 Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Mechanism of methane activation and graphene growth on oxide ceramics
Hanzhang
Zhou
 a,
Mengxuan
Zhang
a,
Mengxuan
Zhang
 a,
Takeharu
Yoshii
a,
Takeharu
Yoshii
 *a,
Devis
Di Tommaso
*a,
Devis
Di Tommaso
 bc and
Hirotomo
Nishihara
bc and
Hirotomo
Nishihara
 *ad
*ad
aInstitute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University, 2-1-1, Katahira, Aoba-ku, Sendai, 980-8577, Japan. E-mail: takeharu.yoshii.b3@tohoku.ac.jp; hirotomo.nishihara.b1@tohoku.ac.jp
bDepartment of Chemistry, Queen Mary University of London, London E1 4NS, UK
cDigital Environment Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London E1 1HH, UK
dAdvanced Institute for Materials Research (WPI-AIMR), Tohoku University, 2-1-1, Katahira, Aoba-ku, Sendai, 980-8577, Japan
First published on 10th April 2025
Abstract
Three-dimensional (3D) graphene materials have attracted significant attention across various fields, including energy storage and catalysis, due to their exceptional properties such as developed nanoporosity, corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and mechanical flexibility. The first step in synthesizing nanoporous 3D graphene involves the generation of the graphene framework through the decomposition of methane at high temperatures on thermally stable oxide ceramics. Thus, a thorough understanding of the reaction mechanism involved in this initial step is crucial. This article reviews recent advancements in elucidating the mechanisms of methane activation and subsequent graphene growth on various types of oxide ceramics, including alumina (Al2O3), magnesia (MgO), calcium oxide (CaO), and silica (SiO2).
1. Introduction
Graphene is a remarkable carbon material characterized by a two-dimensional, monolayer structure in which carbon atoms are arranged in a hexagonal lattice via sp2 hybridization.1 As one of the thinnest and lightest materials known, graphene exhibits exceptional properties, including high electrical conductivity, outstanding electron mobility (2.5 × 105 cm2 V−1 s−1),2 a large specific surface area (2627 m2 g−1),3 and remarkable thermal conductivity (over 3000 W mK−1).4 Its unique characteristics make it highly versatile for a wide range of advanced applications, including biosensors,5 solar cell electrodes,6 and photocatalysts.7 Recently, graphene has become capable of being mass-produced at a relatively low cost, enhancing its practical value. Spherical molecules composed of sp2 carbon, known as fullerenes,8 and tubular structures, referred to as carbon nanotubes,9,10 are zero-dimensional and one-dimensional graphene-related structures, respectively, each possessing unique characteristics distinct from two-dimensional graphene. Meanwhile, steady progress has recently been made in the synthesis of three-dimensional (3D) graphene structures, theoretically designed by incorporating heptagonal and octagonal rings into carbon hexagonal networks.11,12 Among these developments, the “Graphene MesoSponge® (GMS)”,13 recently developed by the authors, is a novel mesoporous material that strongly reflects the characteristic properties of graphene, such as high specific surface area, electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, lightweight nature, and mechanical flexibility. It holds great potential for applications in various fields, including energy storage,14,15 heat pumps,16 and catalyst supports.17,18This minireview primarily highlights recent advancements in the initial stage of GMS synthesis, specifically the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process. The entire synthesis process of GMS will first be outlined, followed by an in-depth discussion of the CVD process, with an emphasis on the mechanism of graphene growth on the surface of oxide ceramics. Note that in this minireview, “CH4 activation” refers to the initial catalytic weakening of C–H bonds, while “CH4 decomposition” encompasses the entire process of CH4 breakdown into carbon, either catalytic or non-catalytic thermal pathways.
