Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleHydrophosphination reactions with transition metal ferrocenylphosphine complexes†
Julian Rodger Frederic
Pritzwald-Stegmann
,
Peter
Lönnecke
and
Evamarie
Hey-Hawkins
*
Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, Faculty of Chemistry and Mineralogy, Universität Leipzig, Johannisallee 29, 04103 Leipzig, Germany. E-mail: hey@uni-leipzig.de
First published on 9th November 2015
Abstract
The group 6 metal mono-, bis- and tris-ferrocenylphosphine complexes [M(CO)5(PH2Fc)] (1a, M = Cr; 1b, M = Mo; 1c, M = W), cis-[M(CO)4(PH2Fc)2] (2a, M = Cr; 2b, M = Mo; 2c, M = W) and fac-[M(CO)3(PH2Fc)3] (3a, M = Cr; 3b, M = Mo; 3c, M = W) [Fc = Fe(η5-C5H4)(η5-C5H5)] were prepared and fully characterised. IR and NMR spectroscopy and single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis indicate that FcPH2 is as good a σ donor as PhPH2 but is easier to handle and furthermore has a redox-active ferrocenyl group. Complex 1c was employed in the hydrophosphination of acrylonitrile and methyl acrylate in the presence of catalytic amounts of KOtBu giving the secondary phosphine complexes [W(CO)5{PH(Fc)(CH2CH2CN)}] (4a) and [W(CO)5{PH(Fc)(CH2CH2C(O)OMe)}] (4b). In addition, FcP(CH2CH2CN)2 (5) was prepared by a similar method from FcPH2 and acrylonitrile. These hydrophosphination products represent a convenient method for the modification of phosphines.
Introduction
The majority of organometallic phosphine complexes involve mono-, bi- or polydentate tertiary phosphines,1 while primary and secondary phosphines have received much less attention, due to their toxicity and high reactivity (some are even pyrophoric). However, these phosphines are very interesting, as they facilitate post-coordination modification of the P–H bond, allowing for chemical flexibility in the synthesis of new and intriguing transition metal phosphine complexes.2,3 Several air-stable primary and secondary phosphines have been reported;4–10 developments in this area include the use of bulky aryl groups7,8 or aminoalkyl substituents.9 A recent review by Higham et al. gives an excellent overview on primary phosphine chemistry, including air-stable phosphines.3Due to the redox properties of the ferrocenyl unit and the possibility to readily obtain chiral compounds,11 ferrocenylphosphines are an important class of ligands in transition metal chemistry.11,12 Henderson et al.4–6 used the methylferrocenyl fragment to stabilise primary phosphines. FcCH2PH2 [Fc = Fe(η5-C5H4)(η5-C5H5)] proved to be indefinitely air-stable,6 probably due to electronic rather than steric effects, as well as having the ability to coordinate to molybdenum carbonyls or [{RuCl2(p-cymene)}2] (p-cymene = 1-Me-4-iPrC6H4,) without alteration of the PH2 group, whereas P–H activation occurred in the reaction with [Ru3(CO)12] to give two products with capping phosphinidene ligands.5 Ferrocenylphosphine, FcPH2, was first published by Roesky et al. in 1989 as an air-sensitive yellow oil prepared by reduction of FcPCl2 with LiAlH4.13 Henderson et al. have obtained FcPH2 from the reduction of FcP(O)(OEt)2 with a mixture of LiAlH4 and Me3SiCl as a brown oil that crystallises upon standing.4 They reported that a solution of FcPH2 is slowly oxidised in 5 d to the corresponding primary phosphine oxide and phosphinic acid.4 We have previously extended this chemistry to the sterically demanding air-stable secondary and tertiary ferrocenylphosphines PH(CH2Fc)2 and P(CH2Fc)3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 14 and transition metal complexes thereof.14,15–19
14 and transition metal complexes thereof.14,15–19
FcPH2 is a remarkably convenient starting material considering its easy synthesis and stability compared with related compounds, but has mostly been neglected. In contrast, the highly reactive PhPH2 has been used extensively.20 We have previously reported the synthesis of [MI2(CO)3(PH2Fc)2] (M = Mo, W),19 [Cp*TaCl4(PH2Fc)]15 (Cp* = C5Me5) and [RuCl2(p-cymene)(PH2Fc)].17 Presented below is the synthesis and characterisation of the ferrocenylphosphine transition metal carbonyl complexes [M(CO)5(PH2Fc)] (1a, M = Cr; 1b, M = Mo; 1c, M = W), cis-[M(CO)4(PH2Fc)2] (2a, M = Cr; 2b, M = Mo; 2c, M = W) and fac-[M(CO)3(PH2Fc)3] (3a, M = Cr; 3b, M = Mo; 3c, M = W). Furthermore, the reactivity of the P–H bond of the coordinated and free ligand in the hydrophosphination of alkenes was investigated, and the hydrophosphination products [W(CO)5{PH(Fc)(CH2CH2CN)}] (4a), [W(CO)5{PH(Fc)(CH2CH2C(O)OMe)}] (4b) and FcP(CH2CH2CN)2 (5) were obtained.
Results and discussion
Synthesis
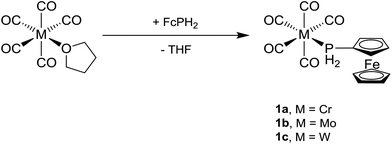
Freshly prepared [M(CO)5(thf)] (M = Cr, Mo, W)21 was added to a solution of FcPH2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 in THF at room temperature and the mixture was stirred for 30 min (Scheme 1). All volatile materials including unconsumed M(CO)6 and FcPH2 were removed under high vacuum (10−3 mbar) at elevated temperature to leave a pale orange powder of crude [M(CO)5(PH2Fc)] (1a, M = Cr; 1b, M = Mo; 1c, M = W), which was purified by column chromatography. Small amounts of cis-[M(CO)4(PH2Fc)2] (2a, M = Cr; 2b, M = Mo; 2c, M = W) were also obtained by this method, since cis-[M(CO)4(thf)2] is a side product in the preparation of [M(CO)5(thf)].21 The three complexes 1a–c are air- and moisture-stable and highly soluble in common organic solvents.
3 in THF at room temperature and the mixture was stirred for 30 min (Scheme 1). All volatile materials including unconsumed M(CO)6 and FcPH2 were removed under high vacuum (10−3 mbar) at elevated temperature to leave a pale orange powder of crude [M(CO)5(PH2Fc)] (1a, M = Cr; 1b, M = Mo; 1c, M = W), which was purified by column chromatography. Small amounts of cis-[M(CO)4(PH2Fc)2] (2a, M = Cr; 2b, M = Mo; 2c, M = W) were also obtained by this method, since cis-[M(CO)4(thf)2] is a side product in the preparation of [M(CO)5(thf)].21 The three complexes 1a–c are air- and moisture-stable and highly soluble in common organic solvents.
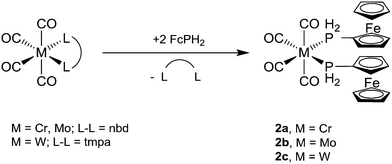
The bis-ferrocenylphosphine complexes cis-[M(CO)4(PH2Fc)2] (2a, M = Cr; 2b, M = Mo) were obtained from two equivalents of FcPH2 and [M(CO)4(nbd)]22 (M = Cr, Mo, nbd = norbornadiene) in toluene after stirring at room temperature for 24 h (Scheme 2). In the case of cis-[W(CO)4(PH2Fc)2] (2c), a mixture of FcPH2 and cis-[W(CO)4(tmpa)]22 (tmpa = N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyl-1,3-propanediamine) in toluene was heated to 60 °C for 1 d. Complexes 2a–c crystallise from dichloromethane/n-hexane as pale orange powders.
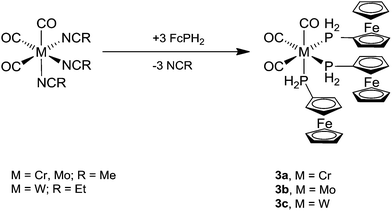
The tris-ferrocenylphosphine complexes fac-[M(CO)3(PH2Fc)3] (3a, M = Cr; 3b, M = Mo; 3c, M = W) were obtained from three equivalents of FcPH2 and fac-[M(CO)3(NCR)3] (M = Cr, Mo, R = Me; M = W, R = Et)21 in dichloromethane overnight at room temperature (Scheme 3). The air- and moisture-stable products were purified by column chromatography.
Spectroscopic data
The 31P{1H} NMR spectra show a remarkable difference between the three complexes with δ(31P) observed at progressively lower ppm in the order Cr > Mo > W (1a: −47.6, 1b: −81.5 and 1c: −101.8 ppm). In the proton-coupled 31P NMR spectra these singlets split into triplets [1JPH ≈ 334 Hz (Table 1)]. In addition, the spectrum of 1c shows 31P–183W coupling of 221 Hz.| Compound | δ 31P (ppm) | 1 J PH (Hz) | ν(CO) (cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FcPH2 | −144.2 | 203.6 | — |
| 1a | −47.5 | 333.9 | 2066, 1946, 1931, 1917 |
| 1b | −81.5 | 328.0 | 2074, 1950, 1933, 1921 |
| 1c | −101.8 | 341.5 | 2073, 1935, 1916, 1898 |
| 2a | −36.3 | 333.1 | 2018, 1922, 1901, 1870 |
| 2b | −72.4 | 326.4 | 2024, 1901, 1879 |
| 2c | −94.2 | 328.0 | 2025, 1922, 1898, 1865 |
| 3a | −25.9 | 306.0 | 1922, 1837 |
| 3b | −63.8 | 307.0 | 1932, 1842 |
| 3c | −82.3 | 315.0 | 1938, 1840 |
| 4a | −45.4 | 345.1 | 2073, 1980, 1916 |
| 4b | −42.6 | 343.0 | 2071, 1978, 1914, 1738 |
| 5 | −74.4 | — | — |
In the 1H NMR spectra, the signals of the hydrogen atoms of the primary phosphine are shifted downfield from 3.81 ppm in FcPH2 to 5.27 ppm in 1a, 5.31 ppm in 1b and 5.65 ppm in 1c (1JHP increases from 203.6 Hz in FcPH2 to 333.9 Hz in 1a, 328 Hz in 1b and 341.5 Hz in 1c).
In the 13C{1H} NMR spectrum, two doublets are observed for the carbonyl carbon atoms (1a: 220.4 ppm, 2JCP = 7.3 Hz, 216.1 ppm, 2JCP = 13.7 Hz; 1b: 208.8 ppm, 2JCP = 23.7 Hz, 205.0 ppm, 2JCP = 9.2 Hz; 1c: 198.1 ppm, 2JCP = 22.2 Hz, 195.9 ppm, 2JCP = 7.1 Hz). The doublet with the larger coupling constant is assigned to the single trans carbonyl group, since 31P–13C coupling through multiple bonds is usually greatest when the bonds are linear.23
The same trends as seen for 1a–c are also observed for 2a–c in the 1H, 13C{1H}, 31P{1H} and 31P NMR spectra, but the spectra exhibit a higher spin system due to coupling with the second magnetically inequivalent phosphorus atom (the 1H and 31P NMR spectra of 2a (experimental and simulated) are shown in Fig. S1 and S2, ESI†). The signals in the 31P NMR spectra of 2a–c show downfield shifts of roughly 10 ppm compared to 1a–c (Table 1). The only significant change in the 1H NMR spectra of 2a–c compared to 1a–c is the increased complexity of the signal of the hydrogen atoms attached to the phosphorus atoms due to the apparent AA′X2X′2 (2a,b) or AA′MX2X′2 (2c) spin system. These signals are observed at 5.23 in 2a, 5.22 in 2b and 5.53 ppm in 2c. Accordingly, the 13C{1H} NMR spectra of 2a–c show increased complexity due to the second phosphorus atom, but the same downfield shift trend is observed from chromium to tungsten. The greatest change is seen in the carbonyl carbon signals, which become more deshielded (downfield shifts of 3.9 to 6.2 ppm). This deshielding of the carbonyl carbon atoms is accompanied by a decrease in ν(CO) of the A1 carbonyl mode (2018–2025 cm−1, Table 1) in the IR spectra of 2a–c by about 50 cm−1 due to increased back-bonding between the dM and π* orbitals of the M–CO bond, which is due to the presence of the second FcPH2 ligand.24
Introduction of a third ferrocenylphosphine ligand further increases the complexity of the 1H, 13C{1H}, 31P{1H} and 31P NMR spectra (AA′A′′X2X′2X′′2 (3a,b) or AA′A′′MX2X′2X′′2 (3c) spin system; the 1H and 31P NMR spectra of 3a (experimental and simulated) are shown in Fig. S3 and S4, ESI†). However, the trends seen in the spectra of 2a–c are also observed in those of 3a–c. δ(31P) of 3a–c is shifted further downfield by about 10 ppm (Table 1). This suggests increasing deshielding of the phosphine with increased substitution. This same deshielding trend is seen between cis-[M(CO)4(PH2Ph)2] and fac-[M(CO)3(PH2Ph)3] (M = Mo, W; M = Mo, δ(31P) is −60.5 and −53.5 ppm; M = W, δ(31P) is −80.9 and −72.0 ppm).25 In addition, the 31P{1H} NMR spectra of the tungsten complexes (1c, 2c and 3c) show 31P–183W coupling which decreases from 221.0 Hz in [W(CO)5(PH2Fc)] (1c) to 209.0 Hz in fac-[W(CO)3(PH2Fc)3] (3c). Coupling to the two NMR active (I = 5/2) molybdenum isotopes, 95Mo and 97Mo, is only observed for fac-[Mo(CO)3(PH2Fc)3] (3b). In the 13C{1H} NMR spectra of 3a–c the signals of the carbonyl carbon atoms are also shifted by about 4 ppm compared to 2a–c.
