Goss, M. Scheringer, F. von der Kammer and M. Elimelech, The road to nowhere: equilibrium partition coefficients for nanoparticles, Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2014, 1, 317–323 RSC.
- T. Hüffer, A. Praetorius, S. Wagner, F. von der Kammer and T. Hofmann, Microplastic Exposure Assessment in Aquatic Environments: Learning from Similarities and Differences to Engineered Nanoparticles, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2017, 51, 2499–2507 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. L. Dale, E. A. Casman, G. V. Lowry, J. R. Lead, E. Viparelli and M. Baalousha, Modeling Nanomaterial Environmental Fate in Aquatic Systems, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49, 2587–2593 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Besseling, J. T. K. Quik, M. Sun and A. A. Koelmans, Fate of nano- and microplastic in freshwater systems: A modeling study, Environ. Pollut., 2017, 220, 540–548 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Domercq, A. Praetorius and M. MacLeod, The Full Multi: An open-source framework for modelling the transport and fate of nano- and microplastics in aquatic systems, Environ. Model. Softw., 2021, 148, 105291 CrossRef.
- J. A. J. Meesters, A. A. Koelmans, J. T. K. Quik, A. J. Hendriks and D. van de Meent, Multimedia Modeling of Engineered Nanoparticles with SimpleBox4nano: Model Definition and Evaluation, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2014, 48, 5726–5736 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Selck, R. D. Handy, T. F. Fernandes, S. J. Klaine and E. J. Petersen, Nanomaterials in the aquatic environment: A European Union–United States perspective on the status of ecotoxicity testing, research priorities, and challenges ahead, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2016, 35, 1055–1067 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Seitz, S. Lüderwald, R. R. Rosenfeldt, R. Schulz and M. Bundschuh, Aging of TiO2 Nanoparticles Transiently Increases Their Toxicity to the Pelagic Microcrustacean Daphnia magna, PLoS One, 2015, 10, e0126021 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Abdolahpur Monikh, A. Praetorius, A. Schmid, P. Kozin, B. Meisterjahn, E. Makarova, T. Hofmann and F. von der Kammer, Scientific rationale for the development of an OECD test guideline on engineered nanomaterial stability, NanoImpact, 2018, 11, 42–50 CrossRef.
- X. Zhu, Y. Chang and Y. Chen, Toxicity and bioaccumulation of TiO2 nanoparticle aggregates in Daphnia magna, Chemosphere, 2010, 78, 209–215 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Dabrunz, L. Duester, C. Prasse, F. Seitz, R. Rosenfeldt, C. Schilde, G. E. Schaumann and R. Schulz, Biological Surface Coating and Molting Inhibition as Mechanisms of TiO2 Nanoparticle Toxicity in Daphnia magna, PLoS One, 2011, 6, e20112 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. S. Eltemsah and T. Bøhn, Acute and chronic effects of polystyrene microplastics on juvenile and adult Daphnia magna, Environ. Pollut., 2019, 254, 112919 CrossRef CAS.
- OECD, Test No. 211: Daphnia magna Reproduction Test, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2, 2012 Search PubMed.
- O. Pikuda, E. R. Dumont, S. Matthews, E. G. Xu, D. Berk and N. Tufenkji, Sub-lethal effects of nanoplastics upon chronic exposure to Daphnia magna, J. Hazard. Mater. Adv., 2022, 7, 100136 CrossRef CAS.
- L.-J. A. Ellis, E. Valsami-Jones and I. Lynch, Exposure medium and particle ageing moderate the toxicological effects of nanomaterials to Daphnia magna over multiple generations: a case for standard test review?, Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2020, 7, 1136–1149 RSC.
- X. He, C. Xie, Y. Ma, L. Wang, X. He, W. Shi, X. Liu, Y. Liu and Z. Zhang, Size-dependent toxicity of ThO2 nanoparticles to green algae Chlorella pyrenoidosa, Aquat. Toxicol., 2019, 209, 113–120 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Wang, X. Zhu, Y. Lao, X. Lv, Y. Tao, B. Huang, J. Wang, J. Zhou and Z. Cai, TiO2 nanoparticles in the marine environment: Physical effects responsible for the toxicity on algae Phaeodactylum tricornutum, Sci. Total Environ., 2016, 565, 818–826 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. M. Skjolding, S. N. Sørensen, N. B. Hartmann, R. Hjorth, S. F. Hansen and A. Baun, Aquatic Ecotoxicity Testing of Nanoparticles—The Quest To Disclose Nanoparticle Effects, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 15224–15239 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Mazurais, B. Ernande, P. Quazuguel, A. Severe, C. Huelvan, L. Madec, O. Mouchel, P. Soudant, J. Robbens, A. Huvet and J. Zambonino-Infante, Evaluation of the impact of polyethylene microbeads ingestion in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae, Mar. Environ. Res., 2015, 112, 78–85 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. M. Canniff and T. C. Hoang, Microplastic ingestion by Daphnia magna and its enhancement on algal growth, Sci. Total Environ., 2018, 633, 500–507 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Yue, R. Behra, L. Sigg, P. Fernández Freire, S. Pillai and K. Schirmer, Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to a fish gill cell line: Role of medium composition, Nanotoxicology, 2015, 9, 54–63 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Arvidsson, S. F. Hansen and A. Baun, Influence of natural organic matter on the aquatic ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles: Recommendations for environmental risk assessment, NanoImpact, 2020, 20, 100263 CrossRef.
- F. Seitz, R. R. Rosenfeldt, M. Müller, S. Lüderwald, R. Schulz and M. Bundschuh, Quantity and quality of natural organic matter influence the ecotoxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles, Nanotoxicology, 2016, 10, 1415–1421 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Philippe and G. E. Schaumann, Interactions of Dissolved Organic Matter with Natural and Engineered Inorganic Colloids: A Review, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2014, 48, 8946–8962 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Lin, J. Ji, Z. Long, K. Yang and F. Wu, The influence of dissolved and surface-bound humic acid on the toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles to Chlorella sp, Water Res., 2012, 46, 4477–4487 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Lüderwald, V. Dackermann, F. Seitz, E. Adams, A. Feckler, C. Schilde, R. Schulz and M. Bundschuh, A blessing in disguise? Natural organic matter reduces the UV light-induced toxicity of nanoparticulate titanium dioxide, Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 663, 518–526 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Li, S. Pokhrel, X. Jin, L. Mädler, R. Damoiseaux and E. M. V. Hoek, Stability, Bioavailability, and Bacterial Toxicity of ZnO and Iron-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles in Aquatic Media, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2011, 45, 755–761 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. E. Wheeler, A. J. Chetwynd, K. M. Fahy, B. S. Hong, J. A. Tochihuitl, L. A. Foster and I. Lynch, Environmental dimensions of the protein corona, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2021, 16, 617–629 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Bouchnak and C. E. W. Steinberg, Modulation of longevity in Daphnia magna by food quality and simultaneous exposure to dissolved humic substances, Limnologica, 2010, 40, 86–91 CrossRef CAS.
- T. U. Bergman Filho, A. M. Soares and S. Loureiro, Energy budget in Daphnia magna exposed to natural stressors, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2011, 18, 655–662 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Gao and G. V. Lowry, Progress towards standardized and validated characterizations for measuring physicochemical properties of manufactured nanomaterials relevant to nano health and safety risks, NanoImpact, 2018, 9, 14–30 CrossRef.
- K. Rasmussen, H. Rauscher, A. Mech, J. Riego Sintes, D. Gilliland, M. González, P. Kearns, K. Moss, M. Visser, M. Groenewold and E. A. J. Bleeker, Physico-chemical properties of manufactured nanomaterials - Characterisation and relevant methods. An outlook based on the OECD Testing Programme, Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 2018, 92, 8–28 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Bahl, B. Hellack, M. Wiemann, A. Giusti, K. Werle, A. Haase and W. Wohlleben, Nanomaterial categorization by surface reactivity: A case study comparing 35 materials with four different test methods, NanoImpact, 2020, 19, 100234 CrossRef.
