Benjamin W. Stein and Martin L. Kirk
Chem. Commun., 2014,50, 1104-1106
DOI:
10.1039/C3CC47705C,
Communication
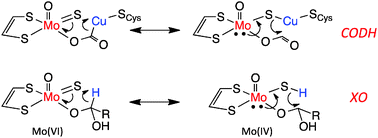
A molecular orbital analysis provides new insight into the mechanism of Mo/Cu carbon monoxide dehydrogenase, and reveals electronic structure contributions to reactivity that are remarkably similar to the structurally related molybdenum hydroxylases. A calculated reaction barrier of ∼12 kcal mol−1 is in excellent agreement with experiment.