2. Synthesis of three-dimensional graphene
Graphene can be synthesized by various methods, including mechanical cleavage,1 chemical exfoliation,19,20 epitaxial growth on SiC surfaces,21 and CVD.22 Among these, CVD is regarded as one of the most promising approaches for fabricating graphene-based 3D nanostructures. Since CVD promotes graphene growth along the substrate surface, removing the substrate after performing CVD on a 3D nanostructured substrate results in 3D graphene with a corresponding morphology.23–25 The substrate used in CVD is referred to as the “template”. CVD needs to be conducted at high temperatures, typically around 600–900 °C to produce high-quality graphene. Consequently, it is challenging to use metal nanostructures with a low melting point as templates, underscoring the need for templates with higher heat resistance. On the other hand, oxide ceramics exhibit excellent heat resistance and serve as templates even at CVD temperatures, allowing for relatively straightforward control over 3D nanostructures.When Al2O3 or zeolite is used as a catalyst for the organic compound conversion reactions at high temperatures, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (coke) are produced as by-products and the catalytic activity is reduced. This phenomenon is widely known as “coking”. Coking causes poisoning of catalysts, and therefore, most researchers tried to avoid coking. On the other hand, Kyotani's group pioneered the utilization of coking reactions for synthesizing templated carbons.26,27 For example, intentional coke deposition, i.e., CVD, inside the three-dimensional network pores of zeolites results in zeolite-templated carbon (ZTC),27 consisting of a three-dimensional framework of single-layer graphene.25,28 ZTC is, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, the most pioneering 3D graphene structure and continues to be actively studied worldwide.3 However, ZTCs have low chemical stability due to the large amount of graphene edge sites. It will quickly degrade when applied to batteries and other devices.3
GMS overcomes this weakness of ZTC by removing edges to the maximum extent possible through a graphene fusion (zipping) reaction,29 achieving chemical stability superior to that of carbon nanotubes.14,30Fig. 1 illustrates the formation of GMS. The typical synthesis of GMS begins with a CVD process using Al2O3 and MgO nanoparticles as spherical templates and CH4 as the carbon source.31 After the CVD, the template surfaces are uniformly coated with a thin carbon layer, approximately equivalent to a single graphene layer. Subsequent chemical etching removes the templates, yielding a carbon mesosponge (CMS) with spherical mesopores. The CMS is then subjected to heat treatment at 1800 °C, promoting the zipping reaction to form a graphene framework with a minimal number of edge sites. Thus, graphene growth on oxide ceramics represents the first critical step in GMS synthesis. However, the detailed reaction mechanisms have been largely unknown. Recent studies have advanced our understanding of graphene growth mechanisms on various types of oxide ceramics, which are discussed in detail in the following sections. Note that thermal stability is a key factor in selecting oxide templates, particularly the ability to maintain surface area and crystal structure under high-temperature conditions above 600 °C. This minireview focuses on thermally stable oxides, including as Al2O3, MgO, CaO, and SiO2. As an example using a different template, graphene has been synthesized at 700 °C using CeO2 under photo-assisted conditions.32
 | ||
| Fig. 1 A schematic of the synthesis of GMS. (a) Al2O3-nanoparticles (NP) as a nanosized substrate for CVD. (b) Carbon-coated Al2O3-NP. (c) GMS prepared by high-temperature treatment (1800 °C) of CMS obtained by removing Al2O3-NP from carbon-coated Al2O3-NP. Reprinted with permission.13 Copyright Wiley 2016. | ||
3. Mechanism of graphene growth on ceramic oxide surface
3.1. Aluminium oxide (Al2O3) and magnesium oxide (MgO)
The synthesis of templated carbon utilizing the coking effect on Al2O3 had been previously reported by Kyotani et al.26 Accordingly, in the development of GMS, naturally aggregated γ-Al2O3 nanoparticles were initially employed as a 3D template framework.13 To form highly crystalline graphene through CVD, thermally stable CH4, which allows for higher reaction temperatures, was used as the carbon source. However, the removal of Al2O3 template after CVD required either high temperature alkaline melting or hydrofluoric acid (HF) treatment, making the process both costly and environmentally burdensome. In response, the authors explored alternative templates and found that MgO, which can be dissolved in hydrochloric acid (HCl), is also suitable for GMS synthesis.33 Interestingly, the following reaction, where CH4 is converted to graphene at high temperatures, occurs on both the solid acid (γ-Al2O3) and the solid base (MgO).| nCH4 → nC(graphene) + 2nH2 | (1) |
Thus, the CVD reaction shown in eqn (1) likely proceeds via a mechanism independent of solid acid or base effects.
