Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Reactivity of highly Lewis acidic diborane(4) towards pyridine and isocyanide: formation of boraalkene–pyridine complex and ortho-functionalized pyridine derivatives†
Yuhei
Katsuma
a,
Hiroki
Asakawa
a and
Makoto
Yamashita
 *b
*b
aDepartment of Applied Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Engineering, Chuo University, 1-13-27 Kasuga, Bunkyo-ku, 112-8551, Tokyo, Japan
bDepartment of Molecular and Macromolecular Chemistry, Graduate School of Engineering, Nagoya University, Furo-cho, Chikusa-ku, Nagoya, 464-8603, Aichi, Japan. E-mail: makoto@oec.chembio.nagoya-u.ac.jp
First published on 11th December 2017
Abstract
The reaction of pinB-BMes2 (pin = pinacolato, Mes = 2,4,6-Me3C6H2) with Xyl-NC (Xyl = 2,6-Me2C6H3) and pyridine results in the formation of a pyridine-coordinated boraalkene that exhibits an intense color caused by an intramolecular charge-transfer interaction. In the presence of an excess of pyridine, the ortho C–H bond of pyridine was selectively functionalized to afford a quinoid compound or an isocyanide-coupled product. Based on the concentration effect, the reaction stoichiometry, and previously reported DFT calculations, a reaction mechanism that involves several rearrangement reactions was proposed. Using the present method, substituted pyridines and N-heterocycles afforded the corresponding functionalized derivatives. A subsequent hydrolysis of one of the resulting products furnished an aminomethylated pyridine derivative in two steps from parent pyridine.
Introduction
Pyridine is an important building block in pharmaceutical, materials, and organometallic chemistry. Due to the presence of the nitrogen atom in the pyridine ring, it should be possible to selectively functionalize the C–H bonds at the 2-, 3- and 4-positions of pyridine to construct bespoke molecular skeletons. Although many reports on the selective functionalization of pyridine derivatives can be found in the scientific literature,1 transition-metal-catalyzed C–H functionalizations of pyridine have become important, as they represent step- and atom-economical synthetic routes.2 Following the very early discovery of a selective functionalization of pyridine with transition-metal-based catalysts,3 several other metal-catalyzed functionalizations of pyridine have been reported.1 Furthermore, a recently reported “cooperative catalyst” system has demonstrated high selectivity and catalytic activity toward the functionalization of pyridine.4 Historically, anionic nucleophiles5 or electron-rich radicals6 have been used to selectively functionalize the 2-position (“ortho”-position) of pyridine. Inspired by these strategies, further new methods based on nucleophilic functionalization7 and radical addition8 are currently developed. It should be noted that the ortho-metalation of pyridine might represent an important method to achieve the selective functionalization of pyridine at the 2-position.9Diborane(4) compounds that contain a B–B single bond10 are widely used in organic synthesis, especially for metal-catalyzed borylation reactions.11 In contrast to the rich chemistry of metal-catalyzed borylations, direct reactions between diborane(4) compounds and organic compounds remain scarce.12 Halogen-substituted diborane(4) compounds can react with alkenes and alkynes in the absence of a catalyst.13 In contrast, there have been no reports of oxygen-substituted diborane(4)s undergoing direct reactions with organic molecules until recently. The addition of nucleophilic or basic activators enables diborane(4)s to react with organic molecules.14 It should also be noted that diazo compounds derived from tosylhydrazone or similar carbenoid species can react with diborane(4) to form the corresponding alkylboronates in the absence of a metal catalyst.15 Independent of these two-electron processes, effective radical activations have been discovered for borylation reactions with diborane(4)s.16 More recently, direct reactions of some pyridine derivatives with diborane(4)s via ionic or radical pathways have been reported.17
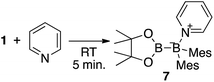
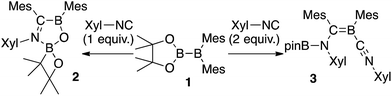
We have recently reported the operationally simple synthesis of unsymmetrical diborane(4) 1,18 its reactivity toward CO and tert-butyl isocyanide inducing a cleavage of multiple bond(s),18 its high Lewis acidity and one-electron reduction to form a radical anion,19 as well as its reactivity toward Xyl-NC (Xyl = 2,6-dimethylphenyl) to form a spirocyclic oxaboretane (2) or isocyanide-coordinated boraalkene (3)20 (Scheme 1). The formation of 2 is a rare example of a ring contraction reaction that affords a four-membered boracycle. DFT calculations showed that several rearrangement reactions are involved in these transformations,18,20 as Lewis-base-coordinated ligands on the diborane(4) are known to undergo migration.21 Herein, we report the selective C–H functionalization of pyridine and other N-heterocycles with 1 and Xyl-NC. The thus obtained products, i.e., pyridine-coordinated boraalkenes, dearomatized ortho-quinoid derivatives of pyridine, and ortho-functionalized pyridines from a reductive coupling of isocyanide, were fully characterized. Complex reaction mechanisms were postulated based on the structures of the products and previously reported DFT-based mechanisms.18,20 One of the obtained functionalized pyridines was subsequently hydrolyzed to afford an aminomethylated pyridine derivative.
 | ||
| Scheme 1 Previously reported reactions of the unsymmetrical diborane(4) 1 with Xyl-NC (Xyl = 2,6-Me2C6H3). | ||
Results and discussion
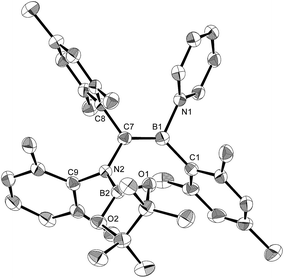
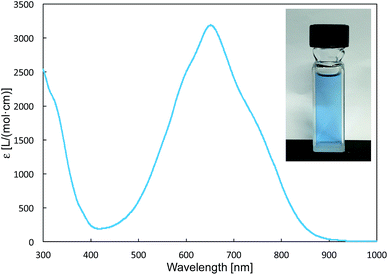
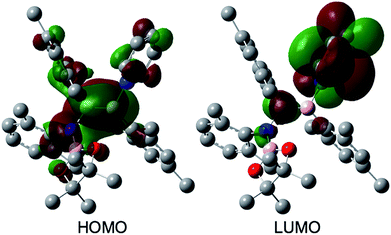
The reaction of a toluene solution of 1 with one equivalent of Xyl-NC in the presence of pyridine (10 equiv.) afforded pyridine-coordinated boraalkene 4. Compound 4 is probably formed via a cleavage of the B–B bond and a migration of the Mes group from the boron to the carbon atom (Scheme 2), as confirmed by a single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis (Fig. 1; B1–C7: 1.441(3) Å). The length of the B–N (pyridine) bond (1.586(3) Å) is essentially identical to that of a twisted pyridine–boraalkene complex.22 It should be noted that 4 contains two Mes groups trans to each other, which is slightly different from the case of previously reported 3, and thus indicates that the steric difference between Xyl-NC and tBu-NC may determine the regiochemistry of the products 3 and 4 upon coordination to the boraalkene intermediate. Interestingly, the UV-vis spectrum of a hexane solution of boraalkene 4 showed an intense blue color, with an absorption maximum at 648 nm (Fig. 2). In hexane solution, boraalkene 4 gradually decomposed at room temperature (cf. ESI†). This decomposition of 4 is decelerated in the presence of pyridine, indicating that the decomposition could be initiated by a dissociation of pyridine from 4. Although all the decomposed products could not be identified, monitoring the decomposition by 1H NMR spectroscopy indicated that 2 was involved as a reaction intermediate (cf. ESI†). DFT calculations at the B3LYP/6-31+G(d) level of theory revealed that the HOMO orbital of 4 consists mainly of the B![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C π bond, and that the LUMO orbital corresponds to the π*-orbital of the pyridine moiety (Fig. 3). TDDFT calculations revealed that the absorption of 4 at 648 nm corresponds to the HOMO–LUMO transition, indicative of an intramolecular charge-transfer character from the electron-rich boraalkene moiety to the electron-poor acid-coordinated pyridine moiety.
C π bond, and that the LUMO orbital corresponds to the π*-orbital of the pyridine moiety (Fig. 3). TDDFT calculations revealed that the absorption of 4 at 648 nm corresponds to the HOMO–LUMO transition, indicative of an intramolecular charge-transfer character from the electron-rich boraalkene moiety to the electron-poor acid-coordinated pyridine moiety.
 | ||
| Scheme 2 Reaction of 1 with Xyl-NC and 10 equiv. of pyridine (yield estimated by 1H NMR spectroscopy). | ||
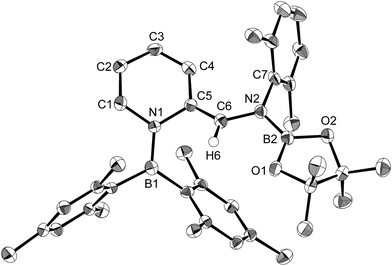
Using the same combination of reagents, albeit in higher concentration, i.e., by using pyridine as a solvent, afforded 5 (Scheme 3), which was formed via the cleavage of the B–B bond in 1 and the C–H bond in pyridine, in 81% NMR yield under concomitant formation of a small amount of 4 (16%). A single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis revealed that 5 contains a dearomatized pyridine ring that exhibits a distorted quinoid structure, evident from the short B1–N1 and C5–C6 bond distances and the bond alternation in the pyridine ring (Fig. 4). Reflecting the restricted rotation of the substituents due to the distorted structure, the 1H and 13C NMR spectra of 5 exhibited several broad signals (cf. ESI†). Reaction of 1 with two equivalents of Xyl-NC under slightly lower concentration resulted in the formation of 6, in which two carbon atoms of two isocyanide molecules were reductively coupled, and the resulting NCCN moiety was inserted into the B–B bond of 1 and the C–H bond of pyridine. A crystallographic analysis of 6 revealed an intramolecular coordination of the pyridine ring to the Bpin moiety, resulting in the formation of a spiroborate structure (Fig. 5). In solution, the 11B NMR spectrum of 6 showed three broad signals, implying an equilibrium of 1 with other isomers. This equilibrium prevented us from assigning all signals in the 1H NMR spectrum of 6 at room temperature. When a CD2Cl2 solution of 6 was cooled to −80 °C, some of the aromatic signals of each isomer, which can be distinguished by COSY measurements, changed their integration ratio to support the notion of such an equilibrium (cf. ESI†). It should be noted that 5 could be considered as an intermediate for the formation of 6. This hypothesis was independently confirmed by addition of 1 equiv. of Xyl-NC to isolated 5, which result in the formation of 6 in high yield.
