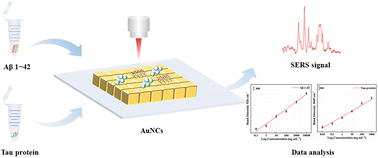
Since presently Alzheimer's disease (AD) is incurable, early diagnosis of AD is crucial. Aβ 1–42 and tau-441 proteins are promising core biomarkers for early diagnosis and early therapeutic intervention in AD. Here we constructed a surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) biosensor for highly sensitive quantitative detection of Aβ 1–42 and tau proteins by preparing gold nanocube (AuNC) superlattices through evaporation self-assembly. The results showed that the method has a wide response range (0.1–10 000 ng mL−1 and 0.01–1000 ng mL−1, respectively) and high sensitivity. The detection limits of Aβ1–42 and tau protein were 0.0416 ng mL−1 and 0.0087 ng mL−1, respectively. In addition, the method was able to rapidly and simultaneously detect the two biomarkers in serum, which showed the feasibility of the method in complex biological environments. The detection of Aβ 1–42 and tau protein has great potential for the accurate prediction and early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease.