Effects of interfacial transition layers on the electrical properties of individual Fe30Co61Cu9/Cu multilayer nanowires†
Abstract
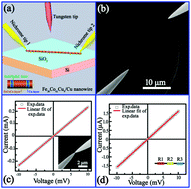
In this work, we accurately measure the electrical properties of individual Fe30Co61Cu9/Cu multilayered nanowires using nanomanipulators in in situ scanning electron microscopy to reveal that interfacial transition layers are influential in determining their transport behaviors. We investigate the morphology, crystal structure and chemistry of the Fe30Co61Cu9/Cu multilayered nanowires to characterize them at the nanoscale. We also compare the transport properties of these multilayered nanowires to those of individual pure Cu nanowires and to those of alloy Fe30Co61Cu9 nanowires. The multilayered nanowires with a 50 nm diameter had a remarkable resistivity of approximately 5.41 × 10−7 Ω m and a failure current density of 1.54 × 1011 A m−2. Detailed analysis of the electrical data reveals that interfacial transition layers influence the electrical properties of multilayered nanowires and are likely to have a strong impact on the life of nanodevices. This work contributes to a basic understanding of the electrical parameters of individual magnetic multilayered nanowires for their application as functional building blocks and interconnecting leads in nanodevices and nanoelectronics, and also provides a clear physical picture of a single multilayered nanowire which explains its electrical resistance and its source of giant magnetoresistance.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2015 Journal of Materials Chemistry C Hot Papers

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...