Molecular structures
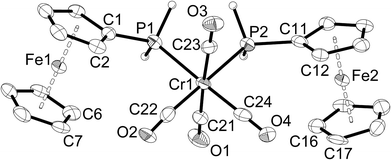
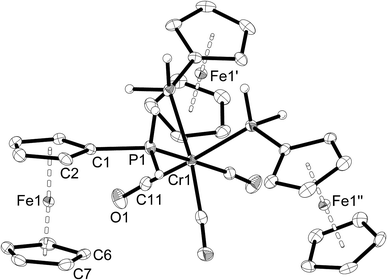
Single-crystal X-ray structure determinations were carried out for 1a, 1c, 2a–c, 3a and 3b. Complexes 1a and 1c are isostructural, as are complexes 2a–c and complexes 3a,b. Therefore, only one representative structure is shown here in each case (1a (Fig. 1, Table 2), 2a (Fig. 2, Table 3), and 3a (Fig. 3, Table 4). Furthermore, in 2a–c two symmetry-independent molecules are present in the asymmetric unit. As these molecules have very similar structures, only one of the two molecules is shown and discussed. Complexes 3a and 3b crystallise in the trigonal space group R3 with three molecules in the unit cell. The chirality arises from the lack of rotoinversion symmetry elements in the molecule. The molecules are located on a crystallographic C3 axis.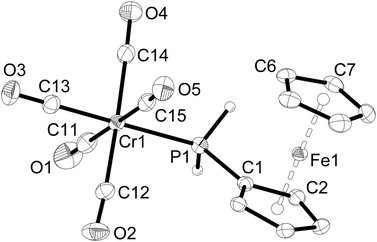 | ||
| Fig. 1 Molecular structure of [Cr(CO)5(PH2Fc)] (1a). The hydrogen atoms of the ferrocenyl moiety are omitted for clarity. Ellipsoids drawn at 50% probability. | ||
| Compound | 1a (M = Cr) | 1c (M = W) |
|---|---|---|
| M(1)–P(1) | 236.30(3) | 251.12(8) |
| M(1)–C(13) | 186.4(1) | 201.0(3) |
| M(1)–C(14) | 189.3(1) | 204.3(3) |
| M(1)–C(15) | 189.7(1) | 203.5(3) |
| M(1)–C(11) | 189.7(1) | 204.3(3) |
| M(1)–C(12) | 190.4(1) | 205.1(3) |
| P(1)–C(1) | 179.9(1) | 180.0(3) |
| O(1)–C(11) | 113.8(2) | 113.6(4) |
| O(2)–C(12) | 113.8(2) | 113.4(4) |
| O(3)–C(13) | 114.8(2) | 114.3(4) |
| O(4)–C(14) | 113.9(2) | 113.6(4) |
| O(5)–C(15) | 113.9(2) | 113.9(4) |
| C(13)–M(1)–P(1) | 179.06(4) | 179.5(1) |
| C(14)–M(1)–P(1) | 90.09(4) | 90.6(1) |
| C(15)–M(1)–P(1) | 90.80(4) | 90.30(9) |
| C(11)–M(1)–P(1) | 89.17(4) | 88.9(1) |
| C(12)–M(1)–P(1) | 91.83(4) | 92.13(9) |
| C(1)–P(1)–M(1) | 122.49(4) | 121.69(9) |
| Compound | 2a (M = Cr) | 2b (M = Mo) | 2c (M = W)a |
|---|---|---|---|
| a As a result of the extremely small and moderately diffracting crystal (small needle), the carbon atoms of 2c were refined isotropically. | |||
| M(1)–P(1) | 234.4(3) | 250.4(1) | 249.3(2) |
| [M(2)–P(3)] | [234.8(3)] | [250.3(1)] | [249.6(3)] |
| M(1)–P(2) | 235.0(3) | 250.2(1) | 249.1(2) |
| [M(2)–P(4)] | [234.4(3)] | [250.3(1)] | [249.2(2)] |
| M(1)–C(24) | 185(1) | 198.1(6) | 197(1) |
| [M(2)–C(48)] | [182.7(9)] | [198.1(6)] | [197(1)] |
| M(1)–C(22) | 187(1) | 198.8(6) | 199(1) |
| [M(2)–C(46)] | [185(1)] | [199.5(5)] | [198(1)] |
| M(1)–C(21) | 187(1) | 204.0(6) | 204(1) |
| [M(2)–C(47)] | [188(1)] | [203.5(5)] | [204(1)] |
| M(1)–C(23) | 189(1) | 201.9(5) | 198(1) |
| [M(2)–C(45)] | [188.9(9)] | [204.1(6)] | [201(1)] |
| P(1)–C(1) | 180(1) | 180.3(5) | 182(1) |
| [P(3)–C(25)] | [181(1)] | [180.5(5)] | [178.5(9)] |
| P(2)–C(11) | 180(1) | 179.7(5) | 180(1) |
| [P(4)–C(35)] | [181(1)] | [181.3(5)] | [180(1)] |
| C(24)–M(1)–P(1) | 178.4(3) | 176.9(2) | 176.9(3) |
| [C(48)–M(2)–P(3)] | [178.5(3)] | [178.5(2)] | [178.2(3)] |
| C(22)–M(1)–P(1) | 93.7(3) | 94.0(2) | 93.9(3) |
| [C(46)–M(2)–P(3)] | [92.8(3)] | [93.3(1)] | [93.2(3)] |
| C(21)–M(1)–P(1) | 93.1(3) | 93.6(2) | 93.3(3) |
| [C(47)–M(2)–P(3)] | [87.1(3)] | [86.5(1)] | [85.8(3)] |
| C(23)–M(1)–P(1) | 87.0(3) | 86.7(1) | 86.4(3) |
| [C(45)–M(2)–P(3)] | [88.8(3)] | [89.1(2)] | [88.9(3)] |
| C(24)–M(1)–P(2) | 93.1(3) | 92.8(2) | 92.8(3) |
| [C(48)–M(2)–P(4)] | [94.1(3)] | [94.2(2)] | [94.0(3)] |
| C(22)–M(1)–P(2) | 178.8(3) | 178.6(2) | 178.2(3) |
| [C(46)–M(2)–P(4)] | [178.4(3)] | [177.6(1)] | [177.5(3)] |
| C(21)–M(1)–P(2) | 89.3(3) | 89.0(2) | 88.7(3) |
| [C(47)–M(2)–P(4)] | [87.3(3)] | [86.6(2)] | [86.5(3)] |
| C(23)–M(1)–P(2) | 86.7(3) | 86.7(2) | 86.6(3) |
| [C(45)–M(2)–P(4)] | [91.5(3)] | [93.7(2)] | [93.0(3)] |
| P(1)–M(1)–P(2) | 85.7(1) | 84.85(4) | 84.52(8) |
| [P(4)–M(2)–P(3)] | [85.7(9)] | [84.88(4)] | [84.69(8)] |
| C(1)–P(1)–M(1) | 122.8(3) | 122.6(2) | 122.6(3) |
| [C(25)–P(3)–M(2)] | [124.5(3)] | [124.2(2)] | [123.9(3)] |
| C(11)–P(2)–M(1) | 124.8(3) | 124.5(2) | 123.9(3) |
| [C(35)–P(4)–M(2)] | [124.2(3)] | [122.9(2)] | [122.6(3)] |
| Compound | 3a (M = Cr) | 3b (M = Mo) |
|---|---|---|
| M(1)–P(1) | 235.15(6) | 250.57(7) |
| P(1)–C(1) | 180.5(2) | 180.6(2) |
| M(1)–C(11) | 184.9(2) | 198.0(3) |
| C(11)–M(1)–C(11)′ | 88.0(1) | 87.8(1) |
| C(11)–M(1)–P(1) | 172.70(7) | 173.64(7) |
| C(11)′–M(1)–P(1) | 87.55(7) | 88.50(7) |
| C(11)′′–M(1)–P(1) | 97.62(7) | 97.22(7) |
| P(1)–M(1)–P(1)′ | 87.26(3) | 86.83(2) |
| C(1)–P(1)–M(1) | 125.87(7) | 125.34(8) |
All complexes retain the octahedral geometry of the parent metal carbonyl complexes with bond angles at the metal centre ranging from 88.0(1) to 92.13(9)° in 1a and 1c, but become more distorted with bond angles ranging from 84.5(1)–94.3(4)° in 2a–c. The most acute angle in 2a–c is the P–M–P angle, which suggests that there is less steric hindrance between the ferrocenylphosphine ligands than between the carbonyl ligands. The P–Cr–P bond angles increase from 85.7(1)° in 2a to 87.26(3)° in 3a. The Cr–P–C bond angles also become more obtuse, increasing from 122.49(4)° in 1a to 123.8(3)° (average) in 2a and finally to 125.87(7)° in 3a. Likewise, the P–Mo–P (86.83(2)° (3b), 84.85(4)° (2b)) and Mo–P–C (125.34(8)° (3b), 123.5(2)° (2b)) (average) bond angles in 3b increase compared to 2b. The P–Mo–P bond angle in cis-[Mo(CO)4(PH2Ph)2]25 is 87.9(1)°, as opposed to the more acute angle of 84.85(4)° in 2b. The M–P–CFc bond angles are large and very similar for all complexes (122.49(4) and 121.69(9)° in 1a and 1c and slightly larger in 2a–c (122.6(3) to 124.8(3)°) and 3a,c (125.87(7) and 125.34(8)°). In comparison, the Mo–P–C bond angles in cis-[Mo(CO)4(PH2Ph)2] are more acute (120.6(1)°) compared to 2b. The P–CFc bond lengths of 1a–c and 2a–c are also very similar (ca. 180 pm) as are the ferrocenyl moieties in these complexes.
