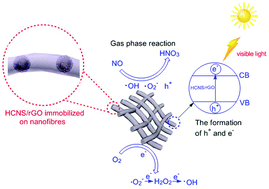
With the deterioration of air quality, great efforts were devoted to designing various photocatalysts for effective removal of NOx in air. However, the present photocatalysts have a fatal problem of low photocatalytic efficiency. In this work, a hollow porous carbon nitride nanosphere coupled with reduced graphene oxide (HCNS/rGO) was exploited as a visible-light photocatalyst to remove nitrogen monoxide in air at a low concentration (600 ppb level) under irradiation of an energy saving lamp. HCNS/rGO showed a NO removal ratio of 64%, which was superior to that of most other visible-light photocatalysts. The excellent photocatalytic ability of HCNS/rGO originates from the hollow porous morphology of HCNS and the grafted rGO on the surface. HCNS/rGO was immobilized on porous carbonized polymer nanofibers to obtain a photocatalytic membrane without affecting photocatalytic efficiency. Furthermore, the membrane showed excellent photochemical stability and recyclability.