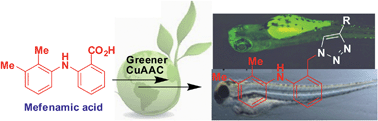
Prompted by the potential of a screening strategy in zebrafish for the identification of valuable pharmacophores, a series of triazole substituted mefenamic acid derivatives were designed and synthesized via a CuAAC under green conditions. A variety of terminal alkynes were reacted with the azide obtained from mefenamic acid to give the expected products in good to excellent yields. When screened for apoptosis, teratogenicity and hepatotoxicity in zebrafish embryos, one of these compounds showed encouraging apoptotic properties and safety profiles and seemed to have medicinal value.