However, the bond lengths around the metal atom differ greatly between the complexes, as expected from the larger differences in atomic radii. For example, the Cr–P bond length of 1a is 236.30(3) pm, and the W–P bond length of 1c is 251.12(8) pm. The Cr–P and W–P bond lengths of 2a and 2c are shorter than those of 1a and 1c. This is again due the second FcPH2 ligand. The Cr–P bond lengths remain relatively constant at 236.30(3) pm in 1a, 234.4(3) and 235.0(3) pm in 2a and 235.15(6) pm in 3a. The Mo–P bond in 3b increases insignificantly to 250.57(7) pm from 250.3(1) pm in 2b. Likewise, the Mo–P bond lengths of cis-[Mo(CO)4(PH2Ph)2] and fac-[Mo(CO)3(PH2Ph)3] do not change at 250.8(3) and 249.8(3) pm, respectively.25
The average Cr–C bond length of 1a is 189.1(1) pm with the shortest bond (186.4(1) pm) trans to phosphorus. Bond lengths of 1c follow the same trend but are longer (average W–C bond length is 203.6(3) pm with the shortest bond (201.0(3) pm) trans to phosphorus). The bond lengths around the Cr and W atoms of 2a and 2c are shorter than those of 1a and 1c (2a: average Cr–C 186.9(1) pm; 2c: W–C average 199.7(1) pm). The same trend is observed in 2b which has an average Mo–C bond length of 200.7(6) pm (Mo–C 202.0(1) pm in [M(CO)4(PH2Ph)2]25) and for 3a,b (3a: Cr–C 184.9(2) pm; 3b: Mo–C 198.0(3) pm). This shortening can be attributed to increased back-bonding between the metal centre and carbonyl ligands and is supported by a decrease in the A1 mode of the CO stretching vibration (Table 1). This correlation was also observed for the phenylphosphine complexes [M(CO)4(PH2Ph)2] and [M(CO)3(PH2Ph)3] (M = Cr, Mo, W).25
Hydrophosphination
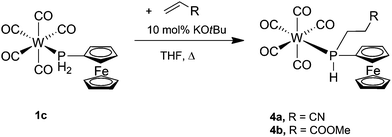
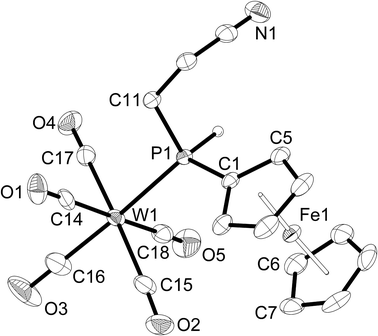
The addition of P–H bonds to C–C double or triple bonds (hydrophosphination reaction) is a very versatile way of synthesising new phosphines.3,26 After seminal work on catalytic hydrophosphination,26g,h renewed activity in this area was observed recently.26i–k Therefore, the ability of the coordinated ferrocenylphosphine to undergo hydrophosphination reactions was tested by screening 1c with a number of alkene substrates. KOtBu (10 mol%) was used to catalyse the hydrophosphination reactions, and dry THF was employed as the reaction medium to allow for sufficient solubility of all reaction components. The general procedure involved mixing 1c with KOtBu in THF followed by addition of one equivalent of one of the alkene substrates, all of which are liquids, after which the mixture was heated to reflux for several hours. Subsequent analysis of the reaction mixture by 31P{1H} NMR spectroscopy showed that alkenes bearing an electron-donating group (EDG), that is, styrene and cyclopentene, did not undergo hydrophosphination even when refluxing was continued for 24 h. However, alkenes with an electron-withdrawing group (EWG) did undergo hydrophosphination, and the stronger the EWG effect the faster the reaction. Thus, hydrophosphination of acrylonitrile, which bears a strong EWG, was complete after 5 h, while that of methyl acrylate, containing a weak EWG, took 20 h. The products [W(CO)5{PH(Fc)(CH2CH2CN)}] (4a) and [W(CO)5{PH(Fc)(CH2CH2C(O)OMe)}] (4b) were purified by column chromatography (they are eluted considerably more slowly than 1c) and fully characterised (Scheme 4).The 1H, 31P{1H} and 31P NMR spectra confirm the anti-Markovnikov addition of the P–H bond across the C–C double bond of the alkene substrate. In the 1H NMR spectrum, the signal of the P–H protons of 4a and 4b is shifted downfield (5.87 or 5.76 ppm, respectively) compared to 1c (5.65 ppm) with a large 31P–1H coupling of 344 Hz, a slight increase from 342 Hz in 1c, but appears as a doublet of triplets due to the 3JHH coupling of 4 or 5.4 Hz with the two methylene protons of the new cyanoethyl or methoxycarbonylethyl substituent. Likewise, a doublet with a large downfield shift to −45.4 ppm (4a, 1JPH = 345 Hz) or −42.6 ppm (4b, 1JPH = 343 Hz) from −101.8 ppm in 1c is observed in the 31P NMR spectrum. The IR spectra of 4a,b show some similarity to that of 1c. The carbonyl stretching frequencies are unchanged at 2073 and 2071 cm−1, respectively. The carbonyl stretching band of the carboxylate moiety of 4b was observed at 1738 cm−1, but no nitrile stretching band was observed for 4a.
The distorted octahedral environment (87.8(1)° to 94.2(1)°) and the bond lengths around the tungsten atom in 4a (Fig. 4) change only slightly compared to 1c (W–P 252.0(8) vs. 251.1(8) pm in 1c). The average W–C bond length is 202.4(4) pm (cf. 203.6(3) pm in 1c). The shortest W–C bond (197.9(4) pm) is again that trans to phosphorus, which is 3.1 pm shorter than that in 1c. These very small changes in bond lengths indicate that there is no significant change in the coordination properties, which would otherwise be expected when moving from a primary to secondary phosphine. The phosphorus atom exhibits a distorted tetrahedral environment with large W–P–CFc and W–P–CEt bond angles (121.7(1)° and 110.7(1)°, respectively) and a small CFc–P–CEt bond angle (104.0(2)°).
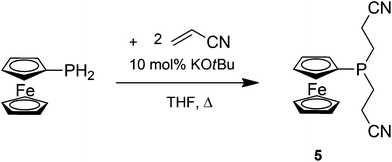
FcPH2 undergoes a similar hydrophosphination reaction as 1c; however, the di-hydrophosphination product, the tertiary phosphine FcP(CH2CH2CN)2 (5), is observed even with only one equivalent of acrylonitrile in refluxing THF and a catalytic amount of KOtBu (Scheme 5). 5 is obtained in a better yield when two equivalents of acrylonitrile are empoloyed. 5 was isolated as a viscous orange oil by column chromatography under an inert atmosphere, since it is rapidly oxidised upon exposure to air.
In the 31P NMR spectrum, the signal of the phosphorus atom of 5 is shifted downfield to −74.4 ppm compared to FcPH2 (−144.2 ppm). This signal is still significantly upfield from those of the related compounds FcCH2P(CH2CH2CN)2 (−22.1 ppm)27 and PhP(CH2CH2CN)2 (−23.8 ppm).28 The 13C{1H} NMR spectrum of 5 reveals an increase in the 13C–31P coupling constants compared with FcPH2. The signal of the ipso carbon atom shifts downfield to 68.1 ppm from 64.1 ppm in FcPH2 with similar 1JCP values (5.0 Hz in FcPH2, 5.1 Hz in 5). Likewise, the signal of the meta carbon atom is shifted downfield to 71.2 ppm with an increased 13C–31P coupling constant of 10.1 Hz compared with 4.0 Hz in FcPH2.
Conclusions
The mono-, bis- and tris-ferrocenylphosphine complexes [M(CO)5(PH2Fc)] (1a–c), [M(CO)4(PH2Fc)2] (2a–c) and [M(CO)3(PH2Fc)3] (3a–c) with M = Cr, Mo, W are readily available from FcPH2 and suitable metal carbonyl complexes. The molecular structures of 1a,c, 2a–c and 3a,b and a comparison of the X-ray structural and spectroscopic data of 2b and 3b with those of the known phenylphosphine complexes cis-[Mo(CO)4(PH2Ph)2] and fac-[Mo(CO)3(PH2Ph)3] reveal that FcPH2 exerts similar steric effects on the complex as PhPH2, but its electronic behaviour is significantly different. By comparing the carbonyl stretching frequencies of the complexes, it can be concluded that FcPH2 is as good a σ donor as PhPH2.The coordinated FcPH2 ligand of 1c undergoes hydrophosphination in the presence of catalytic amounts of KOtBu with alkene substrates bearing EWGs, such as acrylonitrile and methyl acrylate, yielding the secondary phosphine complexes [W(CO)5{PH(Fc)(CH2CH2CN)}] (4a) and [W(CO)5{PH(Fc)(CH2CH2C(O)OMe)}] (4b). Extending this method to the free ferrocenylphosphine yielded FcP(CH2CH2CN)2 (5).
The findings presented above show that FcPH2 is a versatile ligand that behaves and interacts much like the far more difficult to handle PhPH2, and it also contains a useful redox-active ferrocenyl moiety.
Experimental
General methods
Preparation of all compounds was carried out under an N2 atmosphere using standard vacuum-line and Schlenk techniques. All reactions were performed at ambient temperature and pressure unless otherwise stated. Where necessary, solvents were degassed using the standard freeze–pump–thaw method.29 The drying and distillation of solvents was conducted according to literature methods29 or solvents were dried with an MB SPS-800 Solvent Purification System. [M(CO)5(thf)] (M = Cr, Mo, W),21 [M(CO)4(L)] (M = Cr, Mo, L = nbd; M = W, L = tmpa) (nbd = 2,5-norbornadiene; tmpa = N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyl-1,3-propanediamine),22 [M(CO)3(L)3] (M = Mo, Cr, L = MeCN; M = W, L = EtCN),21 and FcPH2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 were prepared according to literature methods. Cr(CO)6 (Roth), Mo(CO)6 and W(CO)6 (Acros) were used as supplied without further purification. Silica gel 60A (Acros) was used as the stationary phase for column chromatography. Mass spectra were obtained in ESI mode with a BRUKER Daltonics FT-ICR-MS spectrometer (Type APEX II, 7 Tesla). Elemental analysis was performed with a Heraeus VARIO EL Analyser. IR spectra (4000–400 cm−1) were recorded as Nujol mulls with a PerkinElmer Spectrum 2000 FT-IR spectrometer. 1H, 13C{1H}, 31P{1H} and 31P NMR spectra were recorded with a Bruker AVANCE DRX 400 MHz instrument at 25 °C. Chemical shifts δ of 1H, 13C, 31P are reported in parts per million (ppm) at 400.12, 100.63 and 162.02 MHz, respectively. 1H NMR spectra were referenced to TMS (0.00 ppm) or the protic impurity solvent signals in the solvent CDCl3 (7.26 ppm). 13C NMR spectra were referenced to the solvent signal, CDCl3 (77.16 ppm). 13C{1H} and 31P{1H} experiments were referenced to TMS on the Ξ scale.3031P NMR experiments were referenced to 85% H3PO4 as external standard. Coupling constants of higher spin systems were determined by using the NMR software MestReNova 8 (Mestrelab Research).31
3 were prepared according to literature methods. Cr(CO)6 (Roth), Mo(CO)6 and W(CO)6 (Acros) were used as supplied without further purification. Silica gel 60A (Acros) was used as the stationary phase for column chromatography. Mass spectra were obtained in ESI mode with a BRUKER Daltonics FT-ICR-MS spectrometer (Type APEX II, 7 Tesla). Elemental analysis was performed with a Heraeus VARIO EL Analyser. IR spectra (4000–400 cm−1) were recorded as Nujol mulls with a PerkinElmer Spectrum 2000 FT-IR spectrometer. 1H, 13C{1H}, 31P{1H} and 31P NMR spectra were recorded with a Bruker AVANCE DRX 400 MHz instrument at 25 °C. Chemical shifts δ of 1H, 13C, 31P are reported in parts per million (ppm) at 400.12, 100.63 and 162.02 MHz, respectively. 1H NMR spectra were referenced to TMS (0.00 ppm) or the protic impurity solvent signals in the solvent CDCl3 (7.26 ppm). 13C NMR spectra were referenced to the solvent signal, CDCl3 (77.16 ppm). 13C{1H} and 31P{1H} experiments were referenced to TMS on the Ξ scale.3031P NMR experiments were referenced to 85% H3PO4 as external standard. Coupling constants of higher spin systems were determined by using the NMR software MestReNova 8 (Mestrelab Research).31
Synthesis and characterisation
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 70) as eluent. The orange band corresponding to the product was collected and the solvent evaporated under reduced pressure to obtain [M(CO)5(PH2Fc)] as an orange powder of high purity. Any remaining FcPH2 and/or M(CO)6 in the product was removed by sublimation under high vacuum (10−3 mbar). Yields: 1a 30%, 1b 44%, 1c 52%.
70) as eluent. The orange band corresponding to the product was collected and the solvent evaporated under reduced pressure to obtain [M(CO)5(PH2Fc)] as an orange powder of high purity. Any remaining FcPH2 and/or M(CO)6 in the product was removed by sublimation under high vacuum (10−3 mbar). Yields: 1a 30%, 1b 44%, 1c 52%.
1a: 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 4.16 (s, 5H, Fe–C5H5), 4.35 (s, 4H, Fe–C5H4), 5.27 (d, 1JHP = 333.9 Hz, 2H, PH2); 13C{1H} NMR (CDCl3): δ = 64.5 (d, 1JCP = 45.7 Hz, ipso-C in C5H4), 69.8 (s, C5H5), 71.5 (d, 3JCP = 7.7 Hz, m-C in C5H4), 73.9 (d, 2JCP = 12.2 Hz, o-C in C5H4), 216.1 (d, 2JCP = 13.7 Hz, CO eq), 220.4 (d, 2JCP = 7.3 Hz, CO ax); 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = −47.5 (t, 1JPH = 333.9 Hz, PH2); IR (Nujol, cm−1): 2066w (CO), 1946m (CO), 1931s (CO), 1917vs (CO); MS ESI pos., CH2Cl2/MeOH, m/z = 431.89 [M + Na]+; elemental analysis calcd (%) for C15H11CrFeO5P: C 43.94, H 2.70; found: C 44.05, H 2.68.
1b: 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 4.24 (s, 5H, Fe–C5H5), 4.40 (m, 2H, Fe–C5H4) 4.42 (m, 2H, Fe–C5H4), 5.31 (d, 1JHP = 328.0 Hz, 2H, PH2); 13C{1H} NMR (CDCl3): δ = 63.7 (d, 1JCP = 45.9 Hz, ipso-C in C5H4), 69.9 (s, C5H5), 71.8 (d, 3JCP = 7.7 Hz, m-C in C5H4), 74.7 (d, 2JCP = 13.2 Hz, o-C in C5H4), 205.0 (d, 2JCP = 9.2 Hz, CO eq), 208.8 (d, 2JCP = 23.7 Hz, CO ax); 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = −81.5 (t, 1JPH = 328.0 Hz, PH2); IR (Nujol, cm−1): 2074w (CO), 1950s (CO), 1933s (CO), 1921vs (CO); MS ESI pos., CH2Cl2/MeOH, m/z = 477.86 [M + Na]+; elemental analysis calcd (%) for C15H11FeMoO5P: C 39.68, H 2.44; found: C 39.59, H 2.40.
