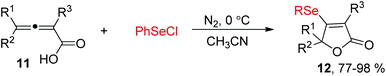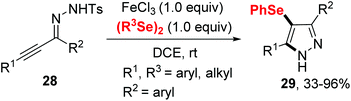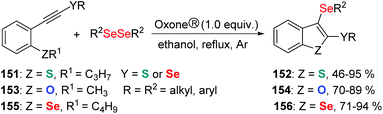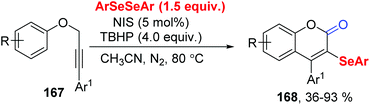Recent advances in tandem selenocyclization and tellurocyclization with alkenes and alkynes
Kai
Sun
 *ab,
Xin
Wang
a,
Chao
Li
b,
He
Wang
*ab,
Xin
Wang
a,
Chao
Li
b,
He
Wang
 b and
Lei
Li
b and
Lei
Li
 *b
*b
aCollege of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Anyang Normal University, Anyang 455000, P. R. China. E-mail: sunk468@nenu.edu.cn
bSchool School of Chemistry and Materials Science, Liaoning Shihua University, Dandong Road 1, Fushun 113001, P. R. China. E-mail: lilei0814.com@163.com
First published on 18th August 2020
Abstract
Seleno-containing heterocycles exist widely in pharmaceutical molecules and the skeletons of natural products. The addition of organoselenium to alkenes and alkynes via intramolecular tandem selenocyclization is an efficient method for preparing selenofunctionalized heterocycles. In this protocol, multiple bonds are formed in a single reaction without the need to isolate intermediates. This review highlights recent progress in this rapidly growing area with an emphasis on the scopes, limitations and the mechanisms of these different reactions. Besides, tandem tellurocyclization with alkenes and alkynes is also briefly discussed.
 Chao Li | Chao Li received his BE degree from Zhoukou Normal University in 2019. He is now pursuing his MSc degree under the guidance of Prof. Lei Li at Liaoning Shihua University. |
1. Introduction
Organoselenium compounds are considered an important class of molecules in organic synthesis. These compounds are widely applied in materials and catalysis and as intermediates in organic synthesis.1 In addition, organoselenium compounds have been shown to have pharmacological activities such as anticonvulsant, antioxidant, antidepressant, anticancer, antitumor, anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties.2 The introduction of a selenium atom into a potentially bioactive molecule can dramatically increase the native biological activity of the substrate. Meanwhile, heterocycles, which exist in natural products and biologically active molecules, play significant roles in the pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries.3 For all these reasons, continuous research effort has been devoted to the development of useful methods for synthesizing selenofunctionalized heterocycles. Currently, one way to access these compounds is the direct functionalization of the heterocycle precursor with a selenium source via transition metal catalysis.4 However, this method is limited by its poor regioselectivity and direct use of preformed or commercially available heteroaromatic counterparts. Alternatively, the addition of organoselenium to alkenes and alkynes via intramolecular tandem selenocyclization is an efficient protocol for preparing selenofunctionalized heterocycles. In this protocol, multiple bonds are formed in a single reaction without the need to isolate intermediates.Over the past decade years, the selenocylization of the selenium electrophiles (e.g., ArSeCl, ArPhBr, and ArthSe) with alkenes or alkynes have been deeply developed.5 However, the sensitivity to moisture and a short shelf life limited the application. In contrast, diselenides are easily accessible and operable selenium reagents in organic synthesis, making them a good choice for selenocyclization.6 Although some approaches have been reported for the intramolecular tandem selenocyclization reactions of diorganyl diselenides with alkenes and alkynes, few efforts have systematically reviewed tandem selenocyclization with alkenes and alkynes. In consideration of recent research progress and to better understand selenium-based intramolecular tandem selenocyclization, this review article firstly introduce the traditional selenocylization with some selenium electrophiles, and then summarize the latest contributions to selenocyclization reactions of diorganyl diselenides with alkenes and alkynes between 2010 and 2020 and highlights the insights gained from previous methodological and mechanistic studies. The content is categorized by the type of catalysis, including metal catalysis, visible-light catalysis, electrochemical catalysis, organocatalysis, and other catalysis types involving hypervalent iodine- and peroxide-promoted reactions.
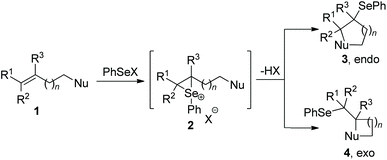
2. Traditional selenocyclization
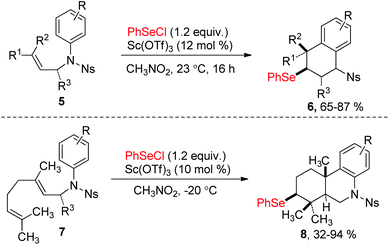
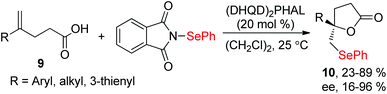
Since the discovery in the late 1960s that species of type RSeX added stereospecifically to simple alkenes to the formation of a selenolactone,7 these reactions were extensively developed to construct the selenofunctionalized heterocycles. Mechanistically, seleniranium ion 2 was formed by the addition of RSeX to unsaturation bond, which then was captured by a pendant nucleophilic group to generate a cyclic product with chemo-, regio-, stereo-specificity (Scheme 1).8 For example, in 2013, the group of Shaw reported tandem monocyclization and bicyclization reactions between alkenes and PhSeCl in the presence of catalytic quantities of Sc(OTf)3 to access polysubstituted tetrahydroquinoline 6 and octahydrophenanthridine 8 in moderate to high yields (Scheme 2).9 In this process, two rings, three bonds, and three stereogenic centers were formed with excellent stereo- and regio-control in one step.Moreover, N-(2-nitrophenylselenenyl)succinimide (NPSP) was also used as the electrophilic selenium source. In 2015, Yeung and co-workers described an enantioselective selenolactonization of olefinic acids 9 and NPSP, using hydroquinidine 1,4-phthalazinediyl diether ((DHQD)2PHAL) as the catalyst (Scheme 3).10 A series of functional groups were tolerant with this catalytic system, giving the corresponding selenolactones 10 with good yields and ee values. Additionally, heteroaromatic substrate was also reacted well in this catalytic system. Although cyclohexyl substrate was accommodated in 89% yield, the ee was only 16% under this catalytic protocol. The mechanism study shows that the large catalyst pocket was required for this transformation to avoid racemization of the chiral episeleniranium ion, introducing high enantioselectivity.
Allenes owing to two cumulative carbon–carbon double bonds have some unique chemical properties.11 For example, in 2004, the Ma's group demonstrated a electrophilic cyclization of 2,3-allenoic acids 11 with PhSeCl for the synthesis of β-organoselenium butenolides 12 (Scheme 4).12 The reaction showed a broad substrate scope, and 4-mono-substituted, 2,4-disubstituted, and 2,4,4-trisubstituted 2,3-allenoic acids can all be applied to afford the corresponding products in 77–98% yields. Moreover, this protocol can also be compatible to the corresponding electrophilic cyclization of PhSCl.
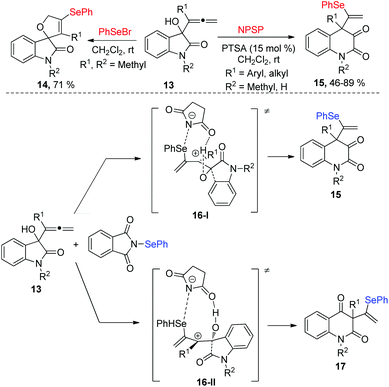
In 2012, Alcaide and co-workers disclosed an electrophilic selenocyclization of 2-indolinone-tethered allenols 13 with various selenenylating reagents, affording different heterocycles, which was shown good chemoselectivity (Scheme 5).13 PhSeBr, N-phenylselenosuccinimide (NPSS), or diphenyl diselenide as donors of PhSe+ in reactions with 2-indolinone-tethered allenol XX delivered spirocyclic selenolactams 14, and PhSeBr was the optimal selenenylating reagents, giving the target product with 71% yield in 1 hour without any additives Moreover, quinoline-2,3-diones 15 were obtained by using NPSP and catalytic amounts of p-toluenesulfonic acid (PTSA) in dichloromethane at room temperature. The mechanism of NPSP-promoted ring expansions was proposed in Scheme 5. First, the addition of PhSe+ cation to the proximal allenic double bond produces the intermediate 16. The intermediate 16 has two regioisomer: 16-I and 16-II, which occur a ring expansion to give the corresponding products 15 and 17. The migration of the phenyl group is preferred to the migration of the carbonyl one, and 15 is the major product.
 | ||
| Scheme 5 The selenocyclization of 2-indolinone-tethered allenols for the synthesis of spirocyclic selenolactams and quinoline-2,3-diones. | ||
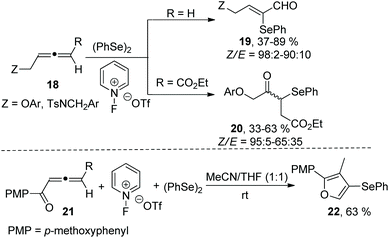
In subsequent work, Alcaide and coworkers reported a metal-free oxidative selenofunctionalized reaction between allenes and diphenyl diselenide (Scheme 6).14 This reaction employed 1-fluoropyridinium compounds as oxidative functionalization reagents to access two types of α-seleno-α,β-unsaturated carbonyls (α-selenoenals 19 and α-selenoenones 20) by changing the substituents at the allene end. In the case of allenone as a substrate, the α-selenoenone was failed to obtained, and the cyclized selenated furan 22 was afforded in 63% yield. The protocol disclosed the oxidation of (PhSe)2 promoted by 1-fluoropyridinium triflate to generate the electrophilic species PhSe(OTf).
3. Diorganyl diselenides promoted selenocyclization
3.1 Transition metal-catalyzed selenocyclization
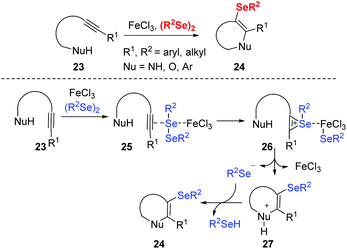
The group of Zeni reported a series of iron(III)-promoted cyclization of alkynes and diselenides. This strategy provides a new approach to obtain various selenofunctionalized heterocycles such as benzo[b]furans chromenones, indoles, isoxazoles, benzoxazines, dihydrofurans, isochromenimines, naphthalenes from readily accessible starting materials under mild conditions with efficiency and operability (Scheme 7).17 The authors proposed the mechanism that the key of these selenocyclizations are the iron-seleno complex generated from the reaction of FeCl3 and diorganyl diselenide (RSe)2. The electrophilic portion of the selenium species coordinates to the triple carbon–carbon bond to generate the seleniranium ion 26. The cyclized cationic intermediate 27 is then generated via intramolecular nucleophilic attack. Finally, deprotonation of 27 gives the selenocyclized product 24.
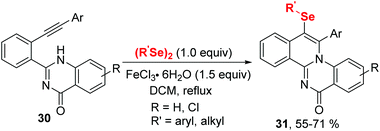
In 2020, the group of Ji established an iron(III) chloride-promoted cyclization between α,β-alkynic tosylhydrazones 28 and diselenides (Scheme 8).18 The reaction proceeded efficiently in the presence of 1.0 equiv. FeCl3 in 1,2-dichloroethane (DCE) at room temperature, providing a series of 4-(arylselanyl)-1H-pyrazoles 29 with good functional group tolerance. Meanwhile, Koketsu et al. reported seleno-cyclization of alkyne 30 and diselenides, furnishing a series of 6H-isoquinolino[2,1-a]quinazolin-6-one 31 (Scheme 9).19 In this reaction, C–N and C–Se were constructed in one step using 1.5 equivalent of FeCl3·6H2O in dichloromethane at room temperature. The plausible mechanisms of these two reactions are similar to above mentioned.
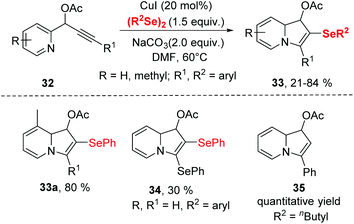
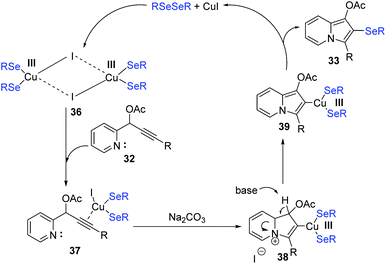
To get insight the mechanism aspect of this cyclization, some control experiments were performed. These experiments revealed that the copper-selenolate species 36 generated by mutual action between copper(I) iodide and diorganyl diselenide was essential for the reaction. In the mechanism (Scheme 11), an intermediate 37, as an electrophile through the activation by coordination of the Cu(I) ion to the alkyne, is formed. Intermediate 37 is then converted into 38via intramolecular nucleophilic attack of N atom. Deprotonation then produces the 2-copper-indolizine 39. The subsequent reductive elimination of copper leads to the formation of the final product 33.
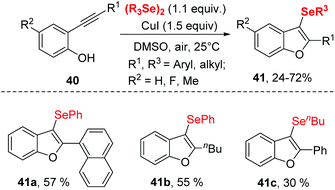
A similar transformation was achieved by Godoi.22 The selenocyclization between 2-alkynylphenols and diorganyl diselenides enabled selenocyclization provided 3-organoselanylbenzo[b]furan derivatives in moderate to good yields (Scheme 12). In contrast to the Zeni's work,21 this reaction did not need any base and worked smoothly in DMSO at room temperature by promotion of 1.5 equiv. CuI. The protocol performed excellent functionality tolerance. 2-Alkynylphenol, containing electron-donating groups, electron-withdrawing groups and halogen groups were all tolerated. Moreover, naphthyl-substituted alkyne also reacted well in this catalytic system. In particular, low reactive aliphatic alkyne was accommodated with moderate yields. Moreover, the dialkyl diselenides was proven to be applicable in this reaction.
Notably, 3-organoselanylbenzo[b]furan could be used to prepare for different functionalized benzo[b]furans, demonstrating the synthetic applicability of this protocol.
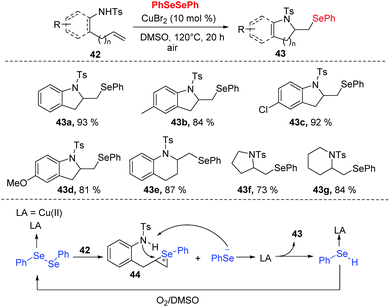
In 2018, Zhong and co-workers developed a copper-catalyzed tandem selenoamination reaction of alkenes, successfully affording a series of seleno-N-heterocycles (e.g., indoline, tetrahydroquinoline, pyrroline, and piperidine derivatives) with 73–93% yields (Scheme 13).23 In this approach, 10 mol% of CuBr2 was utilized in DMSO at 120 °C in air. During the mechanistic investigation, oxygen and DMSO as co-oxidants were necessary for this transformation. Moreover, radical quenching experiments suggested a radical mechanism is not likely the case in the present catalytic system. As shown in Scheme 13, the Se–Se of diselenide could be polarized by CuBr2 to access the coordination 44, which undergoes an electrophilic addition to the olefin moiety of 42. The intramolecular nucleophilic attack by nitrogen and deprotonation then furnish the desired product 43 and selenophenol. Selenophenol is oxidized to diselenide by O2 and DMSO, and re-enter to the catalytic cycle.
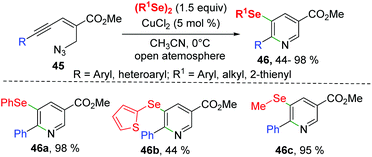
Soon after, Reddy's group reported a CuCl2-catalyzed synthesis of selenyl nicotinates from enynyl azide 45 with diorganyl diselenides (Scheme 14).24 The enynyl azide bearing aryl groups with different electron-donating or electron-withdrawing groups and 2-thienyl all underwent this transformation smoothly, leading to desired 5-selenyl nicotinates 46 with yields ranging from 78–98%. It is worth noting that aryl-substituted, heterocyclic, and alkyl-substituted diselenides are also compatible to this reaction. The mechanism for this intramolecular selenoamination is similar to that described in Zhong's work.23
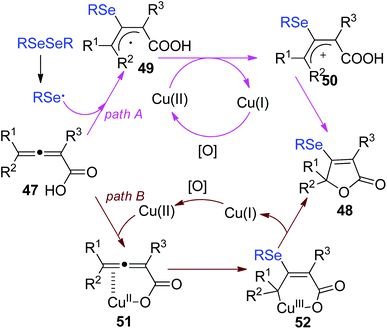
In 2018, Xu and co-workers demonstrated a selenocyclization of 2,3-allenoic acids 47 with diselenides in the combination of CuCl and (NH4)2S2O8 as catalytic oxidation system (Scheme 15).25 The reaction enabled sulfenylation/cyclization and subsequent oxidation to provide selenylated butenolides 48 in 63–82% yields. (NH4)2S2O8 played dual roles as a radical initiator as well as oxidant. Moreover, selenylated butenolides could be applied for synthesis of the corresponding furan derivatives.
The proposed mechanism by the authors was depicted in Scheme 16. First, a selenyl radical is formed via the homolysis of RSeSeR in the presence of (NH4)2S2O8. The addition of selenyl radical to 2,3-allenoic acids gives the radical intermediate 49. The further oxidation of intermediate 49 by Cu(II) affords the intermediate 50. Finally, the intramolecular attack of intermediate 50 leads to the cyclized products 51. Another pathway is also proposed. Cu(II) coordinated to 2,3-allenoic acids, generating the complex 51. Then, the addition of selenyl radical to 51 gives Cu(III) intermediate 52. Finally, reductive elimination is occurred to release the desired product 48.
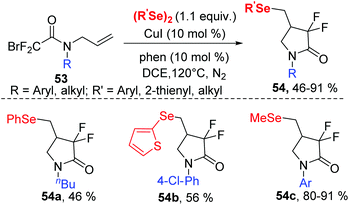
Organofluorine compounds constitute an attractive class of compounds that have attracted significant attention from researchers in a variety of disciplines. In 2019, the group of Sun successfully synthesized a series of 4-seleno-substituted α,α-difluoro-γ-lactams 54 using N-allyl-2-bromo-2,2-difluoroacetamides 53 and diorganyl diselenides catalyzed by 10 mol% CuI in DCE at 120 °C under external-oxidant-free conditions (Scheme 17).26 Various N-aryl-substituents of bromodifluoroacetamides with different electron-donating or electron-withdrawing groups undergo this transformation smoothly, leading to desired products with yields ranging from 63–82%. Notably, N-alkyl-substituted bromodifluoroacetamide could proceed well in this reaction. Furthermore, diphenyl diselenides, 1,2-di(thiophen-2-yl)diselane and dimethyldiselenide were also compatible to this reaction.
Regarding the mechanism, control experiments and radical quenching experiments demonstrated this process proceeded through a radical pathway. The authors proposed the following possible reaction mechanism (Scheme 18).
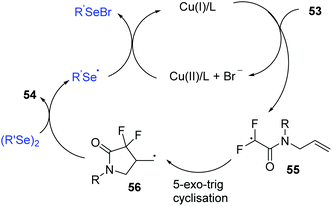 | ||
| Scheme 18 Proposed mechanism of the CuI-catalyzed synthesis of 4-seleno-substituted α,α-difluoro-γ-lactams. | ||
A single-electrontransfer (SET) between Cu(I) and 53 occurs to afford a Cu(II) species and radical intermediate 55. Next, the addition of the fluoroalkyl radical to the unsaturated double bond affords alkyl radical intermediate 56via a 5-exo-trig cyclization. The alkyl radical intermediate 56 reacts with diphenyl diselenide to form the desired product 54 and selenyl radical, which further reduces Cu(II) to Cu(I) and selenyl anion (PhSeX) to complete the catalytic system.
3.2 Visible light-promoted selenocyclization
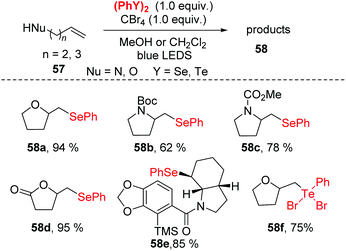
Recently, photoredox catalysis has emerged as a useful tool for radical reactions via visible light-induced processes. Compared with previous methods, photoredox catalysis is inexpensive and has the advantages of environmentally-benign (it does not require excess amounts of transition metals or oxidants), high efficiency and easy to use.27 Notably, diselenide bonds possess a lower bond energy (172 kJ mol−1), which could facilitate the generation a selenium radical species via the homolytic cleavage of the Se–Se single bond under visible-light irradiation without any photocatalyst. Therefore, the construction C–Se to synthesize selenofunctionalized heterocycles under visible-light irradiation has become more appealing.In 2013, Ragains and co-workers reported a visible light-promoted selenocyclization of alkenes at room temperature (Scheme 19).28 In this reaction, bench-stable PhSeSePh is combined with CBr4 under the irradiation of a 5 W blue light-emitting diode (LED), resulting in the in situ generation of reactive PhSeBr. This reaction showed a broad substrate scope, generating O-heterocycles in high yields along with N-heterocycles in moderate to high yields. Notably, diphenyl ditelluride was successfully suitable for this strategy to afford the tellurofunctionalization products in 53–75% yields in dichloromethane as solvent. To further demonstrate the application of this method, the Amaryllidaceae alkaloid γ-lycorane was synthesized. Mechanistic studies and DFT calculation suggested visible light irradiation promoted the phenylselenyl radical abstraction of bromine from CBr4 to generate phenylselenyl bromide in situ. The detailed mechanism of these reactions is still under investigation.
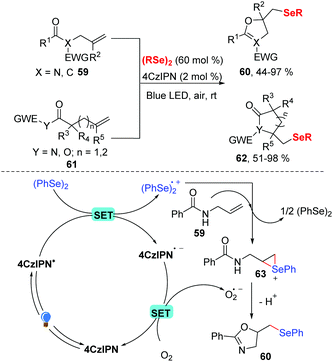
Later, the group of Liu developed a visible light-driven selenocyclization of N-allylamides in MeCN in the presence of 2 mol% 4CzIPN under visible-light and in air (Scheme 20).29 While dihydroisoxazole was produced in 73% yield without any photocatalyst under these optimized reaction conditions, the use of 4CzIPN as a photocatalyst promoted the reaction process. In contrast to other seleno cylization reactions, this protocol only needed 60 mol% diselenides. In addition, many substituted the allylic amides and various diselenides were well tolerated in this transformation and gave the corresponding products 60 in good to excellent yields. Inspired by this result, a series of heterocycles were prepared by investigating the scope of the nucleophilic reagent, generating the corresponding products 62 in 51–98% yields. A possible reaction mechanism (Scheme 20) was proposed based on fluorescence quenching experiments. In this mechanism, the ground state 4CzIPN is excited to *4CzIPN under visible light irradiation. The excited state then undergoes a SET reaction with diphenyl diselenide to generate (PhSe)2˙+ radical cation and 4CzIPN˙− radical anion. Then, the molecular oxygen oxidized 4CzIPN˙− to the ground state completes the photoredox cycle. Meanwhile, the addition of diselane radical cation (PhSe)2˙+ to N-alkenylamide 59 produces seleniranium cation 63, which undergoes intramolecular nucleophilic cyclization to obtain the desired product 60.
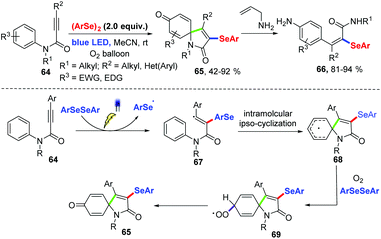
In 2017, an efficient approach for the preparation of selenium substituted spiro[4,5]trienones based on visible light-induced selenium radical-cyclization of N-aryl alkynamides 64 under oxygen atmosphere at room temperature without external photocatalyst was described for Baidya and coworkers (Scheme 21).30 This reaction showed a wide range of functional groups tolerances. Diverse N-aryl alkynamide and diaryl diselenides bearing electron-donating as well as electron-withdrawing groups in aryl ring can achieve the products 65 in moderate to excellent yields. In addition, good yields were achieved in gram-scale reactions. A spiro-ring-opening strategy was realized to give fully substituted acryl amides 66. Based on several control experiments, a possible radical pathway mechanism was proposed. First, under visible light irradiation, the addition of selenyl radical produced via homolytic cleavage of the Se–Se single bond to the triple bond produces a vinyl radical 67. Subsequently, intramolecular radical ipso-cyclization affords 68. Oxidative dearomatization would then occurs under oxygen atmosphere and in the presence of diaryl diselenide to afford the desired product.
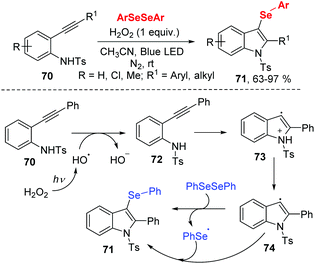
In 2017, the group of Wang developed a facile route to prepare 3-selenylindoles from N-(2-(ethynyl)aryl)benzenesulfonamide 70 and diaryl diselenides under 3 W blue LED irradiation (Scheme 22).31 The authors optimized reaction conditions and found that H2O2 (30% aqueous solution) as oxidant was necessary for this transformation. Moreover, this methodology exhibited good functional group tolerance, giving rise to the 3-selenylindoles 71 in moderate to excellent yields. With the result of radical-trapping experiment, a radical free mechanism was proposed. Initially, hydroxyl radical generates from the homolytic cleavage of H2O2 under blue LED irradiation. Then a single electron transfer between 70 and hydroxyl radical gives the intermediate 72. After the intramolecular cyclization and deprotonation, radical intermediate 74 is formed. Finally, the reaction between diphenyl diselenide and 74 leads the desired product 71 and phenylselenyl free radical. The phenylselenyl free radical further reacts with 74, delivering the final product.
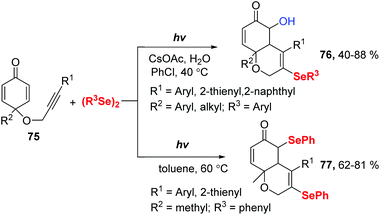
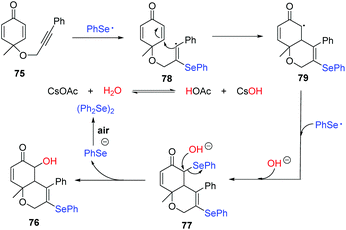
In 2019, Xu and coworkers reported a Se radical-triggered multi-component tandem cyclization of alkyne-tethered cyclohexadienones 75 and diaryl diselenides under the irradiation of 25 W white LEDs at 40 °C temperature (Scheme 23).32 This reaction gave 5-hydroxy-3-selenyl-4a,8a-dihydro-2H-chromen-6(5H)-ones 76 in 40–88% yields in the presence of 2 equiv. H2O and CsOAc in chlorobenzene at 40 °C. Moreover, the reaction could be performed in the absence of a base in dry toluene at 60 °C, producing 3,5-diselenyl-4a,8a-dihydro-2H-chromen-6(5H)-ones 77 in 62–81% yields. These results demonstrate water is crucial for this transformation. To gain more insight into the effect of water, some control experiments were performed. First, decreasing the amount of H2O to 1 equiv. provided 76 in 40% yield and 77 in 30% yield. Next, 77 was converted to the desired product 76 under the standard conditions indicating that 77 is a possible intermediate. 18O-Labelling experiments showed that the oxygen atom of the hydroxyl group originated from water. Moreover, a radical-trapping experiment using 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPO) was performed to probe the possibility of a radical mechanism in this transformation.
Through a series of experimental observations and surveys of previous literature, they proposed the following possible reaction mechanism (Scheme 24). First, under visible-light irradiation, phenylselenyl free radical generated from diphenyl diselenide undergoes a radical addition to substrate 75 to produce alkenyl radical 78. Subsequently, intramolecular radical cyclization gives intermediate 79, which is trapped by another phenylselenyl free radical to deliver the product 77. In the presence of CsOAc, nucleophilic substitution occurs with water and 77, leading to the desired product 76. Interestingly, some products showed potent inhibition activities against cancer cell growth in vitro.
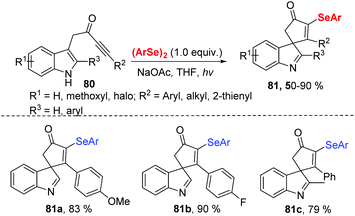
In 2020, Xu and coworkers further developed visible light-induced selenocyclization reaction of indolyl-ynones 80 with diselenides at room temperature under air atmosphere (Scheme 25).33 Diverse 3-selenospiroindolenines bearing various functional groups were obtained in moderate to good yields. Similarly, phenylselenyl free radical is generated from diphenyl diselenide under visible-light irradiation. The desired product is then obtained through the radical addition/oxidation/deprotonation pathway. Compounds 81a and 81b were tested for in vitro anticancer activity by MTT assay and showed potent inhibitory activity against cancer cell growth.
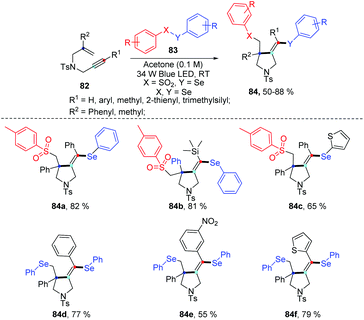
Very recently, the group of Wang disclosed a regio- and chemoselective radical cascade cyclization of 1,6-enynes 82 and areneselenosulfonates 83a under 34 W blue LED irradiation in the air without any photocatalysts (Scheme 26).34 Numerous substrates (82) were examined, and the corresponding cyclized products (84) were obtained in good to excellent yields. This reaction also proceeded smoothly using diaryl diselenides 83b with 1,6-enynes, and observed desired products with moderated to goods yields. However, this method was not applicable when the chain length was increased from one to two or three. The internal alkene and free amine in enyne were also not tolerant for this transformation. This protocol offers an efficient approach to build selenium substituted pyrrolidine derivatives via multiple chemical bond constructions in 5-exo-dig fashion, including one C–S bond, one C–Se bond, and one C–C bond.
Notably, some control experiments indicated the reaction proceeded in a radical way, and the visible-light irradiation was necessary. The reactivity of the chalcogen group in the reaction was tested by the combination of 82a with 83a and 83b. The result suggested that tosyl radical was more reactivity than phenylselenyl, demonstrating the regio- and chemoselectivity. The proposed mechanism is described in Scheme 27. The tosyl (85) and phenylselenyl free radical (86) are generated by visible light irradiation. Tosyl radical 85 is added to 1,6-enynes 82a to generate alkyl radical intermediate radical 87. Then intramolecular 5-exo-dig cyclization gives rise to the corresponding vinyl radical 88, which is further trapped by phenylselenyl free radical (86) to generate desired product 84a. The reverse transformation products were not observed, probably due to the higher stability of the tertiary alkyl radical intermediate 87 compared to the vinyl generated by the tosyl radical addition to alkyne. This protocol showed excellent regio- and chemoselectivity, good functional tolerance.
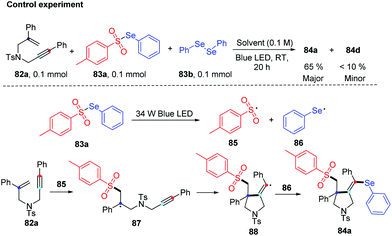 | ||
| Scheme 27 Control experiments and proposed mechanism of visible light-promoted synthesis of seleno-containing pyrrolidine. | ||
3.3 Electrochemically enabled selenocyclization
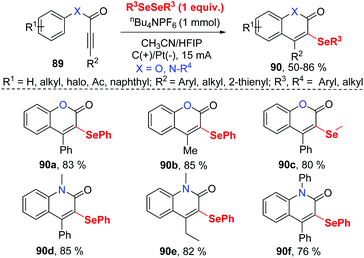
In the past few years, electrochemistry has been recognized as one of the most powerful and sustainable methods in organic chemistry since electrochemical methods avoid chemical oxidants, reductants, and transition-metal catalysts.35 Compared to traditional chemical synthetic methods, electrochemically induced selenocyclization methods for the difunctionalization of alkenes and alkyne are relatively rare. More selenocyclization reactions for the synthesis selenyl heterocycles should be developed.In 2019, Guo and co-workers reported an electrochemically induced oxidative cyclization of alkynoates or alkynamides with diselenides by using nBu4NPF6 as supporting electrolyte (Scheme 28).36 In the cases of diselenides with aryl groups or alkyl groups, the reaction proceeded smoothly, giving the corresponding coumarins or quinolinones 90 in moderate to good yields. This protocol also demonstrated a broad substrate scope of alkynoates and alkynamides, except when para-OMe was substituted on the aryl group. However, terminal alkyne was ineffective for this transformation. Moreover, the reaction can be conducted on a gram scale with excellent efficiency, demonstrating the practical application in future industry. Comparing to the previous report on the related selenocyclization reaction of alkynoates and alkynamides by Zeni's17e and Liu's49 work, this strategy requires no transition metals or chemical oxidants. Cyclic voltammetric (CV) experiments show that diphenyl diselenide had a lower oxidative potential than the substrate, indicating that diphenyl diselenide is more easily electrochemically oxidized to generate phenylselenium radical than the alkyne moiety.
Based on control experiments and radical quenching experiments, they proposed a possible reaction mechanism (Scheme 29). Diphenyl diselenide initially undergoes anodic oxidation to generate cationic radical intermediate 91, which is decomposed to give phenylselenium radical 92 and phenyl selenium cation 93. Thereafter, the radical addition of 92 to triple bond provides vinyl radical 94 in high regioselectivity. The resulting radical 94 participated in an intramolecular radical reaction to generate intermediate 95, which is further oxidized on anode to afford the cation 96. At last, deprotonation affords the final product 90.
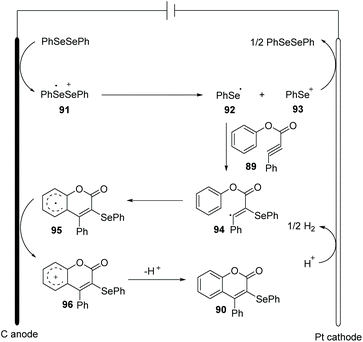 | ||
| Scheme 29 Proposed mechanism of electrochemically induced synthesis of selenated coumarins and quinolinones. | ||
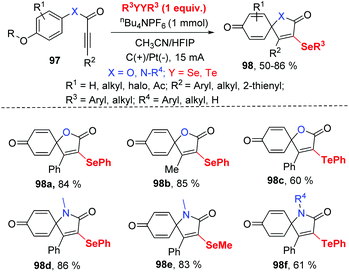
Inspired by this protocol, the group of Guo further developed the electrocatalytic oxidative radical dearomative spirocyclization for the preparation of selenation spiro[4.5]trienones 98 from alkynes 97 with diselenides (Scheme 30).37 As mentioned above, when the substrates are alkynoates and alkynamides bearing a methoxy group at para substituted of aryl ring, the ipso-cyclization was occurred. Then, they optimized the reaction condition; the reaction worked well in CH3CN/HFIP (v![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) v = 3
v = 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) at room temperature with nBu4NPF6 as electrolyte. The use of the optimized reaction parameters led to the corresponding 49 examples of selenation spiro[4.5]trienones in moderate to good yields with broad substrate scope and high functional group tolerance. It is note that diphenyl ditelluride was also compatible for this transformation, giving tellurium-substituted products in good yields. It should be mentioned that terminal alkyne was not suitable for this system.
1) at room temperature with nBu4NPF6 as electrolyte. The use of the optimized reaction parameters led to the corresponding 49 examples of selenation spiro[4.5]trienones in moderate to good yields with broad substrate scope and high functional group tolerance. It is note that diphenyl ditelluride was also compatible for this transformation, giving tellurium-substituted products in good yields. It should be mentioned that terminal alkyne was not suitable for this system.
Notably, scale-up reaction was performed in electrochemical continuous flow system, and nearly the same yield was obtained (73% yield in nearly 15 h on the 10 mmol scale).
The authors also provided the possible mechanism (Scheme 31). Vinyl radical 99 is generated in the similar path and then undergoes intramolecular spirocyclization to provide 100, different from their earlier work. Meanwhile, the anodic oxidation of the intermediate 100 generates oxygenium cation intermediate 102. Finally, the sequential the demethylation of cation 102 and the dearomatization of the aromatic ring give access to the desired product.
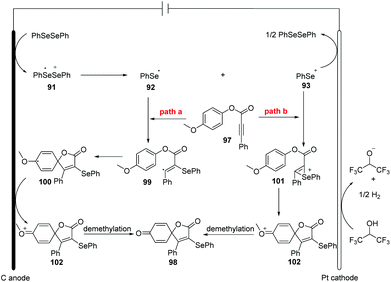 | ||
| Scheme 31 Proposed mechanism of electrochemically induced synthesis of selenation spiro[4.5]trienones. | ||
In 2019, Pan and co-workers reported the electrochemical selenocyclization of olefins and diselenides for the generation of selenomethyl-substituted cyclic ethers or lactones (Scheme 32).38 The olefines including unsaturated alcohols and unsaturated carboxylic acids 103, were all suitable for this reaction with NH4I as electrolyte and electrocatalyst, affording the corresponding products 104 in good yields. Moreover, the difficult-to-synthesize medium-sized ethers (7-, 9-, and 11-membered rings) and 4–6-membered ring lactones could be obtained smoothly. However, the reaction was limited to diphenyl diselenides bearing electron-donating groups (OMe), failing to produce the desired product with 2-vinylbenzoic acid. According to the results of cyclic voltammetry studies and control experiments, the reaction mechanism is depicted in Scheme 32. Iodine ion is first oxidized at anode to produce I+, which then reacts with olefnic alcohols to form iodonium cations intermediate 105. Subsequently, intramolecular cyclization and deprotonation lead to intermediate 106. Finally, rapid chemical selenation by diphenyl diselenide gives access to the desired product and a half molar equivalent of I2. At the cathode, reduction of I2 and proton to iodine anion and hydrogen completes the reaction cycle.
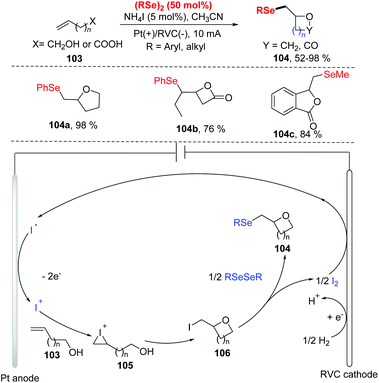 | ||
| Scheme 32 Electrochemically induced synthesis of selenomethyl-substituted cyclic ethers, lactones and isobenzofuranones. | ||
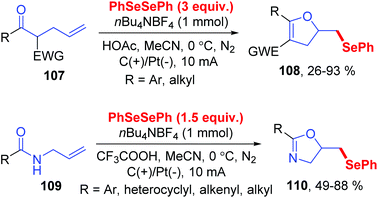
Dihydrofurans and oxazolines play important roles in numerous biologically active molecules, pharmaceuticals and agronomicals. As a straightforward and highly atom-economic method for synthesizing these derivatives, the selenocylization of olefinic carbonyls has attracted the attention of chemists. In 2019, the group of Lei realized an electrochemical oxidative cyclization between olefinic carbonyls and diaryl diselenides, providing a practical and enconomical approach to the preparation of selenium-functionalized dihydrofurans (Scheme 33).39 This reaction could proceed smoothly in CH3CN at room temperature with nBu4NBF4 as electrolytes, HOAc as additive, graphite as the working anode, and platinum as the cathode. This method shows good compatibility for symmetric and unsymmetric olefinic carbonyls 107 with different substituents, giving the corresponding dihydrofurans compounds 108 in moderate to good yields. In addition, this protocol also tolerated unsaturated amides 109, affording the corresponding seleno oxazolines 110 in moderate to excellent yields.
To gain more insight into this cascade cyclization, they added stoichiometric radical inhibitor TEMPO to reaction systems and perform this reaction under standard conditions. The yield of the desired product decreased obviously, indicating that the process involves a free radical pathway. Based on mechanistic studies, cyclic voltammetry studies, and the literature, the authors proposed two possible reaction pathways (Scheme 34). In path a, the anion radical intermediate 91 is generated by cathode reduction, and then decomposes to give phenylselenium radical 92 and phenyl selenium anion 93. Then, the radical addition of phenylselenium radical 92 to the alkene results in the formation of C-radical intermediate 111, which is further oxidized at anode. Finally, an intramolecular cyclization is occurred by nucleophilic attack of the oxygen atom of carbonyl, subsequent deprotonation to render the final product 108. In path b, the phenylselenium radical is generated by phenyl diselenide anode oxidation and decomposition.
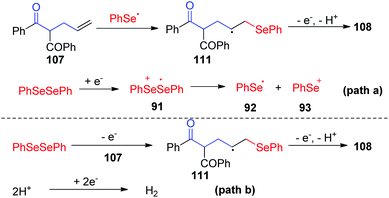 | ||
| Scheme 34 Proposed mechanism of electrochemically induced synthesis of selenylated dihydrofurans and oxazolines. | ||
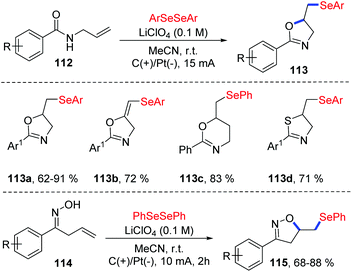
The group of Sarkar reported the similar method for the electrochemical oxidative cyclization of N-allyl amides 112 and diaryl diselenides, providing a practical and flexible approach for the preparation of selenium-functionalized oxazolines 113 (Scheme 35).40 The reaction could proceed smoothly in CH3CN at room temperature with LiClO4 as electrolytes, and graphite and platinum as the working anode and cathode, respectively. A variety of substituents on both electronic and steric effects can tolerate the oxidative conditions well. Moreover, amides with varying chain length were also compatible in the oxidative cyclization process. Notably, the thiazoline derivative was synthesized from corresponding N-allylthiobenzamide 113d. Comparing to the Lei's work,39 this method could also be suitable for β,γ-unsaturated oximes 114 and various isoxazolines 115 were achieved under the standard reaction conditions.
A plausible mechanism for this reaction was proposed based on mechanistic studies, cyclic voltammetry studies, and the literature (Scheme 36). In this mechanism, diphenyl diselenide is oxidized to generate cationic radical intermediate, which is then decomposed to give phenyl selenium cation 93 and phenylselenium radical 92. Further oxidation of phenylselenium radical 92 leads to phenyl selenium cation 93. Subsequently, the addition of phenyl selenium cation 93 to alkenes 112 affords the cyclic seleniranium ion 116, which then is captured by the nucleophile amide oxygen to afford the final product 113. At the cathode, proton is reduced to the hydrogen, completing the reaction cycle.
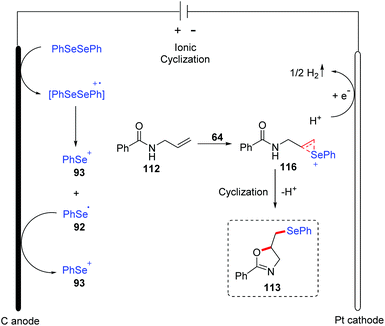 | ||
| Scheme 36 Proposed mechanism of electrochemically induced synthesis of selenylated oxazolines and isoxazolines. | ||
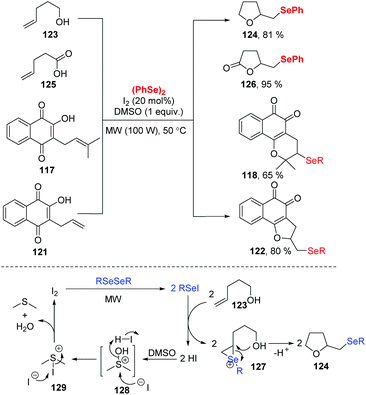
Very recently, Ackermann and coworkers investigated an electrochemical oxidative cyclization of quinones and diaryl diselenides using a platinum plate anode and cathode under the constant current (10 mA) in an undivided cell (Scheme 37).41 Using lapachol 117, the quinone-hybrid compounds 118 were afforded with moderate to high yield via 6-endo-trig way. When this selenylation method was applied to the C-allyl lawsone 121, 5-exo-dig cyclization occurred to give the corresponding products 122 in good to moderate yields. Unlike a previous report in which a I2/DMSO oxidant system was employed,42 this electrochemical reaction was conducted at room temperature without chemical oxidants. Moreover, some products exhibited considerable antitumor activity, indicating the promising in the application prospects.
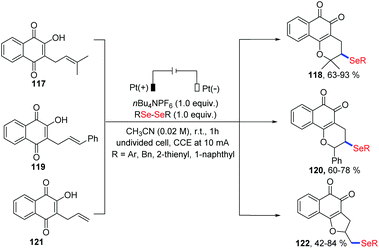 | ||
| Scheme 37 Electrochemically induced synthesis of selenylated 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[h]chromene and 2,3-dihydronaphtho[1,2-b]furan. | ||
3.4. I2 and hypervalent iodine-catalyzed selenocyclization
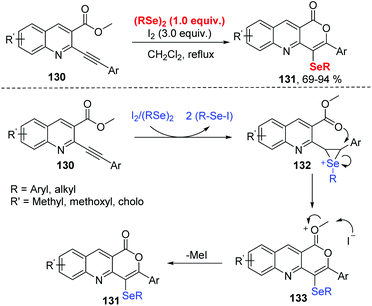
In 2019, Koketsu and co-workers reported an iodine mediated selenocyclization of 2-phenylalkynylquinoline-3-carboxylate 130 with diorganyl diselenides to access seleno pyrano[4,3-b]quinolin-1-one 131 (Scheme 39).43 The reaction featured a wide range of functional group tolerances, including strong/weak electron-withdrawing/donating groups along with alkyl and aryl groups, affording the corresponding products in high yields. The possible mechanism proposed by the authors is disclosed in Scheme 39. R–Se–I to is generated in situ by the reaction of I2 and (R–Se)2. The electrophilic addition of R–Se–I to compound 130 forms seleniranium ion 132. The intramolecular nucleophilic attack by O atom gives the intermediate 133. Finally, the elimination of Me–I leads to target compounds. In a control experiment, MeI was detected based on NMR spectroscopy.
3.5 Peroxide-promoted selenocyclization
As an oxidant, Oxone® has been widely explored in organic synthesis due to its low cost, stability under various conditions, simple handling, and environmental nontoxicity. In 2019, Perin and coworkers described an efficient Oxone®-and dialkyl diselenides-promoted seleno-cyclization of 1,3-diynes 139 for the construction of diverse 5H-selenopheno[3,2-c]isochromen-5-ones 140 (Scheme 41).45 This protocol enables the formation of four new chemical bonds, including one C–O bond and three C–Se bonds through a double intramolecular cyclization. Aryl-and alkyl-substituted 1,3-diynes were found to be suitable for this transformation. When 2-CH3OC6H4-substituted 1,3-diyne was used as the substrate in the reaction, the yield of the target product was only 40% because of the competing reactions (intramolecular Se-cyclization and O-cyclization). A radical-trapping experiment using TEMPO and hydroquinone suggested this reaction does not involve a radical path. Furthermore, the 77Se NMR experiment indicated that the active electrophilic selenium species are generated by the overoxidation of dibutyl diselenide by Oxone®.Based on experimental findings, a plausible mechanism is proposed (Scheme 42). Firstly, the reaction of potassium peroxymonosulfate with diselenide affords two electrophilic selenium species nC4H9SeOSO3− (141) and nC4H9SeOH (142). nC4H9SeOH2+ (145) is then formed by protonation of 142. Both electrophiles 141 and 145 can react with 1,3-diyne 139 to deliver the cyclic intermediate 146via the elimination of HSO4− or water. Subsequently, the methyl group leaves under the attack of nucleophile to produce intermediate 149. Finally, the expected product 140 is afforded in the same way as above.
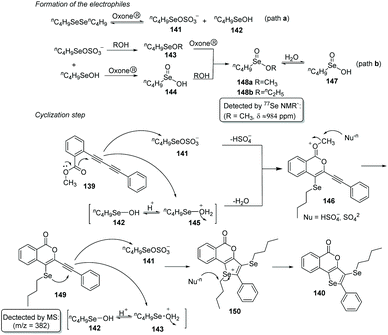 | ||
| Scheme 42 Proposed mechanism of Oxone® promoted synthesis of 5H-selenopheno[3,2-c]isochromen-5-ones. | ||
Subsequently, the authors further developed this methodology for the formation of 2,3-bis-organylselenylbenzo[b]chalcogenophenes (Scheme 43)46 and 4-organoselanyl-1H-pyrazoles (Scheme 44)47 by employing chalcogenoalkynes and α,β-alkynyl hydrazones as substrates by promotion of Oxone® and diselenides.
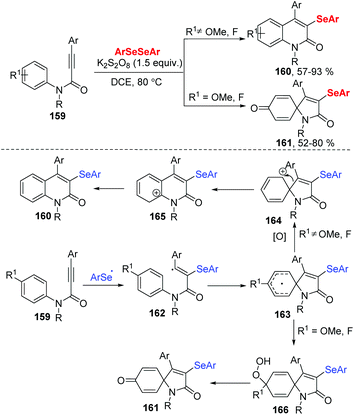
In 2019, the group of Baidya developed an efficient radical selenocyclization of N-aryl alkynamides 159 using K2S2O8 as an oxidant in DCE at 80 °C (Scheme 45).48 This method worked well in a switchable selectivity ortho/ipso-cyclization by the change the substituent of N-aryl alkynamides 159, resulting in a variety of 3-selenyl quinolin-2-ones 160 and 3-selenospiro[4,5]trienones 161 in good to excellent yields. Moreover, diaryl diselenides and dialkyl diselenides were well tolerated in ortho cyclization. When propiolamides bearing para-fluoro and para-methoxy in the N-aryl ring were reacted with diaryl diselenides, the spiro-cyclic products were isolated in good to high yields. Alkyl-substituted propiolamides were also suitable for the ortho/ipso-cyclization. Radical trapping experiments by using TEMPO, butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) or 1,1-diphenylethylene indicated that the process involves a free radical pathway. The authors carried out the reaction between 4-phenyl-quinolin-2-one and diphenyldiselenide under the standard reaction conditions and found that the selenylation process occurred before the ring-closure step. A tentative radical mechanism was depicted in Scheme 37. Initially, the K2S2O8-mediated cleavage of the Se–Se bond of diselenide forms an aryl selenium radical, which undergoes a radical addition to N-aryl alkynamide and intramolecular spirocyclization to give radical intermediate 163. The intermediate 163 is oxidized to afford the intermediate 164, which is rapidly converted into the desired quinolone product 160 through 1,2-C-migration and aromatization. When the N-aryl alkynamide bears para-F/OMe substituents, the intermediate 163 further reacts with solvated molecular oxygen to produce intermediate 166, which undergoes defluorination/demethoxylation via O–O bond cleavage leading to the product 161.
In 2019, Liu group reported the tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP)-initiated radical cyclization of propargylic aryl ethers 167 with diaryl diselenides for the synthesis of diverse 3-organoselenyl-2H-coumarins 168 (Scheme 46).49 The use of N-iodo-succinimid (NIS) could be in situ generation ArSeI with diaryl diselenides, increasing the reaction yield. For insight the mechanism, some control experiments were performed. TBHP was essential for this method, not only as radical initiator, but also with H2O providing O atom proved via18O-labeling experiment.
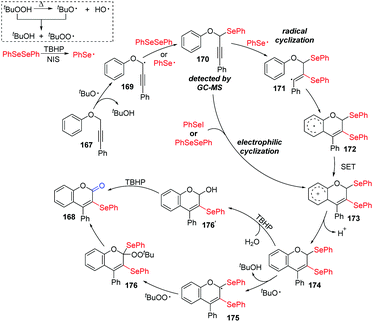
According to the proposed mechanism (Scheme 47), aryl selenium radical and propargyl radical are generated in situ in the presence of TBHP as the oxidant and react with each other, leading to the key intermediate 170, which was detected by GC. Aryl selenium radical then adds to alkyne triple bond 170 to produce the highly reactive alkenyl radical 171. This radical undergoes intramolecular cyclization onto the phenyl moiety, giving intermediate 174, which might be obtained by electrophilic cyclization of PhSeI in another path. Product 168 is generated by one of two pathways. In the first pathway, the solvent H2O participates in the nucleophilic attack of 174 to generate an alcohol, which is further oxidized by TBHP to furnish 168. In the second pathway, tert-butoxy radical gets an allylic hydrogen from 174 to generate radical intermediate 175, which is subsequently trapped by the tert-butylperoxy radical to afford intermediate 176. Finally, the cleavage of C–Se and O–O bonds intermediate 176 gives the targeted product 168.
4. Conclusions
We have summarized recent advances in tandem selenocyclization and tellurocyclization between diselenides and alkenes or alkynes categorized by metal catalysis, visible-light catalysis, electrochemical catalysis, organocatalysis etc. Using such approaches, various important seleno-containing heterocycles can be efficiently accessed with high chemo- and regioselectivity and often with high atom economy. Additionally, the mechanistic features of these transformations have been discussed. The many successful examples presented in this review convincingly document the high potential of this approach in drug discovery, and some seleno-containing heterocycles have shown potent inhibitory activity against cancer cell growth. Despite the substantial advances in this area over the past few years, many challenges and problems remain to be solved. For instance, most of the tandem selenocyclization reactions discussed herein are based on two distinct reaction components. Reactions comprising three or even more components, which would further increase the structural space of the accessible compounds, are not well explored. Furthermore, designs for new diselenides should be developed. Asymmetric control also remains an important challenge. We hope that this review contributes to stimulating further advancement in the emerging research area of seleno cyclization reactions.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21702087, 21801007, and 21801105), the Program for Innovative Research Team of Science and Technology in the University of Henan Province (18IRTSTHN004), the Science and Technology Plan Projects of Henan Province (20B150002), the LiaoNing Revitalization Talents Program (XLYC1907010), the Research Project Fund of Liaoning Provincial Department of Education (L2020033) and the Jilin Province Key Laboratory of Organic Functional Molecular Design & Synthesis (130028911 and 130028836), Talent Scientific Research Fund of Liaoning Shihua University (2016XJJ-078 and 2016XJJ-079).Notes and references
- (a) T. Ando, T. S. Kwon, A. Kitagawa, T. Tanemura, S. Kondo, H. Kunisada and Y. Yuki, Synthesis and Free Radical Polymerization of p-Methylseleno- and p-Phenylselenostyrenes, Macromol. Chem. Phys., 1996, 197, 2803–2810 CrossRef CAS; (b) P. K. Khanna and B. K. Das, Novel Synthesis of Silver Selenide Nano-Powder from Silver Nitrate and Organo-Selenium Compound, Mater. Lett., 2004, 58, 1030–1034 CrossRef CAS; (c) C. W. Nogueira, G. Zeni and J. B. T. Rocha, Chem. Rev., 2004, 104, 6255–6286 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) G. Perin, E. J. Lenardão, R. G. Jacob and R. B. Panatieri, Organoselenium and Organotellurium Compounds: Toxicology and Pharmacology, Chem. Rev., 2009, 109, 1277–1301 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) A. J. Mukjerjee, S. S. Zade, H. B. Singh and R. B. Sunoj, Organoselenium Chemistry: Role of Intramolecular Interactions, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 4357–4416 CrossRef PubMed; (f) A. Kumar, G. K. Rao, F. Saleem and A. K. Singh, Organoselenium Ligands in Catalysis, Dalton Trans., 2012, 41, 11949–11977 RSC; (g) S. Debnath, S. Chithiravel, S. Sharma, A. Bedi, K. Krishnamoorthy and S. S. Zade, Selenium Containing Fused Bicyclic Heterocycle-Diselenolodiselenole: Field Effect Transistor Study and Structure-Property Relationship, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8, 18222–18230 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) L. X. Shao, Y. Li, J.-M. Lu and X.-F. Jiang, Recent Progress in Selenium-Catalyzed Organic Reactions, Org. Chem. Front., 2019, 6, 2999–3041 RSC.
- (a) M. P. Rayman, The Importance of Selenium to Human Health, Lancet, 2000, 356, 233–241 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) G. Mugesh, W. W. Du Mont and H. Sies, Chemistry of Biologically Important Synthetic Organoselenium Compounds, Chem. Rev., 2001, 101, 2125–2180 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) K. P. Bhabak and G. Mugesh, Functional Mimics of Glutathione Peroxidase: Bioinspired Synthetic Antioxidants, Acc. Chem. Res., 2010, 43, 1408–1419 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) M. Ninomiya, D. R. Garud and M. Koketsu, Biologically Significant Selenium-Containing Heterocycles, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2011, 255, 2968–2990 CrossRef CAS; (e) E. Jablonska and M. Vinceti, Selenium and Human Health: Witnessing a Copernican Revolution, J. Environ. Sci. Health, Part C: Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev., 2015, 33, 328–368 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) E. C. Taylor and J. E. Saxton, The Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds, Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1983–1994 Search PubMed; (b) J. A. Joule and K. Mills, Heterocyclic Chemistry, Blackwell Science, Oxford, 2000 Search PubMed; (c) T. Eicher, S. Hauptmann and A. Speicher, The Chemistry of Heterocycles, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co, Weinheim, 2nd edn, 2003 CrossRef; (d) A. R. Katritzky, Introduction: Heterocycles, Chem. Rev., 2004, 104, 2125–2126 CrossRef CAS; (e) P. Ratcliffe, J. Maclean, L. Abernethy, T. Clarkson, M. Dempster, A.-M. Easson, D. Edwards, K. Everett, H. Feilden, P. Littlewood, D. McArthur, D. McGregor, H. McLuskey, O. Nimz, L. A. Nisbet, R. Palin, H. Tracey and G. Walker, Identification of Potent, Soluble, and Orally Active TRPV1 Antagonists, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2011, 21, 2559–2563 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) W. Guo, M.-M. Zhao, W. Tan, L.-Y. Zheng, K.-L. Tao and X.-L. Fan, Developments towards Synthesis of N-heterocycles from Amidines via C-N/C-C Formation, Org. Chem. Front., 2019, 6, 1906–1928 Search PubMed; (g) J. S. S. Neto and G. Zeni, Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Indoles from Alkynes and Nitrogen Sources, Org. Chem. Front., 2020, 7, 155–210 RSC.
- For selected reviews, see: (a) A. Ivanova and P. Arseyan, Rise of Diselenides: Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Heteroarylselenides, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2018, 370, 55–68 CrossRef CAS; (b) G. M. Martins, A. G. Meirinho, N. Ahmed, A. L. Braga and S. R. Mendes, Recent Advances in Electrochemical Chalcogen (S/Se)–Functionalization of Organic Molecules, ChemElectroChem, 2019, 6, 5928–5940 CrossRef CAS; (c) W. Ma, N. Kaplaneris, X. Fang, L. Gu, R. Mei and L. Ackermann, Chelation-assisted transition metal-catalysed C-H chalcogenylations, Org. Chem. Front., 2020, 7, 1022–1060 RSC.
- (a) K. B. Sharpless and R. F. Lauer, Electrophilic Organoselenium Reagents. New Route to Allylic Acetates and Ethers, J. Org. Chem., 1974, 39, 429–430 CrossRef CAS; (b) G. H. Schmid and D. G. Garratt, The Noncumulative Effect of Methyl Substituents on the Rate of Addition of Benzeneselenenyl Chloride to Olefins, Tetrahedron, 1978, 34, 2869–2872 CrossRef CAS; (c) T.-Y. Luh, W.-H. So, K. S. Cheung and S. W. Tam, Mechanistic Studies on the Addition Reactions of Benzeneselenenyl Bromide to Substituted Styrenes, J. Org. Chem., 1985, 50, 3051–3053 CrossRef CAS.
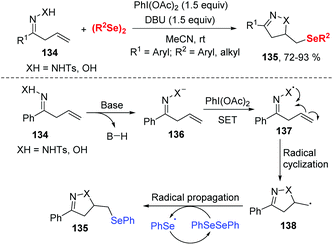
- (a) C. W. Nogueira and J. B. T. Rocha, Diphenyl Diselenide a Janus-Faced Molecule, J. Braz. Chem. Soc., 2010, 21, 2055–2071 CrossRef CAS; (b) F. L. Lovato, J. B. T. da Rocha and C. L. D. Corte, Diphenyl Diselenide Protects against Methylmercury-Induced Toxicity in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae via the Yap1 Transcription Factor, Chem. Res. Toxicol., 2017, 30, 1134–1144 Search PubMed; (c) K. Sun, X. Wang, Y.-H. Lv, G. Li, H.-Z. Jiao, C.-W. Dai, Y.-Y. Li, C. Zhang and L. Liu, Peroxodisulfate-mediated Selenoamination of Alkenes Yielding Amidoselenide-containing Sulfamides and Azoles, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 8471–8474 RSC; (d) K. Sun, X. Wang, F.-F. Fu, C. Zhang, Y. Chen and L. Liu, Metal-free Selenosulfonylation of Alkynes: Rapid Access to -(Seleno)vinyl Sulfones via a Cationic-species-induced Pathway, Green Chem., 2017, 19, 1490–1493 RSC; (e) K. Sun, Y.-H. Lv, Z.-D. Shi, F.-F. Fu, C. Zhang and Z.-G. Zhang, Direct Access to β-seleno Sulfones at Room Temperature through Selenosulfonylation of Alkenes, Sci. China: Chem., 2017, 60, 730–733 CrossRef CAS.
- M. M. Campos and N. Pentragnani, Nachbargruppenbeteiligung bei Additionsreaktionen, IV. Darstellung von α.α–disubstituierten δ–Arylselenenyl–und δ–Aryltelluro–γ–valerolactonen, Chem. Ber., 1960, 93, 317–320 CrossRef.
- (a) G. H. Schmid and D. G. Garratt, The Isolation of an Episelenurane from the Reaction of 4-Tolueneselenenyl Chloride with Ethylene, Can. J. Chem., 1974, 52, 1027–1028 CrossRef; (b) G. H. Schmid and D. G. Garratt, The Preparation of Seleniranium and Selenirenium Ions, Tetrahedron Lett., 1975, 16, 3991–3994 CrossRef; (c) G. H. Schmid and D. G. Garratt, in The Chemistry of double bonded functional groups, ed. S. Patai, Wiley, New York, 1977, Supplement A, Part 2, pp. 854–866 Search PubMed; (d) T. G. Back, in The Chemistry of Organic Selenium and TelluriumCompounds, ed. S. Patai, Wiley, New York, 1987, vol. 2, pp. 94–215 Search PubMed; (e) S. E. Denmark and M. G. Edwards, On the Mechanism of the Selenolactonization Reaction with Selenenyl Halide, J. Org. Chem., 2006, 71, 7293–7306 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. T. Moore, C. Soldi, J. C. Fettinger and J. T. Shaw, Catalytic Alkene Cyclization Reactions for the Stereoselective Synthesis of Complex “Terpenoid-like” Heterocycles, Chem. Sci., 2013, 4, 292–296 RSC.
- W.-X. Niu and Y.-Y. Yeung, Catalytic and Highly Enantioselective Selenolactonization, Org. Lett., 2015, 17, 1660–1663 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For selected reviews, see: (a) S. Ma, Electrophilic Addition and Cyclization Reactions of Allenes, Acc. Chem. Res., 2009, 42, 1679–1688 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) S. Yu and S. Ma, Allenes in Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis and Natural Product Syntheses, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 3074–3112 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) W. Yang and A. S. K. Hashmi, Mechanistic Insights into the Gold Chemistry of Allenes, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 2941–2955 RSC; (d) J. M. Alonso, M. T. Quirós and M. P. Muñoz, Chirality Transfer in Metal-catalysed Intermolecular Addition Reactions involving Allenes, Org. Chem. Front., 2016, 3, 1186–1204 RSC; (e) B. Yang, Y. Qiu and J.-E. Backvall, Control of Selectivity in Palladium(II)-Catalyzed Oxidative Transformations of Allenes, Acc. Chem. Res., 2018, 51, 1520–1531 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) L. Liu, R. M. Ward and J. M. Schomaker, Mechanistic Aspects and Synthetic Applications of Radical Additions to Allenes, Chem. Rev., 2019, 119, 12422–12490 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Ma, F. Pan, X. Hao and X. Huang, Reaction of PhSeCl or PhSCl with 2,3-Allenoic Acids: An Efficient Synthesis of β-Organoselenium or β-Organosulfur Substituted Butenolides, Synlett, 2004, 85–88 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Alcaide, P. Almendros, A. Luna, G. Campillos and M. Toledano-Pinedo, Ring Enlargement versus Selenoetherification on the Reaction of Allenyl Oxindoles with Selenenylating Reagents, J. Org. Chem., 2012, 77, 3549–3556 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Alcaide, P. Almendros, T. M. del Campo, L. Martín, G. Palopa and M. Toledano-Pinedo, Oxidative Selenofunctionalization of Allenes: Convenient Access to 2-(phenylselanyl)-but-2-enals and 4-oxo-3-(phenylselanyl)pent-2-enoates, Org. Chem. Front., 2019, 6, 2447–2451 RSC.
- For reviews on iron-catalyzed reactions, see: (a) C. Bolm, J. Legros, J. L. Paih and L. Zani, Iron-Catalyzed Reactions in Organic Synthesis, Chem. Rev., 2004, 104, 6217–6254 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) Iron Catalysis in Organic Chemistry: Reactions and Applications, ed. B. Plietker, WileyVCH, Weinheim, 2008 Search PubMed; (c) A. A. O. Sarhan and C. Bolm, Iron(III) Chloride in Oxidative C-C Coupling Reactions, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38, 2730–2744 RSC; (d) C.-L. Sun, B.-J. Li and Z.-J. Shi, Direct C-H Transformation via Iron Catalysis, Chem. Rev., 2011, 111, 1293–1314 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) A. Welther and A. J. Wangelin, Iron(0)Nanoparticle Catalysts in Organic Synthesis, Curr. Org. Chem., 2013, 17, 326–335 CrossRef CAS; (f) K. Gopalaiah, Chiral Iron Catalysts for Asymmetric Synthesis, Chem. Rev., 2013, 113, 3248–3296 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) F. Jia and Z.-P. Li, Iron-catalyzed/mediated Oxidative Transformation of C-H bonds, Org. Chem. Front., 2014, 1, 194–214 RSC.
- E. M. Burbidge, G. R. Burbidge, W. A. Fowler and F. Hoyle, Synthesis of the Elements in Stars, Rev. Mod. Phys., 1957, 29, 547–650 CrossRef.
- (a) R. M. Gay, F. Manarin, C. C. Schneider, D. A. Barancelli, M. D. Costa and G. Zeni, FeCl3-Diorganyl Dichalcogenides Promoted Cyclization of 2-Alkynylanisoles to 3-Chalcogen Benzo[b]furans, J. Org. Chem., 2010, 75, 5701–5706 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) B. Godoi, A. Sperance, C. A. Bruning, D. F. Back, P. H. Menenzes, C. W. Nogueira and G. Zeni, Iron(III) Chloride/Diorganyl Diselenides-Promoted Regioselective Cyclization of Alkynyl Aryl Ketones: Synthesis of 3-Organoselenyl Chromenones under Ambient Atmosphere, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2011, 353, 2042–2050 CrossRef CAS; (c) A. Speranca, B. Godoi, P. H. Menezes and G. Zeni, Application of FeCl3/Diorganyl Diselenides to Cyclization of o-Alkynyl Anilines: Synthesis of 3-Organoselenyl-(N-methyl)indoles, Synlett, 2013, 24, 1125–1132 CrossRef CAS; (d) A. Speranca, B. Godoi and G. Zeni, Iron(III) Chloride/Diorganyl Diselenides: A Tool for Intramolecular Cyclization of Alkynone O-Methyloximes, J. Org. Chem., 2013, 78, 1630–1637 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) A. C. Mantovani, T. A. C. Goulart, D. F. Back, P. H. Menezes and G. Zeni, Iron(III) Chloride and Diorganyl Diselenides-Mediated 6-endo-dig Cyclization of Arylpropiolates and Arylpropiolamides Leading to 3-Organoselenyl-2H-coumarins and 3-Organoselenyl-quinolinones, J. Org. Chem., 2014, 79, 10526–10536 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) A. L. Stein, F. N. Bilheri, D. F. Back and G. Zeni, Iron(III) Chloride/Diorganyl Diselenides Promoted Regio- and Stereoselective Cyclization of ortho-Alkynylanilides: Synthesis of (Z,)-4-(chalcogen)methylenebenzoxazines, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2014, 356, 501–508 CrossRef CAS; (g) T. Prochnow, D. F. Back and G. Zeni, Iron(III) Chloride and Diorganyl Diselenide–Promoted Nucleophilic Closures of 1−Benzyl–2−alkynylbenzenes in the Preparation of 9−(Organoselanyl)–5H–benzo[7]annulenes, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2016, 358, 1119–1129 CrossRef CAS; (h) A. M. S. Recchi, D. F. Back and G. Zeni, Sequential Carbon-Carbon/Carbon-Seleniun Bonds Formation Mediated by Iron(III) Chloride and Diorganyl Diselenides: Synthesis and Reactivity of 2-Organoselenyl-Naphthalenes, J. Org. Chem., 2017, 82, 2713–2723 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) T. A. C. Goulart, J. A. G. Kazmirski, D. F. Back and G. Zeni, Iron(III)-Promoted Synthesis of 3-(Organoselanyl)-1,2-Dihydroquinolines from Diorganyl Diselenides and N-Arylpropargylamines by Sequential Carbon-Carbon and Carbon-Selenium Bond Formation, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2019, 361, 96–104 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Yao, F. Li, J. Li, S. Wang and S. Ji, Iron(III) Chloride-Promoted Cyclization of α,β-Alkynic Tosylhydrazones With Diselenides: Synthesis of 4-(Arylselanyl)-1H-Pyrazoles, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2020, 18, 1987–1993 RSC.
- A. Sonawane, R. A. Sonawane, K. M. Win, M. Ninomiya and M. Koketsu, In Situ Air Oxidation and Photophysical Studies of Isoquinoline-Fused N-Heteroacenes, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2020, 18, 2129–2138 RSC.
- (a) S. R. Chemler and H. P. Fuller, Heterocycle Synthesis by Copper Facilitated Addition of Heteroatoms to Alkenes, Alkynes and Arenes, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2007, 36, 1153–1160 RSC; (b) W.-H. Rao and B.-F. Shi, Recent Advances in Copper-mediated Chelation-assisted Functionalization of unactivated C-H Bonds, Org. Chem. Front., 2016, 3, 1028–1047 RSC.
- T. A. C. Goulart, D. F. Back and G. Zeni, Copper-Catalyzed Carbon-Nitrogen/Carbon-Selenium Bonds Formation: Synthesis of 2-(Organochalcogenyl)-Indolizines, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2017, 359, 1901–1911 CrossRef CAS.
- J. C. Kazmierczak, A. M. S. Recchi, F. Gritzenco, E. B. Balbom, T. Barcellos, A. Speranca and B. Godoi, Copper-Iodide- and Diorganyl-Diselenide-Promoted Cyclization of 2-Alkynylphenols: Alternative Approach to 3-Organoselanylbenzo[b]furans, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2017, 6382–6389 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Ni, H. Zuo, Y. Li, Y. Wu and F.-R. Zhong, Copper-Catalyzed Regioselective Intramolecular Electrophilic Sulfenoamination via Lewis Acid Activation of Disulfides under Aerobic Conditions, Org. Lett., 2018, 20, 4350–4353 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. R. Reddy, R. Ranjan and S. K. Prajapti, Copper-Catalyzed Intramolecular Chalcogenoamination of Enynyl Azides: Synthesis of 5-Selenyl/Sulfenyl Nicotinates, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 623–626 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y.-X. Xin, S. Pan, Y. Huang, X.-H. Xu and F.-L. Qing, Copper-Catalyzed Sulfenylation, Sulfonylation, and Selenylation of 2,3-Allenoic Acids with Disulfides or Diselenides, J. Org. Chem., 2018, 83, 6101–6109 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Sun, S.-N. Wang, R.-R. Feng, Y.-X. Zhang, X. Wang, Z.-G. Zhang and B. Zhang, Copper-Catalyzed Radical Selenodifluoromethylation of Alkenes: Access to CF2-Containing γ-Lactams, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 2052–2055 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For selected reviews, see: (a) J. W. Beatty and C. R. J. Stephenson, Amine Functionalization Via Oxidative Photoredox Catalysis: Methodology Development and Complex Molecule Synthesis, Acc. Chem. Res., 2015, 48, 1474–1484 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) K. L. Skubi, T. R. Blum and T. P. Yoon, Dual Catalysis Strategies in Photochemical Synthesis, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 10035–10074 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) N. A. Romero and D. A. Nicewicz, Organic Photoredox Catalysis, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 10075–10166 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) D. Ravelli, S. Protti and M. Fagnoni, Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions via Photogenerated Intermediates, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 9850–9913 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) X. Lang, J. Zhao and X. Chen, Cooperative Photoredox Catalysis, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45, 3026–3038 RSC; (f) M. D. Kärkäs, J. A. Porco and C. R. J. Stephenson, Photochemical Approaches to Complex Chemotypes: Applications in Natural Product Synthesis, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 9683–9747 CrossRef PubMed; (g) N. Corrigan, S. Shanmugam, J. Xu and C. Boyer, Photocatalysis in Organic and Polymer Synthesis, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45, 6165–6212 RSC; (h) J.-R. Chen, X.-Q. Hu, L.-Q. Lu and W.-J. Xiao, Visible Light Photoredox-Controlled Reactions of N-Radicals and Radical Ions, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45, 2044–2056 RSC; (i) Q. Yang, Z.-B. Jia, L. J. Li and S.-Z. Luo, Visible-light Promoted Arene C-H/C-X Lactonization via Carboxylic Radical Aromatic Substitition, Org. Chem. Front., 2018, 5, 237–241 RSC; (j) Y.-L. Yin, X.-W. Zhao, B.-K. Qiao and Z.-Y. Jiang, Cooperative Photoredox and Chiral Hydrogen-bonding Catalysis, Org. Chem. Front., 2019, 6, 1283–1296 Search PubMed; (k) T.-Y. Shang, L.-H. Lu, Z. Cao, Y. Liu, W.-M. He and B. Yu, Recent advances of 1,2,3,5-tetrakis(carbazol-9-yl)-4,6-dicyanobenzene (4CzIPN) in photocatalytic transformations, Chem. Commun., 2019, 55, 5408–5419 RSC; (l) Y. Zhang, K. Sun, Q. Lv, X. Chen, L. Qu and B. Yu, Recent applications of radical cascade reaction in the synthesis of functionalized 1-indenones, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2019, 30, 1361–1368 CrossRef CAS.
- E. S. Conner, K. E. Crocker, R. G. Fernando, F. R. Fronczek, G. G. Stanley and J. R. Ragains, Visible-Light-Promoted Selenofunctionalization of Alkene, Org. Lett., 2013, 15, 5558–5561 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q.-B. Zhang, P.-F. Yuan, L.-L. Kai, K. Liu, Y.-L. Ban, X.-Y. Wang, L.-Z. Wu and Q. Liu, Preparation of Heterocycles Via Visible-Light-Driven Aerobic Selenation of Olefins with Diselenides, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 885–889 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Sahoo, A. Mandal, S. Dana and M. Baidya, Visible Light-Induced Synthetic Approach for Selenylative Spirocyclization of N-Aryl Alkynamides with Molecular Oxygen as Oxidant, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2019, 360, 1099–1103 CrossRef.
- Q. Shi, P.-H. Li, Y. Zhang and L. Wang, Visible Light-induced Tandem Oxidative Cyclization of 2-alkynylanilines with Disulfides (diselenides) to 3-Sulfenyl- and 3-Selenylindoles under Transition Metal-free and Photocatalyst-free Conditions, Org. Chem. Front., 2017, 4, 1322–1330 RSC.
- X.-L. Ma, Q. Wang, X.-Y. Feng, Z.-Y. Mo, Y.-M. Pan, Y.-Y. Chen, M. Xin and Y.-L. Xu, Metal-free Visible-light Induced Cyclization/Substitution Cascade Reaction of Alkyne-tethered Cyclohexadienones andDiselenides: Access to 5-Hydroxy-3-Selenyl-4a,8a-Dihydro-2H-Chromen-6(5H)-Ones, Green Chem., 2019, 21, 3547–3551 RSC.
- X.-J. Zhou, H.-Y. Liu, Z.-Y. Mo, X.-L. Ma, Y. Chen, H.-T. Tang, Y.-M. Pan and Y.-L. Xu, Visible–Light–Induced Ortho–Selective Migration on Pyridyl Ring: Trifluoromethylative Pyridylation of Unactivated Alkenes, Chem. – Asian J., 2020, 15, 1536–1539 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. R. Mutra, V. S. Kudale, J. Li, W.-H. Tsai and J.-J. Wang, Alkene versus Alkyne Reactivity in Unactivated 1,6-enynes: Regio- and Chemoselective Radical Cyclization with Chalcogens Under Metal- and Oxidant-Free Conditions, Green Chem., 2020, 22, 2288–2300 RSC.
- (a) M. Yan, Y. Kawamata and P. S. Baran, Alkene versus Alkyne Reactivity in Unactivated 1,6-enynes: Regio- and Chemoselective Radical Cyclization with Chalcogens under Metal- and Oxidant-Free Conditions, Chem. Rev., 2017, 117, 13230–13319 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) S. R. Waldvogel, S. Lips, M. Selt, B. Riehl and C. J. Kampf, Electrochemical Arylation Reaction, Chem. Rev., 2018, 118, 6706–6765 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) J.-i. Yoshida, K. Kataoka, R. Horcajada and A. Nagaki, Modern Strategies in Electroorganic Synthesis, Chem. Rev., 2008, 108, 2265–2299 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) K. D. Moeller, Synthetic Applications of Anodic Electrochemistry, Tetrahedron, 2000, 56, 9527–9554 CrossRef CAS; (e) Y. Jiang, K. Xu and C. Zeng, Use of Electrochemistry in the Synthesis of Heterocyclic Structures, Chem. Rev., 2018, 118, 4485–4540 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) H. Long, J.-S. Song and H.-C. Xu, Electrochemical Synthesis of 7-membered Carbocycles through Cascade 5-exo-trig/7-endo-trig Radical Cyclization, Org. Chem. Front., 2018, 5, 3129–3132 RSC; (g) Y.-C. Wu, R.-J. Song and J.-H. Li, Recent advances in photoelectrochemical cells (PECs) for organic synthesis, Org. Chem. Front., 2020, 7, 1895–1902 RSC.
- J. W. Hua, Z. Fang, J. Xu, M.-X. Bian, C.-K. Liu, W. He, N. Zhu, Z. Yang and K. Guo, Electrochemical Oxidative Cyclization of Activated Alkynes with Diselenides or Disulfides: Access to Functionalized Coumarins or Quinolinone, Green Chem., 2019, 21, 4706–4711 RSC.
- J.-W. Hua, Z. Fang, M. Bian, T. Ma, M. Yang, J. Xu, C.-K. Liu, W. He, N. Zhu, Z. Yang and K. Guo, Electrochemical Synthesis of Spiro[4.5]Trienones through Radical-Initiated Dearomative Spirocyclization, ChemSusChem, 2020, 13, 2053–2059 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X.-J. Meng, P.-F. Zhong, Y.-M. Wang, H.-S. Wang, H.-T. Tang and Y.-M. Pan, Electrochemical Difunctionalization of Olefines: Access to Selenomethyl–Substituted Cyclic Ethers or Lactones, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2020, 362, 506–511 CrossRef CAS.
- Z.-P. Guan, Y.-K. Wang, H.-M. Wang, Y.-G. Huang, S.-Y. Wang, H.-D. Tang, H. Zhang and A. Lei, Electrochemical Oxidative Cyclization of Olefinic Carbonyls with Diselenides, Green Chem., 2019, 21, 4976–4980 RSC.
- S. Mallick, M. Baidya, K. Mahanty, D. Maiti and S. D. Sarkar, Access to Functionalized 3,5-Disubstituted 1,2-Dioxolanes under Mild Conditions through Indium(III) Chloride/Trimethylsilyl Chloride or Scandium(III) Triflate Catalysis, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2020, 362, 1046–1052 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Kharma, C. Jacob, Í. A. O. Bozzi, G. A. M. Jardim, A. L. Braga, K. Salomão, C. C. Gatto, M. F. S. Silva, C. Pessoa, M. Stangier, L. Ackermann and E. N. da Silva Júnior, Electrochemical Selenation/Cyclization of Quinones: A Rapid, Green and Efficient Access to Functionalized Trypanocidal and Antitumor Compounds, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2020, 2020, 4474–4486 CrossRef CAS.
- A. A. Vieira, J. B. Azeredo, M. Godoi, C. Santi, E. N. Júnior and A. L. Braga, Catalytic Chalcogenylation Under Greener Conditions: A Solvent-Free Sulfur- and Seleno-Functionalization of Olefins Via I2/DMSO Oxidant System, J. Org. Chem., 2015, 80, 2120–2127 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. M. N. Win, A. D. Sonawane and M. Koketsu, Iodine Mediated in situ Generation of R-Se–I: Application Towards the Construction of Pyrano[4,3-b]Quinoline Heterocycles and Fluorescence Properties, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2019, 17, 9039–9049 RSC.
- J.-M. Yu and C. Cai, Iodine(III)-Mediated Intramolecular Sulfeno-and Selenofunctionalization of β,γ-Unsaturate Tosyl Hydrazones and Oximes, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2018, 16, 490–498 RSC.
- H. A. Goulart, J. S. Neto, A. M. Barcellos, T. Barcellos, M. S. Silva, D. Alves, R. G. Jacob, E. J. Lenardão and G. Perin, Synthesis of 5H-Selenopheno[3,2-c]Isochromen-5-ones Promoted by Dialkyl Diselenides and Oxone, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2019, 361, 3403–3411 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Perin, L. K. Soares, P. S. Hellwig, M. S. Silva, J. S. Neto, J. A. Roehrs, T. Barcellos and E. J. Lenardão, Synthesis of 2,3-bis-Organochalcogenyl-Benzo[b]Chalcogenophenes Promoted by Oxone, New J. Chem., 2019, 43, 6323–6331 RSC.
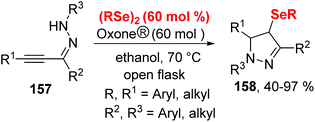
- G. Perin, P. C. Nobre, D. H. Mailahn, M. S. Silva, T. Barcellos, R. G. Jacob, E. J. Lenardão, C. Santi and J. A. Roehrs, Synthesis of 4-Organoselanyl-1H-Pyrazoles: Oxone-Mediated Electrophilic Cyclization of α,β-Alkynyl Hydrazones by Using Diorganyl Diselenides, Synthesis, 2019, 51, 2293–2304 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Sahoo, G. S. Grandhi, I. Ramakrishna and M. Baidya, Metal-Free Switchable Ortho/Ipso-Cyclization of N-aryl Alkynamides: Divergent Synthesis of 3-Selenyl Quinolin-2-Ones and Azaspiro[4,5]Trienones, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2019, 17, 10163–10166 RSC.
- J.-D. Fang, X.-B. Yan, L. Zhou, Y.-Z. Wang and X.-Y. Liu, Synthesis of 3-Organoselenyl-2H-Coumarins from Propargylic Aryl Ethers Via Oxidative Radical Cyclization, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2019, 361, 1985–1990 CrossRef CAS.
| This journal is © the Partner Organisations 2020 |