Facile proton-coupled electron transfer enabled by coordination-induced E–H bond weakening to boron†
Abstract
We report the facile activation of aryl E–H (ArEH; E = N, O, S; Ar = Ph or C6F5) or ammonia N–H bonds via coordination-induced bond weakening to a redox-active boron center in the complex, 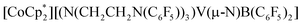 (1−). Substantial decreases in E–H bond dissociation free energies (BDFEs) are observed upon substrate coordination, enabling subsequent facile proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET). A drop of >50 kcal mol−1 in H2N–H BDFE upon coordination was experimentally determined.
(1−). Substantial decreases in E–H bond dissociation free energies (BDFEs) are observed upon substrate coordination, enabling subsequent facile proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET). A drop of >50 kcal mol−1 in H2N–H BDFE upon coordination was experimentally determined.

- This article is part of the themed collection: Boron Chemistry in the 21st Century: From Synthetic Curiosities to Functional Molecules


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...