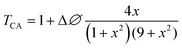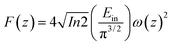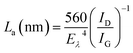Improved third-order optical nonlinearity and optical limiting behaviour of (nanospindle and nanosphere) zinc ferrite decorated reduced graphene oxide under continuous and ultrafast laser excitation†
M. Saravanana,
T. C. Sabari Girisun*a,
G. Vinithab and
S. Venugopal Rao c
c
aNanophotonics Laboratory, School of Physics, Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli, India. E-mail: sabarigirisun@bdu.ac.in
bDivision of Physics, School of Advanced Science, VIT Chennai, Chennai-600 127, Tamilnadu, India
cAdvanced Centre of Research in High Energy Materials (ACRHEM), University of Hyderabad, Hyderabad 500046, Telangana, India. E-mail: soma_venu@uohyd.ac.in
First published on 14th September 2016
Abstract
Nanohybrids consisting of uniform nanospheres and nanospindles of zinc ferrite attached to reduced graphene oxide were prepared by hydrothermal reaction. Zinc ferrite decorated reduced graphene oxide exhibited enhanced nonlinear absorption, refraction and optical limiting (OL) action under continuous wave (532 nm, 50 mW) and ultrafast (800 nm, 150 fs) excitation. The enhancement can possibly be attributed to the synergistic effect stemming from the observed reverse saturable absorption and self-defocusing in the material. The role of defects in improving the nonlinear optical (NLO) performance of ZnFe2O4–rGO was explained with the aid of Raman spectroscopy and ground state absorption studies. Using fs and cw excitation, the estimated nonlinear absorption coefficient [γ3PA(fs) = 4.0 × 10−12 m W−1, β(cw) = 6.5 × 10−5 m W−1], nonlinear refractive index [n2(fs) = 4.2 × 10−18 m2 W−1, n2(cw) = 4.7 × 10−12 m2 W−1] and third order nonlinear optical (NLO) susceptibility [χ (3) (fs) = 1.9 × 10−15 esu, χ (3) (cw) = 4.2 × 10−6 esu] of nanospindle ZnFe2O4–rGO were found to be higher than those of its other counter parts. The estimated NLO parameters were found to be higher than those of other known OL materials such as functionalized hydrogen exfoliated graphene, CdO. Thus zinc ferrite decorated rGO nanostructures with proficient NLO coefficients have potential scope for utilizing them as smart materials for OL applications.
Introduction
Graphene has excellent third-order nonlinear optical (NLO) properties due to its unique electronic band structure and wide band gap tunability (energy dispersion being in the vicinity of K point).1 Particularly, metal decoration in low dimensional materials such as graphene oxide (GO) has attracted significant attention due to their superior NLO behaviour, which include the phenomena of nonlinear absorption (two-photon absorption-TPA, reverse saturable absorption-RSA and saturable absorption-SA) and nonlinear refraction (self-focusing, defocusing).2 This is because unlike graphene which has sp2 hybridized π-conjugated carbon, GO has both sp2 and sp3 carbon domains. Therefore, by adjusting the ratio of sp2 and sp3 carbon atoms, the optical properties can be tuned over a wide spectral range. Also due to the presence of various oxygen containing functional groups like epoxy (–COO–) and hydroxyl (OH–) groups at the basal plane and carboxyl groups (–COO–) at the edge of the molecular structure, GO can interact with varied organic and inorganic materials.3 The most important consequences of these functionalization is that these materials offer the tunability of optical bandgap through the variation in the concentration of induced sp3 defect states leading to the display of unique NLO properties.4 In this quest, Wang et al.5 recently demonstrated broad-band optical limiting behaviour of graphene dispersed in an organic solvent studied by Z-scan technique at 532 nm and 1064 nm wavelengths. Reji Philip et al.6 investigated the nonlinear absorption of GO nanosheets in 400–700 nm spectral region with ultrafast laser pulses and found that the nonlinear absorption arose from the non-degenerate two-photon absorption. Zhu et al.7 reported that graphene oxide (GO) covalently functionalized with zinc phthalocyanine exhibited high NLO extinction coefficient and strong OL performance than pure GO. Kalanoor et al.8 investigated the NLO properties of silver decorated graphene in picosecond regime by Z-scan method and observed that the material exhibited SA behaviour. Wang et al.9 and Kavitha et al.10 fabricated TiO2 and ZnO decorated reduced GO with enhanced NLO performance in the nanosecond regime. Zhang et al.11 demonstrated the nonlinear refraction in graphene oxides sheets through reorientation and thermal effects. Also in dispersed medium, the switching of saturable absorption behaviour to optical limiting at high fluencies due to the nonlinear scattering from light induced microbubbles and microplasma was also reported recently.12 Altogether strong NLO effects and OL response of GO nanostructures originate mainly due to nonlinear absorption (TPA, ESA), nonlinear refraction (self-focusing/defocusing) and nonlinear scattering under different laser pulses excitation. For the sake of developing high performance photonic devices, it is indisputably important to have a comprehensive understanding on the correlation of NLO properties of the graphene oxide with molecular engineering. Accompanied by the rapid development of ultrafast lasers (800 nm) and continuous wave (cw) lasers (532 nm) in the fields of communication, material processing13 and photo-thermal cancer therapy,14 it is imperative to understand the NLO behaviour of the material in this domain and develop an efficient optical limiter to protect eyes and photosensitive components from laser damage. It has long been recognized that to protect sensors against both ultrafast and continuous wave laser damage simultaneously using a single material is challenging. To achieve this, it will be very interesting to combine together the outstanding properties of spinel ferrites (magneto-tunable NLO properties and high laser damage) and reduced graphene oxide (high linear transmittance, fast optical response and high thermal stability) to form hybrid material.Although plethora of studies have been performed using the Z-scan experiments with GO, the investigation of NLO behaviour of nanostructured spinel ferrite systems decorated on GO still remain unexplored. Among the ferrite systems, zinc ferrite (ZnFe2O4) is a normal spinel structure, in which all nonmagnetic Zn2+ cations and magnetic Fe3+ cations are placed at octahedral (A) and tetrahedral (B) structure respectively. In the case of a normal spinel structure, all of the A atoms are tetrahedrally coordinated while the B atoms are octahedrally coordinated by oxygen atoms. But in the case of an inverse spinel structure, the A atoms occupy half of the B-sites.15 Recent studies suggest that the implantation and growth of these nanoparticles on graphene oxide led directly to severe damage to the regular structure of graphene, which disrupts the extended π conjugation, resulting in an impaired device performance.16 Also the implantation of these ferrites on the layered structure of rGO enhance phonon transfer which can be effectively utilized to achieve improved thermal nonlinearity. Hence, the main motivation of this article is to investigate the optical limiting performance of functionalized graphene oxide by attaching uniform zinc ferrite (nanostructures). The third-order NLO properties of the ZnFe2O4–rGO nanohybrids were studied using the closed and open aperture Z-scan technique with cw and ultrafast laser pulses at 532 nm and 800 nm excitation. In the present case these excitation sources were chosen for following reasons: (a) utilization of ultrafast IR (800 nm) laser pulses with high repetition rate and continuous wave (532 nm) laser is tremendously increasing in human interactive sectors, which facilitate the urgent need for safety devices (b) understanding thermal nonlinearity is imperative to realize non-local NLO phenomena such as optical limiting, spatial soliton propagation and shock waves. The prepared nanohybrid exhibited superior NLO properties and optical limiting action compared to their individual compounds, making them potential candidates for optical limiting applications both in cw and fs domain.
