Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei M5L induces cell cycle arrest and calreticulin translocation via the generation of reactive oxygen species in HT-29 cell apoptosis
Abstract
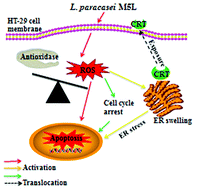
Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei M5L (L. paracasei M5L) was isolated and co-cultured with HT-29 colon cancer cells to study its anti-colorectal cancer effects and mechanism. Using the MTT assay we found that L. paracasei M5L significantly inhibits HT-29 cell proliferation. Morphological and biochemical characteristics of apoptosis were observed and confirmed by hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Lactobacilli could change the cell cycle distribution and induce calreticulin (CRT) translocation from the endoplasmic reticulum to the surface of the cytomembrane. We also determine that vast reactive oxygen species (ROS) were generated, while the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) were noticeably diminished following L. paracasei M5L treatment. This study reveals that L. paracasei M5L induces apoptosis in HT-29 cells through ROS generation followed by CRT accompanied endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and S phase arrest. These results provide new insights into the possible molecular mechanism of L. paracasei M5L as a novel probiotic with the potential for further application.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...