1c: 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 4.25 (s, 5H, Fe–C5H5), 4.42 (m, 2H, Fe–C5H4), 4.46 (m, 2H, Fe–C5H4), 5.65 (d, 1JHP = 341.5 Hz, 2H, PH2); 13C{1H} NMR (CDCl3): δ = 63.5 (d, 1JCP = 51.9 Hz, ipso-C in C5H4), 70.0 (s, C5H5), 71.9 (d, 3JCP = 8.1 Hz, m-C in C5H4), 74.6 (d, 2JCP = 13.2 Hz, o-C in C5H4), 195.9 (d, 2JCP = 7.1 Hz, CO eq), 198.1 (d, 2JCP = 22.2 Hz, CO ax); 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = −101.8 (t with 183W satellites, 1JPH = 341.5 Hz, 1JPW = 221.0 Hz, PH2); IR (Nujol, cm−1): 2073w (CO), 1935vs (CO), 1916vs (CO), 1898s (CO); MS ESI pos., CH2Cl2/MeOH, m/z = 563.90 [M + Na]+; elemental analysis calcd (%) for C15H11FeO5PW: C 33.25; H 2.05; found: C 33.30; H 1.99.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) as eluent. The orange band corresponding to the product was collected and the solvent evaporated under reduced pressure until pale orange crystals of pure cis-[M(CO)4(PH2Fc)2] formed. The crystals were isolated by filtration, washed with n-hexane (3 × 10 mL) and dried under vacuum. Yields: 2a 59%, 2b 58%, 2c 69%.
1) as eluent. The orange band corresponding to the product was collected and the solvent evaporated under reduced pressure until pale orange crystals of pure cis-[M(CO)4(PH2Fc)2] formed. The crystals were isolated by filtration, washed with n-hexane (3 × 10 mL) and dried under vacuum. Yields: 2a 59%, 2b 58%, 2c 69%.
2a: 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 4.22 (s, 10H, Fe–C5H5), 4.38 (br s, 4H, Fe–C5H4), 4.41 (br s, 4H, Fe–C5H4), 5.23 (m, 1JHP = 333.1 Hz, 3JHP = 13.0 Hz, 4H, PH2, AA′X2X′2 spin system, simulated31 (see ESI†)); 13C{1H} NMR (CDCl3): δ = 65.9 (t, 1JCP = 49.5 Hz, 3JCP = 25.3 Hz, ipso-C in C5H4), 69.9 (s, C5H5), 71.3 (t, 3JCP = 7.1 Hz, 5JCP = 3.3 Hz, m-C in C5H4), 74.0 (t, 2JCP = 11.1 Hz, 4JCP = 5.6 Hz, o-C in C5H4), 220.1 (t, 2JCP = 14.4 Hz, CO cis), 226.0 (d, 2JCP = 9.3 Hz, CO trans); 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = −36.3 (m, 1JPH = 333.1 Hz, 2JPP = −29.0 Hz, PH2, AA′X2X′2 spin system, simulated31 (see ESI†)); IR (Nujol, cm−1): 2018w (CO), 1922s (CO), 1901s (CO), 1870vs (CO); MS ESI pos., CH2Cl2/MeOH, m/z = 622.9 [M + Na]+; elemental analysis calcd (%) for C24H22CrFe2O4P2: C 48.04, H, 3.70; found: C 47.93, H, 3.61.
2b: 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 4.24 (s, 10H, Fe–C5H5), 4.40 (br s, 4H, Fe–C5H4), 4.42 (br s, 4H, Fe–C5H4), 5.22 (m, 1JHP = 327.0 Hz, 3JHP = 11.0 Hz, 4H, PH2, AA′X2X′2 spin system); 13C{1H} NMR (CDCl3): δ = 64.8 (t, 1JCP = 48.5 Hz, 3JCP = 24.2 Hz, ipso-C in C5H4), 69.9 (s, C5H5), 71.5 (t, 3JCP = 7.1 Hz, 5JCP = 3.5 Hz, m-C in C5H4), 74.7 (t, 2JCP = 12.1 Hz, 4JCP = 6.1 Hz, o-C in C5H4), 208.1 (t, 2JCP = 9.5 Hz, CO cis), 214.1 (d, 2JCP = 9.3 Hz, CO trans); 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = −72.4 (m, 1JPH = 326.4 Hz, 2JPP = −17.0 Hz, PH2 AA′X2X′2 spin system); IR (Nujol, cm−1): 2024w (CO), 1901vs (CO), 1879s (CO); MS ESI pos., CH2Cl2/MeOH, m/z = 668.8 [M + Na]+; elemental analysis calcd (%) for C24H22Fe2MoO4P2: C 44.76, H 3.44; found: C 44.74, H 3.50.
2c: 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 4.25 (s, 10H, Fe–C5H5), 4.46 (s, 8H, Fe–C5H4), 5.53 (m, 1JHP = 328.0 Hz, 3JHP = 12.0 Hz, 4H, PH2, AA′X2X′2 spin system); 13C{1H} NMR (CDCl3): δ = 64.6 (m, 1JCP = 50.6 Hz, 3JCP = 26.3 Hz, ipso-C in C5H4), 69.9 (s, C5H5), 71.6 (p, 3JCP = 8.1 Hz, 5JCP = 4.0 Hz, m-C in C5H4), 74.6 (t, 2JCP = 12.1 Hz, 4JCP = 6.1 Hz, o-C in C5H4), 200.0 (t, 2JCP = 7.3 Hz, CO cis), 204.3 (m, CO trans); 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = −94.2 (m, 1JPH = 328.0 Hz, 2JPP = −11.0 Hz, 1JWP = 214.9 Hz, PH2 AA′MX2X′2 spin system); IR (Nujol, cm−1): 2025w (CO), 1922s (CO), 1898s (CO), 1865vs (CO); MS ESI pos., CH2Cl2/MeOH, m/z = 754.9 [M + Na]+; elemental analysis calcd (%) for C24H22Fe2O4P2W: C 39.38, H 3.03; found: C 39.35, H 2.86.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of CH2Cl2 and n-hexane to elute any cis-[M(CO)4(PH2Fc)2], followed by a 3
1 mixture of CH2Cl2 and n-hexane to elute any cis-[M(CO)4(PH2Fc)2], followed by a 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture to elute the product. The orange band corresponding to the product was collected and the solvent evaporated under reduced pressure until pale orange crystals of pure fac-[M(CO)3(PH2Fc)3] formed. The crystals where isolated by filtration, washed with n-hexane (3 × 10 mL) and dried under vacuum. Yields: 3a 43%, 3b 31%, 3c 52%.
1 mixture to elute the product. The orange band corresponding to the product was collected and the solvent evaporated under reduced pressure until pale orange crystals of pure fac-[M(CO)3(PH2Fc)3] formed. The crystals where isolated by filtration, washed with n-hexane (3 × 10 mL) and dried under vacuum. Yields: 3a 43%, 3b 31%, 3c 52%.
3a: 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 4.16 (s, 15H, Fe–C5H5), 4.35 (s, 6H, Fe–C5H4), 4.42 (s, 6H, Fe–C5H4), 5.10 (m, 1JHP = 306.3 Hz, 3JHP = 15.0 Hz, 6H, PH2, AA′A′′X2X′2X′′2 spin system, simulated31 (see ESI†)); 13C{1H} NMR (CDCl3): δ = 67.1 (m, ipso-C in C5H4), 69.8 (s, C5H5), 70.9 (m, m-C in C5H4), 73.9 (m, o-C in C5H4), 230.3 (m, CO); 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = −25.9 (m, 1JPH = 306.0 Hz, 2JPP = −11.0 Hz, PH2, AA′A′′X2X′2X′′2 spin system, simulated31 (see ESI†)); IR (Nujol, cm−1): 1922s (CO), 1837vs (CO); MS ESI pos., CH2Cl2/MeCN, m/z = 812.9 [M + Na]+, 789.9 [M]+; elemental analysis calcd (%) for C33H33CrFe3O3P3: C 50.17, H 4.21; found: C 50.02, H 4.17.