Experimental details
Synthesis of zinc ferrite decorated rGO nanostructures
Preparation of decorated graphene oxide by physical methods such as CVD offers the disadvantages of high temperature, special equipment and complicated experimental conditions. Recently Tian et al.17 and Qin et al.18 have successfully demonstrated the preparation of decorated graphene oxide by a simple, one-step, rapid hydrothermal method. Therefore, ZnFe2O4 decorated rGO was prepared by hydrothermal method. Initially, GO was prepared from natural graphite powder by using a modified Hummers and Offeman's method with H2SO4 and KMnO4 as oxidants.19 The spinel ferrite nanostructures decorated upon various graphene oxide content (40, 25, 15 wt%) were synthesized via a one-step hydrothermal reaction of Zn(NO3)2·6H2O and Fe(NO3)3·9H2O in the presence of graphene oxide. In a typical reaction, initially 40 wt% of the prepared GO was dispersed in 60 mL of ethanol by sonication for 60 minutes. Zn(NO3)2·6H2O and Fe(NO3)3·9H2O were dissolved in 20 mL ethanol in 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 molar ratio and were further added into the GO dispersion solution with constant stirring for 30 minutes at 32 °C. The solution was transferred into 150 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave and heated at 180 °C under autogenously pressure. The reaction mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature (32 °C) and the obtained precipitate was filtered, washed with distilled water several times and dried in oven at 60 °C for 12 hours. The above procedure was repeated with 25 and 15 wt% of GO to attain the other ZnFe2O4–rGO contents. Pure ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles were prepared by similar treatment without using GO. All the above mentioned synthesis procedures were environmental friendly as the reaction uses aqueous solution as a reaction medium and it was carried out in autoclaves.
2 molar ratio and were further added into the GO dispersion solution with constant stirring for 30 minutes at 32 °C. The solution was transferred into 150 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave and heated at 180 °C under autogenously pressure. The reaction mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature (32 °C) and the obtained precipitate was filtered, washed with distilled water several times and dried in oven at 60 °C for 12 hours. The above procedure was repeated with 25 and 15 wt% of GO to attain the other ZnFe2O4–rGO contents. Pure ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles were prepared by similar treatment without using GO. All the above mentioned synthesis procedures were environmental friendly as the reaction uses aqueous solution as a reaction medium and it was carried out in autoclaves.
Physical measurements
Morphologies of the samples were investigated by Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FEI – QUANTA–FEG 250) and high resolution transmission electron microscopy (TECNAI F (S-Twin)). Raman spectra of the GO pure and spinel ferrite decorated rGO were obtained using a Raman spectrometer (Horiba-Jobin, Lab RAM HR) at ambient temperature using 632 nm excitation wavelengths. The linear and nonlinear optical properties of the synthesized materials dispersed in ethylene glycol by ultrasonication with concentration (5 mg/5 mL) were studied by JASCO V-570 UV-Vis spectrophotometer and Z-scan technique (open and closed aperture mode) respectively. Here in Z-scan experiment, the samples were excited by continuous wave (532 nm, 50 mW) and ultrafast (800 nm, 150 fs) lasers. In cw excitation Gaussian profile from diode pumped Nd:YAG laser beam was focused on a 1 mm cuvette by lens of focal length 3.5 cm to produce a beam waist (ω0) of 15.35 μm. In ultrafast excitation, 150 fs pulse with 80 MHz repetition rate wave delivered from a tunable oscillator (Chameleon, coherent), operated at central wavelength of 800 nm was used. An input beam diameter at 2 mm and plano convex lens with focal length 100 cm were used to focus the laser on the sample. A set of neutral density filter were used to attenuate the input energy of laser pulses. Closed Z-scan aperture data was collected at low input energies to ensure that there was negligible contribution from higher order nonlinearities. The sample cell was moved using a translation system along the propagation direction (Z-axis) and corresponding output transmittance was measured. The transmission of the beam through an aperture placed in the far field was measured using a photo detector fed to the digital power meter. For open aperture Z-scan mode, a lens to collect the entire laser beam transmitted through the sample replaced the aperture. The experiments were repeated several times to ensure repeatability of the results and the best data were taken from different sets for all the samples.Results and discussion