 | ||
| Scheme 3 Reaction of 1 with Xyl-NC in the presence of an excess of pyridine (yields estimated by 1H NMR spectroscopy. The concentration of 1 or 5 is given in parentheses below pyridine). | ||
Next, we investigated the dependency of the product ratio between 4 and 5 on the concentration of 1 and the stoichiometry of pyridine in the reaction of 1 with 1 equiv. of Xyl-NC (Table 1). When pyridine was used as the solvent, dearomatized 5 was the major product for any concentration of 1 (runs 1–4). Maintaining the concentration of 1 at 266 mM, which produced the largest amount of 5 in run 1, by keeping the volume of the total solvent (0.300 mL) constant, the amount of the added toluene was varied to change the stoichiometry of pyridine (runs 1 and 5–7). Reducing the stoichiometry of pyridine led to a higher and lower yield of 4 and 5, respectively. These results indicate that the formation of 5, via a cleavage of the C–H bond requires an excess of pyridine.
We also investigated the dependency of the product ratio among 3, 4 and 6 on the concentration of 1 and the stoichiometry of pyridine in the reaction of 1 with 2 equiv. of Xyl-NC (Table 2). When pyridine was used as the solvent, the yield of the C–C coupled product 6 increased upon lowering the concentration of 1 (runs 1–4), which stands in contrast to the results of Table 1. Maintaining the concentration of 1 at 5 mM, which produced the highest yield of 6 (run 4), and fixing the volume of the total solvent to 16 mL, the amount of toluene added was varied to reduce the stoichiometry of pyridine (runs 5–8). Considering that reducing the stoichiometry of pyridine led to a significant increase of 3 and 4, and that 5 is an intermediate for the formation of 6, it seems feasible to expect that a large amount of pyridine is required for the formation of 5 and 6. These results indicate that the complexation of 1 with pyridine prior to a reaction with Xyl-NC is the key step for the cleavage of the C–H bond of pyridine.
| Run | Conc.a (mM) | x (mL) | y (mL) | Pyridine (equiv.) | Yieldb (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | 6 | |||||
| a Concentration of 1. b Estimated 1H NMR yield. | |||||||
| 1 | 200 | 0.4 | 0 | 62 | 49 | 7 | 25 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.798 | 0 | 124 | 35 | 10 | 40 |
| 3 | 10 | 8 | 0 | 1240 | 5 | 9 | 49 |
| 4 | 5 | 16 | 0 | 2481 | 1 | 9 | 52 |
| 5 | 5 | 6.5 | 9.5 | 1000 | 6 | 13 | 50 |
| 6 | 5 | 0.645 | 15.4 | 100 | 20 | 40 | 18 |
| 7 | 5 | 0.0645 | 15.9 | 10 | 22 | 32 | 2 |
| 8 | 5 | 0.0323 | 16 | 5 | 28 | 46 | 1 |
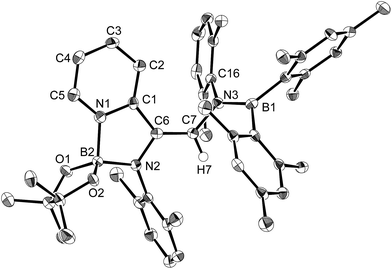
In order to determine the mechanism for the formation of 5 and 6, a potential intermediate was synthesized and isolated from the reaction of 1 with pyridine (Scheme 4). Simple dissolution of 1 in pyridine followed by recrystallization from hexane afforded pyridine-coordinated sp2–sp3 species 7. A C6D6 solution of 7 exhibited two broad signals in the 11B NMR spectrum at δB = 37 and 26 ppm. The former signal was assigned to an sp3-hybridized BMes2 moiety, even though it is high-field shifted in comparison with the BMes2 moiety of 1 (δB = 89 ppm).18 The presence of this signal indicates that the coordination of pyridine is retained in C6D6. The sp2–sp3 structure of 7 was unambiguously determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis (Fig. 6). Despite the coordination of pyridine, the B–B bond (1.717(3) Å) of 7 was identical to that of 1 (1.722(4) Å).23,24 The hybridization of the B1 atom is slightly distorted (B2–B1–C6 = 94.31(16)°) from ideal sp3 hybridization as observed in similar sp2–sp3 diborane(4) derivatives that contain a BMes2 moiety,25 which is probably due to the steric demand of the Mes groups.