To investigate this, a detailed analysis of the CVD reaction was performed on the surfaces of both materials.33Fig. 2a compares graphene growth rates on both catalyst surfaces at various temperatures. Here, the weight change resulting from graphene deposition on the template during the CVD reaction was measured using the thermogravimetric analyser (TG). The weight gain was then converted to the average number of graphene layers by dividing it by the specific surface area of the template. On either solid surface, the growth rate of the first graphene layer was two to three times faster than that of the second and subsequent layers. The activation energy for forming the first graphene layer was 114 kJ mol−1 for γ-Al2O3 and 134 kJ mol−1 for MgO,33 both of which are significantly lower than the activation energy for non-catalytic CH4 decomposition (370–433 kJ mol−1).34 In contrast, the activation energy for forming subsequent layers was higher, at 234 kJ mol−1 for γ-Al2O3 and 210 kJ mol−1 for MgO activation energies, respectively.33 These values are comparable to the activation energy for CH4 decomposition on carbon black (205–236 kJ mol−1),35 suggesting that subsequent graphene layers form on the first layer. This sequential graphene growth mechanism makes it easy to achieve the uniform coating of single-layer graphene.
 | ||
| Fig. 2 Analysis of graphene growth reactions via CVD using CH4 as a precursor on γ-Al2O3 and MgO. (a) Plot of the number of graphene layers formed versus CVD reaction time. (b) Gas analysis during the CVD reaction on MgO. CH4 was introduced to preheated MgO at 900 °C at the time labelled “CH4 supply starts”. Reprinted with permission.33 Copyright Royal Society of Chemistry 2021. | ||
Furthermore, as shown in the inset of Fig. 2a, an induction period of 5–10 min was observed from the time the template was exposed to CH4 (CVD time = 0) to the onset of carbon deposition. Gas analysis during this induction period (Fig. 2b) detected not only the CH4 precursor and the H2 product but also the release of CO, a common feature observed on both Al2O3 and MgO. These results indicate that CH4 extracts oxygen from the surfaces of γ-Al2O3 or MgO in the form of CO, generating oxygen vacancies that serves as active sites for converting CH4 into graphene. Notably, similar CVD reactions were observed on θ-Al2O3 as well.36 These insights into the formation of oxygen vacancy sites and their role in the activation of CH4 were further corroborated by density functional theory (DFT) calculations. Fig. 3 summarizes the mechanism of graphene formation on Al2O3 and MgO surfaces.33
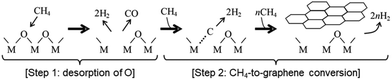 | ||
| Fig. 3 Mechanism of graphene formation via CVD using CH4 as a precursor on γ-Al2O3 and MgO (M = Al or Mg). | ||
The initial step of graphene nucleation on the γ-Al2O3 surface was studied in more depth by Di Tommaso and co-workers using computational methods.37 The process begins with C–H activation, involving proton abstraction by surface oxygen atoms, followed by β-hydrogen elimination, leading to the formation of H2. Fig. 4a shows the energy diagram for dehydrogenation on the most active (100) surface of γ-Al2O3. While the removal of two hydrogen atoms from CH4 to form the CH2 adsorbate species (CH2*) proceeds with a low energy barrier, the removal of the third hydrogen atom faces a significantly higher energy barrier. This suggests that CH2* is a key intermediate in the graphene nucleation process. Furthermore, the energy diagram for the coupling reaction of CH2* on the (100) surface (Fig. 4b) demonstrates that CH2* readily grows into CnH2n* species (n = 2–6). The length of C–C bond length in the CnH2n species on the γ-Al2O3 surface expands with increasing chain length. During the early stages of nucleation, the unsaturated CH2* groups at both ends of the carbon chain strongly adsorb to the catalyst surface, while the middle part detaches from the surface, forming a loop-like structure, contributing to the nucleation of graphene.
 | ||
| Fig. 4 Energy profiles of (a) the complete CH4* dehydrogenation and (b) the formation of CnH2n* (n = 2–6) species via CH2* coupling on the γ-Al2O3 (100) surface. Adapted from ref. 37 with modifications. | ||
Di Tommaso and co-workers also adopted a computational approach based on DFT calculations with machine learning forcefield molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the stability and growth investigation of larger graphene clusters, Cn (n = 16–26), on MgO.38 Among the various Cn clusters examined, the C21 cluster, which features a bowl-shaped molecular structure with three pentagons and three hexagons alternately arranged around a central hexagon, exhibited unique stability on MgO surface. Furthermore, the high electron density at the central hexagon suggests that this cluster acts as a low-mobility nucleation site for graphene growth during CVD. Additionally, it was found that the stability of the C21 cluster is enhanced when impurities such as Si, Mn, Fe, Ca, or Al are doped onto the MgO surface. These computational results suggest that graphene clusters formed in the early stages of CVD tend to adopt specific structures, such as the C21 cluster.
3.2. Calcium oxide (CaO)
CaO is a more cost-effective template compared to Al2O3 and MgO, as it can be readily produced through the low-cost thermal decomposition of enriched calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and easily removed using hydrochloric acid (HCl). Our group has already demonstrated the synthesis of GMS using CaO nanoparticles as templates.39 Additionally, CaO offers higher catalytic activity for CH4 decomposition compared to Al2O3 and MgO, allowing CVD to occur at lower temperatures.A detailed study of the mechanism of graphene formation via CVD using CH4 as a precursor on CaO template was conducted through experimental and computational methods.40 DFT calculations revealed that the stepped oxygen sites on the CaO (110) surface possess significantly lower energy barriers for CH4 dehydrogenation reactions, regardless of the presence of oxygen vacancies (Fig. 5). Specifically, even without oxygen vacancies, the C–H cleavage step of CH4 to form CH3* and CH2* proceeds spontaneously, and the resulting CH2* species can subsequently transform into graphene. Indeed, gas emission in the early stage of CVD indicates that, unlike Al2O3 and MgO, there is no induction period on the CaO template. That is, graphene formation begins immediately upon CH4 contacting the CaO surface.40
 | ||
| Fig. 5 The energy profiles for the C–H activation on the (a) pristine CaO (111) surface and (b) CaO (111) surface with oxygen vacancy sites. The blue, red, brown, and white balls represent Ca, O, C, and H atoms, respectively. Adapted from ref. 40 with modifications. | ||
Although the CaO surface is active even without oxygen vacancies, analysis of the emission gas composition during CVD reveals that CaO releases more CO than Al2O3 and MgO. This release continues even after the graphene layer reaches a single layer in thickness. The total CO emission during CVD on CaO reaches 4.04 μmol m−2.40 In contrast, CO desorption from Al2O3 and MgO terminates before the graphene layer reaches 0.5 layers, with total emissions of only 0.52 and 1.37 μmol m−2, respectively. These findings indicate that, on the CaO surface, the decomposition of CH4 leading to graphene growth and the desorption of surface oxygen as CO occur simultaneously. Furthermore, CO desorption from the CaO surface persists even after the CaO surface is completely coated with graphene. To elucidate this mechanism, the interaction between the formed graphene layer and the underlying CaO was calculated. It was found that the presence of the surface graphene layer destabilizes the oxygen atoms in CaO and induces the further transfer of oxygen to the outer surface of the graphene layer. Following this oxygen transfer process, CH4 molecules preferentially bind to the acquired oxygen, generating CH3OH via the reaction, which is further decomposed at CVD temperatures to produce CO. Additionally, the calculation results indicate that the energy required for oxygen transfer on the stepped CaO (110) surface is significantly lower than that on the MgO (110) surface, highlighting a unique oxygen desorption pathway specific to CaO. Following oxygen desorption from the graphene coated CaO surface, the CaO structure undergoes rearranges itself, restricting further oxygen desorption from neighbouring sites. Consequently, CO emissions cease experimentally after a certain period.
