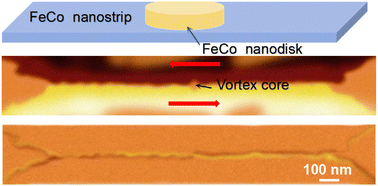
Despite rapid advances in magnetic domain imaging techniques, high-resolution imaging of 3D magnetic field components remains a great challenge. Magnetic force microscopy has been utilized to observe the 1D magnetic field component from the sample surface; however, the 1D stray-field component lacks sufficient conditions to clarify the nature of nanomagnetism. Herein, we propose a method for the detection of 3D stray-field components by using a Fe3O4-nanoparticle sensor. We employed this Fe3O4-nanoparticle sensor to detect nanoscale magnetic domains, domain walls, and magnetic vortices (resolution ∼5 nm), and our findings demonstrate its potential in imaging both out-of-plane and in-plane magnetic-field components. Our technique overcomes the limitations of 3D stray-field detection and high-resolution imaging and provides the possibility of observing both out-of-plane and in-plane magnetic field components with a 5 nm resolution, thereby paving the way for the development of future spin-based devices.