Morphology and growth mechanism
Fig. 1(A) shows the FESEM image of the GO. It is evident that the structure of GO was layered with some crumples and partially transparent. Fig. 1(B) depicts the FESEM image of pure zinc ferrite projecting the formation of very fine and homogenous nanospheres with some agglomeration. The agglomeration of particles can be related to many factors such as surface area and density. The FESEM images of decorated rGO [Fig. 1(C–E)] illustrate the presence of slight wrinkles and folding on the surface of GO along with the appearance of ZnFe2O4 as bright dots. No obvious conglomeration of ZnFe2O4 was observed. In the present synthesis procedure, the formation of nanospheres and nanospindles of zinc ferrite on reduced graphene oxide were observed. To understand the chemical basis and elemental composition of prepared ZnFe2O4–rGO, EDS was recorded and is as shown in Fig. 1. The observed atomic percent of C, Zn, Fe and O was found to be in good agreement with the estimated elemental content of the performed synthesis procedure. As expected, the atomic percent of Zn and Fe was found to be maximum along with lowest atomic percent of carbon for ZnFe2O4–(15 wt%) rGO. This further confirmed the presence of densely decorated ZnFe2O4 on the surface of (15 wt%) GO. Likewise the content of Zn and Fe was found to decreasing with increase in the graphene oxide content. Thus the estimated chemical composition matched very well with the expected decoration of ZnFe2O4 on the rGO.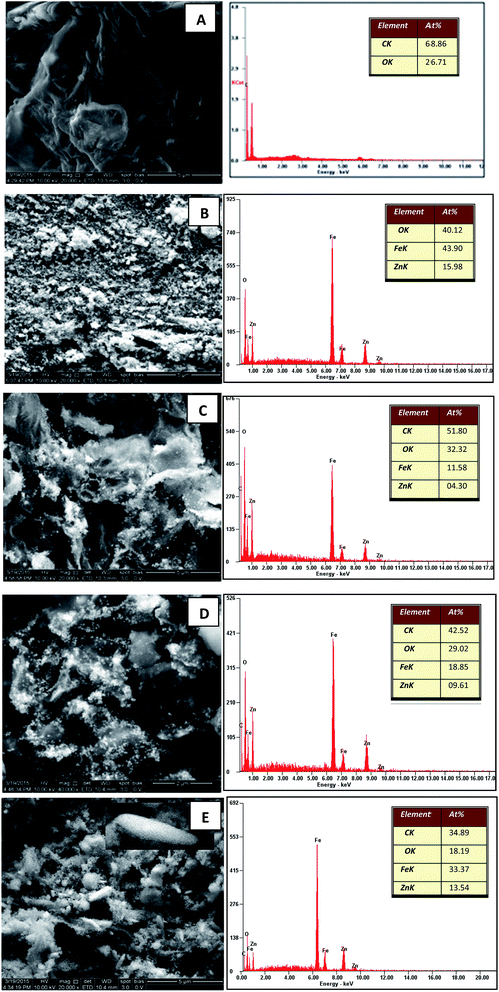 | ||
| Fig. 1 FESEM and EDS images of (A) GO (B) ZnFe2O4 (C) ZnFe2O4–(40 wt%) rGO (D) ZnFe2O4–(25 wt%) rGO and (E) ZnFe2O4–(15 wt%) rGO. | ||
To further elucidate the growth mechanism, recorded TEM images are displayed in Fig. 2. The TEM image of GO (Fig. 2(A)) displayed a wrinkled paper like structure of the ultrathin sheets with stacking. During the reaction, GO which consists of covalently attached oxygen-functional groups such as epoxy, hydroxyl and carboxyl groups in the surfaces act as a nucleation site for nanostructure growth and facilitate the formation of zinc ferrite via electrostatic interaction. In particular, metal ions was adsorbed on the GO nanosheets by coordination with functional moieties in GO through electrostatic force. The Zn2+ and Fe3+ ions anchored on the GO sheets form themselves into ZnFe2O4 and then these nucleuses grew into nano spheres of 101 and 32 nm average diameters [Fig. 2(B and C)]. Since the reaction involved in the synthesis process was slow and takes place at atmospheric pressure and room temperature, molecules have an opportunity to attain the most stable sphere shape in the reaction. However in the case of 15 wt% graphene oxide, the formation of nanospindles with 55 nm length and 17 nm diameters [Fig. 2(D)] was observed upon the surface of graphene sheets. Due to the lower concentration of graphene sheets (15%), nanospheres aggregate themselves due to cohesion and grow as the stack to form nanospindles. Also gradual increase in the concentration of zinc ferrite upon the surface with the decrease in the content of graphene oxide was clearly witnessed. In general, hydrothermal methods do not provide the provision of controlling the particle size and loading of zinc ferrite. However in the present case, loading of zinc ferrite was altered by varying GO content. This also led to the provision of altering shape from nanospheres to nanospindles.
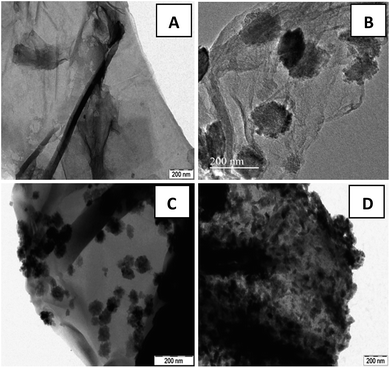 | ||
| Fig. 2 TEM images of (A) GO sheets and ZnFe2O4–rGO composites with (B) 40 wt% (C) 25 wt% (D) 15 wt% graphene contents. | ||
Fig. 2(B–D) clearly demonstrate the nanospheres and spindles uniformly deposited on the surface of (40, 25 and 15 wt%) rGO sheets, respectively. Thus, formations of nanospindle ZnFe2O4 upon 15 wt% rGO and nanosphere ZnFe2O4 upon 25 and 40 wt% rGO were clearly confirmed by morphology analysis. In the HRTEM images (Fig. 3) of decorated rGO the lattice fringes had an interlayer distance of 0.25 nm which agree well with the spacing between (311) planes of ZnFe2O4 crystals. The schematic diagram of growth mechanism is depicted in Fig. 4.
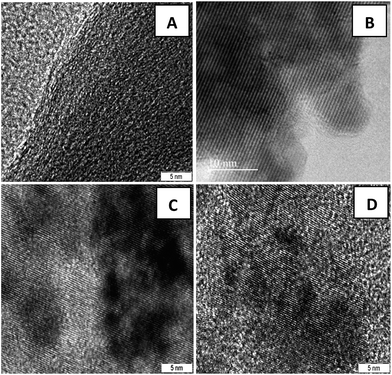 | ||
| Fig. 3 HRTEM images of (A) GO sheets and ZnFe2O4–rGO composites with (B) 40 wt% (C) 25 wt% (D) 15 wt% graphene contents. | ||
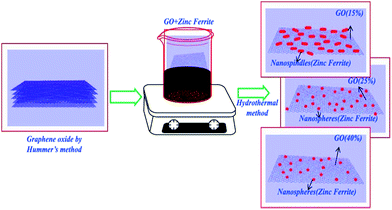 | ||
| Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of the growth mechanism of zinc ferrite–reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. | ||
Linear absorption studies
Fig. 5 shows optical absorption spectra of graphene oxide and spinel ferrite decorated graphene oxide. In the absorption spectra of GO, an absorption peak at 235 nm and a shoulder at 292 nm correspond to π–π* transition for aromatic C–C and n–π* transition due to C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bonds respectively.20 The characteristic absorption peak of zinc ferrite was observed around 570 nm in the absorption spectra of pure zinc ferrite. However, in the decorated graphene oxide, peak at 570 nm (due to ZnFe2O4) got suppressed and the characteristic peak of GO got red shifted to 284 nm and 385 nm. These changes can be attributed to the de-oxygenation of GO sheets and the formation of a composite between the ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles and the graphene sheets during the hydrothermal reaction. The shift in absorption peak was also witnessed from the change of colour from light brown (pure GO) to dark black (composite). The black colour of the decorated graphene oxide was due to the partial restoration of π network prevailing between the rGO sheets.
O bonds respectively.20 The characteristic absorption peak of zinc ferrite was observed around 570 nm in the absorption spectra of pure zinc ferrite. However, in the decorated graphene oxide, peak at 570 nm (due to ZnFe2O4) got suppressed and the characteristic peak of GO got red shifted to 284 nm and 385 nm. These changes can be attributed to the de-oxygenation of GO sheets and the formation of a composite between the ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles and the graphene sheets during the hydrothermal reaction. The shift in absorption peak was also witnessed from the change of colour from light brown (pure GO) to dark black (composite). The black colour of the decorated graphene oxide was due to the partial restoration of π network prevailing between the rGO sheets.
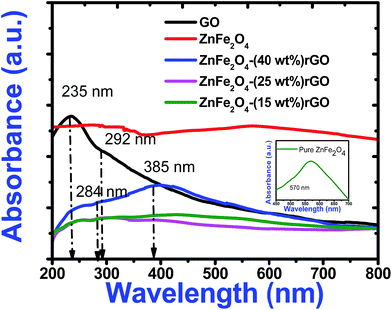 | ||
| Fig. 5 UV-Visible absorption spectra of pure GO, zinc ferrite and decorated reduced graphene oxide. Inset illustrates the expanded absorption spectrum of pure zinc ferrite. | ||
Nonlinear absorption studies
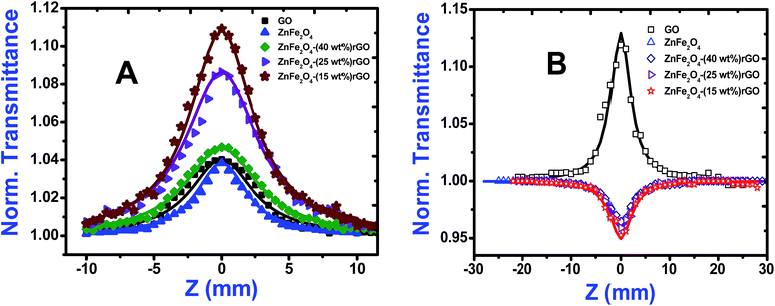
Open aperture (OA) Z-scan measurement was performed to reveal the different mechanisms, like multi-photon absorption (MPA), excited state absorption (ESA) responsible for nonlinear absorption (NLA) in the synthesized materials.21 The recorded OA patterns with two different excitations are shown in Fig. 6. Under low power (cw) and high intensity (fs) laser excitation, GO exhibited saturable absorption (SA) characteristic similar to graphene.22 The Z-scan data for bare GO exhibited a peak with respect to the focus indicating SA. Here, under photo excitation a non-equilibrium population was formed in valence and conduction band of GO attaining the steady state and further absorption of photons (fs pulse width) was restricted due to Pauli blocking. Thus saturable absorption behaviour of depicting high linear transmittance at higher intensities possesses potential applications in optical switching, pulse shape and mode locking.23 Furthermore, the optical transitions (2.33 eV and 1.55 eV) in the sp3 domains of GO are forbidden and, therefore, optical absorption decreases as state filling of the interband transitions in the sp2 domains dominates transient response.While in the case of pure zinc ferrite and decoration of rGO with zinc ferrite the pattern shifted from peak to valley, indicating reverse saturable absorption (RSA) kind of behaviour with fs excitation. This is because when zinc ferrite was decorated upon GO due to the interactions of spinel ferrite with oxygen functional groups sp3 defect (σ-states) turns more dominant, thus giving rise to RSA kind of behaviour. The nonlinear absorption with fs pulses can involve either two photons (two-photon absorption, β) or three photons (three-photon absorption, γ). To identify the possible nonlinear mechanism, the corresponding net nonlinear transmission for open aperture data was fitted with the following equation24
with q0 = β LeffI0, ρ0 = (2γLeff′I02)1/2, β is the 2 PA co-efficient, and γ is the 3 PA coefficient, I00 is the peak intensity, Z is the sample position, z0 = πω02/λ is the Rayleigh range; ω02 is the beam waist at the focal point (Z = 0), λ is the laser wavelength;
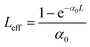 ,
, 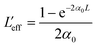 are the effective path lengths in the sample of length L for 2 PA and 3 PA. Based on the above mentioned equation, attempts were made to plot the theoretical fits for both 2 PA and 3 PA mechanism (see ESI file†). With fs pulse excitation, the theoretical plots (solid lines) for two-photon absorption process (pure ZnFe2O4) and two/three-photon absorption process (ZnFe2O4 decorated rGO) matched well with the experimental data (open circles).
