Jordan M. Cox, Ian M. Walton and Jason B. Benedict
J. Mater. Chem. C, 2016,4, 4028-4033
DOI:
10.1039/C6TC00131A,
Paper
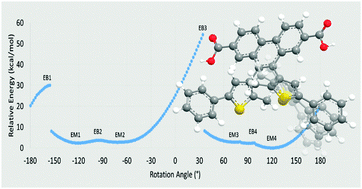
The relative stability and accessibility of atropisomers plays a prominent role in the efficacy of diarylethene-based photochromic materials. Herein, DFT methods, using the ωB97XD functional and a 6-31G(d) basis, are employed to determine the local energetic minima and maxima which describe the rotation of a thiophene group in derivatives of 9,10-bis(2-methyl-5-pheylthiophen-3-yl)phenanthrene-2,7-dicarboxylic acid, a photochromic linker molecule which exhibits atropisomer-formation-related fatigue when incorporated into a metal–organic framework. Results of these potential energy surface mapping calculations as well as their applications to atropisomer separability are discussed.