3b: 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 4.25 (s, 15H, Fe–C5H5), 4.36 (s, 6H, Fe–C5H4), 4.44 (s, 6H, Fe–C5H4), 5.08 (m, 1JHP = 307.0 Hz, 3JHP = 8.0 Hz, 6H, PH2, AA′A′′X2X′2X′′2 spin system); 13C{1H} NMR (CDCl3): δ = 66.1 (m, ipso-C in C5H4), 69.9 (s, C5H5), 71.2 (m, m-C in C5H4), 74.7 (m, o-C in C5H4), 218.8 (m, CO); 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = −63.8 (m, 1JPH = 307.0 Hz, 2JPP = −17 Hz, 1J95MoP = 121.5 Hz, 1J97MoP = 166.9 Hz, PH2, AA′A′′MX2X′2X′′2 spin system); IR (Nujol, cm−1): 1932s (CO), 1842vs (CO); MS ESI pos., CH2Cl2/MeOH, m/z = 858.8 [M + Na]+; elemental analysis calcd (%) for C33H33Fe3MoO3P3: C 47.52; H 3.99; found: C 47.26, H 3.93.
3c: 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 4.25 (s, 15H, Fe–C5H5), 4.38 (s, 6H, Fe–C5H4), 4.45 (s, 6H, Fe–C5H4), 5.41 (m, 1JHP = 315.0 Hz, 3JHP = 9.0 Hz, 6H, PH2, AA′A′′MX2X′2X′′2 spin system); 13C{1H} NMR (CDCl3): δ = 65.9 (d, 1JCP = 57.6 Hz, ipso-C in C5H4), 70.0 (s, C5H5), 71.3 (m, m-C in C5H4), 74.6 (m, o-C in C5H4), 209.9 (m, CO); 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = −82.3 (m, 1JPH = 315.0 Hz, 2JPP = −9.0 Hz, 1JPW = 209.0 Hz, PH2, AA′A′′MX2X′2X′′2 spin system); IR (Nujol, cm−1): 1938s (CO), 1840vs (CO); MS ESI pos., CH2Cl2/MeOH, m/z = 944.9 [M + Na]+; elemental analysis calcd (%) for C33H33Fe3O3P3W: C 42.99; H 3.61; found: C 42.85, H 3.63.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30) as eluent. The product was collected in the second orange band (the first band contained unconsumed 1c, which was pure enough to be recycled). The solvent was removed to give pure 4a as an orange powder. Yield: 0.40 g, 72%. Crystals of 4a were obtained from CH2Cl2/n-hexane.
30) as eluent. The product was collected in the second orange band (the first band contained unconsumed 1c, which was pure enough to be recycled). The solvent was removed to give pure 4a as an orange powder. Yield: 0.40 g, 72%. Crystals of 4a were obtained from CH2Cl2/n-hexane.
1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 2.2–2.5 (m, 4H, CH2CH2CN), 4.22 (s, 5H, Fe–C5H5), 4.32 (s, 1H, Fe–C5H4), 4.35 (s, 1H, Fe–C5H4), 4.45 (s, 1H, Fe–C5H4), 4.50 (s, 1H, Fe–C5H4), 5.81 (dt, 1JHP = 346.0 Hz, 3JHH = 5.4 Hz, 1H, PH); 13C{1H} NMR (CDCl3): δ = 15.5 (CH2CN), 28.1 (d, 1JCP = 26.3 Hz, PCH2) 68.8 (d, 1JCP = 48.5 Hz, ipso-C in C5H4), 69.9 (s, C5H5), 72.0 (d, 3JCP = 10.1 Hz, m-C in C5H4), 75.0 (d, 2JCP = 21.2 Hz, o-C in C5H4), 118.4 (s, CH2CN), 196.1 (d, 2JCP = 7.1 Hz, CO eq), 197.6 (d, 2JCP = 23.2 Hz, CO ax); 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = −45.4 (d with 183W satellites, 1JPH = 345.1 Hz, 1JPW = 235.1 Hz, PH); IR (Nujol, cm−1): 2073w (CO), 1980m (CO), 1916vs (CO); MS ESI pos., CH2Cl2/MeOH, m/z = 618.0 [M + Na]+; elemental analysis calcd (%) for C18H14NFeO5PW: C 36.34, H 2.37; found: C 36.18, H 2.35.
1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 2.3–2.6 (m, 4H, CH2CH2C(O)OMe), 3.69 (s, 3H, C(O)OMe), 4.27 (s, 5H, Fe–C5H5), 4.39 (d, J = 13.2 Hz, 2H, Fe–C5H4), 4.49 (d, J = 13.2 Hz, 2H, Fe–C5H4), 5.76 (dt, 1JHP = 344 Hz, 3JHH = 5.6 Hz, 1H, PH); 13C{1H} NMR (CDCl3): δ = 26.5 (d, 1JCP = 29.7 Hz, PCH2), 31.0 (s, CH2C(O)OMe), 52.2 (s, OMe), 69.8 (s, C5H5), 70.7 (d, 1JCP = 47.7 Hz, ipso-C in C5H4), 71.6 (d, 3JCP = 9.1 Hz, m-C in C5H4), 74.5 (d, 2JCP = 19.2 Hz, o-C in C5H4), 172.4 (d, 3JCP = 12.1 Hz, C(O)OMe), 196.5 (d, 2JCP = 7.1 Hz, CO eq), 198.3 (d, 2JCP = 21.1 Hz, CO ax); 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = −42.6 (d with 183W satellites, 1JPH = 343.0 Hz, 1JPW = 231.7 Hz, PH); IR (Nujol, cm−1): 2071m (CO), 1978w (CO), 1914vs (CO), 1738m (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O); MS ESI neg., CH2Cl2/MeOH, m/z = 626.8 [M − H]−; elemental analysis calcd (%) for C19H17FeO7PW: C 36.34, H 2.73; found: C 36.40, H 2.75.
O); MS ESI neg., CH2Cl2/MeOH, m/z = 626.8 [M − H]−; elemental analysis calcd (%) for C19H17FeO7PW: C 36.34, H 2.73; found: C 36.40, H 2.75.
1H NMR (CDCl3,): δ = 1.78 (m, 4H, CH2CH2CN), 2.36 (br, 4H, CH2CH2CN), 4.13 (s, 5H, Fe–C5H5), 4.18 (br, 2H, Fe–C5H4), 4.27 (s, 2H, Fe–C5H4); 13C{1H} NMR (CDCl3): δ = 16.5 (d, 2JCP = 7.4 Hz, CH2CN), 20.5 (d, 1JCP = 15.1 Hz, PCH2), 68.1 (d, 1JCP = 5.1 Hz, ipso-C in C5H4), 69.0 (s, C5H5), 71.2 (s, m-C in C5H4), 74.6 (d, 2JCP = 13.4 Hz, o-C in C5H4), 119.3 (s, CH2CN); 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = −74.4 (s); MS ESI pos., CH2Cl2/MeOH, m/z = 325.06 [M + H]+.
Crystal structure determinations
The data were collected on a Gemini area detector diffractometer (Rigaku Inc.) using Mo-Kα radiation (λ = 71.073 pm) and ω-scan rotation. Data reduction was performed with CrysAlis-Pro32 including the program SCALE3 ABSPACK for empirical absorption correction. The structures of 1a,c, 2a–c and 3a,b were solved by direct methods and that of 4a was solved with Patterson methods with SHELXS-9733 or SIR92.34 The refinement was performed with SHELXL-97.33 As a result of the extremely small and moderately diffracting crystal (small needle), the carbon atoms of 2c were refined isotropically. The non-hydrogen atoms of all other structures were refined with anisotropic thermal parameters. A difference-density Fourier map was used to locate all hydrogen atoms of 1a and 1c, whereas H atoms of all other structures were calculated on idealised positions by using the riding model. The structures 1a and 1c are isostructural. This is also the case for the series 2a–c and 3a,b (see Table S1, ESI†). Structure figures were generated with ORTEP35 and DIAMOND-3.36 CCDC 1420127 (1a), 1420128 (1c), 1420129 (2a), 1420130 (2b), 1420131 (2c), 1420132 (3a), 1420133 (3b) and 1420134 (4a) contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper.Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from by the European Union and the Free State of Saxony (Landesinnovationspromotion for J. P. S.) and the Graduate School Leipzig School of Natural Sciences – Building with Molecules and Nano-objects (BuildMoNa).References
- (a) T. B. Rauchfuss, in Homogeneous Catalysis with Metal Phosphine Complexes, ed. L. H. Pignolet, Plenum Press, New York, 1993, ch. 7 Search PubMed; (b) Phosphorus(III) Ligands in Homogeneous Catalysis: Design and Synthesis, ed. P. C. Kamer and P. W. N. M. van Leeuven, John Wiley & Sons Ltd., UK, 2012 Search PubMed; (c) A. Behr and P. Neubert, Applied Homogeneous Catalysis, Wiley-VCH Verlag & Co. KGaA, 2012 Search PubMed.
- D. E. C. Corbridge, Phosphorus: Chemistry, Biochemistry and Technology, CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, FL, 6th edn, 2013 Search PubMed.
- J. T. Fleming and L. J. Higham, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2015, 297–298, 127 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Henderson and S. R. Alley, J. Organomet. Chem., 2002, 656, 120 CrossRef CAS.
- N. J. Goodwin, W. Henderson, B. K. Nicholson, J. Fawcett and D. R. Russell, J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans., 1999, 1785 RSC.
- N. J. Goodwin, W. Henderson and B. K. Nicholson, Chem. Commun., 1997, 31 RSC.
- P. P. Power, R. A. Bartlett, M. M. Olmstead and G. A. Sigel, Inorg. Chem., 1987, 26, 1941 CrossRef.
- P. P. Power, B. Twamley, C. Hwang and N. J. Hardman, J. Organomet. Chem., 2000, 609, 152 CrossRef.
- K. V. Katti, K. R. Prabhu, N. Pillarsetty and H. Gali, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2000, 122, 1554 CrossRef.
- R. M. Hiney, L. J. Higham, H. Müller-Bunz and D. G. Gilheany, Angew. Chem., 2006, 118, 7406 ( Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. , 2006 , 45 , 7248 ) CrossRef.
- (a) P. Štěpnička, Ferrocenes. Ligands, Materials and Biomolecules, John Wiley & Sons Ltd., West Sussex, 2008 Search PubMed; (b) A. Togni and T. Hayashi, Ferrocenes. Homogeneous Catalysis. Organic Synthesis. Material Science, VCH, New York, Weinheim, 1995 Search PubMed.
- S. Tschirschwitz, P. Lönnecke and E. Hey-Hawkins, J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans., 2007, 1377 RSC.
- C. Spang, F. T. Edelmann, M. Noltemeyer and H. W. Roesky, Chem. Ber., 1989, 122, 1247 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Kalio, P. Lönnecke and E. Hey-Hawkins, J. Organomet. Chem., 2008, 693, 590 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Kalio, P. Lönnecke, A. Cinquantini, P. Zanello and E. Hey-Hawkins, Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 2007, 633, 2470 CrossRef CAS.
- S. I. M. Paris, F. R. Lemke, R. Sommer, P. Lönnecke and E. Hey-Hawkins, J. Organomet. Chem., 2005, 690, 1807 CrossRef CAS.
- S. I. M. Paris, J. L. Petersen, E. Hey-Hawkins and M. P. Jensen, Inorg. Chem., 2006, 45, 5561 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Sommer, P. Lönnecke, P. K. Baker and E. Hey-Hawkins, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2002, 5, 115 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Sommer, P. Lönnecke, J. Reinhold, P. K. Baker and E. Hey-Hawkins, Organometallics, 2005, 24, 5256 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Svara, N. Weferling and T. Hofmann, Phosphorus Compounds, Organic, in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2008 Search PubMed.
- W. A. Herrmann and A. Salzer, Synthetic Methods of Organometallic and Inorganic Chemistry, Thieme, New York, 1996, vol. 1 Search PubMed.
- J. C. Kotz, C. L. Nivert, J. M. Lieber and R. C. Reed, J. Organomet. Chem., 1975, 84, 255 CrossRef CAS.
- O. Kühl, Phosphorus-31 NMR Spectroscopy: A Concise Introduction for the Synthetic Organic and Organometallic Chemist, Springer, 2008 Search PubMed.
- R. H. Crabtree, The Organometallic Chemistry of the Transition Metals, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New Jersey, 5th edn, 2009 Search PubMed.
- T. Campbell, A. M. Gibson, R. Hart, S. D. Orchard, S. J. A. Pope and G. Reid, J. Organomet. Chem., 1999, 592, 296 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) L. Rosenberg, ACS Catal., 2013, 3, 2845 CrossRef CAS; (b) S. A. Pullarkat and P.-H. Leung, Top. Organomet. Chem., 2013, 43, 145 CrossRef CAS; (c) Science of Synthesis, Stereoselective Synthesis, ed. A. L. Reznichenko and K. C. Hultzsch, J. G. De Vries, G. A. Molander and P. A. Evans, 2011, vol. 1, p. 689 Search PubMed; (d) D. S. Glueck, Top. Organomet. Chem., 2010, 31, 65 CrossRef CAS; (e) O. Delacroix and A. C. Gaumont, Curr. Org. Chem., 2005, 9, 1851 CrossRef CAS; (f) W. Malisch, B. Klupfel, D. Schumacher and M. Nieger, J. Organomet. Chem., 2002, 661, 95 CrossRef CAS; (g) D. K. Wicht and D. S. Glueck, in Catalytic Heterofunctionalization, ed. A. Togni and H. Grützmacher, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, 2001, ch. 5 Search PubMed; (h) I. P. Beletskaya, V. P. Ananikov and L. L. Khemchyan, in Phosphorus Chemistry: Catalysis and Material Science Applications, ed. M. Peruzzini and L. Gonsalvi, Springer, 2011, ch. 8, vol. 37 Search PubMed; (i) M. B. Ghebreab, C. A. Bange and R. Waterman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 9240 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (j) I. V. Basalov, V. Dorcet, G. K. Fukin, J.-F. Carpentier, Y. Sarazin and A. A. Trifonov, Chem. – Eur. J., 2015, 21, 6033 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (k) C. A. Bange, M. B. Ghebreab, A. Ficks, N. T. Mucha, L. Higham and R. Waterman, Dalton Trans., 2015 10.1039/C5DT03544A.
- A. J. Downard, N. J. Goodwin and W. Henderson, J. Organomet. Chem., 2003, 676, 62 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Tong, S. Liu, S. Zhang and S. Z. Li, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2007, 67, 837 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. L. F. Armarego and C. L. L. Chai, Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, Butterworth-Heinemann, Burlington, 5th edn, 2003 Search PubMed.
- R. K. Harris, E. D. Becker, S. M. Cabral De Menezes, R. Goodfellow and P. Granger, Concepts Magn. Reson., 2002, 14, 326 CrossRef CAS.
- Spectra have been simulated with the software MestReNova Version: 8.0.2-11021, 2012 Mestrelab Research S. L.
- CrysAlis-Pro: Data collection and data reduction software package, Rigaku Inc.
- SHELX includes SHELXS-97, SHELXL-97: G. M. Sheldrick, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. A: Fundam. Crystallogr., 2008, 64, 112 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Altomare, G. Cascarano, C. Giacovazzo and A. Guagliardi, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 1994, 27, 435 Search PubMed.
- ORTEP3 for Windows: L. J. Farrugia, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 1997, 30, 565 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Brandenburg, DIAMOND 3, Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany Search PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Experimental and simulated 1H and 31P NMR spectra of 2a and 3a (only PH2 region); summary of data collection, structure solution and refinement details for 1a,c, 2a–c, 3a,b and 4a. CCDC 1420127–1420134. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c5dt03374h |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |