Liam D. Curless, Ewan R. Clark, Jay J. Dunsford and Michael J. Ingleson
Chem. Commun., 2014,50, 5270-5272
DOI:
10.1039/C3CC47372D,
Communication
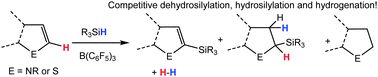
In the presence of B(C6F5)3 five-membered heteroarenes undergo dehydrosilylation and hydrosilylation with silanes. The former, favoured on addition of a weak base, produces H2 as a by-product making the process catalytic in B(C6F5)3 but also enabling competitive heteroarene hydrogenation.