Oxidation–reduction assisted exfoliation of LiCoO2 into nanosheets and reassembly into functional Li-ion battery cathodes†
Abstract
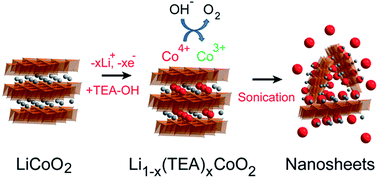
A common approach used to obtain 2D nanosheet materials is through the exfoliation of layered compounds by osmotic, chemical/electrochemical, or mechanical means, with a proton exchange step usually implemented for materials characterized by strong interlayer ionic bonding. However, in lithium metal oxides, due to the strong adsorption of protons at Li+ sites, this approach is less effective for obtaining nanosheets with good electrochemical properties that can be used in Li-ion battery applications. Here LiCoO2 (LCO) was exfoliated into nanosheets using electrochemical oxidation followed by intercalation of tetraethylammonium cations. The nanosheets were purified using dialysis and electrophoresis. The nanosheets were successfully restacked into the O2-polytype of LCO with microwave hydrothermal assistance, indicating that non-equilibrium structures can be obtained by reassembling nanosheets. After high temperature annealing, the materials exhibited electrochemical properties characteristic of O3-type LCO with good capacity retention when passivated with atomic layer deposition Al2O3 coatings. This work shows that the proton exchange step usually required for the exfoliation of layered metal oxides can be circumvented, and moreover, that the obtained nanosheets could be restacked into functional electrode materials. This could pave the way for the synthesis of materials with novel structures and electrochemical properties, as well as facilitate the fabrication of hybrid and composite structures from different nanosheets as building blocks.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emerging Investigators 2016: Novel design strategies for new functional materials

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...