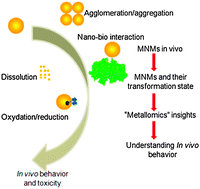
With the rapid development of engineered nanomaterials (NMs) and wide biomedical applications for new types of multifunctional NMs, an understanding of the behavior patterns of NMs in vivo and clarification of their potential health impact as a result of their novel physicochemical properties is essential for ensuring safety in biomedical applications of nanotechnology. NMs have heterogeneous characteristics in that they combine the bulk properties of solids with the mobility of molecules, and present phase transformation, dissolution, oxidation/