- L. Khatmullina and I. Isachenko, Settling velocity of microplastic particles of regular shapes, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2017, 114, 871–880 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Waldschläger and H. Schüttrumpf, Effects of Particle Properties on the Settling and Rise Velocities of Microplastics in Freshwater under Laboratory Conditions, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2019, 53, 1958–1966 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Wang, M. Dou, P. Ren, B. Sun, R. Jia and Y. Zhou, Settling velocity of irregularly shaped microplastics under steady and dynamic flow conditions, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2021, 28, 62116–62132 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Elagami, P. Ahmadi, J. H. Fleckenstein, S. Frei, M. Obst, S. Agarwal and B. S. Gilfedder, Measurement of microplastic settling velocities and implications for residence times in thermally stratified lakes, Limnol. Oceanogr., 2022, 67(4), 934–945 CrossRef CAS.
- E. J. Petersen, S. A. Diamond, A. J. Kennedy, G. G. Goss, K. Ho, J. Lead, S. K. Hanna, N. B. Hartmann, K. Hund-Rinke, B. Mader, N. Manier, P. Pandard, E. R. Salinas and P. Sayre, Adapting OECD Aquatic Toxicity Tests for Use with Manufactured Nanomaterials: Key Issues and Consensus Recommendations, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49, 9532–9547 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Nasser, J. Constantinou and I. Lynch, Nanomaterials in the Environment Acquire an “Eco-Corona” Impacting their Toxicity to Daphnia Magna—a Call for Updating Toxicity Testing Policies, Proteomics, 2020, 20, 1800412 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. M. Louie, R. D. Tilton and G. V. Lowry, Critical review: impacts of macromolecular coatings on critical physicochemical processes controlling environmental fate of nanomaterials, Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2016, 3, 283–310 RSC.
- M. C. Surette and J. A. Nason, Nanoparticle aggregation in a freshwater river: the role of engineered surface coatings, Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2019, 6, 540–553 RSC.
- K. Giannopoulos, O. J. Lechtenfeld, T. R. Holbrook, T. Reemtsma and S. Wagner, Exploring the potential of laser desorption ionisation time-of-flight mass spectrometry to analyse organic capping agents on inorganic nanoparticle surfaces, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2020, 412, 5261–5271 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Giannopoulos, P. Benettoni, T. R. Holbrook, T. Reemtsma, S. Wagner and O. J. Lechtenfeld, Direct analysis of fulvic acids adsorbed onto capped gold nanoparticles by laser desorption ionization Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry, Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021, 8, 2336–2346 RSC.
- O. Witschger and J. F. Fabriès, Particules ultra-fines et santé au travail. 1 - Caractérisation des effets potentiels sur la santé, INRS, 2005, vol. 199, pp. 21–35 Search PubMed.
- N. Timmer, D. Gore, D. Sanders, T. Gouin and S. T. J. Droge, Application of seven different clay types in sorbent-modified biodegradability studies with cationic biocides, Chemosphere, 2020, 245, 125643 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- OECD, Test No. 301: Ready Biodegradability, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 3, 1992 Search PubMed.
- OECD, Test No. 310: Ready Biodegradability - CO2 in sealed vessels (Headspace Test), OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 3, 2014 Search PubMed.
- OECD, Test No. 302A: Inherent Biodegradability: Modified SCAS Test, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 3, 1981 Search PubMed.
- OECD, Test No. 302B: Inherent Biodegradability: Zahn-Wellens/EVPA Test, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 3, 1992 Search PubMed.
- OECD, Test No. 302C: Inherent Biodegradability: Modified MITI Test (II), OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 3, 2009 Search PubMed.
