Progress and perspectives on the development of inorganic nanofibres/nanowires for functional electrolytes of solid-state lithium metal batteries
Nanping
Deng
 *a,
Wenwen
Duan
a,
Wen
Yu
a,
Yang
Feng
b,
Zichun
Feng
a,
Xiaofan
Feng
a,
Zhaozhao
Peng
a,
Hengying
Xiang
a,
Yong
Liu
*a,
Wenwen
Duan
a,
Wen
Yu
a,
Yang
Feng
b,
Zichun
Feng
a,
Xiaofan
Feng
a,
Zhaozhao
Peng
a,
Hengying
Xiang
a,
Yong
Liu
 *a and
Weimin
Kang
*a and
Weimin
Kang
 *a
*a
aState Key Laboratory of Separation Membranes and Membrane Processes/National Center for International Joint Research on Separation Membranes, School of Textile Science and Engineering, Tiangong University, Tianjin 300387, PR China. E-mail: dengnanping@tiangong.edu.cn; liuyong@tiangong.edu.cn; kangweimin@tiangong.edu.cn
bKey Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry (Ministry of Education), Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, China
First published on 9th September 2024
Abstract
All solid-state lithium batteries (ASSLBs) have high safety and high energy density, and thus, are considered one of the most promising directions for battery development. However, solid-state electrolytes (SSEs), as the key components of ASSLBs, are associated with some issues such as high interfacial impedance at room temperature and serious lithium dendrite growth. In this case, the application of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires to modify the structure and function of SSEs is an effective strategy to improve the ionic conductivity of the electrolyte, enhance the interfacial stability between the electrodes/electrolyte, and solve the above-mentioned problems encountered in ASSLBs. This review provides a comprehensive summary of the latest applications of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires in SSEs for high-performance lithium-metal batteries, focusing on the basic principles of lithium-ion transport, high-voltage and high-pressure resistance stability and anode protection in SSEs for lithium-metal batteries. Moreover, the common methods currently employed for the preparation of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires and the relevant applications of inorganic nanofibers in SSEs for lithium-metal batteries are systematically summarized based on the classification of the fillers used in inorganic nanofibers/nanowires. Finally, future research directions are proposed to address all the challenges in the application and commercialization of this technology. This review aims to provide timely and important guidance for the development and application of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires in high-performance SSEs.
1. Introduction
After the second energy revolution, society has achieved rapid development. However, as the energy demand continues to increase, the environmental problems caused by fossil fuels have become increasingly severe and the energy system dominated by fossil fuels gradually cannot satisfy the increasing requirements of human development. Thus, it is urgent to find alternative novel energy sources.1 However, green energy sources, including solar and wind, are plagued by a series of problems such as intermittent natural factors and low energy transmission and must rely on energy storage systems such as pumped storage, flywheel storage and electrochemical storage to maintain a constant stream of energy. In this case, among the many energy storage methods, electrochemical energy storage stands out due to its strong environmental adaptability and convenience.2As a representative of electrochemical energy storage, lithium-ion batteries “boast” some strengths including high specific energy, large capacity, excellent cycle performance and environmental friendliness. Thus, they are widely utilized in electric-powered vehicles, handheld gadgets, space exploration and aviation technology.3 However, the liquid-state electrolyte used in conventional lithium-ion cells undergoes some side reactions with the highly active lithium metal anode, and the formed lithium dendrites tend to puncture the battery separator and short-circuit the battery, hindering the extensive-scale application of lithium-ion cells.4 Furthermore, the energy density of Li+ cells composed of the liquid electrolyte is close to the theoretical limit (≈260 W h kg−1); thus, it is difficult to satisfy the urgent demand for efficient energy storage devices. Therefore, the extensive search for a novel generation of lithium-ion batteries has become particularly important and additional research and development is urgently needed.5,6
Solid-state lithium batteries, especially all-solid-state lithium batteries (ASSLBs), (which use solid-state electrolytes (SSEs) instead of liquid electrolytes) are regarded as the most promising future-generation battery technology due to their high energy density and safety.7 SSEs can offer superior electrochemical stability, enhanced safety and stability and high energy density compared to that of liquid electrolytes.8,9 The application of SSEs can enable stable Li+ transport, thus ensuring the uniform lithium deposition and better cycling performance of solid-state lithium batteries.
In general, solid-state lithium batteries can be classified into three main categories in accordance with their composition: inorganic, polymer and composite solid-state electrolytes (CSEs).10 Among these distinct types of SSEs, inorganic solid-state electrolytes have some advantages such as high ionic conductivity, excellent mechanical properties and outstanding stability.11 However, they also have some disadvantages, including difficult workability, serious brittleness, high susceptibility to side reactions and point-to-point contact mode with cell electrodes, resulting in poor contact between the electrode/electrolyte interfaces and high interface impedance.12,13 In comparison with inorganic solid electrolytes, polymer electrolytes usually exhibit notable advantages in terms of compatibility with battery electrodes, film formation and processability. Moreover, they are well suited to accommodate large volume changes in battery electrodes. However, polymer electrolytes typically exhibit high impedance at room temperature, which results in low ionic conductivity and weak mechanical strength. In particular, under high-temperature working conditions, lithium dendrite growth and electrolyte make it difficult to match the high voltage cathode, resulting in more serious problems.14–17
CSEs are a blend of polymer matrix, lithium salts, and inorganic fillers. They combine some advantages of two types of SSEs and overcome the limitations of single-component SSEs. In CSEs, polymer materials are utilized to augment the compatibility between the interface of the cell electrolyte and electrode. Some of the common polymer materials are polyethylene oxide (PEO), polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and polyacrylonitrile (PAN). Also, inorganic fillers have demonstrated notable effects in enhancing the ionic conductivity, Li+ mobility number, and mechanical strength, as well as expanding the electrochemical stabilization window in the final CSEs.18 These polymer electrolytes are capable of disrupting the otherwise regular molecular chain arrangement in the polymer and interacting with the polymer and Li salts to facilitate the disintegration of Li salts while also constructing transport channels with high ionic conductivity.19 Inorganic ceramic fillers can be classified into two categories based on their mechanisms of action, namely, active ceramic fillers and passive ceramic fillers. The majority of passive ceramic fillers are derived from oxides such as silicon dioxide (SiO2), alumina (Al2O3) and titanium dioxide (TiO2).20 However, these fillers cannot transfer lithium-ions. Instead, they usually affect ion transport indirectly by inhibiting the crystallization of the polymer and building some Li+ transport interfaces.21 In addition to affecting the ion transport by diminishing the degree of crystallinity of the polymer matrix, active ceramic fillers can provide an efficient Li+ transport pathway. The active ceramic fillers mainly include oxide SSEs (e.g., LLZTO), sulfide SSEs (e.g., Li10GeP2S12) and halide SSEs (e.g., Li2InxSc0.666−xCl4). Compared to inert ceramic fillers, the application of active fillers in CSEs is more favourable for the enhancement of ionic conductivity, which greatly improves the electrochemical performance of CSEs.22,23 Therefore, the use of active fillers in CSEs is more conducive to enhancing the ionic conductivity, thus significantly improving the electrochemical performance of CSEs. In summary, CSEs can fully leverage the respective advantages of inorganic and polymer electrolytes; they possess high ionic conductivity, excellent electrochemical stability and good interfacial compatibility, thus demonstrating tremendous potential for fast development. Therefore, CSEs have become one of the effective ways to develop high-performance solid-state lithium batteries.15,21,24
In recent years, some scholars have developed a sequence of novel CSEs by introducing some functional materials or designing some special structures, and the ionic conductivities of these electrolytes have all been greatly improved.25,26 However, zero-dimensional (0D) inorganic nanoparticles are relatively short in length and diameter and cannot establish a certain range and continuity of interfacial ion channels. Furthermore, when these nanoparticles attain a critical level, it inevitably leads to severe agglomeration of the particles, which seriously hinders the transport of Li+ in bulk electrolyte.27 Accordingly, some researchers have successively designed and developed inorganic nanomaterials with one-dimensional (1D), two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) structures in terms of morphologies and structures. These structural designs are used to construct long-range continuous Li+ transport pathways and aim to solve the agglomeration problem. The application of 1D materials with high aspect ratios to SSEs and electrodes has become one of the most widespread and effective approaches.28 Moreover, both inorganic nanofibers and nanowires usually possess a relatively high aspect ratio in terms of their structures, thereby exhibiting similar physicochemical properties while their conduction mechanisms and preparation methods are analogous. Therefore, in this review, the introduction of both is combined for discussion. Compared to 2D nanosheets, inorganic nanofibers/nanowires can provide a higher specific surface area and add more active sites to effectively accelerate the reaction kinetics. Given that nanofillers can provide contact interfaces, they can create more lithium-ion transport ways with the polymer matrixes. Inorganic nanofibers/nanowires can be tightly stacked in terms of size and morphology to form 3D nanofiber network structures, which not only possess similar mechanical strength but also provide more continuous oriented and long-distance Li+ transport channels and reaction interfaces compared to one-piece 3D nanoframeworks. These advantages can synergistically improve the ionic conductivity and enhance the electrochemical stability of CSEs.29 Especially with the large-scale application of electrospinning technology, the study of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires in CSEs also has attracted significant attention.30 For example, in 2015, Chan et al.31 successfully designed and synthesized pure-phase polycrystalline LLTO nanowire active fillers with a good tetragonal structure for CSEs for the first time using electrospinning and calcination techniques. In the same year, Cui et al.32 discovered that a 3D Li+ conductive network connected by nanowires resulted in a three-fold increase in ionic conductivity for CSEs compared to that of composite electrolytes with added some nanofillers. These studies triggered a boom in the application of inorganic nanofibres or nanowires as fillers for SSEs. Since then, the further application of inorganic nanofibres in CSEs for solid-state lithium batteries also has emerged. For example, Hu and collaborators33 firstly synthesized Li6.4La3Zr2Al0.2O12 (LLZO) nanofibres and reported the fabrication of a solid-state composite electrolyte membrane reinforced with PEO-based polymer using 3D LLZO nanofibre networks, pioneering the use of continuous ionic conductors in polymer matrices, subsequently becoming an important direction in the development of membranes for CSEs.
In numerous studies, the results showed that inorganic fillers such as LLZTO,34 LZO,35 Al2O3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 36 and MgO37 exhibit superior properties compared to 0D materials after being prepared into different nanofibre morphologies through various means. Therefore, inorganic nanofibres/nanowires as fillers in SSEs for lithium batteries play a crucial role in facilitating the transportation of Li+ in CSEs, thus improving the chemical stability of the interface between the cathode or anode and the electrolyte and effectively inhibiting the growth of lithium dendrites. Recently, the development of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires has exhibited novel trends. In terms of morphology, researchers have increasingly focused on fabricating long-range continuous nanofibers/nanowires for providing efficient Li+ transport pathways. In regard to the strategies for the modification of nanofibers/nanowires, some researchers have primarily focused on the construction of heterogeneous structures to enhance the transmission rate of Li+.
36 and MgO37 exhibit superior properties compared to 0D materials after being prepared into different nanofibre morphologies through various means. Therefore, inorganic nanofibres/nanowires as fillers in SSEs for lithium batteries play a crucial role in facilitating the transportation of Li+ in CSEs, thus improving the chemical stability of the interface between the cathode or anode and the electrolyte and effectively inhibiting the growth of lithium dendrites. Recently, the development of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires has exhibited novel trends. In terms of morphology, researchers have increasingly focused on fabricating long-range continuous nanofibers/nanowires for providing efficient Li+ transport pathways. In regard to the strategies for the modification of nanofibers/nanowires, some researchers have primarily focused on the construction of heterogeneous structures to enhance the transmission rate of Li+.
In view of the wide range of applications and studies on inorganic nanofibers/nanowires in SSEs for lithium-metal batteries, it is particularly necessary to systematically summarize the results in this field. Numerous researchers have already conducted relevant works in this area, and there are many research-type articles reporting the application of inorganic nanofibres/nanowires in solid-state lithium-metal battery electrolytes. Furthermore, the advantages of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires in improving electrochemical performances have also been well demonstrated. However, although scholars have discussed inorganic nanofibers/nanowires for electrospinning SSEs, there are still limited comprehensive reviews on the methods for the preparation of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires and their applications in solid-state lithium batteries to date. Especially, a summary of the underlying mechanisms and structural designs related to ion transport, high-voltage stability of cell cathodes, anode protection and other functionalities of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires remains an unexplored territory. Based on this, as shown in Fig. 1, this review provides a comprehensive summary of the latest applications of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires in SSEs for high-performance lithium-metal cells. It primarily concentrates on the basic principles of lithium-ion transport, high-voltage and high-pressure resistance stability and anode protection in SSEs for lithium metal cells. Moreover, the common methods currently used for the preparation of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires and the relevant applications of inorganic nanofibers in SSEs for lithium-metal batteries are systematically summarized based on the classification of fillers used in inorganic nanofibers/nanowires. Finally, the future research directions to address some challenges in the application and commercialization of this technology are proposed. We firmly believe that this review will provide some novel ideas and inspiration for scientific researchers, academics and industry professionals investigating the application of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires in SSEs for high-performance lithium batteries. Furthermore, we are confident that with further advancements in research and development, numerous inorganic nanofibers/nanowires will find increasing widespread applications in SSEs for high-performance lithium batteries.
2. Mechanisms of inorganic nanofibres in solid-state lithium-metal battery electrolytes
The functional mechanism of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires in solid-state lithium batteries is mainly manifested in three aspects, including the transport mechanisms of lithium-ions, mechanisms of high voltage stability and mechanisms of cell anode protection. Clarifying the key functional mechanisms of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires in high-performance solid-state lithium batteries is conducive to a better understanding of their impacts on ion conductivity and interface stability. These important factors can provide some deep theoretical guidance and suggestions for the fast development of SSEs for solid-state lithium batteries with high energy density and safety.2.1 Transport mechanisms of lithium-ions
Designing high-performance SSEs requires a comprehensive understanding of the Li+ transport mechanisms. As early as the 20th century, some researchers predicted that the movement of polymer chain segments is related to ion transport and also proved that ion transport in PEO-based solid polymer electrolyte systems (often referred to as “salts in polymers”) occurs predominantly in their amorphous regions.38,39 Subsequently, Angell et al. conducted a thorough examination of the ionic transportation characteristics in PEO-based solid polymer electrolyte (SPE) systems, revealing a significant correlation between the Li+ transport and the dynamic behavior of the polymer chain segments.40 Nowadays, PEOs and their derivatives have been studied in-depth owing to the widespread use of “coupled” solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs).41–44 The ion transport mechanism is based on the strong affinity of the oxygen atom (–CH2CH2O–, EO) on the repeating unit of ethylene oxide to form complexes with metal ions, which can considerably promote the solubilisation of alkali metal salts. Moreover, the transport of lithium-ions through the coupling–decoupling of polymer chain segments can be realized, which is dependent on the segmental motion and local relaxation of the polymer chains.45 Influenced by the “salt-in-polymer” theory, Angell et al. also proposed the concept of “polymers in salt”, referring to the formation of “uncoupled” SSE systems using large amounts (>50 wt%) of low melting point lithium salts with high dissociation properties. Unlike the previously mentioned coupled systems, Li+ transport in the “uncoupled” system does not depend on the segmental motion of the polymer chains, but rather the interconnection of cation/anion clusters to form an ion-conducting network.46In inorganic solid-state electrolytes, the transport of lithium-ions is closely related to the defects present in the crystal structure such as point defects, line defects, plane defects, volume defects and electronic defects. Among them, point defects are one of the most significant factors affecting the transport of Li+. This study showed that the Li+ transport mechanisms in inorganic solid electrolytes mainly include the vacancy mechanism and the gap mechanism. The vacancy mechanism usually comprises a large number of vacancies generated by Schottky defects for lithium-ions to recycle and migrate, achieving the continuous transport of lithium-ions. In comparison, the gap mechanism mainly involves the diffusion of gap ions through Frenkel defects, which mainly occurs in lattices comprising larger skeleton atoms, where smaller-sized gap atoms jump from a gap position to another neighbouring position, successively displacing adjacent active sites to achieve diffusion between molecular skeletons.47,48 In addition, the lattice of the electrolyte may be distorted at the boundaries and near the interfaces, where lithium-ions will re-mobilise and re-arrange themselves according to the potential difference and create additional interfacial charge transport pathways.49
However, the migration paths of lithium-ions in CSEs are still controversial, and the determinants of the altered migration pathways and the migration mechanisms have not been presented and clarified to date, which has led to the lack of “unified” design and preparation (optimisation) principles for CSEs and also seriously hindered the development of CSEs. In this section, we explain how pairs of inorganic nanofibres/nanowires affect the lithium-ion transport behaviour mainly from three aspects including Lewis acid–base interactions, interfacial transport theory and built-in electric field.
The preparation of inorganic ceramic particles containing Lewis acidic or basic sites as 1D inorganic nanofibres/nanowires has wide-ranging applications in CSEs. The surface of inorganic nanofibres can provide continuous acidic or basic groups, which can construct continuous and uniform lithium salt dissociation interfaces and lithium-ion transport pathways through Lewis acid–base interactions, and it is easier to reduce the energy barrier between fillers. Moreover, the elevated specific surface area with the introduction of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires effectively diminishes the crystallinity of the polymer matrix, thereby fostering enhanced chain segment mobility within the polymer structure, and thus facilitating the efficient transportation of lithium-ions. For example, Chan et al.55 introduced LLZO nanowires in the PAN/LiClO4 electrolyte system and observed a significant enhancement in ionic conductivity by three orders of magnitude (reaching 1.31 × 10−4 S cm−1) at room temperature, with a mere 5 wt% content of LLZO nanowires, as presented in Fig. 2a1. According to the Lewis acid–base interaction theory, they speculated that the LLZO nanowires may attenuate the interaction of PAN with Li+ through the acidic or basic groups on their surface, thus significantly producing more free Li+ at the interfaces. Moreover, LLTO nanofibers also have higher ionic conductivity than that of LLTO nanoparticles due to the advantage of long-range continuous lithium conduction.
 | ||
| Fig. 2 Transportation mechanisms of lithium-ions. (a1) Images comparing the ionic conductivity LLZO nanowires doped with different elements and SEM images of the prepared sample.55 Copyright 2017. Reproduced with permission from the American Chemical Society. (a2) Galvanostatic cycling of LFP/Li cells at 0.5C and 50 °C.59 Copyright 2022. Reproduced with permission from Elsevier. (b1) Molecular configuration of LiTFSI and the CeO2 interface at the onset of DFT-MD simulation and subsequent to the simulation.52 Copyright 2021. Reproduced with permission from Elsevier. (b2) Organic–inorganic interface facilitates lithium-ion transport.63 Copyright 2023. Reproduced with permission from Wiley-VCH. (c1) Schematic diagram of BTO–LLTO synergistic promotion of lithium salt dissociation and Li+ transport.68 Copyright 2023. Reproduced with permission from Springer Nature. (c2) Graphical illustrating the process by which BIT–BOB HNFs enhance lithium salt ionization and expedite the movement of Li+.69 Copyright 2023. Reproduced with permission from Wiley-VCH. | ||
Metal oxides including rich oxygen vacancies can also provide a multitude of Lewis acid sites, and the positively charged oxygen vacancies on their surfaces can further enhance the electrostatic adsorption with the anions present in lithium salts as Lewis acid sites considerably enhancing the mobility of dissociated Li+ through PEO chains. Thus, building a lithium-rich environment at the organic–inorganic interfaces becomes rather important.56,57 Furthermore, a CSE with both robust mechanical properties and exceptional ionic conductivity was prepared by compositing lanthanum cobaltate (LaCoO3) nanowires with dendritic sulfonated polyethersulfone nanofibrous membranes. The large number of oxygen vacancies and Lewis acid sites in the uniformly distributed LaCoO3 nanowires could effectively adsorb anions, while the resulting 3D structure increasing the effective contact interface between ions and PEO and promoting the Li+ transport along the nanowire interface.58 Based on the above-mentioned work, 1D lithium-doped magnesium oxide (LMO) nanofibres with reactive surface defects were introduced into the PEO/LiTFSI system. The presence of oxygen vacancies on the surface of LMO, together with the establishment of Li–N and Li–O bonds considerably enhanced the adsorption of TFSI− on the nanofibres, thereby facilitating the dissociation of the lithium salts. Moreover, the doped lithium-ions exposed near the oxygen vacancies could separate from the lattice and aid in building lithium-dense areas. Given these merits, the CSE achieved the remarkable ionic conductivity of 1.48 × 10−4 S cm−1 at 30 °C, together with excellent long cycling stability, as depicted in Fig. 2a2.59
In conclusion, a multitude of experimental evidence and simulations have demonstrated that fast Li+ transport interfaces can be realized. However, there is no clear explanation for the mechanism of Li+ transport via inorganic–organic interfaces. Based on related studies, we hypothesize that the following factors may be responsible: (1) there are complex interactions among the polymer chains, inorganic filler surface groups and lithium salts. At the macro level, the primary significance of inorganic fillers mainly lies in adding amorphous regions in the polymer matrix and elevating the count of mobile polymer chain segments. At the microscopic level, inorganic additives can provoke alterations in the dynamics of ion transportation. As a consequence of Lewis acid–base interactions or hydrogen bonding interactions, the addition of inorganic fillers can create some polymer–filler interfaces, establishing new lithium-ion transport channels. (2) The electronic interactions between the organic and inorganic constituents can effectively lower the energy barrier required for lithium-ion migration. (3) The overlap of the space charge regions between neighboring active particles also allows the formation of conductive ions in the absence of close physical contact conditions to form conductive pathways. Although the deeper mechanism of interfacial transport of lithium-ions is still unknown, it presents significant guidance and suggestions in the structural design of advanced CSEs. For instance, the incorporation of nanofibres with high aspect ratio and large specific surface area and the construction of three-dimensional nanofiber networks have an excellent effect on increasing the area of the inorganic ceramic filler and polymer, greatly increasing the lithium-ion transport interfaces.62 Furthermore, the incorporation of sub-nanometer (diameter less than 1 nm) inorganic cluster chains with an outstanding aspect ratio can provide more polymer contact sites. These monodisperse cluster chains are interwoven to form staggered interconnected 3D structures, resulting in homogeneous, wide-range and continuous all-active Li+ conduction networks. Overall, the formed network facilitates the rapid transport of Li+ (ref. 63) (Fig. 2b2).
According to the interfacial transport theory, it is known that fibre–polymer interactions can form facilitated lithium-ion transport interfaces distributed along the nanofibres. The construction of randomly aligned nanofibres results in the formation of continuous and fast long-range Li+ transport channels. However, the number of effective transport channels perpendicular to the electrode direction can be reduced. Compared with other structures, inorganic nanofibers with a vertical electrolyte membrane oriented arrangement show some significant advantages. On the one hand, their unique arrangement effectively reduces the interfacial impedance. On the other hand, they considerably improve the transport efficiency by constructing continuous and short transport channels for lithium-ions. All these merits can ensure the existence of multiple consecutive ionic transport paths along a specific direction, thus greatly improving the ion conduction efficiency. Furthermore, the formed structure also can effectively shorten the ion diffusion pathway and avoid the potential waste of space resulting from the parallel arrangement of nanofibres on the electrolyte surface.64 For instance, Li and colleagues65 successfully crafted a vertically oriented LLTO nanowire composite integrated with PEO/LiClO4–PEG, aiming to obtain high-performance SSEs. This innovative framework boasted an impressive ionic conductivity of 4.67 × 10−4 S cm−1 at ambient temperatures. In addition, Hu et al.66 combined functionalized seafoam using magnetic field-oriented vertically aligned (KFSEP) nanowires mixed with PEO to prepare a CSE with high ionic conductivity. The prepared nanowires were vertically aligned in the PEO matrix under the action of a magnetic field, which endowed the electrolyte with excellent ionic conductivity. The corresponding experimental and simulation analyses also both corroborated that the swift ion transport pathways within the prepared KFSEP nanowires can offer enhanced ionic conductivity for CSEs. Additionally, the prepared KFSEP nanowires were proven to play a pivotal role in significantly suppressing the formation of lithium dendrites.
In summary, additional in-depth and methodical investigations are essential for the conductive properties of CSEs, building on the comprehensive theoretical analyses and precise experimental assessments. By developing more refined theoretical frameworks and the accumulation of experimental data, it is expected to comprehensively reveal the conductive mechanisms of lithium-ions for solid polymer electrolytes, thereby providing more solid scientific support and theoretical basis for optimizing their performance and broadening their application scope.71
2.2 Mechanisms of high voltage stability
The majority of SSEs exhibit a limited electrochemical stability window, making them incapable of functioning across the entire potential range of both cathode and anode materials. When SSEs are in substantial contact with some materials with good electrical conductivity, transition metal ions originating from the anode or conductive carbon are capable of triggering and facilitating the oxidative decomposition of SSEs under elevated voltage conditions. Typically, in high-performance lithium metal solid-state batteries, the degradation of SSEs predominantly takes place at the interfaces between the cell cathode and electrolyte, and the formation of a high ion-conducting, low electron-conducting interface can greatly help inhibit the decomposition process. On the cathode side, the formation of interfaces by electrochemical reactions mainly occurs during the charge–discharge processes, and the reaction behaviors that occur between different electrolytes and various cathode materials have some differences, while various battery pre-treatment conditions also greatly affect the occurrence of reactions. Therefore, the electrochemical reactions between different electrolytes and cathode materials are more complex when various electrolytes and cathodes are applied.Firstly, there is a strong positive correlation between the high-voltage stability of inorganic solid electrolytes and the oxidative stability of their anionic frameworks, which is usually limited to the anion with the lowest ionization potential, following the general trend of nitrides < sulfides < oxides < chlorides.72 Secondly, chemical bonding and specific structure affect their high-pressure stability. For example, in the case of Li3PO4 and Li3PS4, the formed P–O bond can be weaker than the P–S bond, and therefore Li3PO4 is more resistant to oxidation than that of Li3PO4. Also, the decomposition of polymer electrolytes may begin at the formed interfaces.73 The typical polymer electrolytes (e.g., PEO) have a low electrochemical window (<4.2 V) and are commonly used in low-voltage LiFePO4 (LFP) applications. When a high-voltage cathode electrode is introduced, the polymer matrix can be oxidized owing to the instability of the functional groups of the PEO molecular chains. As demonstrated by Sun et al.,74 the primary factor contributing to the instability of a PEO polymerized electrolyte even under high voltage was the –OH functional group on its molecular chain rather than the –C–O–C bond, which was typically considered (Fig. 3a1). Replacing the –OH functional group on the molecular chain of PEO with the –OCH3 functional group has also been demonstrated to effectively improve the durability of PEO materials during high-voltage charge–discharge cycles. The application of organic–inorganic composite electrolytes can effectively augment the stability under high-voltage conditions to a notable degree. This phenomenon is primarily attributed to the inorganic additives, which alter the interactions between the lithium-ions and polymer chains, consequently elevating the decomposition voltage of CSEs. The organic constituents within CSEs are capable of engaging in the creation of an interfacial layer at the anode/electrolyte junctions, thereby further enhancing the stability of the anode/electrolyte interfaces.75,76 Therefore, in the case of inorganic solid-state electrolytes, the high-voltage stability of electrolytes can be enhanced by screening suitable anionic backbones such as chloride and fluoride. For instance, AlF3 has been extensively reported owing to its significant advantages in maintaining the electrode/electrolyte stability, and considerably enhancing the electrochemical properties of cathode materials.
 | ||
| Fig. 3 Mechanisms of high voltage stability. (a1) Illustrative representation of the electrochemical oxidation mechanism of ether-based polymers under high-voltage conditions.74 Copyright 2020. Reproduced with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry. (a2) Structure and principle of SPEs in solid-state lithium batteries.77 Copyright 2020. Reproduced with permission from the American Chemical Society. (b1) Schematic illustration of LIPF6-based electrolyte forming a solid superacid around LiCoO2 particles.82 Copyright 2006. Reproduced with permission from Electrochemical Society, Inc. (b2) Schematic diagram of average charge and discharge voltages.83 Copyright 2006. Reproduced with permission from Electrochemical Society, Inc. (c) Schematic structure diagram of ASSLBs assembled using AHPAA–PEO–LiTFSI SSEs.88 Copyright 2023. Reproduced with permission from Elsevier. | ||
In the case of polymer electrolytes, the selected polymers with high electrochemical stabilities (e.g. PPC, PVDF, PAN, PEGDE, PMMA, and PVC) can be employed to completely replace or partially replace PEO-based polymer electrolytes, thereby greatly enhancing the oxidation resistance. Furthermore, the use of CSEs can enhance the high-voltage resistance of SSEs. In this regard, we can employ a multitude of strategies, as follows: (1) adding functional fillers to the polymer to construct a composite electrolyte, such as adding high-voltage-resistant inorganic functional fillers and functional electrolyte additives; (2) incorporating lithium salts with elevated voltage stability to the electrolyte adjacent to the cathode region; and (3) introducing an interfacial modification layer between the cathode/electrolyte to construct an ideal interface with high ionic and low electronic conductivity, such as coating the surface of the cathode electrode with a buffer layer or introducing a stabilizing artificial interlayer, such as LLZO coating layer, as shown in Fig. 3a2.77 Simultaneously, these strategies can substantially reduce the decomposition of SSEs at high voltages.78,79
Another strategy is to modify the interfaces with an electrolyte additive. Some additives typically have higher ability to occupy the molecular orbitals (HOMO) than the electrolyte solvents and lithium salts. Consequently, it is probable that they will be oxidised prior to the main electrolyte components during the charging processes, creating a decomposition layer atop the surface of the cathode electrode, thereby significantly preventing the further decomposition of the electrolyte. Currently, some scholars have explored some functional additives suitable for different cathodes such as Li2CO3 and Al2O3 additives suitable for the LiCoO2 cathode81,82 (Fig. 3b1). Also, incorporating a modest amount of the fluorine-enriched compound di-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)carbonate as an additive in high-voltage electrolytes can also substantially mitigate the voltage-induced degradation and preserve the structural integrity of the cathode83 (Fig. 3b2). Although electrolyte additives play a very important role in the protection of high-voltage positive electrodes, single-component electrolyte additives still have a single form of action in applications and are not highly adaptable. Therefore, the development of multifunctional and hybrid electrolyte additives can be considered, and thus the electrolyte additives can have a variety of functions at the same electrode and be applied to various electrodes. Conversely, the stability of the electrode/electrolyte interfaces can be enhanced more effectively through the synergistic effect between different functional additives in the electrolyte.
Employing an inorganic buffer layer for interfacial modification is a promising approach to considerably mitigate elemental inter-diffusion and enhance electrochemical efficiency. The prepared buffer layer functions as a physical barricade, promoting the creation of two novel and dependable interfaces between the electrolyte and anode of the cell. For example, Wang et al.84 constructed an Li2.3C0.7B0.3O3 (LCBO) interface with excellent electrochemical performance through the in situ reaction between Li2.3C0.7B0.3O3 and Li2CO3 coating during sintering treatment. The produced interfacial phase can facilitate intimate contact between the formed LLZO@Li2CO3 and LiCoO2@Li2CO3, thereby ensuring that good interfacial compatibility between LiCoO2 and LLZO can be realized. Also, it is highly likely to further improve the cycling performance by enhancing the mechanical strength of the cathode composite. For instance, the application of LLZO nanowires as the reinforcing phase for the prepared SSEs to maintain the structure stability of the cycled electrode.
Although the modification of rigid inorganic coating layers can effectively mitigate the issue between the cathode/electrolyte interfaces to a certain extent, it remains challenging to achieve sustained physical contact during the cycling process. However, the application of functional polymer materials can effectively form a buffer layer on the surface of the cathode, which is more conducive to avoiding side reactions and substance diffusion at the cathode/electrolyte interfaces. Concurrently, due to the soft nature of polymers, they are effective in realizing close contact at the solid–solid interfaces, thus greatly reducing dynamic interfacial stresses.85,86 For example, Cui et al. synthesized a poly(ethylene cyanoacrylate) (PECA) buffer layer in situ on the surface of LiCoO2via a simple low-temperature polymer coating method.87 The introduction of the PECA coating layer could greatly reduce the oxidizing ability of LiCoO2 and considerably suppresses the sequential decomposition of lithium meso-difluoro(oxalate)borate (LiDFOB) salts in the PEO-based electrolyte. Consequently, the assembled PECA-coated LiCoO2/PEO-LiDFOB/Li cells exhibited reduced interfacial resistance and enhanced cycling stability during high-voltage cycling in comparison to the assembled LiCoO2/PEO-LiDFOB/Li cells.
Furthermore, in the design of the electrode/electrolyte interfaces, achieving concurrent electrochemical stability at both the cathode/electrolyte and anode/electrolyte interfaces can also be effectively addressed by introducing a variety of functional interfacial modification layers, creating asymmetric layers. This approach provides a practical solution for enhancing the stability across these critical interfaces. Based on this idea, as shown in Fig. 3c, our group also proposed an asymmetric structure for CSEs for high-performance ASSLBs88 and designed and prepared an asymmetric bi-functional CSE, which simultaneously achieved the compatibility of Li anode and high voltage cathode. The hierarchically structured fluorine-containing nanofiber membrane in the electrolyte was oriented toward the cell cathode, which endowed the CSE with excellent antioxidant capacity. The Al2O3 nanoflake layers formed and encapsulated on the lithium–anode interface engage with the PEO terminal groups, thereby significantly enhancing the stability of the PEO-based electrolyte and effectively suppressing the increase of lithium dendrites. The asymmetric structure exerted a synergistic effect, greatly broadening the electrochemical stabilization window (5.3 V) and improving the cycling stability of the cathode (LFP and NCM811)/Li cells. After enduring over 800 cycles, the reversible specific discharge capacity attained a noteworthy value of 104.7 mA h g−1, further proving the promising application of the asymmetric structure in matching high-voltage cathodes.
2.3 Mechanism of anode electrode protection
Due to the continuous progress in characterization techniques, a growing number of researchers have delved deeper into elucidating the underlying mechanism of lithium dendrite formation in state-of-the-art solid-state lithium batteries. In inorganic solid-state electrolytes, lithium dendrite growth mainly depends on the following factors: (1) the presence of some defects within the electrolyte, such as grain boundaries,89 holes, and pinholes; (2) inhomogeneities in the surface morphology90 including cracks,91 protrusions and impurities;92 and (3) high electronic conductivity.93 In polymer electrolytes, the relatively low ionic conductivity and poor mechanical strength of polymers are believed to be the main reasons for the growth of lithium dendrites and their eventual puncturing of the prepared electrolyte.94 In addition to the above-mentioned factors, some properties of lithium metal itself, such as its significant volume change during charge–discharge processes, its susceptibility to side reactions, and the lack of lithium metal surface flatness, are also significant reasons contributing to the severe growth of lithium dendrites.95–97 Therefore, the anode protection of solid-state lithium batteries mainly depends in the improvement of the SSE itself, the anode/electrolyte interface modification and the optimized design of the anode of high-performance lithium metal cell.The issue of lithium dendrite growth in inorganic SSEs can be resolved by reducing the internal defects, adding insulating substances to reduce their electronic conduction, electrolyte surface treatment and introducing coating layers at the electrolyte/anode interfaces. As depicted in Fig. 4a1, Sun and co-workers98 introduced a technique to mitigate the elevated electronic conductivity of inorganic solid-state electrolytes by incorporating insulating LiF into LiBH4-based SSEs. Furthermore, Wang et al.99 combined LiF and Li3N materials to prepare Li3N–LiF composite coatings to inhibit the growth of lithium dendrites by enhancing the nucleation energy (Fig. 4a2). In another instance, Botros et al.100 also successfully developed a uniform and dense inorganic solid-state electrolyte. Through the rapid high-temperature sintering technique, the growth size of the grains could be effectively controlled, while the porosity of the electrolyte could also be significantly reduced, thus effectively preventing the occurrence of structural defects within the final electrolyte. However, the structure of the polymer electrolyte differed from the prepared inorganic solid electrolyte, and its soft characteristics were not conducive to effectively inhibiting the growth of lithium dendrites. Accordingly, the initial step is to enhance the mechanical strength of the fabricated polymer electrolytes. In addition, the ionic conductivities of these electrolytes can be further enhanced, facilitating the fast and uniform deposition of Li+ on the anode side. Finally, the construction of functional interlayers between the cell electrolyte and anode, as well as the functional modification of lithium metal are also common strategies to significantly hinder the significant growth of lithium dendrites.
 | ||
| Fig. 4 Mechanism of anode electrode protection. (a1) Schematic diagram of lithium dendrite formation in normal SSE and inhibition in modified SSE system.98 Copyright 2019. Reproduced with permission from Wiley-VCH. (a2) Depiction of the Butler–Volmer mechanism for lithium deposition in SSEs.99 Copyright 2020. Reproduced with permission from Wiley-VCH. (b) Schematic illustration depicting the mechanical strength properties and lithium dendrite inhibition of three CPEs.102 Copyright 2024. Reproduced with permission from Wiley-VCH. (c) Structural visualization captured by MD simulations showcasing swift Li+ movement within a Li–Cu–CNF composite.107 Copyright 2021. Reproduced with permission from Springer Nature. (d) Differences in charge density and the corresponding plane-averaged electron density between the initial state and the deformed state of BIT NFs.110 Copyright 2022. Reproduced with permission from Elsevier. | ||
According to the above-mentioned works, the incorporation of 1D nanofibers/nanowires can effectively circumvent the isolated, sporadic distribution of nanoparticles within the polymeric matrix, and thereby the degree of aggregation of the inorganic fillers in the polymer matrix and the concentration gradient of Li+ can be reduced. However, the agglomeration effect between nanofibers/nanowires remains unavoidable. The formation of an interconnected 3D nanofiber/nanowire network can well address the issue of aggregation, thereby greatly improving the ionic conductivity of CSEs and reducing the Li concentration gradient. For example, Guo et al.108 introduced 3D LLZO inorganic nanofibers in the PEO/LiTFSI system to prepare 3D LLZO-PEO CSEs. Due to the continuous LLZO cross-linked network for enhancing the interfacial contact area between LLZO and PEO, as well as constructing a long-range space-charge layer region, the final CSE exhibited the excellent room-temperature ionic conductivity of 3.2 × 10−4 S cm−1 and excellent Li+ mobility number of 0.33, both of which were much higher than that of the CSE of LLZO nanoparticle composite with PEO/LiTFSI. Despite the development of various 3D skeletons and their applications in CSEs to enhance the Li+ transport and mitigate the Li+ concentration gradients, their ionic conductivities often fall below 10−3 S cm−1, especially at room temperature. Therefore, there is an urgent requirement for novel ideas and approaches.
In contrast to the conventional approach of inserting a separate interlayer between the electrolyte and electrode, the innovative strategy of directly engineering an in situ protective coating on the lithium anode surface can also offer a novel modification, which can tackle the challenges posed by building an electrolyte/lithium metal interface in a more direct and effective manner. Recently, some researchers also treated 1D inorganic nanofibers on the Li anode surface. The objective was to leverage the high specific surface area of the inorganic nanofibers and their capacities to provide continuous, rapid and uniform lithium conduction pathways for achieving an effective combination of filler components with the lithium metal matrix. For example, Luo et al.114 introduced TiO2 nanofibers into the lithium anode and generated a lithiated TiO2 composite anode (Li–TiO2) in situ on the surface of metal lithium. Li–TiO2 formed a seamless interfacial contact with LLZTO, which made the interfacial resistance much smaller than that of the pristine lithium metal. Furthermore, the prepared Li–TiO2 exhibited a significant role in bolstering the interfacial wettability. Notably, the symmetric Li–TiO2||LLZTO||Li–TiO2 cells demonstrated an impressive critical current density of 2.2 mA cm−2, and the assembled Li–TiO2||LLZTO||LFP full cells also exhibited robust cycling stability.
3. Inorganic nanofiber preparation methods
3.1 Electrospinning method
Among the numerous preparation methods, electrospinning technology is one of the most promising methods for the preparation of 1D nanostructures due to its simple operation, easy preparation and combination with different components to efficiently synthesize composite nanofibers with high porosity and good flexibility.115–117 The underlying principle is that under the influence of a high-voltage electric field, the droplets of the spinning liquid can overcome the surface tension and form a fine jet stream. As shown in Fig. 5a1, during the jetting process, the solvent is evaporated or solidified. Subsequently, a nanofiber material can be formed on the spinning receiver.118,119 Typically, the preparation of inorganic nanofibers begins with the mixing of inorganic nanoparticles with organic components to form a mixed spinning solution. Subsequently, the mixed solution can be spun into nanofibers as precursors using electrospinning technology. Finally, the organic composition can be removed through a high-temperature calcination step, resulting in the formation of inorganic nanofibers. Similarly, Li et al.120 designed and prepared the LLTO nanofibers via electrospinning and calcination processes, which were used in solid polymer electrolytes after compositing with the PEO/LiClO4 matrix. However, although electrospinning has a wide range of applications, it also has several inherent drawbacks. The most common issues are the safety risk of high electric fields, the difficulty of obtaining a precisely controlled scaffold morphology, low productivity and the wide application of halogenated and toxic solvents.121,122 Consequently, numerous enhanced technologies have been developed and applied in the preparation of various functional electrolyte. | ||
| Fig. 5 Methods for the preparation of inorganic nanofiber. (a1) Schematic illustration of the electrospinning setup to prepare various 1D nanostructures.119 Copyright 2021. Reproduced with permission from Elsevier. (a2) Schematic diagram of electro-blown spinning equipment. (b1) Schematic depicting the synthesis pathway and characterization process of Mg2B2O5 nanowires and (b2) schematic representation of Li+ transport enhancement in SSEs utilizing Mg2B2O5.104 Copyright 2018. Reproduced with permission from the American Chemical Society. (c1) Diagrammatic illustration of SSE and ASSLB based on HAP fiber membranes and (c2) schematic diagram of deposition of Li+ from HAP–PEO SSE and conventional liquid electrolyte to lithium anodes.136 Copyright 2020. Reproduced with permission from the American Chemical Society. | ||
As is known, the coaxial electrospinning process represents an advancement over the conventional single-needle spinneret, which is primarily due to the incorporation of one or more coaxial needles within the spinneret. This design allows the injection of two or three distinct polymer solutions into the inner and outer flow channels, respectively. Under a high-voltage electric field, the coaxial spinning solution streams are elongated to form composite fibers possessing a distinct “core–sheath” structure.123,124 For example, our group also reported the fabrication of a PVDF–PEO composite nanofiber membrane with a core–shell structure developed using coaxial electrospinning, which helped to facilitate the formation of 3D ionic conductive networks in polymer-based solid electrolytes.125 Although coaxial electrospinning technology has some significant advantages in terms of special structural designs, there are still some issues that need to be considered. For example, the inner and outer layers of the spinning liquid cannot react in the coaxial spinning process. Additionally, the viscosity of the two layers must be similar. In the parameter setting, the outer layer of the flow rate can be greater than the inner layer to prevent the formation of droplets.126,127
Needleless electrospinning technology can also enable the spinning liquid to fully cover the spinning roller by adjusting the feeding method during the electrospinning process. Under the influence of a high-voltage electric field, the spinning liquid on the spinning roller is ejected from the microporous holes to form nanofibers. The applied method not only significantly improves the spinning efficiency, but also successfully avoids the complex problems of needle-to-needle interference and cleaning in multi-needle electrospinning.124,128 For example, Chan et al.129 designed and prepared precursors of Al-doped LLZO using the needleless electrospinning technique and subsequent calcination. In contrast to single-needle electrospinning, needless electrospinning requires a much lower viscosity of the spinning solution, which is also more affected by environmental factors. For example, during the spinning process, the generation of a significant number of solution jets in a confined space can lead to a series of safety issues. Additionally, a larger liquid surface can increase the uptake of moisture from the atmosphere, diluting the spinning solution, and finally affecting the quality of the spun fibers.130
Side-by-side electrospinning technology refers to the technique of performing electrospinning using side-by-side syringe needles. The applied technology can enable the production of nanofibers with two polymers coexisting on the cross-section of the same fiber. The resulting composite membrane can retain some advantages of a single component, while exhibiting superior performance through the synergistic effect of the two components.131 For example, as mentioned earlier, Kang et al.68 also successfully constructed a nanowire composite (BTO–LLTO) with a side-by-side heterostructure consisting of BaTiO3 and Li0.33La0.56TiO3−xvia the side-by-side electrospinning method combining their merits. Between them, the polar dielectric BaTiO3 could significantly enhance the dissociation of lithium salts, leading to the production of a higher concentration of mobile Li+, ultimately achieving efficient Li+ transport combining LLTO with excellent lithium-ion conductivity.
In recent years, electro-blown spinning (EBS) technology combined with a carbonization process has gained recognition as an efficient and continuous approach for the preparation of inorganic nanofibers, offering some advantages such as convenience, safety and controllability.132,133 EBS technology is an innovative improvement based on the traditional electrospinning technology through the use of a high-velocity airflow field. As shown in Fig. 5a2, during the spinning process, the spinning liquid is subjected to the stretching action of a high-pressure air stream from compressed air and splits under the action of electric field force and Coulomb force. This technique can effectively promote fiber refinement and the formation of a uniform nanofiber structure. Also, some related studies have shown that EBS technology can significantly enhance the spinning efficiency.134,135 Considering these findings, numerous scholars have actively explored the application of EBS in the preparation of inorganic nanofibers. For example, our group innovatively prepared MgO nanofibers and MgF2 nanofibers using EBS combed with calcination processes. Also, the prepared inorganic nanofibers were applied for the first time in high-performance solid-state lithium batteries. Due to the functional nanofibers with a high aspect ratio, the prepared CSEs possessed continuous conductive pathways.37
3.2 Direct calcination method
Calcination is a process that can selectively build a specific crystalline form or composition of compounds by reasonably regulating the temperature and adjusting the gas-phase constituents in a high-temperature environment. Also, the calcination procedure can be employed to eliminate impurities and enriching useful groups. As shown in Fig. 5b1 and b2, Tao et al.104 prepared Mg2B2O5 nanowires for SSEs via the direct calcination method by mixing MgCl2·6H2O, Na2B4O7·10H2O, KCl and NaCl as raw materials in a certain ratio and grinding them well. The incorporation of Mg2B2O5 nanowires significantly enhanced the ionic conductivity of the final SSEs. Furthermore, their inherent high strength and excellent flame retardant properties also effectively improved the mechanical and flame retardant properties of the prepared SSEs, respectively, therefore further enhancing the safety and reliability of the assembled batteries. However, although the direct calcination method has some applications in the synthesis of inorganic nanofibers for SSEs, there are fewer related studies on this topic. The majority of scholars still use the electrospinning method to firstly prepare the fiber precursor. Afterward, the calcination process is employed to purge organic components, yielding pure and functional inorganic nanofibers for high-performance solid-state lithium batteries.3.3 Hydrothermal method
The hydrothermal method, as nanomaterial preparation technology, has been widely applied for the preparation of materials. Also, the core of the hydrothermal method is the use of water or other solvents in a sealed container as the reaction medium to dissolve and recrystallize substances that are insoluble in water at room temperature and pressure under specific temperature and pressure conditions. This preparation method has a broad spectrum of applications in the preparation of 1D materials. As depicted in Fig. 5c1 and c2, Xu et al.136 designed and synthesized a self-supported hydroxyapatite (HAP) nanowire membrane for PEO-based SSEs via the hydrothermal method. The obtained results showed that the HAP membrane hybridized polymer electrolyte had enhanced properties such as good ionic conductivity, excellent Li+ mobility number, wide electrochemical window and outstanding resilience to extreme temperatures. The hydrothermal method for the preparation of inorganic nanofibers also has some advantages including cheap raw materials and easy process to obtain the appropriate crystalline form. However, several hydrothermal methods still require harsh reaction conditions including the requirement of high temperatures and pressures, which not only consume a significant amount of energy, but also pose a risk of causing a series of safety issues. All these factors can impede its further and fast application in the preparation of inorganic nanofibers to a certain extent.3.4 Template method
The template approach can serve as a potent technique for fabricating nanomaterials, where utilizing the template as a carrier enables precise manipulation of the morphology, configuration and dimensions of nanomaterials. This method can realize the integration of nanomaterial synthesis and assembly, while the problem of dispersion stability of nanomaterials can also be effectively addressed. In recent years, templating using nanofibers such as cellulose nanofibers also has shown great promise as a template method. For example, in the case of cellulose fibers, the main process is as follows: the cellulose material is impregnated in a solution containing ceramic precursors (usually in the form of metal salts), which causes them to be fully absorbed, finally forming a mixture with cellulose as the skeleton and the ceramic precursor solution as the filler. Next, the organic components in the mixture are effectively removed through a calcination process, resulting in the formation of inorganic nanofibers enriched with the desired ceramic components.137 For example, Wang et al.138 reported the synthesis of an anode material for lithium batteries using bacterial cellulose nanofibers (BC) as a template. By coating the BC surface with SnCl2 particles and removing the cellulose template via a calcination process, a 3D conductive skeleton for supporting the lithium anode could be obtained. Thus, a 3D porous anode structure was constructed to maintain the structural stability, which can be applied in SSEs for solid-state lithium metal batteries in the future.Besides serving as a cell electrode, the cellulose template method has also been used for the construction of 1D structures in CSEs. For example, Hu et al.139 grafted the metal adsorbent EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) with cotton cloth as a template for the adsorption of metal ions, which was subsequently immersed into the LLZO precursor solution for full absorption. Finally, after the calcination process, structurally stabilized LLZO ceramic fabrics, together with a double-layer cast composite solid electrolyte, were successfully crafted. The fabricated ceramic fabric retained the macroscopic shape and microscopic details of the original cotton fabric, while maintaining a well-ordered, long-range structure in the composite materials. The optimized architecture significantly aided in the rapid diffusion of lithium-ions, thus enhancing the ionic conductivity of the composite electrolyte and greatly improving its cycling stability. However, although the template method also has some applications in the preparation of 1D materials, it is usually constrained by the size of the template and the generally polycrystalline structure of the prepared nanowires. Also, these factors can have uncertain effects on the properties of the nanowires, thus limiting their wide applications.
3.5 Vapor deposition method
Physical vapor deposition (PVD) mainly involves the physical vaporization of a metal source under vacuum, followed by its deposition on the surface of a substrate to achieve the desired structural formation. PVD has some advantages such as low pollution and fewer consumables. Moreover, the morphology of the resulting product can be precisely adjusted by manipulating the crucial process parameters including heating temperature, substrate temperature, metal source concentration and carrier gas flow rate. Also, glancing angle deposition (GLAD), a type of PVD, differs from the conventional PVD, in which the target and substrate surfaces are tilted rather than aligned parallel, greatly aiding the preparation of tilted nanowire arrays. For example, Kim et al.140 successfully designed and fabricated well-aligned inclined LiCoO2 nanowires as 1D nanostructured cathodes using the GLAD method, which solved the problem of the conventional methods requiring additional etching/post-annealing steps and producing poorly dispersed and aligned nanostructures. The prepared LiCoO2 film was characterized by low thickness (∼500 nm) and high porosity, which facilitated the achievement of close contact between the solid-state electrolyte (SSE) and the cathode, effectively minimizing the stress and strain resulting from significant volume changes during the cycling of the battery. The results showed that the performance of the solid-state lithium metal battery assembled from the LiCoO2 nanowires electrode was significantly improved in terms of rate capability and long-term cycling stability.Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is essentially gaseous mass transfer technology in the air. The principle is that the gaseous or vaporous precursor reactants produce physical or chemical phenomenon under external high temperature conditions, and then diffuse into the deposition area, nucleate and crystallize at the deposition site, finally growing the corresponding nanomaterials. CVD is a commonly used method for preparing 1D nanomaterials. This process requires simple equipment and is an easy operation. Furthermore, the prepared materials are characterized by high purity and good dispersion and uniformity. The morphology of nanowires can be reasonably controlled by adjusting the process parameters such as metal source types, substrate types and various heating temperatures. For instance, Xie and colleagues141 developed a novel composite anode comprised of carbon-coated silicon nanowires (SiNW/GM) on the surface of graphite microspheres, utilizing chloromethylsilane as the silicon source through the CVD process. After undergoing carbon coating, the fabricated C/SiNW/GM composites displayed noteworthy electrochemical characteristics, demonstrating a substantial specific capacity of 580 mA h g−1 and an initial coulombic efficiency of 76.2% following 100 cycles at a current density of 0.2C. However, although the CVD method exhibits greater flexibility in operation compared to the PVD technique, it still suffers from a slower deposition rate. Additionally, in numerous instances, the reactive sources involved in the deposition process and the residual gases post-reaction pose safety concerns due to their flammability, explosive nature or even toxicity.142 Also, it is necessary to treat the exhaust gas, which can pose a significant challenge to environmental sustainability. Although the PVD and CVD methods have been widely used to prepare 1D nanowires for solid-state lithium batteries, there are still few studies related to their direct application in SSEs. Accordingly, future improvements in modified PVD and CVD technologies are expected for their wide application in the preparation of inorganic nanofibers for the SSEs of solid-state lithium batteries.
4. Application of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires in SSEs
To overcome some challenges encountered in solid-state lithium batteries at ambient temperature, especially low ionic conductivity, severe lithium dendrite growth and poor stability of electrode/electrolyte interfaces, some scholars have proposed various solutions in recent years, as follows: (1) adopting some electrolyte materials with high-conductivity of lithium-ions to evenly distribute their flow, and significantly suppressing lithium dendrite growth by reducing the local current density. (2) Incorporating a protective layer at the interface between the cathode/electrolyte or anode/electrolyte. (3) Based on 0D nanoparticle fillers, constructing 1D, 2D and 3D structures to provide long-range continuous lithium-ion transport pathways. As a representative of 1D materials, the applied nanofibers/nanowires have been used extensively in functional electrolytes of solid-state lithium batteries. Given that various functional inorganic fillers have different gain effects on high-performance SSEs, we mainly classify the components of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires according to their main elements and summarize the research progress in this area in recent years below.4.1 Alkali metal-based compounds
Alkali metal-based compounds as inorganic fillers are mainly composed of lithium-based types, such as garnet-type fillers. The most common types of compounds mainly include Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO) and Li6.5La3Zr1.5Ta0.5O12 (LLZTO). In addition, some cesium-based materials belonging to alkali metal-based compounds have also been prepared and introduced for high-performance SSEs. Since their discovery in 2007, garnet-structured LLZO SSEs have gained notable interest for use in solid-state batteries. They stand out due to their high ionic conductivity (around 10−3 S cm−1 at room temperature), excellent electrochemical stability and robust compatibility with the cathode and Li anode. As depicted in Fig. 6a, Ding et al.143 reported the synthesis of a well-oriented LLZO nanofiber, which was subsequently composited with elastic ion-conducting poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) to prepare a flexible and well-arranged ceramic LLZO nanofiber (EACN) composite electrolyte. The interaction of the LLZO nanofibers with PVDF could effectively provide a long and rapid conductance pathway for Li+, while the elastic surface of EACN could also help enhance its surface area in contact with SSEs. These factors resulted in the formation of an electrolyte exhibiting excellent ionic conductivity (1.16 × 10−4 S cm−1) and low interfacial resistance (87 Ω) at 30 °C. More importantly, the assembled flexible solid-state lithium batteries can be extensively used in wearable clothing and other products. The research and synthesis of flexible solid-state electrolytes are crucial for producing flexible solid-state lithium batteries. Also, as shown in Fig. 6b, Huang et al.144 successfully designed and synthesized a type of LLZO nanofiber and compounded it with a PVDF-HFP matrix to prepare a new solid polymer electrolyte (SPE). Given that the LLZO nanofibers provided long-range and sequential Li+ transfer channels, the prepared SPE exhibited the excellent ionic conductivity and electrochemical window of 6.5 × 10−3 S cm−1 and 5.3 V under room-temperature conditions, respectively. Based on its good flexibility and electrochemical performances, the obtained SPE is desirable for application in flexible solid-state lithium batteries. The doping of LLZO with other elements with ionic radii similar to that of its main ions represents an effective method to improve both the stability and ionic conductivity of LLZO at room temperature. This is because of the ability to create charge-compensated vacancies or gaps by displacing or doping a dopant with a different valence state than the primary ion. For example, Wang et al.145 doped Nb in LLZO and prepared garnet-type Li6.75La3Zr1.75Nb0.25O12 (LLZN) nanowires, which had excellent crystallinity and aspect ratio, and composited them with the PMMA/LiClO4 matrix. The interwoven 3D network structure of LLZN nanofibers could significantly lower the polymer matrix crystallinity and enhance the mechanical strength of the composite electrolyte. Furthermore, the strong interaction between the nanowire surface and the polymer chains also provided a special pathway, leading to the fast conduction of Li+, which significantly enhanced the ionic conductivity of the electrolyte (2.2 × 10−5 S cm−1 at room temperature). Building on the preceding work, this team also further designed and synthesized a bi-layer heterostructured solid electrolyte with LLZN nanowires@poly(vinylidene fluoride hexafluoropropylene) (PVDF-HFP) as a ductile matrix, and a well interfacial gel was also formed using the modified MOF particles@PEO@PVDF-HFP. In addition to the LLZN nanowires providing a long-distance transport pathway for Li+, the micrometer-scale MOFs also helped to suppress the lithium dendrite growth effectively, and the nanoscale MOFs could also fill in the gaps between the micrometer-scale MOFs, which helped to construct more continuous pathways within the matrix or along the interfaces. Consequently, the prepared SSE exhibited excellent ionic conductivity and stable chemical/electrochemical interfaces, and was also effective in inhibiting the serious growth of lithium dendrites.146 The agglomeration effect hinders the optimization of the performance exhibited by current CSEs, which leads to the fact that the content of the added functional nanofillers cannot be too high. However, this is not conducive to Li+ transport. Thus, to effectively overcome the above-mentioned problem, Zhang et al.147 developed a silane-modified, Al-doped LLZO-based Li6.28La3Al0.24Zr2O12(S@LLAZO) nanofiber filler with poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA) to form novel CSEs. The prepared silane coupling agent enabled the high content of LLAZO monomer to be cross-linked inside the PEGDA matrix, forming a 3D LLAZO network with a uniform distribution and good permeability, which successfully solved the problem of traditional CSEs. However, the increase in inorganic fiber content can be limited due to the agglomeration effect. Additionally, it further strengthened the interplay between the LLAZO nanofibers and the polymer matrix,148 which effectively promoted the electrochemical performance of the final electrolyte. | ||
| Fig. 6 Alkali metal-based compounds. (a) Sol–gel electrospinning and calcination employed to fabricate aligned ceramic LLZO nanofibers.143 Copyright 2021. Reproduced with permission from Elsevier. (b) Images showing a flexible battery and the illuminated LED lamps powered by a fully charged cell in both flat and bent configurations.144 Copyright 2020. Reproduced with permission from the American Chemical Society. (c1) A diagrammatic representation of lithium dendrite growth within the 3D-CPEs.150 Copyright 2022. Reproduced with permission from Wiley-VCH. (c2) CsPbI3-NWs increase the Lewis acid–base interactions, reducing the crystallinity in PLN SSEs.153 Copyright 2023. Reproduced with permission from the American Chemical Society. | ||
At present, the preparation and application of Ta-doped LLTO electrolytes are also prevalent for CSEs. Their optimal internal Li+ vacancies can ensure the stable cubic phase and optimal Li+ migration at ambient temperature. For example, Liu et al.149 prepared Li6.75La3Zr1.75Ta0.25O12 (LLZTO) nanofibers and introduced them in a salt-rich PEO/LiTFSI system for the first time. The prepared composite structure could facilitate the strong adsorption of TFSI− and provide Li+ transport channels. Building on the preceding studies, Liu and co-workers also successfully grew ceramic LLZTO nanowires directly onto both surfaces of ceramic LLZTO sheets in situ and designed and prepared a nanowire-ceramic sheet-nanowire skeleton with a “corrugated cardboard-like” structure for PEO-based SSEs. The formed 3D structure can facilitate the continuity of the ceramic networks, thereby ensuring uniform and rapid lithium conduction. Moreover, the 3D network framework is also conducive to hindering the anion mobility in the composite electrolyte and effectively mitigating the concentration polarization of Li+ at the interfaces, thus significantly eliminating the energy barriers generated by charge carrier redistribution and homogenizing the Li+ flux at the interfaces. Based on these merits, the SSEs can significantly improve the ionic conductivity and effectively address the significant issue of severe lithium dendrite growth150 (Fig. 6c1). Moreover, Guan et al.34 prepared a novel composite polymer electrolyte (CPE) by compositing LLZTO nanofibers with PPC/PVDF. The resulting LLZTO nanofibers underwent calcination and were interconnected to create a 3D network, offering uninterrupted Li+ transport pathways. The porous structures between the nanofibers also facilitated the penetration of lithium salts and the applied polymers. Moreover, the anions immobilized by the LLZTO nanofibers in conjunction with the polymer matrix could also guide the uniform distribution of Li+ and effectively inhibit the growth of lithium dendrites. Consequently, the obtained electrolyte exhibited excellent mechanical properties and high ionic conductivity (3.1 × 10−4 S cm−1) and lithium transfer number (0.62) even at room temperature. It has been demonstrated that CSEs possess remarkable capability for suppressing the growth of lithium dendrites in lithium-metal batteries, thus markedly enhancing the safety and electrochemical performance of solid-state batteries. However, the development and fabrication of CSEs that exhibit high ionic conductivity and minimal interfacial resistance at ambient temperature remain a considerable hurdle.
Thus, to address these problems, Pazhaniswamy and colleagues151 developed ultra-thin SSEs by compositing Al-LLZO ceramic nanofibers with PVDF/LiTFSI and integrated them directly on the porous cathode surface. The obtained electrolyte had a core–shell structure, which can provide good interfacial contact between the cathode/electrolyte and facilitate Li+ conduction between the cell electrolyte and cathode. Therefore, the prepared electrolyte has significant advantages over conventional self-supported SSEs in terms of specific capacity and internal resistance. As is known, in the case of Cs-based metal compounds, given that Cs+ and Li+ have similar charge features, an electrostatic shielding effect will be generated for them. These factors can remarkably alleviate the deposition of excessive Li+, and ultimately decrease the loss of Li+ during the cycling process.152 Therefore, some scholars have used 1D Cs-based inorganic nanofillers in the preparation of CSEs. For example, as shown in Fig. 6c2, Zhang and colleagues153 designed and employed CsPbI3 nanowires to enhance PEO-based electrolytes. The integration of the CsPbI3 nanowires effectively diminished the degree of crystallinity in the PEO-based electrolyte. Moreover, the strong Lewis acid–base interaction between PEO and the CsPbI3 nanowires also significantly enhanced the ionic conductivity of the electrolyte and promoted the formation of a stable electrochemical interface. Overall, these factors enabled the composite electrolyte to not only suppress lithium dendrites, but also demonstrate an excellent electrochemical performance.
4.2 Transition metal-based compounds
Transition metals are a group of metallic elements located in the middle of the periodic table with partially filled d-orbitals, which allow them to easily form complex compounds and exhibit multiple oxidation states. Among the inorganic ceramic fillers composed of transition metal elements, some perovskite-type materials such as Li0.33La0.557TiO3 (LLTO) are the most common. Moreover, some transition metal oxides such as ZrO2, TiO2, Y2O3 and NASICON-type fillers such as Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 (LATP) are also commonly used as nanofillers for the preparation of inorganic nanofibers. Moreover, inorganic nanofibers including LLTO fibers also have a diverse range of applications in SSEs. For instance, Zhang et al.154 synthesized CSEs by dispersing high aspect ratio LLTO nanofibers within a PEO/LiTFSI matrix. The prepared LLTO nanofibers can be employed to decrease crystallinity and facilitate the transportation of lithium-ions along the continuous conductive pathways. Thus, the assembled cell using the electrolyte exhibited excellent electrochemical properties at room temperature. The construction of a directional arrangement structure has a notable influence on enhancing the ionic conductivity. As shown in Fig. 7a1–a3, Li et al.65 successfully prepared a vertically aligned LLZO nanowire using a modified electrospinning process and composited it with a PEO/LiClO4–PEG matrix to create a CSE. Due to the efficient ion transport facilitated by the vertically aligned structure, the fabricated CSE displayed an impressive ionic conductivity of 4.67 × 10−4 S cm−1 at ambient temperature, exceeding the performance of randomly oriented nanowires by approximately two-fold, together with a broad electrochemical window spanning from 0 to 5 V. However, although SSEs have made significant progress in effectively suppressing the growth of lithium dendrites, there are still many challenges to be addressed. Thus, to tackle these problems efficiently, besides incorporating functional fillers, which can enhance the properties of the electrolyte, a pivotal approach is mainly selecting polymer matrices that possess a broad electrochemical stability window, robust mechanical strength and excellent thermal stability. For instance, as presented in the research conducted by Su et al.,155 they successfully prepared composite electrolytes by compositing LLTO nanofibers with PVDF materials. The resulting LLTO nanofiber network and PEO–LLTO interface could facilitate the transportation of lithium-ions along a continuously interconnected ionic conduction pathway. The fabricated flexible electrolyte membranes displayed a remarkable performance, including high ionic conductivity of 5.3 × 10−4 S cm−1, a broad electrochemical window of 5.1 V, substantial mechanical strength of 9.5 MPa and outstanding cycling stability. | ||
| Fig. 7 Transition metal-based compounds. (a1) Illustration of vertically aligned LLTO structures, simulation of the conductive mechanism, and TEM and HRTEM images of LLTO nanowires. (a2) Peak intensity of the LLTO solid electrolyte varying with sintering temperature and (a3) peak intensity of the LLTO SSE varying with sintering time.65 Copyright 2022. Reproduced with permission from Elsevier. (b1) Illustrative representation of the CLP-P4-LLTO CSE, (b2) XRD pattern and (b3) SEM image of the calcined LLTO nanofibers.158 Copyright 2019, Reproduced with permission from Elsevier. (c1) Illustrative flowchart outlining the process for the preparation of LATP nanofibers and the CSE, (c2) long cycle performance of the assembled full battery, (c3) comparison of lithium dendrite growth in “single-ion conducting” CSEs and traditional SPEs and (c4) SEM digital images of CSE.164 Copyright 2021. Reproduced with permission from the American Chemical Society. | ||
A prevalent approach to enhance the ionic conductivity of metal oxide-based Li+ conductors involves the doping of cations. For example, Wu et al.156 reported an interesting work by doping nitrogen in LLTO chalcogenide-type nanofibers and compositing them with the PVDF-HFP/LiTFSI matrix as the final SSEs. According to density functional theory simulations, nitrogen doping can modify the interplay between the perovskite anions and Li+, consequently lowering the hopping activation energy of Li+ ions substantially, and thereby enhancing their migratory hopping capacity. Compared with undoped pure LLTO, the ionic conductivity of doped LLTO nanofibers can be greatly improved, thus improving the electrochemical performance of the cell.
A common strategy for improving ion transport in SSEs is the design of 3D nanofiber/nanowire cross-linked networks. The nanofiber/nanowire cross-linked networks, which form the backbone of the SSE, not only improve the contact area between the filler and the polymer matrix, leading to an enhanced interfacial percolation efficiency, but also establish an extensive space charge layer, facilitating more uninterrupted pathways for Li+ transport. In the past few years, some researchers have also devoted significant efforts to designing and preparing 3D network structures. For instance, Nan et al.157 utilized a 3D LLTO nanofiber cross-linked network as the structural backbone and successfully synthesized a 3D interpenetrating network composite polymer electrolyte (3D-CPEs) by compositing it with a PEO matrix through the thermal compression and quenching techniques. Furthermore, they conducted a thorough examination of how the LiTFSI concentration impacted the conductivity of 3D-CPEs. The results indicated that the optimal LiTFSI concentration for 3D-CPEs was 40 wt%. The prepared 3D-CPE membranes exhibited excellent ionic conductivity at ambient temperature and effectively reduced the growth rate of lithium dendrites as well as significantly reduced the issue of polarization. The conventional PEO-based CPEs had poor ionic conductivity, and agglomeration easily occurred when the concentration of the inorganic fillers increased. All these factors can hinder the improvement in the electrochemical performance of PEO-based CPEs. Therefore, the reasonable structural and functional modification of PEO-based CPEs is a common idea. For example, as shown in Fig. 7b1–b3, Zhang et al.158 synthesized a novel PEO-based cross-linked polymer (CLP) and plasticized it with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) as the CPE of a solid-state lithium metal battery. The obtained CPE showed the excellent ionic conductivity of 2.40 × 10−4 S cm−1 at ambient temperature.
However, the poor compatibility between the electrodes and SSE is still an unsolved problem. Thus, to overcome this key problem, applying the design concept of multi-layer structure is a good solution to enhance the stability of the interface. The construction of an interfacial layer on the lithium metal anode side is aimed at preventing penetration from lithium dendrites. Also, constructing an interfacial layer on the anode side can also effectively overcome the drawbacks of the rigid interface between the cell anode and the electrolyte, enabling favorable contact and promoting smooth operation under high-pressure conditions. Numerous scholars have also done extensive work in this area. For example, Yu and co-workers designed and prepared a symmetric sandwich structure (PVDF/LLTO–PEO/PVDF) solid-state electrolyte (SWEs) with a middle layer of nanowire membranes composed of PEO and LLTO flanked by PVDF nanofiber membranes.159 In the designed structure, the LLTO nanowire-filled PEO layer was employed to improve the electrochemical stability and enhance both the ionic conductivity and ionic mobility. The PVDF skin layer was utilized to impede the interfacial reaction between LLTO and Li metal anode. The results showed that SWEs had a low interfacial resistance and a high lithium-ion mobility number (0.74). More impressively, the SWEs exhibited an ionic conductivity of 3.01 × 10−3 S cm−1 at ambient temperature. Moreover, some scholars conducted similar work to Yu’ work. For instance, Zhao et al.160 presented the PEO–LiTFSI|PEO–LLTO–LiTFSI|PEO–LiTFSI multi-layer structure of flexible CSEs. The adopted structure provided a buffer between the LLTO nanofibers and Li anode, effectively avoiding their direct contact, and thereby eliminating interfacial side reactions. Additionally, it also significantly reduced the interfacial impedance between the two components and minimized the volumetric variation of the electrolyte during cycling. Moreover, the emergence of 3D nanofiber cross-linked networks can also greatly improve the ion conductivity of CSE. However, the problem of excessive impedance at the electrode/electrolyte interfaces faced by SSEs is still a bottleneck, limiting their fast development. Thus, to effectively reduce the interfacial impedance, Chang et al.161 prepared a quasi-solid electrolyte by introducing LLTO nanofibers in the PVDF-HFP/LiTFSI system. A fluorine-rich interlayer (SNI) based on butanedinitrile (SN), fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC) and LiTFSI was further developed with the objective of observably reducing the interfacial resistance between the Li anode/electrolyte and inhibiting the unfavorable interfacial side reactions. After testing, both the assembled Li||CSE@SNI||Li and Li||CSE@SNI||LFP batteries exhibited an excellent charging–discharging performance and cycle stability.
As is known, ZrO2 exhibits a pronounced dielectric constant, which can effectively protect the surface of the cathode electrode material and reduce the electrode polarization. Additionally, the ZrO2 nanofiber framework possesses hydrophilic properties and demonstrates robust mechanical strength. For example, Li et al.162 showed the feasibility of a self-supporting, ultra-thin, fully inorganic solid electrolyte, achieving a minimal thickness of 25 μm. The composite electrolyte was prepared through a simple solution casting method, wherein ZrO2 nanowires served as the backbone and Li3InCl6 acted as the Li+ conductor. Due to the high content of Li3InCl6 and the soft nature of the halide solid electrolyte, the prepared electrolyte was highly conductive and did not require any modification to be in intimate contact with the composite cathode without a gap, which allowed the further optimization of the interface impedance.
As is known, the NASICON-type LATP active filler exhibits a wide range of positive working voltages, and its raw materials can be readily available at low cost. In addition, LATP used as an electrolyte filler is not only easy to prepare, but also has some advantages of significantly improving the electrochemical performance of the final electrolyte.163 For example, as shown in Fig. 7c1–c4, Yu and colleagues164 devised and fabricated a 3D interconnected network of LATP nanofibers as a backbone structure. Subsequently, the prepared backbone was integrated with poly[bis(2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethoxy)phosphazene] (MEEP) and LiSTFSI to yield a single-ion-conducting CSE. Due to the synergistic advantages of the two, the assembled all-solid-state battery equipped with the electrolyte exhibited an excellent long-cycle performance at ambient temperature. Through further research on LATP, some scholars found that pressure adversely affects the uniformity of LATP nanofiber membranes.165 In addition to LATP, LiGe2(PO4)3 (LAGP) is also one of the most studied structures in the NASICON family. For example, Monaca et al.166 designed and synthesized ceramic LAGP nanofibers to construct PEO-based CSEs. The results demonstrated that the ionic conductivity of CSE with 10% LAGP nanofibers at ambient temperature was doubled in comparison to the pure PEO electrolyte without any fillers. This phenomenon can mainly be attributed to the fact that the LAGP nanofibers can provide longer ionic conduction pathways and significantly reduce the crystallinity of PEO.
4.3 Alkaline earth metal-based compounds
Alkaline earth metals, such as Mg and Ca, can serve as ideal candidates for the development of Li-based rechargeable batteries with high energy density.167 The compounds derived from alkaline earth metals have been extensively employed as inorganic additives in SSEs. Mg belongs to alkaline earth metals and is one of the most abundant light metal elements explored on the earth. Compared with other elements, Mg-based compounds are abundant, cheap and safe. Adding heterogeneous metals and their compounds to electrolytes is conducive to forming a good interface with the lithium metal anode.168 For example, Tao et al.104 composited Mg2B2O5 nanowires with the PEO/LiTFSI for high-performance SSEs. The Lewis acid center of Mg2B2O5 nanowires exhibited a property for interaction with TFSI−, which can serve to diminish the interaction force between Li+ and TFSI−. All these factors contributed to the efficient dissociation of the Li salts, ultimately leading to the release of a greater amount of Li+. The addition of Mg2B2O5 nanowires helped to promote the motion of the polymer chain segments, resulting in a significant improvement in the electrochemical performance of CSE. Finally, the addition of Mg2B2O5 nanowires also conferred excellent flame retardant properties to the prepared composite electrolyte.In addition to the above-mentioned applications, Mg-based nanofillers are also used to improve the problems of poor interfacial compatibility and slow ion migration in solid-state lithium batteries. For example, our group successfully prepared MgO nanofibers and MgF2 nanofibers using EBS and subsequent high-temperature calcination method, and composited these nanofibers with the PEO/LiTFSI matrix for the first time for high-performance ASSLBs.37 Due to the formed Lewis acid–base interactions and the continuous conductive pathways formed by the organic–inorganic interfaces, this scheme could significantly promote the increase in Li+ concentration in the electrolyte. Moreover, the obtained MgF2 nanofibers, with their low electronic conductivity, effectively mitigated the uncontrolled growth of lithium dendrites. Subsequently, our group also designed and prepared a CSE by compositing lithium-doped MgO nanofibers with PEO/LiTFSI based on previous work and conducted an in-depth study. As shown in Fig. 8a, we confirmed that the surface defects in 1D oxide nanostructures can significantly promote the diffusion of Li+.59 Numerous can offer some insights into the formation of lithium-rich zones in high-pressure ASSLBs.
 | ||
| Fig. 8 Alkaline earth metal-based compounds and metalloid-based compounds. (a) Illustration of a CSE containing nanofibers and its use for the assembly of an ASSLB.59 Copyright 2023. Reproduced with permission from the American Chemical Society. (b1) CSE with porous BNNFs, (b2) LSV images of CSE with different BNNF contents and (c) voltage distribution diagram of constant current deposition/stripping for the assembled Li symmetric battery.176 Copyright 2023. Reproduced with permission from Elsevier. | ||
Hydroxyapatite (HAP) was firstly used in biomaterials due to its good biocompatibility with the human body.169 Alternatively, in recent years, some scholars have also investigated its potential in energy storage applications. For example, Xu et al.136 designed and used self-supported HAP nanowire membranes composited with PEO to prepare a CSE. The HAP membrane endowed the CSE with an excellent performance at elevated temperatures, ensuring that when the HAP–PEO composite electrolyte burnt, the HAP backbone remained operational and did not burn with the polymer. This significantly reduced the risk during its application. Moreover, the nanofibers as fillers with rich oxygen groups can also significantly reduce the crystallinity of PEO and promote the dissociation of lithium salts. This study can provide new insights into the development of solid-state lithium batteries, which can withstand the condition of high temperatures.
4.4. Metalloid-based compounds
Metalloids are intermediates between metals and non-metals, showing metallic properties in appearance but exhibiting both metallic and non-metallic properties in chemistry to a certain extent. Metalloid-based inorganic fillers are a common class of materials, which mainly include silica (SiO2) and boron nitride (BN).SiO2 is an inert ceramic filler. However, as a Lewis acid, SiO2 also can promote LiTFSI to dissociate to more free Li+.170 For example, Guo et al.171 prepared a CSE comprised of 3D SiO2 nanofibers as the backbone and polyethylene oxide-lithium(bistrifluoromethyl) sulfate-succinonitrile (PLS) as the matrix. The homogeneous 3D SiO2 nanofiber framework was conducive to promoting the formation of a continuous lithium-conducting interface between PLS and SiO2, thereby achieving uniform Li transport and inhibiting lithium dendrite growth. It is worth noting that PLS can decompose above 400 °C, resulting in the separation of the electrodes by the solid framework of 3D SiO2 nanofibers. Thus, the process will automatically turn off the power, thereby greatly enhancing the security of high-performance solid-state lithium batteries.
To enhance the electrochemical performance of solid-state batteries, researchers have proposed the utilization of SiO2 nanofibers in the fabrication of the cell. For example, Zhang and colleagues172 proposed a novel concept for fabricating an integrated cathode–electrolyte structure. This strategy mainly involves positioning the cathode and electrolyte on opposite sides of 3D SiO2 nanofibers, thus forming an integrated component, which facilitated a secure and tight bond between the cell cathode and electrolyte. The obtained self-supporting 3D SiO2 nanofiber skeleton could function as a bridge between the electrolyte and cathode, and thus the integration of the CSE and cathode was significantly promoted, and its electrochemical performance also improved. The obtained electrolyte and cathode in the flexible integrated cathode–electrolyte structure (ICES) shared the same frame and could be interconnected to reduce the Li+ polarization and interfacial resistance, while the ICES structure also enabled the electrolyte and Li metal anode to achieve firm contact. Thus, it can be employed to prevent the formation and growth of lithium dendrites. This method has good application prospects in solid-state lithium metal batteries. Moreover, Wu et al.173 prepared a gel electrolyte by compositing a helical mesoporous SiO2 nanofiber (HMSF) backbone with P(VDF-HFP), and subsequently anode materials were prepared using the same HMSF skeleton. Based on the design of natural integration at the electrolyte/anode interfaces, the gel electrolyte possessed numerous advantages, including excellent mechanical properties, remarkable thermal stability with a decomposition temperature of up to 372 °C, a wide electrochemical window spanning 5.3 V, high ionic conductivity of 1.2 × 10−3 S cm−1, and a superior lithium-ion mobility number of 0.43. Flexible oxide ceramic membranes are an indispensable component in the construction of flexible SSEs. However, although some preparation methods have been proposed, they are usually complex and not scalable. For example, Ding et al.174 reported the designed and preparation of a flexible SiO2 nanofiber membrane featuring a controllable morphology. The porous ceramic membrane was further filled with PEO to form a CSE with a “reinforced concrete architecture” structure. The SiO2 nanofibers exhibited strong Lewis acid–base interaction and continuous ion transport channels, which greatly reduced the polymer crystallinity and Li+ concentration polarization. The results revealed that the electrolyte possessed a remarkably high ionic conductivity of 1.3 × 10−4 S cm−1 when tested at 30 °C, while the “reinforced concrete architecture” structure also imparted excellent structural stability to the prepared composite electrolyte.
Boron nitride is an inorganic material composed of boron and nitrogen atoms, with abundant exposed boron atoms on its surface. The electronegativity of boron atoms exposed on the surface of boron nitride is considerably less than that of nitrogen atoms, resulting in an electron-deficient state. This property makes it easy to bind to TFSI− in LiTFSI and effectively promote the dissociation of lithium salts.175 As shown in Fig. 8b1–c, Yan et al.176 constructed a PEO-based CSE using porous boron nitride nanofibers (BNNFs), and the pore-like structures with different diameters could effectively promote an increase in the amorphous region of PEO and form more cross-links, which was conducive to promoting lithium-ion transmission. In addition, due to the excellent hardness and good stability of BNNFs, the prepared CSE with BNNFs showed outstanding electrochemical properties and mechanical properties compared with traditional pure PEO electrolytes, which provides a feasible direction for the development of high-performance solid-state lithium batteries.
4.5 Main group metal compounds
Main group metal compounds are employed as inorganic fillers for composite electrolytes, including Al2O3, AlF3, SnO2, and Bi4Ti3O12. Among them, Al-based compounds such as Al2O3 and AlF3 have been extensively applied in lithium batteries due to their superior electrochemical properties and low cost, which can be applied as separator coatings, electrode surface modifications and electrolyte fillers. 1D Al2O3 materials have also attracted wide attention from scholars due to their exceptional aspect ratios.177 In the preparation of SSEs, numerous scholars have focused on Al2O3 and carried out in-depth and extensive research. For example, Jing et al.36 prepared a flexible–rigid γ-Al2O3 fiber reinforced composite electrolyte (PPO-AFs CSE) of polypropylene oxide (PPO) for solid-state lithium metal batteries. On the one hand, the Lewis acid groups of the γ-Al2O3 fibers can react with TFSI− to effectively facilitate the dissociation of lithium salts. On the other hand, the incorporation of γ-Al2O3 fibers also shortened the ionic migration pathways, thus improving the ionic conductivity and ionic mobility. Furthermore, the lithiophilic γ-Al2O3 also can react with Li to form an Li–Al–O transition layer, which helped reduce the Li+ concentration gradient during the lithium deposition process and effectively promoted the interfacial compatibility, thus achieving the purpose of effectively suppressing lithium dendrites. Therefore, when the content of γ-Al2O3 fibers was 15 wt%, the electrolyte exhibited a remarkably high ionic conductivity of up to 3.38 × 10−4 S cm−1 at room temperature together with an impressive ionic mobility number of 0.70. Also, the electrolyte also presented a wide electrochemical window of 5.6 V. Simultaneously, our group has also conducted significant research using Al-based compounds. For example, we prepared spiny inorganic nanofiber heterostructures with mullite whiskers grown on AlF3 nanofibers, which were poured into the PEO/LiTFSI matrix to construct 3D lithium-ion transport channels. The obtained CSE exhibited an excellent electrochemical performance and stable cycling performance at 30 °C.80 Furthermore, the surface of the SnO2 material is rich in oxygen vacancies, which can offer an increased number of reactive sites. Consequently, SnO2 materials have a wide range of applications in fields such as lithium metal cells. Furthermore, by incorporating Gd in the material via doping, a higher concentration of oxygen vacancies can be attained, thus significantly enhancing its overall performance.178,179 Herein, we also reported the preparation of Gd-doped SnO2 nanofibers (GDS NTs) with a high oxygen vacancy concentration for the first time and applied them in SSEs of high-performance ASSLBs. The 1D hollow structure of GDS NTs could provide a continuous transport pathway for Li+ over long distances and reduce the crystallinity of PEO. Additionally, a large number of oxygen vacancies also can interact strongly with TFSI−, thus effectively promoting the dissociation of the lithium salt. Moreover, SnO2 can also effectively inhibit lithium dendrite growth due to its high affinity for metal lithium. The results further confirmed that the CSE displayed remarkable compatibility with diverse electrode materials (such as NCM811 and LFP cathode).180 Taking advantage of this momentum, our research team also further developed a 3D PAN/PVDF nanofiber membrane framework with a multi-scale structure. Also, it was further composited with GDS NFs/PEO/LiTFSI to prepare a CSE for high-performance solid-state lithium batteries. The interconnected network between PAN/PVDF and the abundant interfacial interactions between the GDS NFs and PEO chains resulted in a notable enhancement in the ionic conductivity and mechanical strength of the CSE, which effectively prevented short-circuits caused by lithium dendrite growth. Consequently, the ionic conductivity of the formed CSE was as high as 2.45 × 10−4 S cm−1 at 30 °C. Also, it had outstanding performance of excellent energy density, high specific capacity and outstanding reversible capacity181 (Fig. 9b1–b5).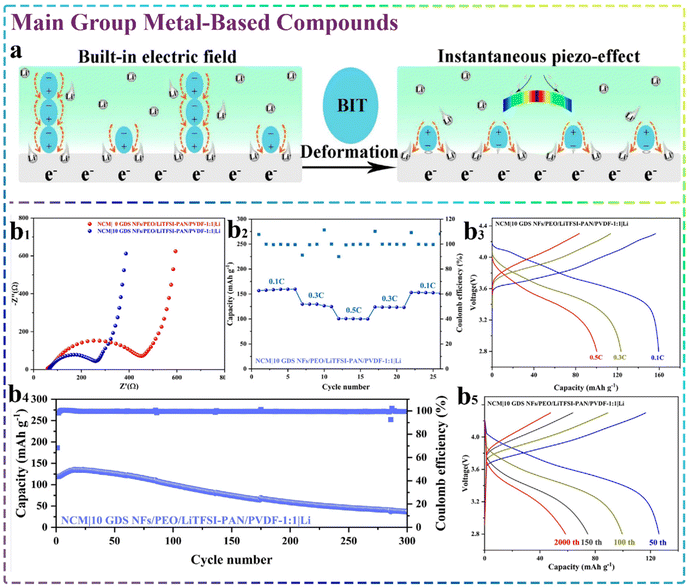 | ||
| Fig. 9 Main group metal-based compounds. (a) Illustration depicting the mechanisms to enhance the speed of Li+ transportation and deposition processes based on BIT-NFs.110 Copyright 2022. Reproduced with permission from Elsevier. (b1) Impedance diagram, (b2) cycle performance under different rates, (b3) charging and discharging voltage curve, (b4) cycle performance and (b5) charging and discharging voltage curve under 0.5C.181 Copyright 2024. Reproduced with permission from Elsevier. | ||
As a typical ferroelectric ceramic material in the Aurivillius family, BIT has some characteristics of high spontaneous polarization and large piezoelectric constant. As shown in Fig. 9a, our group innovatively designed and prepared porous ferroelectric ceramic Bi4Ti3O12 nanofibers (BIT-NFs) and composited them with the PEO/LiTFSI matrix for SSEs.110 The results showed that the lithium–lithium symmetric batteries assembled with the CSE exhibited excellent cycling stability (no short circuit even after 3000 h at 50 °C), and the assembled ASSLBs also showed an excellent long cycle performance. Based on the above-mentioned work, our research group further introduced 1D ferroelectric ceramic-based Bi4Ti3O12–BiOBr heterojunction nanofibers (BIT–BOB HNFs) into PEO CSEs. Through the electric dipole layer and built-in electric field of BIT–BOB HNFs, the Li+ conductive highway with “dissociators” and “accelerating regions” could be constructed. The redistribution of interfacial charges in the prepared BIT–BOB HNFs resulted in the formation of positive–negative electric dipole layers, which was conducive to the effective dissociation of lithium salts. The assembled LFP||BIT–BOB HNF/PEO/LiTFSI||Li batteries had excellent cycling stability, with a high discharge-specific capacity of 135.4 mA h g−1 even after 2200 cycles.69
4.6 Lanthanide metal-based compounds
La2Zr2O7 (LZO) has a similar structure to LLZO, with a large number of oxygen vacancies, which can provide strong Lewis acid–base interactions. As an additive, LZO exhibits high chemical stability and thermal stability, making it a favorable candidate for effective application as a solid-state electrolyte filler. LZO contributes to enhancing the stability and safety of solid-state lithium batteries. As shown in Fig. 10a, Jing et al.182 designed and prepared lanthanum zirconate (LZO) inorganic nanofibers by electrospinning and subsequent calcination processes, and then introduced the nanofibers into a sandwich polypropylene carbonate (PPC)-based SSE for the first time, leading to the development of a novel CSE. Moreover, a graphite coating layer was also applied to the surface adjacent to the cell anode. The Lewis acid sites present in 1D LZO not only improved the solubility of lithium salts, but also constructed faster ion transport pathways than that of 0D particles. More importantly, the graphite coating layer on the surface of the CSE at the lithium anode side also improved the interfacial compatibility of the electrolyte/anode lithium. The results indicated that the ultra-thin CSE exhibited an excellent electrochemical performance at room temperature. Besides, our research group has also explored the application of lanthanide metal compounds for high-performance SSEs.183 For example, the introduction of low-cost, large surface area Gd-doped CeO2 nanowires (GDC) with abundant surface oxygen vacancies in the PEO electrolyte system for the preparation of CSEs also has been designed and conducted. The addition of GDC nanowires is rather beneficial to increase the amorphous region of the PEO matrix and provide a long-distance Li+ transport channel distributed along the surfaces of the GDC nanowires, which are important for facilitating Li+ transport.52,184 Moreover, the addition of can Gd also produce abundant oxygen vacancies, and the interaction with TFSI− can also greatly inhibit the movement of anions and effectively promote the dissociation of lithium salts. Moreover, the high mechanical strength of the composite electrolyte also inhibited lithium dendrites during the lithium deposition process. The results showed that the CSE had good interfacial stability with the lithium anode and high-voltage LiNi0.8Mn0.1Co0.1O2 (NMC) anode, which ensured the stable cycling of the electrolyte-assembled solid-state lithium batteries even at high current densities and exhibited excellent ionic conductivity (5.9 × 10−4 S cm−1) at 30 °C.183 Based on the above-mentioned work, our research group also further developed a PVDF-PEO nanofiber membrane with a core–shell structure and composited it with prepared GDC ceramic nanowires.125 In the core–shell structure, the PVDF core layer can play a supporting role, while the PEO shell layer can form a continuous channel for lithium-ion transfer.103 The optimized composite solid electrolyte (CSE) exhibited high ionic conductivity (2.3 × 10−4 S cm−1) and outstanding Li+ transfer number (0.64), together with excellent mechanical strength (10.8 MPa) at 30 °C. These properties significantly contributed to the effective inhibition of lithium dendrites. It was worth noting that this CSE exhibited good interfacial compatibility with the commonly available electrodes on the market, indicating its extremely broad adaptability. | ||
| Fig. 10 Lanthanide metal-based compounds. (a) LZO nanofibers used as fillers for CSE to promote Li+ transport.182 Copyright 2019. Reproduced with permission from Elsevier. (b1) Interaction between LaCoO3 nanowires and SPES nanofibers with Li+ and (b2) after the LiFePO4/T-SPES-PEO-3LaCoO3/Li bag battery is treated (pouch cell, folded pouch cell, cut-open pouch cell, and cut-open for 24 h), the battery can still work normally.185 Copyright 2023. Reproduced with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry. (c1) SEM of C-SPES/PEO nanofibers and (c2) diagram of inhibition of lithium dendrites by C-SPES-PEO-LaCoO3 and pure PEO electrolyte.58 Copyright 2023. Reproduced with permission from Wiley-VCH. | ||
In addition, our research group also introduced lanthanum cobaltate (LaCoO3) nanowires as functional fillers in the design of CSEs. Also, we reported the development of a rigid–flexible CSE with excellent mechanical strength and high ionic conductivity by combining dendritic sulfonated polyether sulfone (SPES) nanofiber membranes and LaCoO3 nanowires. The surface of the LaCoO3 nanowires was extremely rich in oxygen vacancies and Lewis acid sites, which further increased the number of free lithium-ions in the electrolyte. Moreover, the 3D structure formed by introducing LaCoO3 nanowires effectively promoted the formation of more organic–inorganic interfaces available for Li+ transport and enhanced the mechanical properties. Consequently, the CSE demonstrated an outstanding electrochemical performance at 30 °C (ref. 185) (Fig. 10b1 and b2). Based on these merits, we further designed and prepared crimped sulfonated polyethersulfone-polyethylene oxide (C-SPES/PEO) nanofiber membranes and doped them with prepared LaCoO3 nanowires, thus obtaining a novel composite solid electrolyte (C-SPES-PEO-LaCoO3) supported by a special-shaped fiber framework. In the crimped nanofibers, SPES can provide a robust skeletal support for CSE and enlarge the pore volume between the nanofibers. This not only enhanced the mechanical strength of the electrolyte, but also addressed the issue of ceramic nanowires clogging the nanofiber membrane. The resulting C-SPES-PEO-LaCoO3 electrolyte exhibited high ionic conductivity (2.5 × 10−4 S cm−1 at 30 °C) and high mechanical strength (7 MPa)58 (Fig. 10c1 and c2).
4.7 Others
Palygorskite ((Mg,Al)2Si4O10(OH))186 is a natural product with extremely low cost, which is significantly lower than that of synthetic silica ceramic electrolyte (such as LLZO) nanowires. Fabricating palygorskite into nanofibers or nanowires can form an interconnected network with high mechanical performance. For example, Yang et al.187 introduced palygorskite ((Mg,Al)Si4O10(OH)) nanowires into the prepared PVDF/LiClO4 matrix to form the final CSE. Due to the uniform dispersion of palygorskite nanowires within the CSE, leading to the formation of an interconnected network, the mechanical properties of the CSE were greatly improved. Moreover, due to the interaction between the palygorskite and ClO4− ions, the Li+ transference number was also significantly enhanced from 0.21 to 0.54.As a naturally occurring 1D ceramic nanomaterial, the obtained sepiolite (SEP, Si12O30Mg8(OH)4(H2O)4·8H2O) “boasts” low cost and abundant reserves. Its rich content of siloxane bonds and hydroxyl groups facilitates the fast dissociation of lithium salts and organic modification. Furthermore, its abundant silicon-oxygen linkages and hydroxyl moieties can also significantly promote the dissociation of lithium salts. Moreover, it also can offer a rapid transport pathway for Li+. For example, Hu et al.66 designed and prepared a CSE with high ionic conductivity by incorporating functionalized seafoam (KFSEP) nanowires, which were aligned using magnetic field orientation. The experimental data and simulation analysis both confirmed that the prepared nanowires aligned perpendicularly to the electrolyte/electrode interfaces can effectively establish a direct Li+ transport channel, thus significantly enhancing the lithium-ion transport efficiency. The assembled Li||PEO/LiTFSI/10%SKFSEP||Li battery was capable of functioning smoothly for over 600 h, thus demonstrating the high stability and ability of PEO/LiTFSI/10%SKFSEP to significantly suppress lithium dendrite formation.
The primary components of glass fiber cloth (GFC) are oxides such as SiO2, Al2O3, CaO and others. For example, Huang et al.188 successfully prepared a CSE by infiltrating PEO, LiTFSI and ionic liquids (ILs) in the GFC framework. The even dispersion of GDC within the SPE framework effectively mitigated the crystallinity of PEO and enhanced the thermal stability of the electrolyte, while the unique 3D GFC network structure also endowed the SPE with exceptional mechanical strength. The addition of ILs also further enhanced the ionic conductivity, while also reducing the interfacial impedance between the cell electrolyte and cathode, thereby greatly improving the interfacial compatibility. The results demonstrated that the fabricated SPE possessed robust capability to suppress lithium dendrite growth. Finally, the assembled LFP/PEO@GFC-25%@ILs/Li ASSLB using the prepared electrolyte exhibited a superior electrochemical performance.
5. Conclusions and perspectives
In recent times, the advancement of high-performance solid-state lithium batteries has attracted significant and growing attention, but their electrochemical performances and safety thus far are plagued by many problems. Due to the excellent safety and high specific energy of solid-state lithium batteries, they are regarded as key electrochemical energy storage devices and a potential development direction for future energy storage technology. As the most important component of solid-state lithium batteries, the performances of SSEs will directly affect the key indicators including energy density, cycle stability, safety and available wide temperature range. Consequently, to develop high-performance solid-state lithium batteries, it is necessary to achieve the dual functions of fast Li+ transmission and effective suppression of lithium dendrites simultaneously (even under high-temperature conditions). In addition, to significantly increase the energy density, SSEs equipped with a high voltage cathode and a lithium metal anode must be developed and applied for high-performance solid-state lithium batteries.To provide a more systematic and comprehensive summary of the progress of the application of some inorganic nanofibers in SSEs for solid-state lithium metal batteries, this review discussed the influence mechanisms of inorganic nanofibers on Li+ transportation in SSEs from the perspectives of Lewis acid–base interaction, interfacial transport theory and built-in electric field in detail. Simultaneously, this review also aimed to provide some scientific guidance for the design of high-performance SSEs. In the selection of inorganic components for combination with inorganic nanofibres or nanofiber membranes, we prefer to select some materials that can provide Lewis acidic sites or contain some surface defects (e.g., oxygen-containing vacancies) to effectively promote the dissociation of lithium salts through Lewis acid–base interaction or other ways. Also, some functional materials such as ferroelectric ceramic materials were prepared and used to construct a built-in electric field inside the composite electrolyte, which can be used to neutralize the localized concentrated electric field to effectively promote the dissociation of lithium salts on the micro-scale through the formed polarization electric field generated based on the spontaneous dipole moment. Moreover, in the design of fiber morphology and arrangement, the effective ways are as far as possible to reduce the fiber diameter, reduce the size of the filler, and diminish the inert filler internal ineffective region. Due to the smaller the size, the larger the surface energy, and the more likely to agglomerate, all the processes for reducing the size of the process to improve the dispersion and reduce the agglomeration of the nanofibers are important. For instance, monodisperse chains of sub-nanometer inorganic clusters can provide homogeneous, large-scale and continuous strong interfacial interactions and establish fast Li+ transport channels at the organic–inorganic interfaces. Furthermore, it is beneficial to achieve a high density arrangement of inorganic nanofibres in the monodisperse state by various means, as well as to construct highly oriented vertical structures to increase the degree of ordering to a certain extent. Moreover, the application of inorganic nanofibers for the construction of 3D Li+ transport networks is also a good choice. Furthermore, the mechanisms for the decomposition of solid electrolytes under high voltage conditions were elucidated, and the potential for improving the stability of SSEs at high voltage by adding some functional materials and introducing various intermediate layers was also proposed. We believe that the selection of suitable nanofibre fillers (e.g. fluoride and chloride) as the rigid skeleton and the choice of the final electrolyte with stable functional groups as the polymer matrix also may be an effective strategy to significantly improve the stability of the electrolyte against high voltage. Lastly, we also presented an in-depth analysis and discussion on the anode electrode protection mechanism, and believe that the inorganic solid electrolyte also can be improved by reducing the internal defects and adding insulating substances to greatly reduce the electronic conduction. Given their significance in organic–inorganic composite electrolytes, we also proposed that lithium dendrite inhibition and anode protection can be achieved by improving the mechanical strength of the composite electrolyte, constructing continuous and homogeneous lithium-ion conduction pathways, introducing a coating layer at the electrolyte/anode interface, or synthesizing a functional protective coating layer directly on the surface of lithium anodes based on the application of the in situ method. Furthermore, for example, ferroelectric ceramic materials with piezoelectric effects can build an adaptive built-in electric field inside the composite electrolyte. Some materials with higher dielectric constants or composite materials of ferroelectric organic and ferroelectric inorganic materials will result in more excellent electrochemical performances in composite electrolytes.189,190 These ferroelectric materials can facilitate uniform Li+ deposition and play an important role in effectively inhibiting lithium dendrites, thus achieving the purpose of anode electrode protection. Finally, this review was concluded with a compendium of common methods for preparing inorganic nanofibers/nanowires, as well as a summary of the extensive work done in recent years on the application of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires to greatly enhance the performances of SSEs.
Many researchers have designed and developed a series of novel CSEs by introducing various functional materials and designing 1D inorganic nanofiber structures, significantly enhancing the ionic conductivities of the electrolytes. However, in the case of high-energy-density solid-state lithium batteries with lithium metal as the electrode, the formation of lithium dendrites may severely impair the performance of the battery, resulting in a rapid decline in specific discharge capacity, and even the potential safety hazard of thermal runaway due to an internal short circuit. Thus, the produced phenomenon poses a significant safety hazard, making it huge challenge to meet the requirements of actual applications, particularly under high-temperature working conditions. Furthermore, electrospinning and its post-processing remain one of the most commonly used inorganic nanofiber preparation methods in commercial applications. However, it still faces some significant challenges such as the problem of large-scale production and precise control of the complex nanostructures. Therefore, it is necessary to explore convenient, fast, energy-saving and large-scale production methods for the further optimization and improvement of these problems. In addition, although CSEs can facilitate the transport of Li+, and some scholars also have proposed different theoretical models to explain the corresponding principles of interfacial transport, there is no comprehensive and clear mechanisms through various studies at present. Therefore, the interfacial transport mechanism of organic–inorganic composite electrolytes still has to be further researched and proven by numerous in-depth studies.
Consequently, there is still a considerable distance to traverse before the commercial application of solid-state lithium batteries can be realized, and several significant challenges must be overcome. Considering this, the main avenues for development are as follows (presented in Fig. 11):
(1) The interfacial conduction mechanisms of organic–inorganic composite electrolytes represent an important theoretical basis for guiding the design of multifunctional CSEs. The interfacial conduction mechanism of CSEs is not very clear thus far. Therefore, in-depth studies for these interfacial conduction mechanisms are particularly necessary. Despite the tremendous progress achieved in recent years in overcoming static interface problems, these dynamic interface problems still exist. Conventional electrochemical analysis methods, such as electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and galvanostatic polarization, are limited to a comprehension of interfacial phenomena at the macroscopic level and cannot analyze the detailed working processes of solid-state lithium batteries in-depth from a microscopic perspective. Therefore, the further development of advanced characterization techniques is conducive to realizing the dynamic monitoring of interfaces, which holds immense importance for the profound exploration of interfacial transformation mechanisms at the atomic level. Moreover, it is imperative to integrate additional theoretical calculations with cutting-edge characterization methodologies, particularly that capable of in situ observations, such as in situ SEM, in situ TEM, in situ XRD, XANES, in situ Raman spectroscopy, and NMR, to foster a more profound comprehension of dynamic interfacial phenomena. Thus, providing some theoretical guidance for further improving the stability of SSE/electrode and organic–inorganic interfaces is also important. In the future, we also can explore and conduct some special and multifunctional structures, interfacial reaction mechanisms and other physicochemical properties including ionic conductivities with the help of molecular dynamics simulations. We can also explore the growth behavior of lithium dendrites with Monte Carlo simulations and calculate the migration pathways and migration barriers of Li+ mainly relying on the elastic energy band method. In addition, the interfacial transport, cathode decomposition mechanism and anode protection mechanism can also be studied in detail using both experimental and theoretical simulations in conjunction with some simulation tools such as the COMSOL simulation software.
(2) Three key ideas have been identified as being significant in the field of promoting Li transport, including reducing the diameter of fibres especially nanofibers, achieving the high density alignment of inorganic nanofibres/nanowires in the polymer electrolyte, and constructing highly oriented vertically aligned structures. According to the interfacial transport theory, it is known that lithium-ions are mainly transported through the organic–inorganic interfaces. Therefore, preparing ultra-fine nanofibers and achieving a high-density arrangement can greatly increase the organic–inorganic interfaces. Some scholars have done some preliminary exploration. For example, He et al. prepared Li7La3Zr2O12 nanowires to upgrade the PEO composite electrolyte and PEO cathode binder, significantly enhancing the ionic conductivity and mechanical performance of the composite electrolyte, which resulted in uniform lithium-ion flow, thus greatly suppressing lithium dendrite growth.191 Furthermore, Mai et al.63 constructed sub-1 nm inorganic cluster chains for SSEs. The designed and prepared cluster provided an abundant surface area for interfacial interactions and greatly facilitated Li+ transport. However, the current methods for the preparation of ultra-fine nanofibers/nanowires are still immature, and thus the development of simple and stable, low-cost methods for preparing ultra-fine nanofibers or their membranes/nanowires with high yield is a direction for future efforts. Secondly, ultra-fine nanofibers or their membranes/nanowires are more prone to agglomeration, and the development of a well dispersion method for highly homogeneous nanofibers or their membranes/nanowires is also a prerequisite for achieving a high-density arrangement of inorganic nanofibres or their membranes/nanowires in polymer electrolytes. This is an area that can be deeply explored in future research. Thirdly, for the inorganic nanofibers/nanowires to construct a shorter Li+ transport pathway, it is necessary to devote further studies to highly oriented vertical structures with the aim of reducing the cross-knotting of the inorganic nanofibers/nanowires. Previous studies also have reported some methods for the construction of vertical Li+ transport channels using the magnetic orientation, electric field orientation and ice template methods. In the future, we also should broaden the ideas and optimize the processes based on the existing ones to conduct more in-depth research.
(3) In the aspect of interfacial transport, continuous conducting channels for facilitating lithium-ion transport can be constructed between the interfaces of the polymer matrix and some introduced functional 1D materials.192 Therefore, in the design of 1D materials, we can also design and prepare porous tubular structures with a small diameter to obtain more continuous lithium-conducting interfaces. Based on this rationale, we can also consider introducing ultra-fine active nanoparticles (e.g., LLZTO quantum dots) in the inner and outer walls of the tubular structure. The synergistic effect of the active and inert fillers combined with the advantages of the 1D material structure is expected to promote a significant increase in the lithium-ion transport rate.
(4) Nature offers a plethora of awe-inspiring structures and a multitude of ingenious functions. Thus, learning from nature for bionic structure design and developing bionic materials for multi-functional electrolyte for high-performance solid-state lithium batteries have a broad prospect. In previous research, some scholars employed bionic structure design to realize a great effect. For example, Xu et al.193 proposed a leaf-inspired quasi-solid electrolyte (MOF-QSE) with MOF-based material for solid-state lithium batteries. Also, the unique nano/sub-nano pore structure in MOF-QSE effectively inhibited the side reactions between the cell electrolyte and lithium electrode. For instance, Li et al.194 proposed a design strategy for nacre-like ceramic/polymer electrolyte composite solid-state electrolytes (NCPEs) with a “brick-mortar” microstructure inspired by the “CaCO3 platelet-protein” microstructure in natural nacre. These works also demonstrated that bionic structure design has a wide range of applications in SSEs with remarkable results. In the future, it will be beneficial to continue research in this area. For example, mimicking the self-healing function of animal skin tissues and developing more multifunctional SSEs with self-healing ability are also important for high-performance solid-state lithium batteries. This idea will greatly improve the interface performance and mitigate the secondary reactions triggered by direct physical contact in response to the damage caused by the battery operation. In addition, the distinctive 1D structure of some plants can be employed to facilitate more continuous and uniform lithium-ion transport interfaces for cell SSEs, resulting in a considerable enhancement in the Li+ transport rate. Alternatively, natural structures possessing smooth surfaces can be investigated and implemented in the surface design of lithium anodes. This strategy aims to minimize the roughness of the anode surface, thus diminishing protruding sites and enabling the more uniform deposition of lithium-ions on the anode surface. Consequently, effectively regulating the formation of lithium dendrites and significantly enhancing the safety performance of advanced solid-state lithium batteries become vital. Overall, at present, cell SSEs with a bionic structure design are still in the early research stage. Thus, in the future, we should continue to obtain inspiration for novel structural and functional design from biological systems in nature and combine some significant advantages of 1D materials especially inorganic nanofibres/nanowires to remarkably enhance the electrochemical performance and safety of SSEs.
(5) It is worth noting that at present, the most important method for the preparation of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires is still electrospinning combined with calcination to remove the organic components for obtaining inorganic nanofibers/nanowires. However, the low product yield is still one of the main drawbacks of single-needle electrospinning, and it is difficult to meet the industrialized requirements of mass production thus far. Although some scholars have proposed some solutions such as electro-blown spinning and needleless electrospinning, the challenge of achieving large-scale production still exists. In the future, further advancements and progress in the electrospinning process or the development of other novel methods for the preparation of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires are anticipated to enable their large-scale production.
(6) The cathode material can serve as a pivotal determinant of the electrochemical performance of lithium cells, directly governing the energy density and safety of the cells, and thereby having a significant impact on their comprehensive performance. Therefore, in the future, besides conducting in-depth research on SSEs to ensure their universal compatibility with various anode and cathode materials, it is imperative to refine the SSE/electrode interfaces for achieving good stability. Furthermore, further in-depth research on the cell electrodes is also required. For example, lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) typically holds a preeminent position among cathode materials for high-performance lithium batteries. High-voltage charging can effectively improve the energy density of the LiCoO2 cathode, but it inevitably triggers some problems of capacity, structural stability and drastic decrease in charging and discharging efficiency. Therefore, the features of the applied LiCoO2 can be further enhanced by particle size optimization, elemental doping and surface modification to achieve long cycle stability at high voltage in the future. However, unwanted chemical reactions at the interface and the formation of lithium dendrites also have some adverse effects on the performance of lithium cell. In addition to modifying SSEs and enhancing the stability of the interfaces between the electrolyte and lithium anode, modification of the lithium anode morphology and structure can also be considered (e.g. collector modification, lithium alloy modification, and novel form of lithium anode) in the future. These strategies can enhance the lithium deposition process, regulate the volumetric expansion of the lithium electrodes and inhibit the formation of lithium dendrites.
(7) The deep integration of artificial intelligence (AI) technology with solid-state battery technology should be promoted. In the past, some researchers continuously experimented with different materials and processes, which is inefficient and difficult to meet the rapidly evolving demands of high-tech industries. In this case, AI, with its powerful high-speed and massive data processing capabilities, is the most promising technology to overcome the above-mentioned research bottlenecks. Thus, it may facilitate the development of battery materials, battery device design and fabrication including materials and device characterization. For example, Troyer and colleagues195 used AI to screen 32 million possible materials, ultimately identifying 18 of the most promising candidate materials, which greatly reduced the time required for material screening. Furthermore, they conducted some experimental characterizations on the most important materials among them, thus proving their potential for use in high-performance SSEs. In the future, we can further integrate some techniques such as machine learning, deep learning and image processing analysis with physical simulations. This strategy also can be applied to the construction and performance analysis of SSEs.
 | ||
| Fig. 11 Development prospect of inorganic nanofibers/nanowires in SSEs and the development direction of high-performance solid-state lithium batteries. | ||
In summary, inorganic nanofibers/nanowires occupy a significant position in the construction of high-performance SSEs. In the design of SSEs for high-performance solid-state lithium batteries, the design and preparation of inorganic nanofibers/structures is still an important idea, which is expected to realize their large-scale industrial application in SSEs for high-performance solid-state lithium batteries.
Author contributions
Writing–review & editing: Nanping Deng; writing–review & editing: Wenwen Duan; methodology: Wen Yu; conceptualization: Yang Feng; validation: Zichun Feng; methodology: XiaoFan Feng; visualization: Zhaozhao Peng; data curation: Hengying Xiang; supervision: Yong Liu; resources: Weimin Kang.Data availability
No primary research results, software or code have been included and no new data were generated or analysed as part of this review.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (23JCYBJC00660), Tianjin Enterprise Science and Technology Commissioner Project (23YDTPJC00490), National Natural Science Foundation of China (52203066, 51973157), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Grant (2023M742135, 2024T170525), and State Key Laboratory of Membrane and Membrane Separation, Tiangong University.References
- Y. Li, N. Deng, H. Wang, Q. Zeng, S. Luo, Y. Jin, Q. Li, W. Kang and B. Cheng, Latest progresses and the application of various electrolytes in high-performance solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries, J. Energy Chem., 2023, 82, 170–197 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Guo, Y. Xu, Y. Luo, Y. Wang, X. Li, X. Sun, K. Zhang, Q. Pang and A. Qin, A review of composite organic-inorganic electrolytes for lithium batteries, J. Energy Storage, 2024, 77, 109912 CrossRef.
- J. Feng, L. Wang, Y. Chen, P. Wang, H. Zhang and X. He, PEO based polymer-ceramic hybrid solid electrolytes: a review, Nano Converg., 2021, 8, 1–12 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Zhang, X. Wang, X. Li, J. Zhao, G. Liu, W. Yu, X. Dong and J. Wang, Review on composite solid electrolytes for solid-state lithium-ion batteries, Mater. Today Sustainability, 2023, 21, 100316 CrossRef.
- S. Li, S. Zhang, L. Shen, Q. Liu, J. Ma, W. Lv, Y. He and Q. Yang, Progress and Perspective of Ceramic/Polymer Composite Solid Electrolytes for Lithium Batteries, Adv. Sci., 2020, 7, 1903088 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Zhao, J. Yi, P. He and H. Zhou, Solid-State Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries: Fundamentals, Challenges and Perspectives, Electrochem. Energy Rev., 2019, 2, 574–605 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Liu, L. Jiang, P. Zheng, J. Sun, C. Liu, J. Chai, X. Li, Y. Zheng and Z. Liu, Recent Advances in Stability Issues of Inorganic Solid Electrolytes and Composite Solid Electrolytes for All–Solid–State Batteries, Chem. Rec., 2022, 22, e202200116 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Zheng, M. Kotobuki, S. Song, M. O. Lai and L. Lu, Review on solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries, J. Power Sources, 2018, 389, 198–213 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Wu, Z. Xie, A. Yoshida, Z. Wang, X. Hao, A. Abudula and G. Guan, Utmost limits of various solid electrolytes in all-solid-state lithium batteries: A critical review, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2019, 109, 367–385 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Cheng, T. Liu, B. Zhao, F. Shen, H. Jin and X. Han, Recent advances in organic-inorganic composite solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2021, 34, 388–416 CrossRef.
- Y. Liu, B. Xu, W. Zhang, L. Li, Y. Lin and C. W. Nan, Composition Modulation and Structure Design of Inorganic–in–Polymer Composite Solid Electrolytes for Advanced Lithium Batteries, Small, 2019, 16, 1902813 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Li, L. Zhong, J. Li, H. Wu, W. Shao, P. Wang, M. Liu, G. Zhang and M. Jing, Insights into the effects of different inorganic fillers on the electrochemical performances of polymer solid electrolytes, Colloids Surf., A, 2023, 671, 131704 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Knauth, Inorganic solid Li ion conductors: An overview, Solid State Ionics, 2009, 180, 911–916 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Wang, L. Sheng, G. Yasin, L. Wang, H. Xu and X. He, Reviewing the current status and development of polymer electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2020, 33, 188–215 CrossRef.
- Y. Zheng, Y. Yao, J. Ou, M. Li, D. Luo, H. Dou, Z. Li, K. Amine, A. Yu and Z. Chen, A review of composite solid-state electrolytes for lithium batteries: fundamentals, key materials and advanced structures, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 8790–8839 RSC.
- H. Liu, X. Cheng, J. Huang, H. Yuan, Y. Lu, C. Yan, G. Zhu, R. Xu, C. Zhao, L. Hou, C. He, S. Kaskel and Q. Zhang, Controlling dendrite growth in solid-state electrolytes, ACS Energy Lett., 2020, 5, 833–843 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Liang, L. Wang, A. Wang, Y. Song, Y. Wu, Y. Yang and X. He, Tailoring practically accessible polymer/inorganic composite electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium metal batteries: A review, Nano-Micro Lett., 2023, 15, 42 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Daems, P. Yadav, K. Dermenci, J. Van Mierlo and M. Berecibar, Advances in inorganic, polymer and composite electrolytes: Mechanisms of Lithium-ion transport and pathways to enhanced performance, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2024, 191, 114136 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Sun, C. Liu, H. Liu, J. Li, P. Zheng, Y. Zheng and Z. Liu, Advances in Ordered Architecture Design of Composite Solid Electrolytes for Solid–State Lithium Batteries, Chem. Rec., 2023, 23, e202300044 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Fan, H. He and C. Nan, Tailoring inorganic–polymer composites for the mass production of solid-state batteries, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2021, 6, 1003–1019 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Zhang, X. Xu, Y. Qin, S. Ji, Y. Huo, Z. Wang, Z. Liu, J. Shen and J. Liu, Recent Progress in Organic-Inorganic Composite Solid Electrolytes for All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries, Chem. – Eur. J., 2020, 26, 1720–1736 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Yu and A. Manthiram, A review of composite polymer-ceramic electrolytes for lithium batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2021, 34, 282–300 CrossRef.
- Q. Yu, K. Jiang, C. Yu, X. Chen, C. Zhang, Y. Yao, B. Jiang and H. Long, Recent progress of composite solid polymer electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium metal batteries, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2021, 32, 2659–2678 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Janek and W. Zeier, Challenges in speeding up solid-state battery development, Nat. Energy, 2023, 8, 230–240 CrossRef.
- H. Xu, P. Chien, J. Shi, Y. Li, N. Wu, Y. Liu, Y. Hu and J. Goodenough, High-performance all-solid-state batteries enabled by salt bonding to perovskite in poly(ethylene oxide), Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2019, 116, 18815–18821 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Duan, H. Cheng, Y. Liu, Q. Sun, W. Nie, X. Lu, P. Dong and M. Song, A multifunctional janus layer for LLZTO/PEO composite electrolyte with enhanced interfacial stability in solid-state lithium metal batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2024, 65, 103091 CrossRef.
- Z. Zhang, S. Zhang, S. Geng, S. Zhou, Z. Hu and J. Luo, Agglomeration-free composite solid electrolyte and enhanced cathode-electrolyte interphase kinetics for all-solid-state lithium metal batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2022, 51, 19–28 CrossRef.
- Q. Yang, N. Deng, Y. Zhao, L. Gao, B. Cheng and W. Kang, A review on 1D materials for all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries and all-solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries, Chem. Eng. J., 2023, 451, 138532 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Lei, H. Li, Y. Tang and H. Shao, Progress and perspectives on electrospinning techniques for solid–state lithium batteries, Carbon Energy, 2022, 4, 539–575 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Liu, P. Wang, Z. Gao, X. Li, W. Cui, R. Li, S. Ramakrishna, J. Zhang and Y. Long, Review on electrospinning anode and separators for lithium-ion batteries, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2024, 189, 113939 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Yang, Y. Li and C. Chan, Enhanced lithium-ion conductivity in lithium lanthanum titanate solid electrolyte nanowires prepared by electrospinning, J. Power Sources, 2015, 287, 164–169 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Liu, N. Liu, J. Sun, P. Hsu, Y. Li, H. Lee and Y. Cui, Ionic conductivity enhancement of polymer electrolytes with ceramic nanowire fillers, Nano Lett., 2015, 15, 2740–2745 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Fu, Y. Gong, J. Dai, A. Gong, X. Han, Y. Yao, C. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Chen, C. Yan, Y. Li, E. Wachsman and L. Hu, Flexible, solid-state, ion-conducting membrane with 3D garnet nanofiber networks for lithium batteries, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2016, 113, 7094–7099 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Fang, M. Zhao, Y. Peng and S. Guan, Poly (vinylidene fluoride) binder reinforced poly (propylene carbonate)/3D garnet nanofiber composite polymer electrolyte toward dendrite-free lithium metal batteries, Mater. Today Energy, 2022, 24, 100952 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liu and X. Hua, Preparation of Li6Zr2O7 nanofibers with high li–ion conductivity by electrospinning, Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol., 2016, 13, 579–583 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Li, M. Jing, R. Li, L. Li, Z. Huang, H. Yang, M. Liu, S. Hussain, J. Xiang and X. Shen, Al2O3 Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Solid Electrolyte Films with Excellent Lithium-Ion Transport Properties for High-Voltage Solid-State Lithium Batteries, ACS Appl. Polym. Mater., 2022, 4, 7144–7151 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Yu, N. Deng, Z. Yan, L. Gao, K. Cheng, X. Tian, L. Tang, B. Cheng and W. Kang, Mg-based inorganic nanofibers constructing fast and multi-dimensional ion conductive pathways for all-solid-state lithium metal batteries, J. Energy Chem., 2022, 67, 684–696 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Berthier, W. Gorecki, M. Minier, M. Armand, J. Chabagno and P. Rigaud, Microscopic investigation of ionic conductivity in alkali metal salts-poly(ethylene oxide) adducts, Solid State Ionics, 1983, 11, 91–95 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Farrington and J. Briant, Fast ionic transport in solids, Science, 1979, 204, 1371–1379 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Angell, J. Fan, C. Liu, Q. Lu, E. Sanchez and K. Xu, Li-conducting ionic rubbers for lithium battery and other applications, Solid State Ionics, 1994, 69, 343–353 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Yu, X. Zhang, C. Fu, H. Wang, M. Chen, G. Yin, H. Huo and J. Wang, Dendrites in solid-state batteries: Ion transport behavior, advanced characterization, and interface regulation, Adv. Energy Mater., 2021, 11, 2003250 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Xu, Z. Sun, C. Sun, F. Li, K. Chen, Z. Zhang, G. Hou, H.-M. Cheng and F. Li, Homogeneous and fast ion conduction of PEO–based solid–state electrolyte at low temperature, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 2007172 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Qiu, X. Liu, R. Chen, Q. Li, Y. Wang, P. Chen, L. Gan, S. Lee, D. Nordlund, Y. Liu, X. Yu, X. Bai, H. Li and L. Chen, Enabling stable cycling of 4.2 V high-voltage all-solid-state batteries with PEO-based solid electrolyte, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 1909392 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Xiong, Z. Wang, W. Zhou, Q. Liu, J. Wu, T. Liu, C. Xu and J. Liu, 4.2 V polymer all-solid-state lithium batteries enabled by high-concentration PEO solid electrolytes, Energy Storage Mater., 2023, 57, 171–179 CrossRef.
- M. Ratner and D. Shriver, Ion transport in solvent-free polymers, Chem. Rev., 1988, 88, 109–124 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Angell, C. Liu and E. Sanchez, Rubbery solid electrolytes with dominant cationic transport and high ambient conductivity, Nature, 1993, 362, 137–139 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Zhang, R. Tan, L. Yang, J. Zheng, K. Zhang, S. Mo, Z. Lin and F. Pan, Mechanisms and properties of ion-transport in inorganic solid electrolytes, Energy Storage Mater., 2018, 10, 139–159 CrossRef.
- H. Yang and N. Wu, Ionic conductivity and ion transport mechanisms of solid-state lithium-ion battery electrolytes: A review, Energy Sci. Eng., 2022, 10, 1643–1671 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Zhao, S. Stalin, C. Zhao and L. Archer, Designing solid-state electrolytes for safe, energy-dense batteries, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2020, 5, 229–252 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Wieczorek, Z. Florjanczyk and J. Stevens, Composite polyether based solid electrolytes, Electrochim. Acta, 1995, 40, 2251–2258 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Zhang, S. Zhang, Y. Zhang, X. Wu, L. Lin, X. Hu, L. Wang, J. Lin, B. Sa, G. Wei, D. Peng and Q. Xie, Regulating Lewis Acid-Base Interaction in Poly (ethylene oxide)-Based Electrolyte to Enhance the Cycling Stability of Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries, Small Struct., 2024, 5, 2300301 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Ao, X. Wang, J. Tan, S. Zhang, C. Su, L. Dong, M. Tang, Z. Wang, B. Tian and H. Wang, Nanocomposite with fast Li+ conducting percolation network: Solid polymer electrolyte with Li+ non-conducting filler, Nano Energy, 2021, 79, 105475 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Croce, G. Appetecchi, L. Persi and B. Scrosati, Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries, Nature, 1998, 394, 456–458 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Park, D. Kim, J. Prakash and Y. Sun, Electrochemical stability and conductivity enhancement of composite polymer electrolytes, Solid State Ionics, 2003, 159, 111–119 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Yang, J. Zheng, Q. Cheng, Y. Hu and C. Chan, Composite Polymer Electrolytes with Li7La3Zr2O12 Garnet-Type Nanowires as Ceramic Fillers: Mechanism of Conductivity Enhancement and Role of Doping and Morphology, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 21773–21780 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Song, L. Yang, J. Li, M. Zhang, Y. Wang, S. Li, S. Chen, K. Yang, K. Xu and F. Pan, Synergistic dissociation-and-trapping effect to promote li-ion conduction in polymer electrolytes via oxygen vacancies, Small, 2021, 17, 2102039 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Yang, M. Abdullah, J. Bright, W. Hu, K. Kittilstved, Y. Xu, C. Wang, X. Zhang and N. Wu, Polymer-ceramic composite electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries: Ionic conductivity and chemical interaction enhanced by oxygen vacancy in ceramic nanofibers, J. Power Sources, 2021, 495, 229796 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Yang, G. Li, D. Shi, L. Gao, N. Deng, W. Kang and B. Cheng, Composite Solid Electrolyte with Continuous and Fast Organic–Inorganic Ion Transport Highways Created by 3D Crimped Nanofibers@functional Ceramic Nanowires, Small, 2023, 19, 2301521 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Yu, N. Deng, D. Shi, L. Gao, B. Cheng, G. Li and W. Kang, One-Dimensional Oxide Nanostructures Possessing Reactive Surface Defects Enabled a Lithium-Rich Region and High-Voltage Stability for All-Solid-State Composite Electrolytes, ACS Nano, 2023, 17, 22872–22884 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Yu, N. Deng, Y. Feng, X. Feng, H. Xiang, L. Gao, B. Cheng, W. Kang and K. Zhang, Understanding multi-scale ion-transport in solid-state lithium batteries, eScience, 2024, 100278, DOI:10.1016/j.esci.2024.100278.
- W. Liu, S. Lee, D. Lin, F. Shi, S. Wang, A. Sendek and Y. Cui, Enhancing ionic conductivity in composite polymer electrolytes with well-aligned ceramic nanowires, Nat. Energy, 2017, 2, 1–7 Search PubMed.
- H. Xiang, N. Deng, L. Gao, B. Cheng and W. Kang, Janus nanofibers with multiple Li+ transport channels and outstanding thermal stability for all-solid-state composite polymer electrolytes, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2024, 12, 16022–16033 RSC.
- Y. Cheng, X. Liu, Y. Guo, G. Dong, X. Hu, H. Zhang, X. Xiao, Q. Liu, L. Xu and L. Mai, Monodispersed sub-1 nm inorganic cluster chains in polymers for solid electrolytes with enhanced Li-ion transport, Adv. Mater., 2023, 35, 2303226 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Liu, W. Liu, D. Ba, Y. Zhao, Y. Ye, Y. Li and J. Liu, Filler-integrated composite polymer electrolyte for solid-state lithium batteries, Adv. Mater., 2023, 35, 2110423 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li, Y. Zhai, S. Xu, M. Tang, S. Zhang and Z. Zou, Using LLTO with vertically aligned and oriented structures to improve the ion conductivity of composite solid-state electrolytes, Mater. Today Commun., 2022, 33, 104243 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Han, J. Wang, X. Mu, T. Wu, C. Liao, N. Wu, W. Xing, L. Song, Y. Kan and Y. Hu, Controllable magnetic field aligned sepiolite nanowires for high ionic conductivity and high safety PEO solid polymer electrolytes, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2021, 585, 596–604 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Guo, S. Tan, J. Ma, L. Chen, K. Yang, Q. Zhu, Y. Ma, P. Shi, Y. Wei, X. An, Q. Ren, Y. Huang, Y. Zhu, Y. Cheng, W. Lv, T. Hou, M. Liu, Y. He, Q. Yang and F. Kang, Dissociation mechanism of lithium salt by BaTiO3 with spontaneous polarization, Energy Environ. Sci., 2024, 17, 3797–3806 RSC.
- P. Shi, J. Ma, M. Liu, S. Guo, Y. Huang, S. Wang, L. Zhang, L. Chen, K. Yang, X. Liu, Y. Li, X. An, D. Zhang, X. Cheng, Q. Li, W. Lv, G. Zhong, Y. He and F. Kang, A dielectric electrolyte composite with high lithium-ion conductivity for high-voltage solid-state lithium metal batteries, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2023, 18, 602–610 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Kang, N. Deng, D. Shi, Y. Feng, Z. Wang, L. Gao, Y. Song, Y. Zhao, B. Cheng, G. Li, W. Kang and K. Zhang, Heterojunction-Accelerating Lithium Salt Dissociation in Polymer Solid Electrolytes, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2023, 33, 2307263 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Han, A. S. Westover, J. Yue, X. Fan, F. Wang, M. Chi, D. N. Leonard, N. J. Dudney, H. Wang and C. Wang, High electronic conductivity as the origin of lithium dendrite formation within solid electrolytes, Nat. Energy, 2019, 4, 187–196 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Zhou, J. Ma, S. Dong, X. Li and G. Cui, Intermolecular chemistry in solid polymer electrolytes for high–energy–density lithium batteries, Adv. Mater., 2019, 31, 1902029 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Banerjee, X. Wang, C. Fang, E. A. Wu and Y. S. Meng, Interfaces and interphases in all-solid-state batteries with inorganic solid electrolytes, Chem. Rev., 2020, 120, 6878–6933 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Nakayama, S. Wada, S. Kuroki and M. Nogami, Factors affecting cyclic durability of all-solid-state lithium polymer batteries using poly(ethylene oxide)-based solid polymer electrolytes, Energy Environ. Sci., 2010, 3, 1995–2002 RSC.
- X. Yang, M. Jiang, X. Gao, D. Bao, Q. Sun, N. Holmes, H. Duan, S. Mukherjee, K. Adair, C. Zhao, J. Liang, W. Li, J. Li, Y. Liu, H. Huang, L. Zhang, S. Lu, Q. Lu, R. Li, C. Singh and X. Sun, Determining the limiting factor of the electrochemical stability window for PEO-based solid polymer electrolytes: Main chain or terminal –OH group?, Energy Environ. Sci., 2020, 13, 1318–1325 RSC.
- C. Wang, H. Zhang, S. Dong, Z. Hu, R. Hu, Z. Guo, T. Wang, G. Cui and L. Chen, High polymerization conversion and stable high-voltage chemistry underpinning an in situ formed solid electrolyte, Chem. Mater., 2020, 32, 9167–9175 CrossRef CAS.
- X. L. Zhang, W. Guo, L. Zhou, Q. Xu and Y. Min, Surface-modified boron nitride as a filler to achieve high thermal stability of polymer solid-state lithium-metal batteries, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9, 20530–20543 RSC.
- C. Wang, K. Fu, S. Kammampata, D. McOwen, A. Samson, L. Zhang, G. Hitz, A. Nolan, E. Wachsman, Y. Mo, V. Thangadurai and L. Hu, Garnet-type solid-state electrolytes: Materials, interfaces, and batteries, Chem. Rev., 2020, 120, 4257–4300 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Liu, L. Zhou, J. Han, K. Wen, S. Guan, C. Xue, Z. Zhang, B. Xu, Y. Lin, Y. Shen, L. Li and C.-W. Nan, Super long-cycling all-solid-state battery with thin Li6PS5Cl-based electrolyte, Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12, 2200660 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Li, S. Weng, J. Fu, X. Wang, X. Zhou, Q. Zhang, X. Wang, L. Wei and X. Guo, Nonflammable quasi-solid electrolyte for energy-dense and long-cycling lithium metal batteries with high-voltage Ni-rich layered cathodes, Energy Storage Mater., 2022, 47, 542–550 CrossRef.
- W. Liu, L. Meng, X. Liu, L. Gao, X. Wang, J. Kang, J. Ju, N. Deng, B. Cheng and W. Kang, 3D spiny AlF3/Mullite heterostructure nanofiber as solid-state polymer electrolyte fillers with enhanced ionic conductivity and improved interfacial compatibility, J. Energy Chem., 2023, 76, 503–515 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Wu, Y. Ren, D. Mu, X. Liu, G. Yang and F. Wu, Effect of lithium carbonate precipitates on the electrochemical cycling stability of LiCoO2 cathodes at a high voltage, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 10196–10203 RSC.
- J. Liu, N. Liu, D. Liu, Y. Bai, L. Shi, Z. Wang, L. Chen, V. Hennige and A. Schuch, Improving the performances of LiCoO2 cathode materials by soaking nano-alumina in commercial electrolyte, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2006, 154, A55 CrossRef.
- H. Q. Pham, K. Nam, E. Hwang, Y. Kwon, H. Jung and S. Song, Performance enhancement of 4.8 V Li1.2Mn0.525Ni0.175Co0.1O2 battery cathode using fluorinated linear carbonate as a high-voltage additive, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2014, 161, A2002 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Han, J. Yue, C. Chen, N. Zhao, X. Fan, Z. Ma, T. Gao, F. Wang, X. Guo and C. Wang, Interphase engineering enabled all-ceramic lithium battery, Joule, 2018, 2, 497–508 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Wang, X. Zhang, T. Wang, Y. Yin, J. Shi, C. Wang and Y. Guo, Ameliorating the interfacial problems of cathode and solid-state electrolytes by interface modification of functional polymers, Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8, 1801528 CrossRef.
- Q. Liu, Q. Chen, Y. Tang and H. Cheng, Interfacial modification, electrode/solid-electrolyte engineering, and monolithic construction of solid-state batteries, Electrochem. Energy Rev., 2023, 6, 15 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Ma, Z. Liu, B. Chen, L. Wang, L. Yue, H. Liu, J. Zhang, Z. Liu and G. Cui, A strategy to make high voltage LiCoO2 compatible with polyethylene oxide electrolyte in all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2017, 164, A3454 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Liu, G. Li, W. Yu, L. Gao, D. Shi, J. Ju, N. Deng and W. Kang, Asymmetric organic-inorganic bi-functional composite solid-state electrolyte for long stable cycling of high-voltage lithium battery, Energy Storage Mater., 2023, 63, 103005 CrossRef.
- H. Tian, Z. Liu, Y. Ji, L. Chen and Y. Qi, Interfacial electronic properties dictate Li dendrite growth in solid electrolytes, Chem. Mater., 2019, 31, 7351–7359 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Krauskopf, R. Dippel, H. Hartmann, K. Peppler, B. Mogwitz, F. Richter, W. Zeier and J. Janek, Lithium-metal growth kinetics on LLZO garnet-type solid electrolytes, Joule, 2019, 3, 2030–2049 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Zhao, Q. Sun, C. Yu, S. Zhang, K. Adair, S. Wang, Y. Liu, Y. Zhao, J. Liang, C. Wang, X. Li, X. Li, W. Xia, R. Li, H. Huang, L. Zhang, S. Zhao, S. Lu and X. Sun, Ultrastable anode interface achieved by fluorinating electrolytes for all-solid-state li metal batteries, ACS Energy Lett., 2020, 5, 1035–1043 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Sharafi, E. Kazyak, A. Davis, S. Yu, T. Thompson, D. Siegel, N. Dasgupta and J. Sakamoto, Surface chemistry mechanism of ultra-low interfacial resistance in the solid-state electrolyte Li7La3Zr2O12, Chem. Mater., 2017, 29, 7961–7968 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Liu, R. Garcia-Mendez, A. Lupini, Y. Cheng, Z. Hood, F. Han, A. Sharafi, J. Idrobo, N. Dudney, C. Wang, C. Ma, J. Sakamoto and M. Chi, Local electronic structure variation resulting in Li ‘filament’ formation within solid electrolytes, Nat. Mater., 2021, 20, 1485–1490 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Rosso, C. Brissot, A. Teyssot, M. Dollé, L. Sannier, J. Tarascon, R. Bouchet and S. Lascaud, Dendrite short-circuit and fuse effect on Li/polymer/Li cells, Electrochim. Acta, 2006, 51, 5334–5340 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhao, K. Zheng and X. Sun, Addressing interfacial issues in liquid-based and solid-state batteries by atomic and molecular layer deposition, Joule, 2018, 2, 2583–2604 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Liang, X. Li, Y. Zhao, L. Goncharova, W. Li, K. Adair, M. Banis, Y. Hu, T. Sham, H. Huang, L. Zhang, S. Zhao, S. Lu, R. Li and X. Sun, An air-stable and dendrite-free Li anode for highly stable all-solid-state sulfide-based Li batteries, Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9, 1902125 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Xing, Y. Li, S. Wang, H. Liu, Z. Wu, S. Yu, J. Holoubek, H. Zhou and P. Liu, Graphite-based lithium-free 3D hybrid anodes for high energy density all-solid-state batteries, ACS Energy Lett., 2021, 6, 1831–1838 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Mo, J. Ruan, S. Sun, Z. Lian, S. Yang, X. Yue, Y. Song, Y. Zhou, F. Fang, G. Sun, S. Peng and D. Sun, Inside or outside: Origin of lithium dendrite formation of all solid-state electrolytes, Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9, 1902123 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Ji, S. Hou, P. Wang, X. He, N. Piao, J. Chen, X. Fan and C. Wang, Solid-state electrolyte design for lithium dendrite suppression, Adv. Mater., 2020, 32, 2002741 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Botros, R. Djenadic, O. Clemens, M. Möller and H. Hahn, Field assisted sintering of fine-grained Li7−3xLa3Zr2AlxO12 solid electrolyte and the influence of the microstructure on the electrochemical performance, J. Power Sources, 2016, 309, 108–115 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Zhang, X. Xu, S. Ji, Z. Wang, Z. Liu, J. Shen, R. Hu, J. Liu and M. Zhu, Solvent-free method prepared a sandwich-like nanofibrous membrane-reinforced polymer electrolyte for high-performance all-solid-state lithium batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 21586–21595 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Mu, Y. Chu, Y. Shi, C. Huang, L. Yang, Q. Zhang, C. Li, Y. Feng, Y. Zhou, M. Han, T. Zhao and L. Zeng, Constructing robust LiF-enriched interfaces in high-voltage solid-state lithium batteries utilizing tailored oriented ceramic fiber electrolytes, Adv. Energy Mater., 2024, 14, 2400725 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Gao, J. Li, J. Ju, B. Cheng, W. Kang and N. Deng, Polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibers with embedded Li6.4La3Zr1.4Ta0.6O12 fillers modified polymer electrolytes for high-capacity and long-life all-solid-state lithium metal batteries, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2020, 200, 108408 CrossRef CAS.
- O. Sheng, C. Jin, J. Luo, H. Yuan, H. Huang, Y. Gan, J. Zhang, Y. Xia, C. Liang, W. Zhang and X. Tao, Mg2B2O5 Nanowire Enabled Multifunctional Solid-State Electrolytes with High Ionic Conductivity, Excellent Mechanical Properties, and Flame-Retardant Performance, Nano Lett., 2018, 18, 3104–3112 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Han, Z. Wang, G. Pan and X. Gao, Metal–organic-framework-based gel polymer electrolyte with immobilized anions to stabilize a lithium anode for a quasi-solid-state lithium–sulfur battery, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 18427–18435 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Liu, D. Lin, J. Sun, G. Zhou and Y. Cui, Improved lithium-ionic conductivity in composite polymer electrolytes with oxide-ion conducting nanowires, ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 11407–11413 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Yang, Q. Wu, W. Xie, X. Zhang, A. Brozena, J. Zheng, M. Garaga, B. Ko, Y. Mao, S. He, Y. Gao, P. Wang, M. Tyagi, F. Jiao, R. Briber, P. Albertus, C. Wang, S. Greenbaum, Y. Hu, A. Isogai, M. Winter, K. Xu, Y. Qi and L. Hu, Copper-coordinated cellulose ion conductors for solid-state batteries, Nature, 2021, 598, 590–596 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Li and X. Guo, Integrated interface between composite electrolyte and cathode with low resistance enables ultra-long cycle-lifetime in solid-state lithium-metal batteries, Sci. China: Chem., 2021, 64, 673–680 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Xie, Y. You, K. Yuan, W. Lu, K. Zhang, F. Xu, M. Ye, S. Ke, C. Shen, X. Zeng, X. Fan and B. Wei, Ferroelectric-enhanced polysulfide trapping for lithium–sulfur battery improvement, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1604724 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Kang, Z. Yan, L. Gao, Y. Zhang, W. Liu, Q. Yang, Y. Zhao, N. Deng, B. Cheng and W. Kang, Improved ionic conductivity and enhancedinterfacial stability of solid polymer electrolytes with porous ferroelectric ceramic nanofibers, Energy Storage Mater., 2022, 53, 192–203 CrossRef.
- Z. Zhu, L. Lu, Y. Yin, J. Shao, B. Shen and H. Yao, High rate and stable solid-state lithium metal batteries enabled by electronic and ionic mixed conducting network interlayers, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 16578–16585 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Yu, D. Han, Q. Lu, Y. He, S. Li, Q. Liu, C. Han, F. Kang and B. Li, Constructing effective interfaces for Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 pellets to achieve room-temperature hybrid solid-state lithium metal batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 9911–9918 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Kong, Z. Jiang, Y. Liu, Q. Han, L. Ding, S. Wang and H. Wang, Stabilizing Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3|Li metal anode interface in solid-state batteries by kevlar aramid nanofiber-based protective coating, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2023, 33, 2306748 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Chen, Y. Huang, H. Fu, Y. Wu, D. Zhang, J. Wen, L. Huang, Y. Dai, Y. Huang and W. Luo, TiO2 nanofiber-modified lithium metal composite anode for solid-state lithium batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 28398–28404 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Ji, Y. Lin, X. Guo, B. Ramasubramanian, R. Wang, N. Radacsi, R. Jose, X. Qin and S. Ramakrishna, Electrospinning of nanofibres, Nat. Rev. Methods Primers, 2024, 4, 1 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Wang, Y. Wu, M. Qiu, X. Li, C. Li, R. Li, J. He, G. Lin, Q. Qian, Z. Wen, X. Li, Z. Wang, Q. Chen, Q. Chen, J. Lee, Y. Mai and Y. Chen, Research progress in electrospinning engineering for all-solid-state electrolytes of lithium metal batteries, J. Energy Chem., 2021, 61, 253–268 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Liao, Y. Sun, J. Wang, H. Cui and C. Wang, Three dimensional self-assembly ZnSb nanowire balls with good performance as sodium ions battery anode, Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 211, 11–17 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Wang, J. Liu, W. Cui, X. Li, Z. Li, Y. Wan, J. Zhang and Y. Long, Electrospinning techniques for inorganic–organic composite electrolytes of all-solid-state lithium metal batteries: A brief review, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023, 11, 16539–16558 RSC.
- Y. Wang, Y. Liu, Y. Liu, Q. Shen, C. Chen, F. Qiu, P. Li, L. Jiao and X. Qu, Recent advances in electrospun electrode materials for sodium-ion batteries, J. Energy Chem., 2021, 54, 225–241 CrossRef CAS.
- K. He, J. Zha, P. Du, S. Cheng, C. Liu, Z. Dang and R. Li, Tailored high cycling performance in a solid polymer electrolyte with perovskite-type Li0.33La0.557TiO3 nanofibers for all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries, Dalton Trans., 2019, 48, 3263–3269 RSC.
- J. Hong, M. Yeo, G. Yang and G. Kim, Cell-electrospinning and its application for tissue engineering, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2019, 20, 6208 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Elnabawy, D. Sun, N. Shearer and I. Shyha, Electro-blown spinning: New insight into the effect of electric field and airflow hybridized forces on the production yield and characteristics of nanofiber membranes, J. Sci.: Adv. Mater. Devices, 2023, 8, 100552 CAS.
- Y. Zhao, L. Fan, B. Xiao, S. Cai, J. Chai, X. Liu, J. Liu and Z. Liu, Preparing 3D Perovskite Li0.33La0.557TiO3 Nanotubes Framework Via Facile Coaxial Electro–Spinning Towards Reinforced Solid Polymer Electrolyte, Energy Environ. Mater., 2023, 6, e12636 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Li, X. Liu, G. Wang, Y. Liu, W. Kang, N. Deng, X. Zhuang and X. Zhou, Research progress of ultrafine alumina fiber prepared by sol-gel method: A review, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 421, 127744 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Gao, S. Luo, J. Li, B. Cheng, W. Kang and N. Deng, Core-shell structure nanofibers-ceramic nanowires based composite electrolytes with high Li transference number for high-performance all-solid-state lithium metal batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2021, 43, 266–274 CrossRef.
- H. Zhao, N. Deng, G. Wang, H. Ren, W. Kang and B. Cheng, A core@sheath nanofiber separator with combined hardness and softness for lithium-metal batteries, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 404, 126542 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Ma, S. Tang, H. Wang, Y. Liang, D. Zhang, X. Xu, Q. Wang and W. Li, Bimetallic ZIFs-derived electrospun carbon nanofiber membrane as bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst for rechargeable zinc-air battery, J. Energy Chem., 2023, 83, 138–149 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Klapstova, P. Honzikova, M. Dasek, M. Ackermann, K. Gergelitsova, J. Erben, A. Samkova, R. Jirkovec, J. Chvojka and J. Horakova, Effective needleless electrospinning for the production of tubular scaffolds, ACS Appl. Eng. Mater., 2024, 2, 492–500 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Rosenthal, J. Weller and C. Chan, Needleless Electrospinning for High Throughput Production of Li7La3Zr2O12 Solid Electrolyte Nanofibers, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2019, 58, 17399–17405 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhang, L. Liu, Y. Si, J. Yu and B. Ding, Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes: An Effective Arsenal for the Purification of Emulsified Oily Wastewater, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 2002192 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Cai, J. Zhu, C. Yang, R. Gao, C. Shi and J. Zhao, A parallel bicomponent TPU/PI membrane with mechanical strength enhanced isotropic interfaces used as polymer electrolyte for lithium-ion battery, Polymers, 2019, 11, 185 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Gao, J. Zhang, Y. Su, H. Wang, X. Wang, L. Peng, M. Yu, S. Ramakrishna and Y. Long, Recent progress and challenges in solution blow spinning, Mater. Horiz., 2021, 8, 426–446 RSC.
- J. Daristotle, A. Behrens, A. Sandler and P. Kofinas, A review of the fundamental principles and applications of solution blow spinning, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8, 34951–34963 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Cao, Q. Liu, J. Ren, W. Chen, Y. Pei, D. Kaplan and S. Ling, Electro-blown spun silk/graphene nanoionotronic skin for multifunctional fire protection and alarm, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, e2102500 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Song, Z. Li and H. Wu, Blowspinning: A new choice for nanofibers, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 33447–33464 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wen, R. Zhang, Q. Zhao, W. Liu, G. Lu, X. Hu, J. Sun, R. Wang, X. Jiang, N. Hu, J. Liu, X. Liu and C. Xu, Hydroxyapatite Nanowire-Reinforced Poly(ethylene oxide)-Based Polymer Solid Electrolyte for Application in High-Temperature Lithium Batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 54637–54643 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Chan, T. Yang and J. Weller, Nanostructured garnet-type Li7La3Zr2O12: Synthesis, properties, and opportunities as electrolytes for Li-ion batteries, Electrochim. Acta, 2017, 253, 268–280 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Wang, X. Li, B. Luo, J. Yang, X. Wang, Q. Song, S. Chen and L. Zhi, Pyrolyzed bacterial cellulose: A versatile support for lithium-ion battery anode materials, Small, 2013, 9, 2399–2404 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zeng, X. Zhai, Y. Yu, D. Li and Y. Hu, Garnet Composite Solid Electrolyte with Cotton Modified by Metal Chelator as a Template for Flexible Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries, ACS Appl. Electron. Mater., 2023, 5, 2249–2258 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Yoon, S. Lee, D. Lee, J. Kim and J. Moon, All-solid-state thin film battery based on well-aligned slanted LiCoO2 nanowires fabricated by glancing angle deposition, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 412, 537–544 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Liu, P. Huang, Z. Xie and Q. Huang, Large-scale production of a silicon nanowire/graphite composites anode via the CVD method for high-performance lithium-ion batteries, Energy Fuels, 2021, 35, 2758–2765 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Gleason, Designing Organic and Hybrid Surfaces and Devices with Initiated Chemical Vapor Deposition (iCVD), Adv. Mater., 2024, 36, 2306665 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhao, J. Yan, W. Cai, Y. Lai, J. Song, J. Yu and B. Ding, Elastic and well-aligned ceramic LLZO nanofiber based electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2019, 23, 306–313 CrossRef.
- W. Zhang, X. Wang, Q. Zhang, L. Wang, Z. Xu, Y. Li and S. Huang, Li7La3Zr2O12 Ceramic Nanofiber-Incorporated Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Flexible Lithium Batteries, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 3, 5238–5246 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Sun, Y. Li, Q. Zhang, C. Hou, Q. Shi and H. Wang, A highly ionic conductive poly(methyl methacrylate) composite electrolyte with garnet-typed Li6.75La3Zr1.75Nb0.25O12 nanowires, Chem. Eng. J., 2019, 375, 121922 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Sun, X. Yao, Y. Li, Q. Zhang, C. Hou, Q. Shi and H. Wang, Facilitating Interfacial Stability Via Bilayer Heterostructure Solid Electrolyte Toward High-energy, Safe and Adaptable Lithium Batteries, Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10, 2000709 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Yan, P. Zhu, H. Jia, Z. Du, J. Zhu, R. Orenstein, H. Cheng, N. Wu, M. Dirican and X. Zhang, Garnet-rich composite solid electrolytes for dendrite-free, high-rate, solid-state lithium-metal batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2020, 26, 448–456 CrossRef.
- M. Dirican, C. Yan, P. Zhu and X. Zhang, Composite solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries, Mater. Sci. Eng., R, 2019, 136, 27–46 CrossRef.
- R. Fan, C. Liu, K. He, S. Cheng, D. Chen, C. Liao, R. Li, J. Tang and Z. Lu, Versatile Strategy for Realizing Flexible Room-Temperature All-Solid-State Battery through a Synergistic Combination of Salt Affluent PEO and Li6.75La3Zr1.75Ta0.25O12 Nanofibers, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 7222–7231 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Fan, W. Liao, S. Fan, D. Chen, J. Tang, Y. Yang and C. Liu, Regulating interfacial Li-ion transport via an integrated corrugated 3D skeleton in solid composite electrolyte for all-solid-state lithium metal batteries, Adv. Sci., 2022, 9, 2104506 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Pazhaniswamy, S. Joshi, H. Hou, P. Abhilash and S. Agarwal, Hybrid Polymer Electrolyte Encased Cathode Particles Interface–Based Core–Shell Structure for High–Performance Room Temperature All–Solid–State Batteries, Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 13, 2202981 CrossRef.
- X. Yang, Q. Sun, C. Zhao, X. Gao, K. Adair, Y. Zhao, J. Luo, X. Lin, J. Liang, H. Huang, L. Zhang, S. Lu, R. Li and X. Sun, Self-healing electrostatic shield enabling uniform lithium deposition in all-solid-state lithium batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2019, 22, 194–199 CrossRef.
- H. Zhang, A. Jia, Y. Wang, X. Fu, C. Liu, H. Peng, H. Tang, Z. Xu, J. Huang and W. Yang, Perovskite CsPbI3 Nanowire-Reinforced PEO Electrolytes Toward High-Rate All-Solid-State Lithium–Metal Battery, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2023, 11, 14986–14996 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Zhu, C. Yan, M. Dirican, J. Zhu, J. Zang, R. Selvan, C. Chung, H. Jia, Y. Li, Y. Kiyak, N. Wu and X. Zhang, Li0.33La0.557TiO3 ceramic nanofiber-enhanced polyethylene oxide-based composite polymer electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6, 4279–4285 RSC.
- B. Li, Q. Su, L. Yu, D. Wang, S. Ding, M. Zhang, G. Du and B. Xu, Li0.35La0.55TiO3 Nanofibers Enhanced Poly(vinylidene fluoride)-Based Composite Polymer Electrolytes for All-Solid-State Batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 42206–42213 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Yang, K. Tay, Y. Xu, B. Rajbanshi, S. Kasani, J. Bright, J. Boryczka, C. Wang, P. Bai and N. Wu, Nitrogen-Doped Lithium Lanthanum Titanate Nanofiber-Polymer Composite Electrolytes for All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2021, 168, 110507 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wang, Y. Zhang, X. Zhang, T. Liu, Y. Lin, L. Li, Y. Shen and C. Nan, Lithium-Salt-Rich PEO/Li0.3La0.557TiO3 Interpenetrating Composite Electrolyte with Three-Dimensional Ceramic Nano-Backbone for All-Solid-State Lithium-Ion Batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 24791–24798 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Yan, P. Zhu, H. Jia, J. Zhu, R. K. Selvan, Y. Li, X. Dong, Z. Du, I. Angunawela, N. Wu, M. Dirican and X. Zhang, High-Performance 3-D Fiber Network Composite Electrolyte Enabled with Li-Ion Conducting Nanofibers and Amorphous PEO-Based Cross-Linked Polymer for Ambient All-Solid-State Lithium-Metal Batteries, Adv. Fiber Mater., 2019, 1, 46–60 CrossRef.
- H. Li, M. Li, S. Siyal, M. Zhu, J. Lan, G. Sui, Y. Yu, W. Zhong and X. Yang, A sandwich structure polymer/polymer-ceramics/polymer gel electrolytes for the safe, stable cycling of lithium metal batteries, J. Membr. Sci., 2018, 555, 169–176 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Liu, R. Zhang, J. Sun, M. Wu and T. Zhao, Polyoxyethylene (PEO)|PEO–Perovskite|PEO Composite Electrolyte for All-Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 46930–46937 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. C. Rath, M. Liu, S. Lo, R. Dhaka, D. Bresser, C. Yang, S. Lee and J. Chang, Suppression of Dehydrofluorination Reactions of a Li0.33La0.557TiO3-Nanofiber-Dispersed Poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) Electrolyte for Quasi-Solid-State Lithium-Metal Batteries by a Fluorine-Rich Succinonitrile Interlayer, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2023, 15, 15429–15438 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Wang, Y. Liao, S. Li, C. Cui, J. Liang, G. Du, Z. Tong, L. Yuan, T. Zhai and H. Li, Ultrathin All–Inorganic Halide Solid–State Electrolyte Membranes for All–Solid–State Li–Ion Batteries, Adv. Energy Mater., 2024, 14, 2303641 CrossRef CAS.
- O. Breuer, G. Peta, Y. Elias, H. Alon-Yehezkel, Y. Weng, M. Fayena-Greenstein, N. Wu, M. Levi and D. Aurbach, Understanding the positive effect of LATP in polymer electrolytes in all-solid-state lithium batteries, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2023, 170, 090509 CrossRef.
- S. Yu, Q. Xu, X. Lu, Z. Liu, A. Windmüller, C. Tsai, A. Buchheit, H. Tempel, H. Kungl, H. Wiemhöfer and R. Eichel, Single-Ion-Conducting “Polymer-in-Ceramic” Hybrid Electrolyte with an Intertwined NASICON-Type Nanofiber Skeleton, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 61067–61077 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Monaca, G. Girard, S. Savoie, H. Demers, G. Bertoni, S. Krachkovskiy, S. Marras, E. Mugnaioli, M. Gemmi, D. Benetti, A. Vijh, F. Rosei and A. Paolella, Effect of pressure on the properties of a NASICON Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 nanofiber solid electrolyte, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9, 13688–13696 RSC.
- A. Monaca, G. Girard, S. Savoie, G. Bertoni, S. Krachkovskiy, A. Vijh, F. Pierini, F. Rosei and A. Paolella, Synthesis of Electrospun NASICON Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 Solid Electrolyte Nanofibers by Control of Germanium Hydrolysis, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2021, 168, 110512 CrossRef.
- S. Wu, X. Zhang, R. Wang and T. Li, Progress and perspectives of liquid metal batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2023, 57, 205–227 CrossRef.
- C. Shin, H. Lee, C. Gyan-Barimah, J. Yu and J. Yu, Magnesium: Properties and rich chemistry for new material synthesis and energy applications, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2023, 52, 2145–2192 RSC.
- S. Mondal, S. Park, J. Choi, T. Vu, V. Doan, T. Vo, B. Lee and J. Oh, Hydroxyapatite: A journey from biomaterials to advanced functional materials, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2023, 321, 103013 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Xu, J. Jin, C. Chen and Z. Wen, From nature to energy storage: A novel sustainable 3D cross-linked chitosan–PEGGE-based gel polymer electrolyte with excellent lithium-ion transport properties for lithium batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 38526–38537 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Cui, Z. Zhou, M. Jia, X. Chen, C. Shi, N. Zhao and X. Guo, Solid Polymer Electrolytes with Flexible Framework of SiO2 Nanofibers for Highly Safe Solid Lithium Batteries, Polymers, 2020, 12, 1324 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Li, G. Huang, Y. Yu, Q. Xiong, J. Yan and X. Zhang, Three Birds with One Stone: An Integrated Cathode–Electrolyte Structure for High-Performance Solid-State Lithium–Oxygen Batteries, Small, 2022, 18, 2107833 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhu, C. Liu, Y. Yang, Y. Li and Q.-H. Wu, A novel design of inorganic-polymer gel electrolyte/anode interphase in quasi-solid-state lithium-ion batteries, Electrochim. Acta, 2023, 446, 142097 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Liu, H. Shan, S. Xia, J. Yan, J. Yu and B. Ding, Polymer Template Synthesis of Flexible SiO2 Nanofibers to Upgrade Composite Electrolytes, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 31439–31447 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zheng, H. Li, H. Yuan, H. Fan, W. Li and J. Zhang, Understanding the anchoring effect of graphene, BN, C2N and C3N4 monolayers for lithium–polysulfides in Li–S batteries, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018, 434, 596–603 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Song, Y. Zhang, J. Liang, S. Liu, J. Zhu and X. Yan, Boron nitride nanofibers enhanced composite PEO-based solid-state polymer electrolytes for lithium metal batteries, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2023, 35, 108797 CrossRef.
- X. Hu, Q. Liu, M. Jing, F. Chen, B. Ju, F. Tu, X. Shen and S. Qin, Controllable preparation of alumina nanorods with improved solid electrolyte electrochemical performance, Ceram. Int., 2020, 46, 16224–16234 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Singh and R. Singh, Synthesis and characterization of gd-doped SnO2 nanostructures and their enhanced gas sensing properties, Ceram. Int., 2017, 43, 2350–2360 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liu, C. Hu, L. Chen, Y. Hu, H. Jiang and C. Li, Confining ultrahigh oxygen vacancy SnO2 nanocrystals into nitrogen-doped carbon for enhanced Li-ion storage kinetics and reversibility, J. Energy Chem., 2022, 69, 450–455 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Zhang, N. Deng, J. Kang, X. Wang, H. Gao, Y. Liu, H. Wang, G. Wang, B. Cheng and W. Kang, Enhanced ionic conductivity in a novel composite electrolyte based on Gd-doped SnO2 nanotubes for ultra-long-life all-solid-state lithium metal batteries, J. Energy Chem., 2023, 77, 326–337 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Deng, S. Luo, L. Zhang, Y. Feng, Y. Liu, W. Kang and B. Cheng, Synergistically enhanced roles based on 1D ceramic nanowire and 3D nanostructured polymer frameworks for composite electrolytes, J. Energy Storage, 2024, 75, 109578 CrossRef.
- M. Jing, H. Yang, C. Han, F. Chen, W. Yuan, J. Bowei, F. Tu, X. Shen and Q. Shibiao, Improving room-temperature electrochemical performance of solid-state lithium battery by using electrospun La2Zr2O7 fibers-filled composite solid electrolyte, Ceram. Int., 2019, 45, 18614–18622 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Gao, N. Wu, N. Deng, Z. Li, J. Li, Y. Che, B. Cheng, W. Kang, R. Liu and Y. Li, Optimized CeO2 Nanowires with Rich Surface Oxygen Vacancies Enable Fast Li-Ion Conduction in Composite Polymer Electrolytes, Energy Environ. Mater., 2023, 6, e12272 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Chen, D. Adekoya, L. Hencz, J. Ma, S. Chen, C. Yan, H. Zhao, G. Cui and S. Zhang, Stable seamless interfaces and rapid ionic conductivity of ca–CeO2/LiTFSI/PEO composite electrolyte for high–rate and high–voltage all–solid–state battery, Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10, 2000049 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Yang, N. Deng, Y. Zhao, L. Gao, W. Liu, Y. Liu, B. Cheng and W. Kang, Dendritic sulfonated polyethersulfone nanofiber membrane@LaCoO3 nanowire-based composite solid electrolytes with facilitated ion transport channels for high-performance all-solid-state lithium metal batteries, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023, 11, 2780–2792 RSC.
- Y. Chen, F. Pan, Z. Guo, B. Liu and J. Zhang, Stiffness threshold of randomly distributed carbon nanotube networks, J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 2015, 84, 395–423 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Yao, B. Zhu, H. Zhai, X. Liao, Y. Zhu, W. Xu, Q. Cheng, C. Jayyosi, Z. Li, J. Zhu, K. M. Myers, X. Chen and Y. Yang, PVDF/Palygorskite Nanowire Composite Electrolyte for 4 V Rechargeable Lithium Batteries with High Energy Density, Nano Lett., 2018, 18, 6113–6120 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Zhang, Y. Huang, H. Gao, C. Li, J. Huang and P. Liu, 3D glass fiber cloth reinforced polymer electrolyte for solid-state lithium metal batteries, J. Membr. Sci., 2021, 621, 118940 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Yuan, L. Chen, Y. Li, X. An, J. Lv, S. Guo, X. Cheng, Y. Zhao, M. Liu, Y. He and F. Kang, Functional LiTaO3 filler with tandem conductivity and ferroelectricity for PVDF-based composite solid-state electrolyte, Energy Mater. Devices, 2023, 1, 9370004 CrossRef.
- X. An, Y. Liu, K. Yang, J. Mi, J. Ma, D. Zhang, L. Chen, X. Liu, S. Guo, Y. Li, Y. Ma, M. Liu, Y. He and F. Kang, Dielectric Filler-Induced Hybrid Interphase Enabling Robust Solid-State Li Metal Batteries at High Areal Capacity, Adv. Mater., 2024, 36, 2311195 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Wan, D. Lei, W. Yang, C. Liu, K. Shi, X. Hao, L. Shen, W. Lv, B. Li, Q. Yang, F. Kang and Y. He, Low Resistance-Integrated All-Solid-State Battery Achieved by Li7La3Zr2O12 Nanowire Upgrading Polyethylene Oxide (PEO) Composite Electrolyte and PEO Cathode Binder, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29, 1805301 CrossRef.
- K. Yang, L. Chen, J. Ma, C. Lai, Y. Huang, J. Mi, J. Biao, D. Zhang, P. Shi, H. Xia, G. Zhong, F. Kang and Y. He, Stable interface chemistry and multiple ion transport of composite electrolyte contribute to ultra-long cycling solid-state LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2/lithium metal batteries, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 24668–24675 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Du, B. Zhang, C. Yang, L. Cui, L. Mai and L. Xu, Leaf-inspired quasi-solid electrolyte enables uniform lithium deposition and suppressed lithium-electrolyte reactions for lithium metal batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2023, 61, 102914 CrossRef.
- A. Li, X. Liao, H. Zhang, L. Shi, P. Wang, Q. Cheng, J. Borovilas, Z. Li, W. Huang, Z. Fu, M. Dontigny, K. Zaghib, K. Myers, X. Chuan, X. Chen and Y. Yang, Nacre-inspired composite electrolytes for load-bearing solid-state lithium-metal batteries, Adv. Mater., 2020, 32, 1905517 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Chen, D. Nguyen, S. Lee, N. Baker, A. Karakoti, L. Lauw, C. Owen, K. Mueller, B. Bilodeau, V. Murugesan and M. Troyer, Accelerating Computational Materials Discovery with Machine Learning and Cloud High-Performance Computing: from Large-Scale Screening to Experimental Validation, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2024, 146, 20009–20018 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
| This journal is © the Partner Organisations 2024 |











