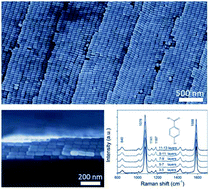
Plasmonic nanomaterials, along with their assemblies, provide numerous applications due to their profound optical properties. In this work, we report the self-assembly of Au@Ag core–shell nanocuboids (NCs) into staircase superstructures in both vertical and horizontal orientations through two-stage droplet evaporation. Each stair is composed of a uniform well-aligned monolayer of NCs. The gap distance between NCs can be greatly shrunk to boost the corresponding surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) performance using an ethanol wash method. The SERS performance of the assembled NCs is calculated by finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) simulation, and studied against the step number using 4-mercaptobenzoic acid as a Raman reporter molecule. The increasing EF with the increase of layer number proves that the plasmon mode propagates well in our uniformly aligned assemblies.