Based on the product ratio and the formation of potential intermediate 7, we tentatively propose a mechanism for the formation of 4–7 (Scheme 5). In reaction mixtures of 1, Xyl-NC and pyridine, 1 should be coordinated by Xyl-NC and pyridine to form sp2–sp3 adducts 8 and 7 (Scheme 5a). According to our previous report on the reaction of 1 with tBu-NC, a boraalkene intermediate could be generated by three consecutive rearrangements, involving a pinB migration to the carbon atom of the isocyanide, a pinB capturing by the nitrogen atom, and an electrophilic migration of the Mes group toward the (push–pull-stabilized) carbenic carbon (Scheme 5b). Coordination of pyridine to the boraalkene intermediate furnished 4. This mechanism is consistent with the fact of that decreasing the amount of pyridine led to a higher yield of 4 (Tables 1 and 2). Pyridine-coordinated intermediate 7 was initially attacked by the isocyanide at the 2-position of pyridine leading to a dearomatization of the pyridine ring (Scheme 5c).26 A subsequent 1,2-hydride migration would lead to the formation of an imidoylpyridine-coordinated sp2–sp3 adduct, and an ensuing nucleophilic migration of the Bpin group to the nitrogen atom would directly afford dearomatized quinoid 5. Further coordination of a second molecule of isocyanide to 5 would induce the formation of a five-membered ring. The subsequent nitrogen-induced 1,2-hydride migration could cleave the N–B coordination bond and generate the three-membered cyclic intermediate. Breaking the azaaboracyclopropane ring should then furnish the diaminopyridylalkene intermediate. The subsequent formation of an intramolecular N–B coordination would finally generate 6.
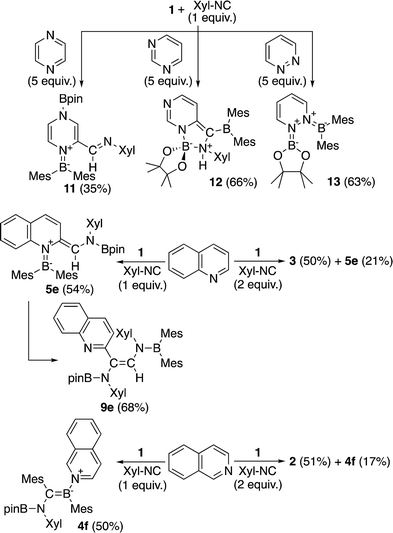
Then, we examined the substrate scope of the present reaction with respect to pyridine derivatives (Scheme 6). In the case of ortho-substituted pyridines, such as 2-methylpyridine and 2-chloropyridine, only 2 and 3 were obtained without incorporation of pyridine-derivatives. The steric hindrance of the ortho-substituent should thus inhibit the coordination of pyridine and the subsequent reactions outlined in the proposed mechanism (Scheme 5c). In the case of pyridine derivatives that contain electron-donating or weakly electron-withdrawing groups,27 such as 3-MeO, 3-Cl and 4-MeO, pyridine-coordinated boraalkene derivatives 4a, 4b and 4c were obtained, respectively. Similar to the case of 4, 4a–c gradually decomposed in solution at room temperature, which hampered a characterization by 13C NMR spectroscopy. We were however able to confirm the formation of sp2–sp3 diborane intermediates 7a–c, which are similar to 7, through coordination of pyridine derivatives to 1 as evident from 11B NMR spectroscopy (cf. ESI†). Therefore, we conclude that the nucleophilic attack of the Xyl-NC on the pyridine derivatives should be suppressed (Scheme 5c). Upon increasing the amount of Xyl-NC to two equivalents, mixtures of 2 and 4a–c were obtained. This result is consistent with Scheme 5a, where the equilibrium is shifted to the left upon increasing the amount of Xyl-NC in order to prevent the formation of pyridine-incorporated products 4a–c. When using pyridines that contain strongly electron-withdrawing groups, such as 3-CF3, 3-MeOCO, 4-CF3 or 4-MeOCO, ortho-functionalized pyridine derivatives 5a–d and 9a–d were obtained, depending on the stoichiometry of Xyl-NC. These compounds are similar to 5 and 6 in the reaction of non-substituted pyridine, although 9a–d do not exhibit intramolecular N–B coordination in the crystal structure (cf. ESI†), which is probably due to the presence of the electron-withdrawing group on the pyridine. Reaction of 1 with one equivalent of Xyl-NC and 4-(N,N-dimethylamino)pyridine (DMAP) afforded oxaboretane 10 (Fig. 7), which can be considered as a ring-opened derivative of 2 upon coordination of DMAP to the boron atom in the four-membered ring. In fact, a reaction of isolated 2 and DMAP smoothly furnished 10. The reaction of 1 with two equivalents of Xyl-NC and DMAP simply afforded 3, whereby DMAP was not incorporated in the product. Thus, the balance of the coordinating ability of the pyridine derivative and the stoichiometry of Xyl-NC affects the structure of the products.
 | ||
| Scheme 6 Reaction of 1 with substituted pyridine derivatives and Xyl-NC (yields estimated by 1H NMR spectroscopy). | ||
The present reaction was also expanded to include N-heterocycles other than pyridines, which afforded a variety of products (Scheme 7) that were all characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis (cf. ESI†). The reaction of 1 with pyrazine and Xyl-NC furnished diboryl pyrazine 11, which contains a 1,4-dihydropyrazine core and an imine functionality that is derived from Xyl-NC (Fig. 8). The formation of 11 may be explained by a prior formation of a quinoid intermediate similar to 5a–d and a subsequent intramolecular 1,5-migration or intermolecular transfer of a Bpin group to the nitrogen atom (cf. ESI†). In the case of pyrimidine, spirocyclic borate 12 with a dearomatized pyrimidine ring was obtained (Fig. 9). Although the mechanism for the formation of 12 is not clear yet, we would like to postulate a mechanism based on those for similar quinoid intermediates (cf. ESI†). The reaction of 1 with pyridazine in the presence of Xyl-NC afforded ortho-quinodimethane 13 (Fig. 10), which contains two borylated nitrogen atoms. The formation of 13 could be explained by a direct addition of 1 to the N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N double bond of pyridazine. Quinoline could also be used in the same reaction to give ortho-functionalized derivatives 5e and 9e, depending on the stoichiometry of Xyl-NC, similarly to the case of the formation of 5a–e and 9a–e (Scheme 5). On the contrary, isoquinoline also reacted with 1 and Xyl-NC, but C–H functionalized quinoline derivatives were not obtained.
