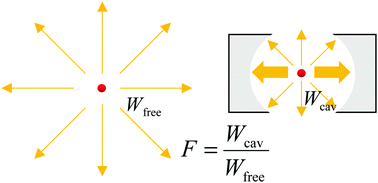
The purpose of this tutorial review is to provide a comprehensive explanation of plasmon-enhanced spectroscopies, such as plasmon-enhanced Raman scattering, fluorescence, absorption, Rayleigh scattering, and hyper Raman scattering. Plasmon-enhanced spectroscopy implies the spectroscopy of enhanced optical responses of molecules in close proximity to plasmonic nanostructures, resulting in a strong enhancement in sensitivity. In this review, we explain the enhancement in plasmon-enhanced spectroscopy as an optical response of a molecule interacting with an optical resonator, which represents a plasmonic nanostructure, in analogy to cavity quantum optics to easily understand all types of plasmon-enhanced spectroscopy in the same manner. The keys to understanding the enhancement factor of each plasmon-enhanced spectroscopy are a quality factor and a mode volume of plasmonic resonators, which are well-known parameters in the Purcell effect of standard optical cavity resonators.