- V. C. Albright, 3rd and Y. Chai, Knowledge Gaps in Polymer Biodegradation Research, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2021, 55, 11476–11488 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Nabeoka, H. Suzuki, Y. Akasaka, N. Ando and T. Yoshida, Evaluating the Ready Biodegradability of Biodegradable Plastics, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2021, 40, 2443–2449 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. McDonough, N. Itrich, K. Casteel, J. Menzies, T. Williams, K. Krivos and J. Price, Assessing the biodegradability of microparticles disposed down the drain, Chemosphere, 2017, 175, 452–458 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Chen, X. Qin and G. Zeng, Biodegradation of Carbon Nanotubes, Graphene, and Their Derivatives, Trends Biotechnol., 2017, 35, 836–846 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. G. Goodwin, Jr., I. Boyer, T. Devahif, C. Gao, B. P. Frank, X. Lu, L. Kuwama, T. B. Gordon, J. Wang, J. F. Ranville, E. J. Bouwer and D. H. Fairbrother, Biodegradation of Carbon Nanotube/Polymer Nanocomposites using a Monoculture, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2018, 52, 40–51 CrossRef.
- P. Laux, C. Riebeling, A. M. Booth, J. D. Brain, J. Brunner, C. Cerrillo, O. Creutzenberg, I. Estrela-Lopis, T. Gebel, G. Johanson, H. Jungnickel, H. Kock, J. Tentschert, A. Tlili, A. Schäffer, A. J. A. M. Sips, R. A. Yokel and A. Luch, Challenges in characterizing the environmental fate and effects of carbon nanotubes and inorganic nanomaterials in aquatic systems, Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2018, 5, 48–63 RSC.
- ECHA, Endpoint summary, Environmental fate & pathways, Carbon black. Retrieved 20 September 2021 from https://echa.europa.eu/registration-dossier/-/registered-dossier/16056/5/1, 2021.
- B. Baensch-Baltruschat, B. Kocher, F. Stock and G. Reifferscheid, Tyre and road wear particles (TRWP) - A review of generation, properties, emissions, human health risk, ecotoxicity, and fate in the environment, Sci. Total Environ., 2020, 733, 137823 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- ISO, Plastics — Determination of aerobic biodegradation of non-floating plastic materials in a seawater/sandy sediment interface — Method by measuring the oxygen demand in closed respirometer (ISO Standard No. 18830), https://www.iso.org/standard/63515.html, International Organization for Standardization, 2016.
- ISO, Plastics — Determination of the ultimate aerobic biodegradability of plastic materials in soil by measuring the oxygen demand in a respirometer or the amount of carbon dioxide evolved (ISO Standard No. 17556), https://www.iso.org/standard/74993.html, International Organization for Standardization, 2019.
- ISO, Determination of the ultimate aerobic biodegradability of plastic materials in an aqueous medium — Method by measuring the oxygen demand in a closed respirometer (ISO Standard No. 14851), https://www.iso.org/standard/70026.html, International Organization for Standardization, 2019.
- ISO, Plastics — Determination of aerobic biodegradation of non-floating plastic materials in a seawater/sediment interface — Method by analysis of evolved carbon dioxide (ISO Standard No. 19679), https://www.iso.org/standard/66003.html, International Organization for Standardization, 2020.
- OECD, Test No. 305: Bioaccumulation in Fish: Aqueous and Dietary Exposure, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 3, 2012 Search PubMed.
- R. Handy, G. Cornelis, T. Fernandes, O. Tsyusko, A. Decho, T. Sabo-Attwood, C. Metcalfe, J. Steevens, S. Klaine, A. Koelmans and N. Horne, Ecotoxicity test methods for engineered nanomaterials: Practical experiences and recommendations from the bench, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2012, 31, 15–31 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Roch, C. Friedrich and A. Brinker, Uptake routes of microplastics in fishes: practical and theoretical approaches to test existing theories, Sci. Rep., 2020, 10, 3896 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Fuentes and F. B. Eddy, Drinking in marine, euryhaline and freshwater teleost fish, Ionic Regulation in Animals: A Tribute to Professor W.T.W.Potts, 1997, pp. 135–149 Search PubMed.
- A. Bermejo-Nogales, I. Rucandio, M. Connolly, M. L. Fernandez-Cruz and J. M. Navas, Preparation of feed with metal oxide nanoparticles for nanomaterial dietary exposure to fish and use in OECD TG 305, MethodsX, 2021, 8, 101413 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Kalman, M. Connolly, F. Abdolahpur-Monikh, R. Fernández-Saavedra, A. I. Cardona-García, E. Conde-Vilda, S. Martínez-Morcillo, W. J. G. M. Peijnenburg, I. Rucandio and M. L. Fernández-Cruz, Bioaccumulation of CuO nanomaterials in rainbow trout: Influence of exposure route and particle shape, Chemosphere, 2023, 310, 136894 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. D. Handy, J. Ahtiainen, J. M. Navas, G. Goss, E. A. J. Bleeker and F. von der Kammer, Proposal for a tiered dietary bioaccumulation testing strategy for engineered nanomaterials using fish, Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2018, 5, 2030–2046 RSC.
- R. D. Handy, N. J. Clark, J. Vassallo, C. Green, F. Nasser, K. Tatsi, T. H. Hutchinson, D. Boyle, M. Baccaro, N. van den Brink and C. Svendsen, The bioaccumulation testing strategy for manufactured nanomaterials: physico-chemical triggers and read across from earthworms in a meta-analysis, Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021, 8, 3167–3185 RSC.
- R. D. Handy, N. J. Clark, D. Boyle, J. Vassallo, C. Green, F. Nasser, T. L. Botha, V. Wepener, N. W. van den Brink and C. Svendsen, The bioaccumulation testing strategy for nanomaterials: correlations with particle properties and a meta-analysis of in vitro fish alternatives to in vivo fish tests, Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022, 9, 684–701 RSC.
- OECD, Test No. 317: Bioaccumulation in Terrestrial Oligochaetes, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 3, 2010, DOI:10.1787/9789264090934-en.
- C. Schlechtriem, S. Kühr and C. Müller, Development of a bioaccumulation test using Hyalella azteca. Final report. 134/2002, On behalf of the German Environment Agency (Umwelt Bundesamt), 2022 Search PubMed.
- S. O'Rourke, V. Stone, B. Stolpe and T. F. Fernandes, Assessing the acute hazards of zinc oxide nanomaterials to Lumbriculus variegatus, Ecotoxicology, 2015, 24, 1372–1384 CrossRef.
- S. Little and T. F. Fernandes, Nanomaterials in aquatic sediments, Ecotoxicology of Nanoparticles in Aquatic Systems, 2019, pp. 208–218 Search PubMed.
- S. Little, H. J. Johnston, V. Stone and T. F. Fernandes, Acute waterborne and chronic sediment toxicity of silver and titanium dioxide nanomaterials towards the oligochaete, Lumbriculus variegatus, NanoImpact, 2021, 21, 100291 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- OECD, Test No. 315: Bioaccumulation in Sediment-dwelling Benthic Oligochaetes, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 3, 2008 Search PubMed.
- S. F. Hansen, S. N. Sørensen, L. M. Skjolding, N. B. Hartmann and A. Baun, Revising REACH guidance on information requirements and chemical safety assessment for engineered nanomaterials for aquatic ecotoxicity endpoints: recommendations from the EnvNano project, Environ. Sci. Eur., 2017, 29, 14 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Connolly, G. Moles, F. C. Carniel, M. Tretiach, G. Caorsi, E. Flahaut, B. Soula, E. Pinelli, L. Gauthier, F. Mouchet and J. M. Navas, Applicability of OECD TG 201, 202, 203 for the aquatic toxicity testing and assessment of 2D Graphene material nanoforms to meet regulatory needs, NanoImpact, 2023, 29, 100447 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- OECD, Test No. 201: Freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria, Growth Inhibition Test, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2, 2011, DOI:10.1787/9789264069923-en.
- R. Griffitt, J. Luo, J. Gao, J.-C. Bonzongo and D. Barber, Effects of particle composition and species on toxicity of metallic nanometerials in aquatic organism, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2008, 27, 1972–1978 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Artells, J. Issartel, M. Auffan, D. Borschneck, A. Thill, M. Tella, L. Brousset, J. Rose, J. Y. Bottero and A. Thiery, Exposure to cerium dioxide nanoparticles differently affect swimming performance and survival in two daphnid species, PLoS One, 2013, 8, e71260 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Hjorth, L. M. Skjolding, S. N. Sørensen and A. Baun, Regulatory adequacy of aquatic ecotoxicity testing of nanomaterials, NanoImpact, 2017, 8, 28–37 CrossRef.
- S. N. Sørensen, C. Giron Delgado, C. Engelbrekt and A. Baun, Platinum nanoparticle toxicity in freshwater algae and crustaceans: A physical or chemical effect?, in Science Across Bridges, Borders and Boundaries: Programme Book SETAC Europe, 2014 Search PubMed.
- S. N. Sørensen, R. Hjorth, C. G. Delgado, N. B. Hartmann and A. Baun, Nanoparticle ecotoxicity—physical and/or chemical effects?, Integr. Environ. Assess. Manage., 2015, 11, 722–724 CrossRef.
- K. Hund-Rinke, T. Sinram, K. Schlich, C. Nickel, H. P. Dickehut, M. Schmidt and D. Kühnel, Attachment Efficiency of Nanomaterials to Algae as an Important Criterion for Ecotoxicity and Grouping, Journal, 2020, 10(6), 1021 CAS.
- K. Hund-Rinke, A. Baun, D. Cupi, T. F. Fernandes, R. Handy, J. H. Kinross, J. M. Navas, W. Peijnenburg, K. Schlich, B. J. Shaw and J. J. Scott-Fordsmand, Regulatory ecotoxicity testing of nanomaterials – proposed modifications of OECD test guidelines based on laboratory experience with silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles, Nanotoxicology, 2016, 10, 1442–1447 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- OECD, Test No. 202: Daphnia sp. Acute Immobilisation Test, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2, 2004 Search PubMed.
- OECD, Test No. 210: Fish, Early-life Stage Toxicity Test, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2, 2013 Search PubMed.
- D. Boyle, H. Boran, A. Atfield and T. Henry, Use of an exposure chamber to maintain aqueous-phase nanoparticle dispersions for improved toxicity testing in fish, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2014, 34(3), 583–588 CrossRef PubMed.
- OECD, Test No. 225: Sediment-Water Lumbriculus Toxicity Test Using Spiked Sediment, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2, 2007 Search PubMed.
- K. Hund-Rinke, M. Herrchen, K. Schlich, K. Schwirn and D. Völker, Test strategy for assessing the risks of nanomaterials in the environment considering general regulatory procedures, Environ. Sci. Eur., 2015, 27, 24 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. A. Ferraz, R. B. Choueri, Í. B. Castro, C. Simon da Silva and F. Gallucci, Influence of sediment organic carbon on toxicity depends on organism's trophic ecology, Environ. Pollut., 2020, 261, 114134 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- OECD, Test No. 307: Aerobic and Anaerobic Transformation in Soil, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 3, 2002 Search PubMed.
- OECD, Test No. 308: Aerobic and Anaerobic Transformation in Aquatic Sediment Systems, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 3, 2002 Search PubMed.
- OECD, Test No. 309: Aerobic Mineralisation in Surface Water – Simulation Biodegradation Test, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 3, 2004 Search PubMed.
- M. Connolly, D. Hernández-Moreno, E. Conde, A. Garnica, J. M. Navas, F. Torrent, I. Rucandio and M. L. Fernandez-Cruz, Influence of citrate and PEG coatings on the bioaccumulation of TiO2 and CeO2 nanoparticles following dietary exposure in rainbow trout, Environ. Sci. Eur., 2022, 34, 1 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Tejamaya, I. Romer, R. C. Merrifield and J. R. Lead, Stability of citrate, PVP, and PEG coated silver nanoparticles in ecotoxicology media, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2012, 46, 7011–7017 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Nasser, J. Constantinou and I. Lynch, Nanomaterials in the environment acquire an “Eco-Corona” impacting their toxicity to Daphnia magna - a call for updating toxicity testing policies, Proteomics, 2020, 20, 1800412, DOI:10.1002/pmic.201800412.
- F. Nasser, A. Davis, E. Valsami-Jones and I. Lynch, Shape and charge of gold nanomaterials influence survivorship, oxidative stress and moulting of Daphnia magna, Nanomaterials, 2016, 6, 222, DOI:10.3390/nano6120222.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4en00056k |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |
