Distinctive stability of a free-standing monolayer clay mineral nanosheet via transmission electron microscopy†
Abstract
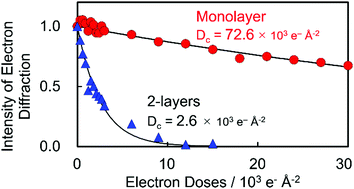
Among 2D materials, clay mineral nanosheets have been extensively studied owing to their specific features, such as high surface charge and large surface area. Recently, we reported a stable free-standing (without any surfactants or matrices) monolayer clay mineral, characterized via annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscopy (ADF-STEM) at the atomic-scale. Herein, we demonstrated that the monolayer clay mineral exhibited outstanding stability under electron beam irradiation compared to two- or three-layered nanosheets via electron diffraction analysis. In addition to its low thickness (∼1 nm-thick), the absence of an interlayer space was the critical factor contributing to the distinctive stability of the monolayer clay mineral, compared to that of the two- or three-layered clay mineral. The findings here inspire further investigation in free-standing clay mineral using (S)TEM and also for a wide variety of nanomaterials which are strongly hydrated.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...