3.3. Silicon Dioxide (SiO2)
Although Al2O3, MgO, and CaO exhibit excellent catalytic performance for graphene formation, these templates face challenges in forming complex nanostructures. In contrast, SiO2 is considered one of the most ideal ceramic oxide candidates for nanostructure formation, as it can form a diverse range of nanostructures, including monodisperse nanoparticles, core–shell particles, nanofibers, silica aerogels, and mesoporous silica. However, the SiO2 surface has negligible catalytic activity for graphene formation via CH4 decomposition. Hoshikawa et al. found that a modification of SiO2 surfaces with trimethylsilyl groups (TMS) significantly enhanced their catalysis for CVD using acetylene (C2H2) as a carbon source.41 Based on this finding, trimethylsilyl functionalized micro-spherical porous silica (TMS–MPS) was employed as a core material to convert CH4 into graphene, thereby synthesizing GMS.42 Furthermore, we analysed the reaction mechanism of CH4 conversion to graphene on the surface of TMS–MPS.43Fig. 6 illustrates the scheme of TMS modification on MPS and graphene coating via CVD using CH4 as a carbon source. After replacing the silanol groups (Si–OH) on the silica surface with TMS groups, the TMS groups are converted to Si radicals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) at 900 °C. The presence of Si radicals substantially enhances carbon deposition and lowers the initial graphene formation temperature from 885 °C on pristine SiO2 to 720 °C. Carbon deposition on TMS–MPS is five times higher than on MPS at 900 °C, demonstrating the catalytic effect induced by Si radicals. DFT calculations also reveal that Si radicals act as active sites for CH4 dissociation. Additionally, both experimental and computational results demonstrated Si radicals promote the growth of the second layers even when the SiO2 surface is already coated with a single graphene layer. Furthermore, unlike Al2O3, MgO and CaO, no CO release was detected on either MPS or TMS–MPS, indicating that oxygen vacancies are not formed in these systems. Thus, it is proposed that the mechanism of CH4 activation on TMS–SiO2 is fundamentally different from that of other oxide ceramics discussed above.
 | ||
| Fig. 6 Trimethylsilylation of the MPS template (top) and modification of the graphene coating process via CVD using CH4 as a precursor (bottom). The φ and d denote the diameter and pore size of samples, respectively.43 | ||
4. Conclusions
This minireview has summarized recent progress on the mechanisms of graphene growth on oxide ceramic substrates via the chemical vapor deposition process (Table 1 and Fig. 7). Al2O3 and MgO facilitate graphene formation through the oxygen vacancy-mediated CH4 decomposition. During the induction period preceding graphene growth, CH4 extracts oxygen from the substrate, releasing CO and generating oxygen vacancies as active sites in situ. In contrast, CaO supports spontaneous graphene growth without an induction period, accompanied by the release of a significant amount of CO through the unique oxygen transfer mechanism. Meanwhile, pristine SiO2 lacks activity for methane conversion; however, surface modification with trimethylsilyl groups generates Si radicals in situ during heat treatment, which promote CH4 activation and enable graphene growth. In conclusion, these findings emphasize that activation mechanisms vary significantly depending on the substrate material, even when using the same CH4 as a carbon source, highlighting the importance of selecting an appropriate system based on the intended application.| Induction period | Active sites | CO generation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3, MgO | Yes | Oxygen vacancies | Yes |
| CaO | No | Surface oxygen sites | Yes |
| TMS modified SiO2 | No | Si radicals | No |
From the perspective of templates for graphene synthesis, oxide ceramics are characterized by their nanostructure-forming capabilities and high thermal stability, making them particularly valuable for fabricating three-dimensional graphene, which holds the potential to play a crucial role in fields such as electronics, energy, and biotechnology. Investigating the distinct CVD mechanisms across various templates expands the library of viable candidates and enables precise control over domain size and defect density of 3D graphene, which are key parameters for tuning material performance. It also opens new possibilities for synthesis on unconventional substrates and under non-standard conditions, thereby broadening the potential applications of graphene-based materials.
In addition, it is worth noting that the CVD process using CH4 offers inherent sustainability advantages. The core reaction (CH4 → C + 2H2) not only provides carbon for graphene formation but also generates hydrogen that can be classified as turquoise hydrogen. This enables efficient utilization of CH4 in terms of resource efficiency and carbon footprint, further reinforcing the appeal of CVD approach as a green synthetic platform.
Looking ahead, the discovery of new template materials, as well as innovations in carbon sources and deposition techniques, is expected to drive further advancements in 3D graphene synthesis. Consequently, elucidating the fundamental mechanisms of graphene growth, including carbon nucleation and crystallization processes, will continue to be a critical research focus. We hope that this minireview will serve as a foundation for further advancements in this field.
