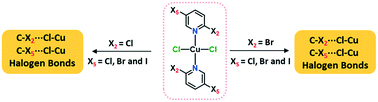
Ten coordination complexes obtained through a facile reaction between 2,5-dihalopyridines and copper(II) chloride (CuCl2) are characterized using single crystal X-ray diffraction. Two series of dihalopyridine complexes based on 2-chloro-5-X-pyridine and 2-bromo-5-X-pyridine (X = F, Cl, Br and I) were prepared to analyze the C–X2/X5⋯Cl–Cu halogen bonds (XB). The influence of X2- and X5-substituents on the respective interactions was examined by comparing them to the X2/X3⋯Cl–Cu XBs found in mono-substituted halopyridine complexes, (n-X-pyridine)2·CuCl2 (n = 2, 3 and X = Cl, Br and I). Varying the X5-halogens in (2,5-dihalopyridine)2·CuCl2, the C5–X5⋯Cl–Cu XBs follow the order F5 < Cl5 < Br5 < I5 for X2 = Cl and Cl5 < Br5 < I5 for X2 = Br. The C2–X2⋯Cl–Cu XB distances did not follow any particular trends, and are slightly longer compared to corresponding distances in (2-halopyridine)2·CuCl2 complexes due to the competition of X2 and X5-halogen based halogen bonds. The C3–X3⋯Cl–Cu contacts in (3-halopyridine)2·CuCl2 have RXB values > 1 and they cannot be considered as halogen bonds. This proves the polarization effect of X2- to X5- rather than X5- to X2-halogen, and the introduction of second halogen substituent in para-position to X5- triggers C2–X2⋯Cl–Cu and C5–X5⋯Cl–Cu XB interactions.