Macroscopic switches constructed through host–guest chemistry
Abstract
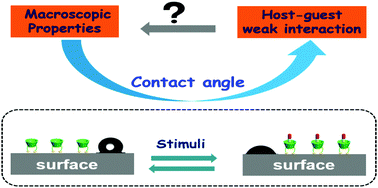
Molecular switch systems, having been extensively studied in the solution phase, have the ability to perform with good controllability and rapid-responsiveness, making them ideally suited for the design of molecular devices for drug delivery, and information or sensing functions. Inspired by a wide range of objects with visual changes, like Mimosa pudica towards external stimuli, in order to understand molecular switches well, they must be interfaced with the macroscopic world so that they can be directly realized by visual detectable changes even observed by the naked eye. This can be critical for fabricating intelligent microfluidics and laboratory-on-chip devices, that may have wide applications in the fields of biology and materials science. But to realize this objective, especially for fabricating macroscopic surface switches, unveiling host–guest weak interactions to achieve visual phenomena is still the greatest thrill. Thankfully, surface contact angles provide us with a wonderful method to further investigate the microscopic origin of the macroscopic changes. Therefore, interfacial modification becomes a paramount process. Macrocyclic compounds, encompassing an innovative concept to deal with reversible noncovalent interactions between macrocyclic hosts and suitable guests, are good candidates for surface functionalization. In this feature article, we discuss recent developments in macroscopic contact angle switches formed by different macrocyclic hosts and highlight the properties of these new functional surfaces and their potential applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Host–guest chemistry

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...