Author contributions
Writing – original draft: H. Z.; Writing – review & editing: M. Z., T. Y., D. D. T., H. N.Data availability
No primary research results, software or code have been included and no new data were generated or analysed as part of this review.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant No. 23H00227; JST A-STEP Grant No. JPMJTR22T6; JST CREST Grant No. JPMJCR24S6; Council for Science, Technology and Innovation (CSTI), Cross-ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program (SIP), the 3rd period of SIP “Creating a materials innovation ecosystem for industrialization” Grant No. JPJ012307 (Funding agency: NIMS); Kondo Memorial Foundation Grant No. 2023-01; “Crossover Alliance to Create the Future with People, Intelligence and Materials” from MEXT, Japan; the Cooperative Research Program of “NJRC Mater. & Dev.”; UK's Royal Society International Exchanges Cost Share (IEC\R3\193106).References
- K. S. Novoselov, A. K. Geim, S. V. Morozov, D. Jiang, Y. Zhang, S. V. Dubonos, I. V. Grigorieva and A. A. Firsov, Science, 2004, 306, 666–669 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. V. Morozov, K. S. Novoselov, M. I. Katsnelson, F. Schedin, D. C. Elias, J. A. Jaszczak and A. K. Geim, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2008, 100, 016602 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Nishihara and T. Kyotani, Chem. Commun., 2018, 54, 5648–5673 RSC.
- N. Wang, M. K. Samani, H. Li, L. Dong, Z. Zhang, P. Su, S. Chen, J. Chen, S. Huang, G. Yuan, X. Xu, B. Li, K. Leifer, L. Ye and J. Liu, Small, 2018, 14, 1801346 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Bai, T. Xu and X. Zhang, Micromachines, 2020, 11, 60 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Li, C. Chen, J. Zhang, S. Li, B. Sun and Q. Bao, Front. Mater., 2014, 1, 26 Search PubMed.
- Q. Xiang, J. Yu and M. Jaroniec, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41, 782–796 RSC.
- H. W. Kroto, J. R. Heath, S. C. O'Brien, R. F. Curl and R. E. Smalley, Nature, 1985, 318, 162–163 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Iijima, Nature, 1991, 354, 56–58 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Iijima and T. Ichihashi, Nature, 1993, 363, 603–605 CrossRef CAS.
- A. L. Mackay and H. Terrones, Nature, 1991, 352, 762–762 CrossRef.
- T. Lenosky, X. Gonze, M. Teter and V. Elser, Nature, 1992, 355, 333–335 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Nishihara, T. Simura, S. Kobayashi, K. Nomura, R. Berenguer, M. Ito, M. Uchimura, H. Iden, K. Arihara, A. Ohma, Y. Hayasaka and T. Kyotani, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26, 6418–6427 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Nomura, H. Nishihara, N. Kobayashi, T. Asada and T. Kyotani, Energy Environ. Sci., 2019, 12, 1542–1549 RSC.
- W. Yu, Z. Shen, T. Yoshii, S. Iwamura, M. Ono, S. Matsuda, M. Aoki, T. Kondo, S. R. Mukai, S. Nakanishi and H. Nishihara, Adv. Energy Mater., 2024, 14, 2303055 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Nomura, H. Nishihara, M. Yamamoto, A. Gabe, M. Ito, M. Uchimura, Y. Nishina, H. Tanaka, M. T. Miyahara and T. Kyotani, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 2559 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Yoshii, D. Umemoto, M. Yamamoto, Y. Kuwahara, H. Nishihara, K. Mori, T. Kyotani and H. Yamashita, ChemCatChem, 2020, 12, 5834–5834 CrossRef.
- A. Ohma, Y. Furuya, T. Mashio, M. Ito, K. Nomura, T. Nagao, H. Nishihara, H. Jinnai and T. Kyotani, Electrochim. Acta, 2021, 370, 137705 CrossRef CAS.
- H. C. Schniepp, J.-L. Li, M. J. McAllister, H. Sai, M. Herrera-Alonso, D. H. Adamson, R. K. Prud'homme, R. Car, D. A. Saville and I. A. Aksay, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 8535–8539 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Eda, G. Fanchini and M. Chhowalla, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2008, 3, 270–274 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Strupinski, K. Grodecki, A. Wysmolek, R. Stepniewski, T. Szkopek, P. E. Gaskell, A. Grüneis, D. Haberer, R. Bozek, J. Krupka and J. M. Baranowski, Nano Lett., 2011, 11, 1786–1791 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. N. Obraztsov, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2009, 4, 212–213 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Ma, T. Kyotani and A. Tomita, Chem. Commun., 2000, 2365–2366, 10.1039/B006295M.
- T. Kyotani, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 2006, 79, 1322–1337 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Nishihara, H. Fujimoto, H. Itoi, K. Nomura, H. Tanaka, M. T. Miyahara, P. A. Bonnaud, R. Miura, A. Suzuki, N. Miyamoto, N. Hatakeyama, A. Miyamoto, K. Ikeda, T. Otomo and T. Kyotani, Carbon, 2018, 129, 854–862 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Kyotani, L.-F. Tsai and A. Tomita, Chem. Mater., 1995, 7, 1427–1428 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Kyotani, T. Nagai, S. Inoue and A. Tomita, Chem. Mater., 1997, 9, 609–615 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Nishihara, Q.-H. Yang, P.-X. Hou, M. Unno, S. Yamauchi, R. Saito, J. I. Paredes, A. Martínez-Alonso, J. M. D. Tascón, Y. Sato, M. Terauchi and T. Kyotani, Carbon, 2009, 47, 1220–1230 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Xia, T. Yoshii, K. Nomura, K. Wakabayashi, Z.-Z. Pan, T. Ishii, H. Tanaka, T. Mashio, J. Miyawaki, T. Otomo, K. Ikeda, Y. Sato, M. Terauchi, T. Kyotani and H. Nishihara, Chem. Sci., 2023, 14, 8448–8457 RSC.
- W. Yu, T. Yoshii, A. Aziz, R. Tang, Z.-Z. Pan, K. Inoue, M. Kotani, H. Tanaka, E. Scholtzová, D. Tunega, Y. Nishina, K. Nishioka, S. Nakanishi, Y. Zhou, O. Terasaki and H. Nishihara, Adv. Sci., 2023, 10, 2300268 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Pirabul, Z.-Z. Pan and H. Nishihara, Front. Mater., 2024, 10, 1345592 CrossRef.
- X. Cai, Q. Yang, Y. Jin, Z. Tang, X. Gong, J. Shen and B. Hu, Chem. Commun., 2022, 58, 12483–12486 RSC.
- S. Sunahiro, K. Nomura, S. Goto, K. Kanamaru, R. Tang, M. Yamamoto, T. Yoshii, J. N. Kondo, Q. Zhao, A. Ghulam Nabi, R. Crespo-Otero, D. Di Tommaso, T. Kyotani and H. Nishihara, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9, 14296–14308 RSC.
- A. Holmen, O. A. Rokstad and A. Solbakken, Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev., 1976, 15, 439–444 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Muradov, F. Smith and A. T-Raissi, Catal. Today, 2005, 102–103, 225–233 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Yamamoto, S. Goto, R. Tang, K. Nomura, Y. Hayasaka, Y. Yoshioka, M. Ito, M. Morooka, H. Nishihara and T. Kyotani, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 38613–38622 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Zhao, M. Yamamoto, K. Yamazaki, H. Nishihara, R. Crespo-Otero and D. Di Tommaso, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022, 24, 23357–23366 RSC.
- Q. Zhao, H. Nishihara, R. Crespo-Otero and D. Di Tommaso, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2024, 16, 53231–53241 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Sunahiro, K. Pirabul, Z. Pan, T. Yoshii, Y. Hayasaka, Q. Zhao, R. Crespo-Otero, D. Di Tommaso, T. Kyotani and H. Nishihara, Catal. Today, 2024, 437, 114763 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Pirabul, Q. Zhao, S. Sunahiro, Z.-Z. Pan, T. Yoshii, Y. Hayasaka, E. Hoi-Sing Pang, R. Crespo-Otero, D. Di Tommaso, T. Kyotani and H. Nishihara, Green Chem., 2024, 26, 6051–6062 RSC.
- Y. Hoshikawa, A. Castro-Muñiz, H. Komiyama, T. Ishii, T. Yokoyama, H. Nanbu and T. Kyotani, Carbon, 2014, 67, 156–167 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Pirabul, Z.-Z. Pan, K. Kanamaru, Y. Horiguchi, Y. Takahashi, A. Kumatani and H. Nishihara, Carbon, 2024, 228, 119376 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Pirabul, Q. Zhao, Z.-Z. Pan, H. Liu, M. Itoh, K. Izawa, M. Kawai, R. Crespo-Otero, D. Di Tommaso and H. Nishihara, Small, 2024, 20, 2306325 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |






