Both protein adsorption and aggregation contribute to shear yielding and viscosity increase in protein solutions†
Abstract
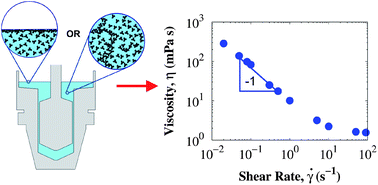
A combination of sensitive rotational rheometry and surface rheometry with a double-wall ring were used to identify the origins of the viscosity increase at low shear rates in protein solutions. The rheology of two high molecular weight proteins is discussed: Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) in a Phosphate Buffered Saline solution and an IgG1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) in a formulation buffer containing small quantities of a non-ionic surfactant. For surfactant-free BSA solutions, the interfacial viscosity dominates the low shear viscosity measured in rotational rheometers, while the surfactant-laden mAb solution has an interfacial viscosity that is small compared to that from aggregation in the bulk. A viscoelastic film forms at the air/water interface in the absence of surfactant, contributing to an apparent yield stress (thus a low shear viscosity increase) in conventional bulk rheology measurements. Addition of surfactant eliminates the interfacial yield stress. Evidence of a bulk yield stress arising from protein aggregation is presented, and correlated with results from standard characterization techniques used in the bio-pharmaceutical industry. The protein film at the air/water interface and bulk aggregates both lead to an apparent viscosity increase and their contributions are quantified using a dimensionless ratio of the interfacial and total yield stress. While steady shear viscosities at shear rates below ∼1 s−1 contain rich information about the stability of protein solutions, embodied in the measured yield stress, such low shear rate data are regrettably often not measured and reported in the literature.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...