N double bond of pyridazine. Quinoline could also be used in the same reaction to give ortho-functionalized derivatives 5e and 9e, depending on the stoichiometry of Xyl-NC, similarly to the case of the formation of 5a–e and 9a–e (Scheme 5). On the contrary, isoquinoline also reacted with 1 and Xyl-NC, but C–H functionalized quinoline derivatives were not obtained.
 | ||
| Scheme 7 Reaction of 1 with Xyl-NC in the presence of N-heterocycles other than pyridines (yields estimated by 1H NMR spectroscopy). | ||
The ortho-functionalized pyridine derivative 5 was then further converted (Scheme 8). Heating 5 with H2O in THF to 50 °C for 12 h afforded the aminomethylated pyridine 1428 in 76% yield. This two-step procedure to obtain 14 from non-substituted pyridine surpasses previously reported synthetic protocols which includes at least five steps.28,29 Therefore, the present method can be considered as an effective route for the functionalization of pyridine. However, limitations exist, especially for examples where the isocyanide substrate is not readily accessible. Although some metal-catalyzed ortho-functionalizations of pyridine with aldimine,30 carbon monoxide,3c and isocyanide,31 have been reported, this method is the only example for a selective formation of methylene-substituted pyridines. Also, the hydrolysis can be considered as a hydrogenative quenching of 5 under concomitant deoxygenation of water.
Conclusions
In conclusion, we have discovered a reaction of the previously reported diborane(4) pinB-BMes2 with Xyl-NC and pyridine that affords pyridine-coordinated boraalkenes, which show an intense color caused by an intramolecular charge-transfer interaction. In the presence of an excess of pyridine, the ortho C–H bond of pyridine was selectively functionalized to form a quinoid compound or an isocyanide-coupled product. Based on the concentration effect, reaction stoichiometry, and previously reported DFT calculations,18,20 a reaction mechanism was proposed that involves numerous rearrangement reactions. Substituted pyridines and other N-heterocycles can also be used in the present method to afford the corresponding functionalized derivatives. A subsequent hydrolysis of one of the resulting products furnished an aminomethylated pyridine derivative, which requires several steps when using a conventional synthetic procedure.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A) (MEXT KAKENHI, 17H01191). The authors thank Prof. T. Hiyama (Chuo University) for providing us with access to an X-ray diffractometer. Theoretical calculations were carried out using resources of the Research Center for Computational Science, Okazaki, Japan.Notes and references
- K. Murakami, S. Yamada, T. Kaneda and K. Itami, Chem. Rev., 2017, 117, 9302–9332 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Nakao, Synthesis, 2011, 3209–3219 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) R. F. Jordan and D. F. Taylor, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111, 778–779 CrossRef CAS; (b) S. Rodewald and R. F. Jordan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1994, 116, 4491–4492 CrossRef CAS; (c) E. J. Moore, W. R. Pretzer, T. J. O’Connell, J. Harris, L. LaBounty, L. Chou and S. S. Grimmer, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1992, 114, 5888–5890 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) Y. Nakao, K. S. Kanyiva and T. Hiyama, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 2448–2449 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) Y. Nakao, Y. Yamada, N. Kashihara and T. Hiyama, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 13666–13668 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) V. Singh, Y. Nakao, S. Sakaki and M. M. Deshmukh, J. Org. Chem., 2017, 82, 289–301 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) L. Yang, K. Semba and Y. Nakao, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 4853–4857 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) A. E. Chichibabin and O. A. Zeide, J. Russ. Phys.-Chem. Soc., 1914, 46, 1216–1236 CAS; (b) J. C. W. Evans and C. F. H. Allen, Org. Synth., 1938, 18, 70–71 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) F. Minisci, R. Bernardi, F. Bertini, R. Galli and M. Perchinummo, Tetrahedron, 1971, 27, 3575–3579 CrossRef CAS; (b) F. Minisci, E. Vismara, F. Fontana, G. Morini, M. Serravalle and C. Giordano, J. Org. Chem., 1986, 51, 4411–4416 CrossRef CAS; (c) F. Minisci, E. Vismara and F. Fontana, Heterocycles, 1989, 28, 489–519 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) P. S. Fier and J. F. Hartwig, Science, 2013, 342, 956–960 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) P. S. Fier and J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 10139–10147 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) J. L. Jeffrey and R. Sarpong, Org. Lett., 2012, 14, 5400–5403 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) F.-F. Zhuo, W.-W. Xie, Y.-X. Yang, L. Zhang, P. Wang, R. Yuan and C.-S. Da, J. Org. Chem., 2013, 78, 3243–3249 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) A. Núñez, A. Sánchez, C. Burgos and J. Alvarez-Builla, Tetrahedron, 2004, 60, 6217–6224 CrossRef; (b) I. B. Seiple, S. Su, R. A. Rodriguez, R. Gianatassio, Y. Fujiwara, A. L. Sobel and P. S. Baran, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 13194–13196 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) G. A. Molander, V. Colombel and V. A. Braz, Org. Lett., 2011, 13, 1852–1855 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) Y. Fujiwara, J. A. Dixon, R. A. Rodriguez, R. D. Baxter, D. D. Dixon, M. R. Collins, D. G. Blackmond and P. S. Baran, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 1494–1497 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) J. Wen, R.-Y. Zhang, S.-Y. Chen, J. Zhang and X.-Q. Yu, J. Org. Chem., 2012, 77, 766–771 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) Y. Fujiwara, J. A. Dixon, F. O/’Hara, E. D. Funder, D. D. Dixon, R. A. Rodriguez, R. D. Baxter, B. Herle, N. Sach, M. R. Collins, Y. Ishihara and P. S. Baran, Nature, 2012, 492, 95–99 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) J. Wang, S. Wang, G. Wang, J. Zhang and X.-Q. Yu, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 11769–11771 RSC; (h) Y. Cheng, X. Gu and P. Li, Org. Lett., 2013, 15, 2664–2667 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) Y. Li, W. Liu and C. Kuang, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 7124–7127 RSC; (j) D. Xue, Z. H. Jia, C. J. Zhao, Y. Y. Zhang, C. Wang and J. Xiao, Chem.–Eur. J., 2014, 20, 2960–2965 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (k) J. Kan, S. Huang, J. Lin, M. Zhang and W. Su, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 2199–2203 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (l) J. Zoller, D. C. Fabry and M. Rueping, ACS Catal., 2015, 5, 3900–3904 CrossRef CAS; (m) J. Jin and D. W. C. MacMillan, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 1565–1569 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (n) S. Ambala, T. Thatikonda, S. Sharma, G. Munagala, K. R. Yempalla, R. A. Vishwakarma and P. P. Singh, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015, 13, 11341–11350 RSC; (o) D. Ma, Y. Yan, H. Ji, C. Chen and J. Zhao, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 17451–17454 RSC.
- (a) J. Verbeek and L. Brandsma, J. Org. Chem., 1984, 49, 3857–3859 CrossRef CAS; (b) S. V. Kessar, P. Singh, K. N. Singh and M. Dutt, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1991, 570–571 RSC; (c) Y. Kondo, M. Shilai, M. Uchiyama and T. Sakamoto, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1999, 121, 3539–3540 CrossRef CAS; (d) M. Jaric, B. A. Haag, A. Unsinn, K. Karaghiosoff and P. Knochel, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 5451–5455 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) S. M. Manolikakes, M. Jaric, K. Karaghiosoff and P. Knochel, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 2124–2126 RSC.
- E. C. Neeve, S. J. Geier, I. A. I. Mkhalid, S. A. Westcott and T. B. Marder, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 9091–9161 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. A. I. Mkhalid, J. H. Barnard, T. B. Marder, J. M. Murphy and J. F. Hartwig, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 890–931 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. B. Cuenca, R. Shishido, H. Ito and E. Fernandez, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46, 415–430 RSC.
- (a) G. Urry, J. Kerrigan, T. D. Parsons and H. I. Schlesinger, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1954, 76, 5299–5301 CrossRef CAS; (b) P. Ceron, A. Finch, J. Frey, J. Kerrigan, T. Parsons, G. Urry and H. I. Schlesinger, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1959, 81, 6368–6371 CrossRef CAS; (c) C. Chambers and A. K. Holliday, J. Chem. Soc., 1965, 3459–3462 RSC; (d) R. W. Rudolph, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1967, 89, 4216–4217 CrossRef CAS; (e) M. Zeldin, A. R. Gatti and T. Wartik, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1967, 89, 4217–4218 CrossRef CAS; (f) W. Haubold and K. Stanzl, J. Organomet. Chem., 1979, 174, 141–147 CrossRef CAS; (g) R. Chadha and N. K. Ray, Theor. Chim. Acta, 1982, 60, 573–578 CrossRef CAS; (h) R. Chadha and N. K. Ray, J. Phys. Chem., 1982, 86, 3293–3294 CrossRef CAS; (i) H. Klusik, C. Pues and A. Berndt, Z. Naturforsch., B: Chem. Sci., 1984, 39, 1042–1045 CrossRef; (j) W. Siebert, M. Hildenbrand, P. Hornbach, G. Karger and H. Pritzkow, Z. Naturforsch., B: Chem. Sci., 1989, 44, 1179–1186 CrossRef CAS; (k) C. Pubill-Ulldemolins, E. Fernanez, C. Bo and J. M. Brown, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015, 13, 9619–9628 RSC; (l) W. B. Fox and T. Wartik, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1961, 83, 498–499 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) A. Bonet, C. Pubill-Ulldemolins, C. Bo, H. Gulyás and E. Fernández, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 7158–7161 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) A. Bonet, C. Sole, H. Gulyas and E. Fernandez, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2012, 10, 6621–6623 RSC; (c) C. Pubill-Ulldemolins, A. Bonet, C. Bo, H. Gulyás and E. Fernández, Chem.–Eur. J., 2012, 18, 1121–1126 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) C. Pubill-Ulldemolins, A. Bonet, H. Gulyas, C. Bo and E. Fernandez, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2012, 10, 9677–9682 RSC; (e) C. Sole, H. Gulyas and E. Fernandez, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 3769–3771 RSC; (f) X. Sanz, G. M. Lee, C. Pubill-Ulldemolins, A. Bonet, H. Gulyas, S. A. Westcott, C. Bo and E. Fernandez, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2013, 11, 7004–7010 RSC; (g) J. Cid, J. J. Carbó and E. Fernández, Chem.–Eur. J., 2014, 20, 3616–3620 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) N. Miralles, J. Cid, A. B. Cuenca, J. J. Carbo and E. Fernandez, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 1693–1696 RSC; (i) N. Miralles, R. M. Romero, E. Fernandez and K. Muniz, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 14068–14071 RSC; (j) N. Miralles, R. Alam, K. J. Szabó and E. Fernández, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 4303–4307 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (k) D. García-López, J. Cid, R. Marqués, E. Fernández and J. J. Carbó, Chem.–Eur. J., 2017, 23, 5066–5075 CrossRef PubMed; (l) A. B. Cuenca, N. Zigon, V. Duplan, M. Hoshino, M. Fujita and E. Fernández, Chem.–Eur. J., 2016, 22, 4723–4726 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (m) L. Fang, L. Yan, F. Haeffner and J. P. Morken, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 2508–2511 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (n) T. P. Blaisdell, T. C. Caya, L. Zhang, A. Sanz-Marco and J. P. Morken, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 9264–9267 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (o) J. Zhang, H. H. Wu and J. Zhang, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2013, 6263–6266 CrossRef CAS; (p) A. Bonet, H. Gulyás and E. Fernández, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 5130–5134 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (q) K. Nagao, H. Ohmiya and M. Sawamura, Org. Lett., 2015, 17, 1304–1307 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (r) A. Morinaga, K. Nagao, H. Ohmiya and M. Sawamura, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 15859–15862 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (s) Y. Nagashima, K. Hirano, R. Takita and M. Uchiyama, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 8532–8535 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (t) K. Harada, M. Nogami, K. Hirano, D. Kurauchi, H. Kato, K. Miyamoto, T. Saito and M. Uchiyama, Org. Chem. Front., 2016, 3, 565–569 RSC; (u) C. Zhu and M. Yamane, Org. Lett., 2012, 14, 4560–4563 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (v) G. Gao, J. Yan, K. Yang, F. Chen and Q. Song, Green Chem., 2017, 19, 3997–4001 RSC; (w) L. Wang, T. Zhang, W. Sun, Z. He, C. Xia, Y. Lan and C. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 5257–5264 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (x) M. Eck, S. Wurtemberger-Pietsch, A. Eichhorn, J. H. J. Berthel, R. Bertermann, U. S. D. Paul, H. Schneider, A. Friedrich, C. Kleeberg, U. Radius and T. B. Marder, Dalton Trans., 2017, 46, 3661–3680 RSC.
- (a) H. Li, L. Wang, Y. Zhang and J. Wang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 2943–2946 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) H. Li, X. Shangguan, Z. Zhang, S. Huang, Y. Zhang and J. Wang, Org. Lett., 2014, 16, 448–451 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) H. Zhao, M. Tong, H. Wang and S. Xu, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2017, 15, 3418–3422 RSC.
- (a) F. Mo, Y. Jiang, D. Qiu, Y. Zhang and J. Wang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 1846–1849 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) X. Qi, H.-P. Li, J.-B. Peng and X.-F. Wu, Tetrahedron Lett., 2017, 58, 3851–3853 CrossRef CAS; (c) S. Ahammed, S. Nandi, D. Kundu and B. C. Ranu, Tetrahedron Lett., 2016, 57, 1551–1554 CrossRef CAS; (d) D. Qiu, L. Jin, Z. Zheng, H. Meng, F. Mo, X. Wang, Y. Zhang and J. Wang, J. Org. Chem., 2013, 78, 1923–1933 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) W.-M. Cheng, R. Shang, B. Zhao, W.-L. Xing and Y. Fu, Org. Lett., 2017, 19, 4291–4294 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) W. Liu, X. Yang, Y. Gao and C.-J. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 8621–8627 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) M. Jiang, H. Yang and H. Fu, Org. Lett., 2016, 18, 5248–5251 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) A. M. Mfuh, J. D. Doyle, B. Chhetri, H. D. Arman and O. V. Larionov, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 2985–2988 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) K. Chen, S. Zhang, P. He and P. Li, Chem. Sci., 2016, 7, 3676–3680 RSC; (j) A. Yoshimura, Y. Takamachi, L.-B. Han and A. Ogawa, Chem.–Eur. J., 2015, 21, 13930–13933 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (k) A. Fawcett, J. Pradeilles, Y. Wang, T. Mutsuga, E. L. Myers and V. K. Aggarwal, Science, 2017, 357, 283–286 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) G. Wang, H. Zhang, J. Zhao, W. Li, J. Cao, C. Zhu and S. Li, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 5985–5989 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) G. Wang, J. Cao, L. Gao, W. Chen, W. Huang, X. Cheng and S. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 3904–3910 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) L. Zhang and L. Jiao, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 607–610 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) Y. T. Xia, X. T. Sun, L. Zhang, K. Luo and L. Wu, Chem.–Eur. J., 2016, 22, 17151–17155 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) K. Oshima, T. Ohmura and M. Suginome, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 8571–8573 RSC; (f) T. Ohmura, Y. Morimasa and M. Suginome, Chem. Lett., 2017, 46, 1793 CrossRef; (g) T. Ohmura, Y. Morimasa and M. Suginome, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 2852–2855 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) D. Chen, G. Xu, Q. Zhou, L. W. Chung and W. Tang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 9767–9770 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Asakawa, K.-H. Lee, Z. Lin and M. Yamashita, Nat. Commun., 2014, 5, 4245 CAS.
- H. Asakawa, K.-H. Lee, K. Furukawa, Z. Lin and M. Yamashita, Chem.–Eur. J., 2015, 21, 4267–4271 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Katsuma, H. Asakawa, K.-H. Lee, Z. Lin and M. Yamashita, Organometallics, 2016, 35, 2563–2566 CrossRef CAS.
- R. D. Dewhurst, E. C. Neeve, H. Braunschweig and T. B. Marder, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 9594–9607 RSC.
- (a) D.-T. Yang, S. K. Mellerup, J.-B. Peng, X. Wang, Q.-S. Li and S. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 11513–11516 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) J. Allwohn, R. Hunold, M. Pilz, R. G. Muller, W. Massa and A. Berndt, Z. Naturforsch., B: Chem. Sci., 1990, 45, 290–298 CrossRef CAS.
- The similarity of the B–B bonds in 7 and 1 is rather unusual, given that all reported B–B bonds in sp2–sp3 diborane(4) coordinated by a pyridine derivative exhibit significant elongation of the B–B bond upon coordination.
- (a) P. Nguyen, C. Dai, N. J. Taylor, W. P. Power, T. B. Marder, N. L. Pickett and N. C. Norman, Inorg. Chem., 1995, 34, 4290–4291 CrossRef CAS; (b) W. Clegg, M. R. J. Elsegood, F. J. Lawlor, N. C. Norman, N. L. Pickett, E. G. Robins, A. J. Scott, P. Nguyen, N. J. Taylor and T. B. Marder, Inorg. Chem., 1998, 37, 5289–5293 CrossRef CAS; (c) W. Clegg, C. Dai, F. J. Lawlor, T. B. Marder, P. Nguyen, N. C. Norman, N. L. Pickett, W. P. Power and A. J. Scott, J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans., 1997, 839–846 RSC; (d) N. Arnold, H. Braunschweig, R. D. Dewhurst, F. Hupp, K. Radacki and A. Trumpp, Chem.–Eur. J., 2016, 22, 13927–13934 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) H. Braunschweig, A. Damme and T. Kupfer, Inorg. Chem., 2013, 52, 7822–7824 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) H. Hommer, H. Noth, J. Knizek, W. Ponikwar and H. Schwenk-Kircher, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 1998, 1519–1527 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Arnold, H. Braunschweig, A. Damme, R. D. Dewhurst, L. Pentecost, K. Radacki, S. Stellwag-Konertz, T. Thiess, A. Trumpp and A. Vargas, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 4898–4901 RSC.
- An almost planar B–B–N–C dihedral angle [7.6° (X-ray) in Fig. 6, −16° (DFT)] in 7 would prevent the Bpin migration, that is, the p-orbitals of pyridine ring could not interact with the B–B bonding orbital. In contrast, the cylindrical p-orbitals around the N
![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C triple bond of coordinating isocyanide in 8 would be able to interact with the B–B bonding orbital in 8 regardless of N
C triple bond of coordinating isocyanide in 8 would be able to interact with the B–B bonding orbital in 8 regardless of N![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C triple bond rotation. See Fig. S60 in ESI† for frontier orbitals of calculated 7 and 8.
C triple bond rotation. See Fig. S60 in ESI† for frontier orbitals of calculated 7 and 8. - (a) A. Fischer, W. J. Galloway and J. Vaughan, J. Chem. Soc., 1964, 3591–3596 RSC; (b) I. Lee, C. K. Kim, I. S. Han, H. W. Lee, W. K. Kim and Y. B. Kim, J. Phys. Chem. B, 1999, 103, 7302–7307 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Huang, K. Song, F. Liu, J. Long, H. Hu, H. Gao and Q. Wu, J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem., 2008, 46, 1618–1628 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) M. T. Leffler, Org. React., 1942, 1, 91–104 Search PubMed; (b) C. F. H. Allen and J. R. Thirtle, Org. Synth., 1955, 26, 16–17 Search PubMed; (c) L. Ashfield and C. F. J. Barnard, Org. Process Res. Dev., 2007, 11, 39–43 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Nagae, Y. Shibata, H. Tsurugi and K. Mashima, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 640–643 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. F. Wicker, J. Scott, A. R. Fout, M. Pink and D. J. Mindiola, Organometallics, 2011, 30, 2453–2456 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Experimental and computational details, and Cartesian coordinate. CCDC 1583725–1583743. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c7sc04759b |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 |