Józef Drabowicz, Frank Jordan, Marcin H. Kudzin, Zbigniew H. Kudzin, Christian V. Stevens and Paweł Urbaniak
Dalton Trans., 2016,45, 2308-2317
DOI:
10.1039/C5DT03083H,
Paper
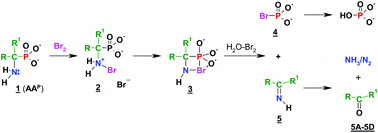
The reactions of 1-aminoalkylphosphonic acids with bromine–water, chlorine–water and iodine–water were investigated. The formation of phosphoric(V) acid, as a result of a halogen-promoted cleavage of the Cα–P bond, accompanied by nitrogen release, was observed. The dephosphonylation of 1-aminoalkylphosphonic acids was found to occur quantitatively. In the reactions of 1-aminoalkylphosphonic acids with other halogen–water reagents investigated by 31P NMR, scission of the Cα–P bond was also observed, the reaction rates being comparable for bromine and chlorine, but much slower for iodine.