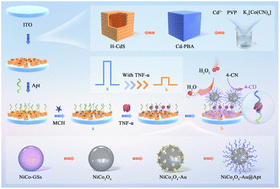
Sensitive detection of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in human serum is beneficial for finding cancer patients early due to overexpressed TNF-α being related to some cancers. Here, a photoelectrochemical (PEC) aptasensor was constructed for ultrasensitive TNF-α assay based on the signal generator of hollow CdS cubes (H-CdS) and the signal extinguishing activity of NiCo2O4-Au. In this work, compared with traditional solid CdS, H-CdS could greatly promote the PEC signal because its hollow structure could accelerate the separation of photogenerated charges, which also possesses abundant active sites and high light absorption capability. Moreover, H-CdS can be prepared facilely with Cd-based Prussian blue analogs as the precursor. Meanwhile, NiCo2O4-Au was fabricated and utilized as a signal extinguisher. In the presence of TNF-α, NiCo2O4-Au could be introduced onto the H-CdS modified electrode, producing competitive consumption of the electron donor effect, the p-n semiconductor quenching effect, and the mimetic enzymatic catalytic precipitation effect, which all can significantly reduce the PEC signal. Based on the signal extinguishing activity of NiCo2O4-Au and the signal generator of H-CdS, TNF-α can be detected sensitively with a lower detection limit (0.63 fg mL−1) and a wide linear range (1 fg mL−1– to 1 ng mL−1), which may have a potential application in the PEC bioanalysis field and the disease diagnostics field.