Control of pore distribution of porous carbons derived from Mg2+ porous coordination polymers†
Yu-ichi
Fujiwara
a,
Satoshi
Horike
*bc,
Kanokwan
Kongpatpanich
b,
Takashi
Sugiyama
a,
Norio
Tobori
a,
Hirotomo
Nishihara
d and
Susumu
Kitagawa
be
aFunctional Materials Science Research Laboratories, Research & Development Headquarters, Lion Corporation, 2-1, Hirai 7-chome, Edogawa-ku, Tokyo 132-0035, Japan
bDepartment of Synthetic Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, Graduate School of Engineering, Kyoto University, Katsura, Nishikyo-ku, Kyoto 615-8510, Japan
cPRESTO, Japan Science and Technology Agency, 4-1-8 Honcho, Kawaguchi, Saitama 332-0012, Japan
dInstitute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University, 2-1-1, Katahira, Sendai 980-8577, Japan
eInstitute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (WPI-iCeMS), Kyoto University, Yoshida, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-8501, Japan
First published on 13th March 2015
Abstract
We have developed porous carbons with various pore sizes from porous coordination polymers (PCPs) with Mg2+ and benzene carboxylate linkers. The pore sizes of the porous carbons were tuned systematically according to the dimensionality of inorganic building blocks and the metal–oxygen–metal connectivity of the PCP frameworks.
Porous carbon materials are used in numerous fields, such as separation, batteries, energy storage and conversion, as adsorbents, electrodes, and catalysts/catalyst supports. The required structures for carbon materials differ depending on the application, and methodologies for controlling carbon structures have become an area of focus in recent years.1 The template carbonization method involving inorganic materials is widely used to prepare carbon with an ordered pore structure and morphology.2,3 From the viewpoint of enabling the flexible design of carbon structures, an understanding of how molecular structures are converted into carbon structures is important. Conversely, because the design of the molecular structure of carbon precursors is difficult, methodologies for the flexible design of carbon structures have not been extensively discussed.
In recent years, the syntheses of porous carbon4–6 have been investigated using crystalline compounds known as porous coordination polymers (PCPs) or metal organic frameworks (MOFs) built from metal ions and organic linkers.7,8 Because PCPs/MOFs have a well-defined tunable structure and organic linkers can be used as carbon precursors, they are superior precursors for elucidating the relationship between the PCP/MOF structures and the resulting carbon structures. Although porous carbons from PCPs/MOFs have been reported to possess high microporosity and some mesoporosities,9–11 strategies for designing pore structures are under investigation. It is expected that the formation of metal oxides from metal ions during carbonization contributes to pore formation, and that the coordination environment around metal ions affects the resulting pore structure.12,13 In this work, we focused on magnesium as a metal species, which is ubiquitous, less toxic, and highly stable as a metal oxide under carbon co-existing conditions. A series of porous carbons with systematic pore structures were synthesized from PCPs/MOFs with different coordination environments of magnesium ions. One of the synthesized porous carbons exhibited good capacitance retention at a high sweep rate, which is desirable to be used as an electrode material for electric double layer capacitors (EDLCs).
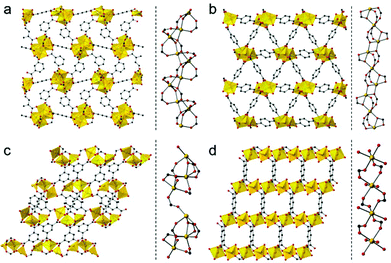
We used four compounds—Mg4(1,3-bdc)3(HCOO)2(DMF)2,14 Mg3(1,4-bdc)3(EtOH)2,15 Mg3(btc)2(DMF)4,16 and [Mg2(btec)(H2O)4]·2H2O17—as precursors to prepare porous carbons. These compounds were synthesized according to reported procedures. They contain benzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid (1,3-bdc), benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid (1,4-bdc), benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid (btc), and benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylic acid (btec) as organic linkers, respectively. Because the 1,3-bdc linker adopts μ4 and μ5 coordination, the 1,4-bdc linker adopts μ5 and μ6 coordination, the btc linker adopts μ6 coordination, and the btec linker adopts μ6 coordination, different coordination modes lead to different 3D network structures as shown in Fig. 1. Each Mg–PCP is denoted as Mg–R, R = C2′, C2, C3, and C4, where R indicates 1,3-bdc, 1,4-bdc, btc, and btec as organic linkers.
The dimensionality of the inorganic and organic connectivity in the structure of PCPs/MOFs can be classified as ImOn (m, n = 0, 1, 2, or 3).18 When we considered the magnesium–oxygen–magnesium (Mg–O–Mg) connectivity of Mg–R compounds, Mg–C2′ has an infinite helical chain of edge-shared dimers of magnesium octahedra in a corner-sharing manner, and Mg–C2 has an infinite chain of corner-shared triads of magnesium octahedra in an edge-sharing manner. On the other hand, Mg–C3 has corner-shared triads of magnesium octahedra. Mg–C4 has independent magnesium octahedra (see Fig. 1, right for details). According to the different Mg–O–Mg connectivities, Mg–C2′ and Mg–C2 are classified as I1O2, and Mg–C3 and Mg–C4 are classified as I0O3. We attempted to control the pore structure of the carbons by using these compounds as they have different inorganic dimensionalities and the metal–oxygen–metal connectivity.
We measured the thermal stability of each compound using thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) coupled with mass spectrometry (TG-MS) as shown in Fig. 2. Each compound exhibited significant weight loss between 550 °C and 700 °C because of the decomposition of the framework structure (Fig. 2a).
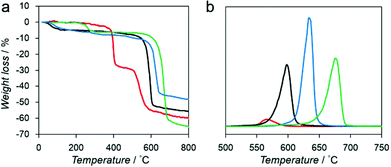 | ||
| Fig. 2 (a) TGA profiles of Mg–R, R = C2′ (red), C2 (black), C3 (blue), and C4 (green). (b) Mass spectrum of benzene (m/z = 78) of Mg–R, R = C2′ (red), C2 (black), C3 (blue), and C4 (green). | ||
We also analyzed the decomposition of benzene fragments in carboxylate linkers by monitoring the mass intensity (m/z = 78) as a function of temperature (Fig. 2b). The decomposition temperatures of benzene fragments in Mg–C2′, Mg–C2, Mg–C3, and Mg–C4 were detected at 565, 597, 639, and 675 °C, respectively. These results suggest that a relationship exists between the decomposition temperature and the dimensionality of the inorganic and organic connectivity. I0O3 compounds including Mg–C3 and Mg–C4 exhibit higher thermal stability than I1O2 compounds (Mg–C2′ and Mg–C2).19 Moreover, Mg–C4, which has the shortest Mg–O–Mg connectivity, exhibits the highest thermal stability.
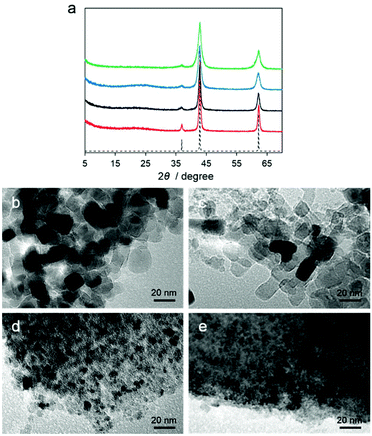
Motivated by the structural properties and thermal stabilities of Mg–R compounds, we conducted carbonization of Mg–R samples at 800 °C under a flowing nitrogen gas with a heating rate of 5 °C min−1 for 5 h without any additional carbon source. The carbonized Mg–R samples are denoted as C–Mg–R, where C indicates the carbonized compound of Mg–R. Powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) patterns of the C–Mg–R samples in Fig. 3a show a broad peak located at 25°, which is assigned to the carbon (002) diffraction, and three peaks located at 37, 43, and 62°, which are assigned to the MgO (111), (200), and (220) diffractions.
According to PXRD patterns, all of the C–Mg–R samples are MgO/carbon composites. The MgO diffraction peaks in each sample have different full-width at half-maxima (FWHMs), suggesting the different MgO particle sizes. We also collected transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of the C–Mg–R samples, as shown in Fig. 3b–e. Each TEM image indicated a different particle size of MgO surrounded by a dense morphology of carbon. The TEM images of C–Mg–C3 and C–Mg–C4, which were prepared from the precursor with I0O3 connectivity, show smaller particle sizes of MgO, and denser morphologies of carbon compared to the sizes and morphologies observed in C–Mg–C2′ and C–Mg–C2, which were prepared from the precursor classified as I1O2. The average domain size of the MgO was also calculated according to the Scherrer equation on the basis of the PXRD. The shape factor (K) of 0.94 in the Scherrer equation was used for the calculation. The calculated particle sizes were 15.7 nm (C–Mg–C2′), 10.7 nm (C–Mg–C2), 7.9 nm (C–Mg–C3), and 6.1 nm (C–Mg–C4). The particle sizes of MgO estimated from PXRD correspond to the sizes observed from the TEM images. When we consider the initial structure of Mg–R compounds in terms of the inorganic dimensionality and the Mg–O–Mg connectivity, the MgO particle sizes in the C–Mg–R samples become large according to the growth.
We removed the MgO particles in the composites using an HCl solution to investigate whether the trend of pore sizes in carbon structures follows the trend as MgO particle sizes. The corresponding samples are denoted as PC–Mg–R, where P indicates the purified compound of C–Mg–R. No MgO remained in the samples after acid washing as indicated by the absence of MgO diffraction peaks. PXRD patterns of all of the PC–Mg–R samples show two broad peaks located at 25 and 44°, which can be assigned to the carbon (002) and (101) diffractions, respectively (see Fig. S3†). The broad peaks indicate that all PC–Mg–R samples are low crystalline carbon. Raman spectra of all of the PC–Mg–R samples show two bands assigned to the tangential G band around 1594 cm−1 and the defect-induced D band around 1351 cm−1 (Fig. S4†). The significant G band indicates the presence of graphene sheets in all the PC–Mg–R samples.20
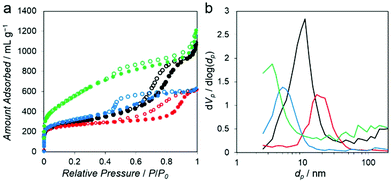
The N2 adsorption isotherms measured at −196 °C for all of the PC–Mg–R samples (Fig. 4a) show a steep increase of N2 uptake in the low relative pressure region and a hysteresis loop in the high relative pressure regions (P/P0 = 0.5–1), suggesting that the samples contain mesoporosity.21
These isotherms can be categorized as combined characteristics of type I and IV isotherms. The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area of the PC–Mg–R samples was in the range of 968 to 1996 m2 g−1, and their pore volumes were in the range of 0.95 to 1.84 cm3 g−1 (see Table S1† for details).21 The pore size distributions calculated on the basis of the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) method indicate systematic mesoporosity with each different pore size, as shown in Fig. 4b.22 The pore size of the PC–Mg–R samples follows the trend of MgO particle sizes because the MgO particles work as templates for the formation of a porous network in the obtained carbons.
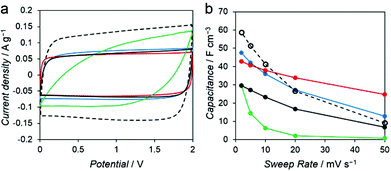
To investigate the influence of various mesoporous structures of the carbon, we evaluated the performance of the PC–Mg–R samples as electrode materials for EDLC. Capacitance measurements were performed with a two-electrode cell in 1 M Et4NBF4/propylene carbonate (PC) as the electrolyte solution. Commercial activated carbon, MSC-30 (Kansai Coke and Chemicals Co., Ltd), was adopted as a reference sample. MSC-30 has micro and mesoporous structures, with pores substantially smaller than those of the PC–Mg–R samples (see Fig. S5†). As shown in Fig. 5a, the cyclic voltammogram (CV) of MSC-30 exhibits a regular rectangular shape, which indicates the formation of an electric double layer.
The volumetric capacitance calculated from the CV curve of MSC-30 was 59 F cm−3 at 2 mV s−1. We observed 84% decay when the sweep rate was increased from 2 to 50 mV s−1 (Fig. 5b). In the case of the PC–Mg–R samples, the CV curves of PC–Mg–C2′, PC–Mg–C2, and PC–Mg–C3 show rectangular shapes derived from ideal capacitive behavior, and the CV curve of PC–Mg–C4 shows a distorted shape. The volumetric capacitance of PC–Mg–C2′, PC–Mg–C2, PC–Mg–C3, and PC–Mg–C4 at a sweep rate of 2 mV s−1 was 43, 30, 48, and 29 F cm−3, respectively. The volumetric capacitance of PC–Mg–C2′, PC–Mg–C2, PC–Mg–C3, and PC–Mg–C4 at a higher sweep rate (50 mV s−1) decreased to 25, 7, 13, and 1 F cm−3, respectively. The degree of mesoporosity in the sample is related to the stability of the capacitance. The stability in the capacitance is affected by the diffusion behavior of the supporting electrolyte, and mesoporous structures contribute to retain the capacitance.23,24 PC–Mg–C2′, which had the largest mesopore size among the PC–Mg–R samples, exhibited the best stability at a higher sweep rate as it retained 58% of its initial capacitance.
Conclusions
We have developed porous carbon with various pore sizes from PCPs with Mg2+ and benzene di, tri, and tetra-carboxylate linkers. According to the dimensionality of inorganic building blocks and the metal–oxygen–metal connectivity of the PCP frameworks, the particle size of the metal oxide in the carbonized PCPs could be tuned, enabling systematic control of the pore structure of the obtained carbons.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the PRESTO of the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST), a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on the Innovative Areas: “Fusion Materials” Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (A) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan, and the World Premier International Research Center Initiative on Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (WPI-iCeMS) from MEXT, Japan.Notes and references
- A. Stein, Z. Wang and M. A. Fierke, Adv. Mater., 2009, 21, 265–293 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Liang, Z. Li and S. Dai, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2008, 47, 3696–3717 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Nishihara and T. Kyotani, Adv. Mater., 2012, 24, 4473–4498 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Chaikittisilp, K. Ariga and Y. Yamauchi, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1, 14–19 CAS.
- J.-K. Sun and Q. Xu, Energy Environ. Sci., 2014, 7, 2071–2100 CAS.
- Q.-L. Zhu and Q. Xu, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 5468–5512 RSC.
- S. Kitagawa, R. Kitaura and S.-i. Noro, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2004, 43, 2334–2375 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. M. Yaghi, H. Li, C. Davis, D. Richardson and T. L. Groy, Acc. Chem. Res., 1998, 31, 474–484 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Hu, J. Reboul, S. Furukawa, N. L. Torad, Q. Ji, P. Srinivasu, K. Ariga, S. Kitagawa and Y. Yamauchi, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 2864–2867 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Srinivas, V. Krungleviciute, Z.-X. Guo and T. Yildirim, Energy Environ. Sci., 2014, 7, 335–342 CAS.
- W. Wang and D. Yuan, Sci. Rep., 2014, 4, 5711–5717 CAS.
- S. Lim, K. Suh, Y. Kim, M. Yoon, H. Park, D. N. Dybtsev and K. Kim, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 7447–7449 RSC.
- P. Pachfule, B. P. Biswal and R. Banerjee, Chem. – Eur. J., 2012, 18, 11399–11408 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. J. Calderone, D. Banerjee, Q. Nizami, R. L. LaDuca and J. B. Parise, Polyhedron, 2012, 37, 42–47 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. P. Davies, R. J. Less, P. D. Lickiss and A. J. P. White, Dalton Trans., 2007, 2528–2535 RSC.
- P. J. Calderone, D. Banerjee, A. M. Plonka, S. J. Kim and J. B. Parise, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 2013, 394, 452–458 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-K. Liu, T.-H. Tsao, Y.-T. Zhang and C.-H. Lin, CrystEngComm, 2009, 11, 1462–1468 RSC.
- A. K. Cheetham, C. N. R. Rao and R. K. Feller, Chem. Commun., 2006, 4780–4795 RSC.
- M. L. Foo, S. Horike, Y. Inubushi and S. Kitagawa, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 6107–6111 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Jawhari, A. Roid and J. Casado, Carbon, 1995, 33, 1561–1565 CrossRef CAS.
- K. S. W. Sing, Pure Appl. Chem., 1985, 57, 603–619 CrossRef CAS.
- E. P. Barrett, L. G. Joyner and P. P. Halenda, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1951, 73, 373–380 CrossRef CAS.
- D.-C. Guo, J. Mi, G.-P. Hao, W. Dong, G. Xiong, W.-C. Li and A.-H. Lu, Energy Environ. Sci., 2013, 6, 652–659 CAS.
- P. Pachfule, V. M. Dhavale, S. Kandambeth, S. Kurungot and R. Banerjee, Chem. – Eur. J., 2013, 19, 974–980 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Experimental details and additional characterization data. See DOI: 10.1039/c5qi00019j |
| This journal is © the Partner Organisations 2015 |