are the effective path lengths in the sample of length L for 2 PA and 3 PA. Based on the above mentioned equation, attempts were made to plot the theoretical fits for both 2 PA and 3 PA mechanism (see ESI file†). With fs pulse excitation, the theoretical plots (solid lines) for two-photon absorption process (pure ZnFe2O4) and two/three-photon absorption process (ZnFe2O4 decorated rGO) matched well with the experimental data (open circles).
As seen from the data presented in the UV-Visible absorption spectra, decorated rGO depicts absorption maxima at 284 nm involving π–π* transition of the rGO. Hence, with IR (800 nm, 1.55 eV) excitation, three photons can simultaneously be absorbed to transit the electron to the above mentioned energy state (284 nm, 4.3 eV). While in the case of pure ZnFe2O4, two-photon absorption is the most probable process to excite the electrons to its band edge (570 nm, 2.2 eV) by absorbing simultaneously two-photons involving virtual excited state. However, in the case of cw exposure, both pure and decorated rGO showed SA behaviour, as it is well known that sp2 clusters gives rise to SA at low intensities. Inorder to further confirm the involved NLA mechanism, OA Z-scan was performed on ZnFe2O4–(15 wt%) rGO at various input powers (4–7 mW) with fs excitation. From the recorded OA pattern the nonlinear absorption coefficient was extracted for different pulse power and extracted β value increased with increase in input power/energy (Fig. 7). Although the fit in both cases (2 PA/3 PA) are found to be good for decorated rGO, based on the variation of NLA coefficient as a function of power of excitation, the observed NLA is attributed predominantly due to 3 PA mechanism. The observed nonlinearity can be understood as arising from higher order nonlinear optical process [an effective three-photon absorption process where in two photons excite the system to higher state (which could be one of the defect states) followed by absorption of another photon, possibly free carrier absorption in this case resulting in a (2 + 1) photon absorption].25,26
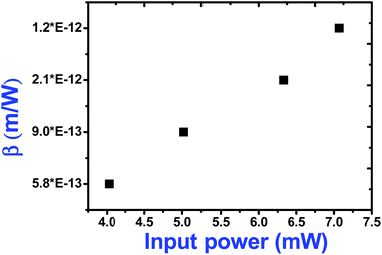 | ||
| Fig. 7 Variation of two-photon absorption coefficient of ZnFe2O4–(15 wt%) rGO with input power under fs (800 nm) excitation. | ||
Nonlinear refraction studies
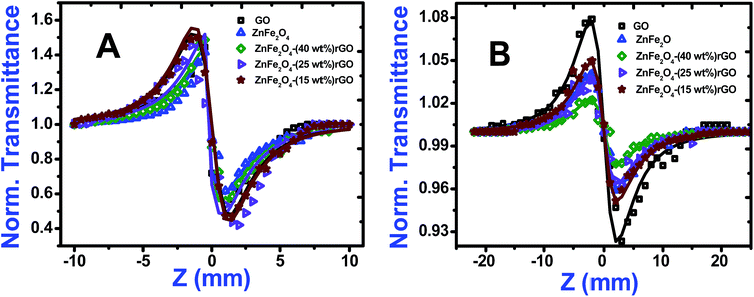
Closed aperture Z-scan (CA) was performed to measure the nonlinear refractive index (n2) of the material. The recorded CA patterns under two excitations are shown in Fig. 8. Different mechanisms can be proposed to describe the observed NLR of pure and decorated rGO in suspension. Electronic polarization, molecular reorientation effect, nonlinear scattering, excited state refraction, free carrier refraction, and thermal effect are most common reason of observed NLR.11 In the present case, an obvious nonlinear self-defocusing signal from all the samples was observed.The n2 value was obtained by fitting the normalized transmittance versus sample position with the theoretical equation27 given by
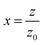 is the diffraction length, ΔØ = kn2I0Leff is the on-axis phase shift at focus, k is the wave number, Z0 is the Rayleigh range (=nπω02/λ) and ω0 is the beam spot radius at focus. In this case, samples acted like a thermal lens and due to negative nonlinear refraction index, convergence to the incoming beam occurs at pre-focal positions and then starts to diverge after focus. Thus the recorded normalized closed aperture Z-scans exhibit a pre-focal peak followed by a post-focal valley indicating the nonlinearity of the samples to be negative and lensing effect to be defocusing (negative nonlinear refraction). Here the observed nonlinearity is mainly of thermal origin in both cases (532 nm and 800 nm). Existence of the thermal lens effect in our experiments arises from absorption of continuous-wave (cw) laser beam energy and high repetition rate (1 MHz) with fs excitation. Interestingly, for photonic applications that require cw or high reputation rates laser, the thermo-optical effects can be very important. In addition, owing to heat conduction process, the thermal nonlinear response presents a nonlocal behaviour, which can be exploited in the investigation of several nonlocal nonlinear phenomena, such as spatial soliton propagation and shock waves. The thermally induced nonlinearity denotes temporal variation of optical parameters due to linear and nonlinear absorptions in the medium followed by a nonradioactive relaxation down to the ground state.28 Furthermore, the laser heating leads to the generation of an acoustic wave that changes the medium density followed by a variation of refractive index.
is the diffraction length, ΔØ = kn2I0Leff is the on-axis phase shift at focus, k is the wave number, Z0 is the Rayleigh range (=nπω02/λ) and ω0 is the beam spot radius at focus. In this case, samples acted like a thermal lens and due to negative nonlinear refraction index, convergence to the incoming beam occurs at pre-focal positions and then starts to diverge after focus. Thus the recorded normalized closed aperture Z-scans exhibit a pre-focal peak followed by a post-focal valley indicating the nonlinearity of the samples to be negative and lensing effect to be defocusing (negative nonlinear refraction). Here the observed nonlinearity is mainly of thermal origin in both cases (532 nm and 800 nm). Existence of the thermal lens effect in our experiments arises from absorption of continuous-wave (cw) laser beam energy and high repetition rate (1 MHz) with fs excitation. Interestingly, for photonic applications that require cw or high reputation rates laser, the thermo-optical effects can be very important. In addition, owing to heat conduction process, the thermal nonlinear response presents a nonlocal behaviour, which can be exploited in the investigation of several nonlocal nonlinear phenomena, such as spatial soliton propagation and shock waves. The thermally induced nonlinearity denotes temporal variation of optical parameters due to linear and nonlinear absorptions in the medium followed by a nonradioactive relaxation down to the ground state.28 Furthermore, the laser heating leads to the generation of an acoustic wave that changes the medium density followed by a variation of refractive index.
Third-order NLO coefficients and optical limiting behaviour
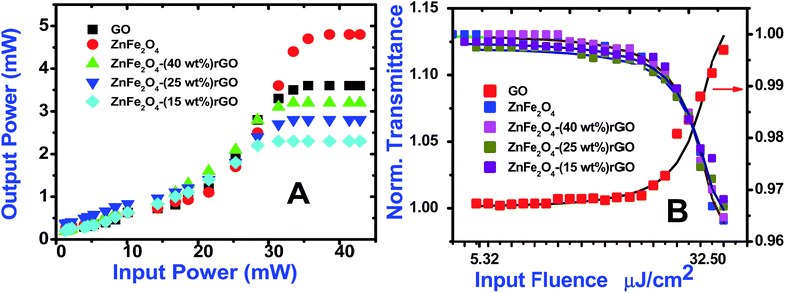
Optical limiting (OL) curves, illustrated in Fig. 9, were extracted from the corresponding open-aperture fs Z-scan data. The position dependent fluence was evaluated from the equation29where F(z) is the input fluence, Ein is the laser energy and ω0 laser beam radius at the focus. The transmittance decreases rapidly with increased input fluence for all the samples. However in the case of cw laser, the output was directly measured by varying the input of the laser beam. From the data presented in Fig. 9 it is evident that the output power rises initially with increase in input power and after a certain threshold value the output beam start deviating from the linearity. The OL onset values, defined as the incident fluence at which optical limiting activity starts, are summarized in Table 1. Possible mechanisms for 2 PA and 3 PA excitation with 800 nm photons are depicted in Fig. 10. The negative nonlinearity due to self-defocusing could be attributed to the observed strong optical limiting behaviour of the material. In liquid sample, due to the large thermal expansion, at the corresponding wavelength the high absorbance of the nonlinear material leads to increase in temperature and density of the samples thus resulting in limiting action. The decorated samples exhibited strong optical limiting due to large number of defect induced states, which enhances NLA, causing attenuation of laser intensity at higher incident fluencies. The estimated third-order NLO parameters are summarized in Table 1. It can be clearly be witnessed that decorated rGO demonstrated enhanced NLO coefficients compared to bare GO and ZnFe2O4.
| Samples | 532 nm, cw excitation | 800 nm, 150 fs excitation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β × 10−3 cm W−1 | n2 × 10−8 cm2 W−1 | χ(3) × 10−6 esu | Optical limiting onset values (mW) | Nonlinear absorption coefficient 10−12 m W−1 | n2 × 10−18 m2 W−1 | χ(3) × 10−15 esu | Optical limiting onset values (μJ cm−2) | |
| GO | 6.1 | 4.0 | 3.2 | 30.4 | 12.0 (SA) | 14.7 | 5.2 | 46.3 |
| ZnFe2O4 | 6.1 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 34.2 | 5.1 (2 PA, β) | 3.4 | 0.1 | 34.2 |
| ZnFe2O4–rGO (40 wt%) | 6.1 | 4.5 | 3.9 | 29.9 | 2.6 (3 PA, γ) | 1.5 | 1.3 | 28.1 |
| ZnFe2O4–rGO (25 wt%) | 6.3 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 28.8 | 3.1 (3 PA, γ) | 2.8 | 1.5 | 22.2 |
| ZnFe2O4–rGO (15 wt%) | 6.5 | 4.7 | 4.2 | 27.7 | 4.0 (3 PA, γ) | 4.2 | 1.9 | 14.7 |
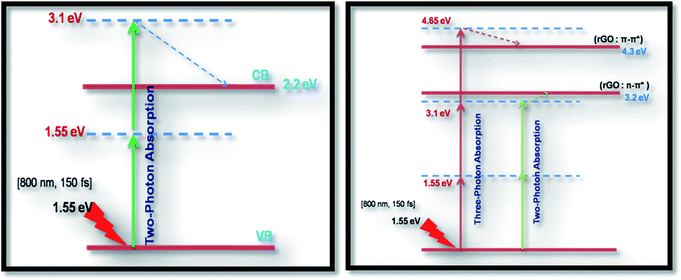 | ||
| Fig. 10 Probable excitation mechanisms for 2 PA (left) and 3 PA (right) for all the samples studied. Dashed line represents non-radiative decay. | ||
To understand the role of defects in the enhancement of NLO behaviour, Raman studies were performed. Fig. 11 presents the Raman spectra of GO, ZnFe2O4 and ZnFe2O4 decorated rGO nanostructures. Raman spectra of GO demonstrates the G band at 1580 cm−1 due to the E2g phonon of sp2 carbon atoms and the D band (1350 cm−1) which is a breathing mode of k-point phonons of A1g symmetry, arising from the disordered carbon structures, edges and other defects. The intensity ratio of D and G peak (ID/IG) provides the level of functionalization factor for measuring the sp2 domain size of a carbon structure containing sp2 and sp3 bonds. The intensity ratio of GO was estimated to be 0.82. In ZnFe2O4, the peak above 600 cm−1 was of the A1g mode, involving motions of the tetrahedral groups. The other low-frequency phonon modes were due to metal ions involved in octahedral groups corresponding to the symmetric and anti-symmetric bending of oxygen atoms in metal-oxygen bonds for octahedral groups. The five Raman modes at 212, 272, 390, 493 and 603 cm−1 can be attributed to the Raman active modes (A1g + Eg + BF2g) of the spinel structure of ZnFe2O4.20 The Raman spectra of ZnFe2O4–(40, 25 and 15 wt%) rGO composite illustrating the characteristics of both GO and ZnFe2O4 were observed. The intensity ratio ID/IG was calculated to be 0.85, 1.20 and 1.25, respectively. However, the ID/IG ratio (1.25) of the ZnFe2O4 (spindle)–rGO nano hybrid was higher than other pure and decorated rGO which was due to the presence of more defects arising from the interactions between the zinc ferrite and the graphene sheets. Also, the perfect graphene domain (La) was estimated using the well-known formula21
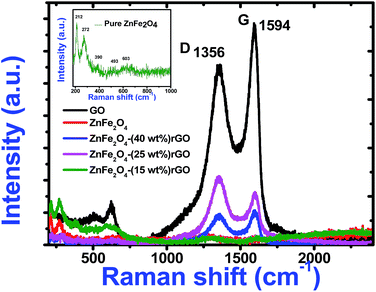 | ||
| Fig. 11 Raman spectra of pure GO, zinc ferrite and decorated reduced graphene oxide. Inset shows the expanded Raman data of pure zinc ferrite. | ||
Conclusions
Pure and decorated graphene based nanostructures were synthesized by hydrothermal reaction method. This method provides the ease of effective reduction of the GO sheets along with attachment of zinc ferrite spinel nanostructures on the rGO sheets in a single step. The incorporation of zinc ferrite upon the GO surface was confirmed by Raman, FESEM, TEM and optical absorption studies. Raman spectra showed the G band (1580 cm−1) of sp2 carbon atoms and the D band (1350 cm−1) of A1g symmetry, which arises from the defects. The five Raman modes at 212, 272, 390, 493 and 603 cm−1 were due to the Raman active modes (A1g + Eg + BF2g) of the spinel structure of ZnFe2O4. The ID/IG ratio (1.25) of the ZnFe2O4 (spindle)–rGO nanohybrid was higher than other pure and decorated rGO compounds, which is attributed to the presence of higher number of defects arising from the interactions between the zinc ferrite and the graphene sheets. Formation of nanospheres with 32 nm and 101 nm diameter (25 and 40 wt%) and nanospindles (15 wt%) with typical size of 17 nm × 55 nm was observed. Due to the lower concentration of graphene sheets (15%), nanospheres aggregate themselves due to cohesion and grow as stack to form nanospindles. Also gradual increase in the concentration of zinc ferrite upon the surface with decrease in the content of graphene oxide was clearly witnessed. In the absorption spectra of GO, an absorption peak at 235 nm (π–π* transition for aromatic C–C were observed) and a shoulder peak at 292 nm (n–π* transition due to C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bonds). The characteristic absorption peak of zinc ferrite was observed around 570 nm in the absorption spectra of pure zinc ferrite. Third order optical nonlinearity and optical limiting action under continuous wave (532 nm, 50 mW) and ultrafast (800 nm, 150 fs) laser excitations were studied by Z-scan technique. The enhanced nonlinear absorption mainly arises due to the defect induced states originating due to functionalization of GO which facilitate interband transition. When zinc ferrite was decorated upon GO, due to the interactions of spinel ferrite with oxygen functional groups, sp3 defect (σ-states) turns more dominants, thus giving rise to RSA behaviour. Hence, under ultrafast (800 nm) excitation, the origin of nonlinear absorption was found to different for GO (SA), zinc ferrite (2 PA) and ZnFe2O4 decorated rGO (3 PA) due to the variation in its electronic states. In the case of cw exposure, both pure and decorated GO exhibited SA behaviour due to the low intensity excitation. The peak followed by a valley normalized transmittance obtained from the closed aperture curves indicated that the sign of nonlinear refractive index is negative and self-defocusing optical nonlinearity. Larger the extent of conjugation, higher the chance for electron/energy transfers, leading to enhanced nonlinear optical response in nanospindle zinc ferrite decorated–(15 wt%) rGO with higher nonlinear absorption coefficient, nonlinear refractive index and third order nonlinear optical susceptibility. The versatile NLO properties of the ZnFe2O4 decorated rGO in different domains of excitation imply a huge potential in the development of optical limiters for the protection of sensors against both ultrafast and continuous wave laser damage simultaneously using a single material.
O bonds). The characteristic absorption peak of zinc ferrite was observed around 570 nm in the absorption spectra of pure zinc ferrite. Third order optical nonlinearity and optical limiting action under continuous wave (532 nm, 50 mW) and ultrafast (800 nm, 150 fs) laser excitations were studied by Z-scan technique. The enhanced nonlinear absorption mainly arises due to the defect induced states originating due to functionalization of GO which facilitate interband transition. When zinc ferrite was decorated upon GO, due to the interactions of spinel ferrite with oxygen functional groups, sp3 defect (σ-states) turns more dominants, thus giving rise to RSA behaviour. Hence, under ultrafast (800 nm) excitation, the origin of nonlinear absorption was found to different for GO (SA), zinc ferrite (2 PA) and ZnFe2O4 decorated rGO (3 PA) due to the variation in its electronic states. In the case of cw exposure, both pure and decorated GO exhibited SA behaviour due to the low intensity excitation. The peak followed by a valley normalized transmittance obtained from the closed aperture curves indicated that the sign of nonlinear refractive index is negative and self-defocusing optical nonlinearity. Larger the extent of conjugation, higher the chance for electron/energy transfers, leading to enhanced nonlinear optical response in nanospindle zinc ferrite decorated–(15 wt%) rGO with higher nonlinear absorption coefficient, nonlinear refractive index and third order nonlinear optical susceptibility. The versatile NLO properties of the ZnFe2O4 decorated rGO in different domains of excitation imply a huge potential in the development of optical limiters for the protection of sensors against both ultrafast and continuous wave laser damage simultaneously using a single material.
Acknowledgements
S. V. Rao acknowledges the financial support from DRDO, India through ACRHEM. The authors thank Ms M. S. S. Bharathi for her assistance in the fs Z-scan experiments.References
- A. C. Neto, F. Guinea, N. M. Peres, K. S. Novoselov and A. K. Geim, Rev. Mod. Phys., 2009, 81, 109–161 CrossRef.
- N. Liaros, A. B. Bourlinos, R. Zboril and S. Couris, Opt. Express, 2013, 21, 21027–21038 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Biswas, A. K. Kole, C. S. Tiwary and P. Kumbhakar, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 10319–10325 RSC.
- N. Liaros, J. Tucek, K. Dimos, A. Bakandritsos, K. S. Andrikopoulos, D. Gournis and S. Couris, Nanoscale, 2016, 8, 2908–2917 RSC.
- J. Wang, Y. Hernandez, M. Lotya, J. N. Coleman and W. J. Blau, Adv. Mater., 2009, 21, 2430–2435 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Perumbilavil, P. Sankar, T. P. Rose and R. Philip, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2015, 10, 051104 CrossRef.
- J. Zhu, Y. Li, Y. Chen, J. Wang, B. Zhang, J. Zhang and W. J. Blau, Carbon, 2011, 49, 1900–1905 CrossRef CAS.
- B. S. Kalanoor, P. B. Bisht, S. A. Ali, T. T. Baby and S. Ramaprabhu, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, 2012, 29, 669–675 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Wang, W. Yu, Y. Fang, Y. Song, D. Jia, L. Long and C. Zhang, Carbon, 2015, 89, 130–141 CrossRef CAS.
- M. K. Kavitha, H. John, P. Gopinath and R. Philip, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2013, 1, 3669–3676 RSC.
- X. L. Zhang, Z. B. Liu, X. C. Li, Q. Ma, X. D. Chen, J. G. Tian and Y. S. Chen, Opt. Express, 2013, 21, 7511–7520 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. K. Lim, Z. L. Chen, J. Clark, R. G. Goh, W. H. Ng, H. W. Tan and L. L. Chua, Nat. Photonics, 2011, 5, 554–560 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Babeela, T. S. Girisun and G. Vinitha, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2015, 48, 065102 CrossRef.
- A. M. Gobin, M. H. Lee, N. J. Halas, W. D. James, R. A. Drezek and J. L. West, Nano Lett., 2007, 7, 1929–1934 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. J. Thomas, S. Krishnan, K. Sridharan, R. Philip and N. Kalarikkal, Mater. Res. Bull., 2012, 47, 1855–1860 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Zheng, W. Chen, Y. Huang, X. Xiao and X. Ye, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 39697–39703 RSC.
- J. Tian, S. Liu, H. Li, L. Wang, Y. Zhang, Y. Luo, A. M. Asiri, A. O. Al-Youbi and X. Sun, RSC Adv., 2012, 2, 1318–1321 RSC.
- X. Qin, W. Lu, A. M. Asiri, A. O. Al-Youbi and X. Sun, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2013, 3, 1027–1035 CAS.
- W. S. Hummers Jr and R. E. Offeman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1958, 80, 1339 CrossRef.
- A. Meidanchi and O. Akhavan, Carbon, 2014, 69, 230–238 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Anand, A. Kaniyoor, S. S. S. Sai, R. Philip and S. Ramaprabhu, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2013, 1, 2773–2780 RSC.
- X. F. Jiang, L. Polavarapu, S. T. Neo, T. Venkatesan and Q.-H. Xu, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2012, 3, 785–790 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Wang, Y. Feng, C. Chang, J. Zhan, C. Wang, Q. Zhao and J. Wang, Nanoscale, 2014, 6, 10530–10535 RSC.
- S. Ramakanth, S. Hamad, S. Venugopal Rao and K. C. J. Raju, AIP Adv., 2015, 5, 057139 CrossRef.
- D. Swain, T. Sarma, P. K. Panda and S. V. Rao, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2011, 514, 98–103 CrossRef.
- T. Sarma, P. K. Panda, P. T. Anusha and S. V. Rao, Org. Lett., 2010, 13, 188–191 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Saravanan, T. S. Girisun and G. Vinitha, J. Mater. Sci., 2016, 51, 3289–3296 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Mashayekh and D. Dorranian, Optik-Int. J. Light and Elec. Opt., 2014, 125, 5612–5617 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Karthikeyan, R. Udayabhaskar, T. P. Rose, T. Pandiyarajan and R. Philip, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 39541–39546 RSC.
- P. Thomas, P. Sreekanth, R. Philip and K. E. Abraham, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 35017–35025 RSC.
- K. Sridharan, T. Endo, S. G. Cho, J. Kim, T. J. Park and R. Philip, Opt. Mater., 2013, 35, 860–867 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Yamuna, S. Ramakrishnan, K. Dhara, R. Devi, N. K. Kothurkar, E. Kirubha and P. K. Palanisamy, J. Nano Res., 2013, 15, 1–9 Search PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: XRD pattern of pure GO, zinc ferrite and decorated reduced graphene oxide. See DOI: 10.1039/c6ra21428b |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |