Themed collection How can chemistry adapt to a low carbon future

The hydrogen evolution reaction: from material to interfacial descriptors
This perspective provides a new look into how electrolyte structure at the interface controls the kinetics of water reduction.
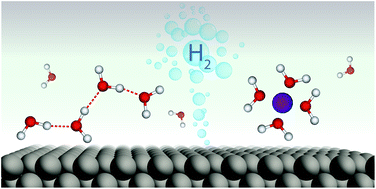
Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 9165-9181
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9SC03831K
Regulating C–C coupling in thermocatalytic and electrocatalytic COx conversion based on surface science
This article outlines the recent advances in catalyst design for controlling C–C coupling in syngas conversion, CO2 hydrogenation and CO2 electroreduction from the viewpoint of surface science.

Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 7310-7326
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9SC02014D
Toward ideal carbon dioxide functionalization
From carbon fixation, Grignard reaction, metal-catalyzed reactions and asymmetric CO2-incorporation, what would be the ideal CO2-functionalization?
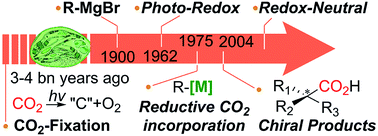
Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 3905-3926
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC05539D
Expanding the biomass derived chemical space
The derivatization and covalent modification of biomass derived platform chemicals expand the biomass derived chemical spaces allowing for the preparation of new bioactive molecules and materials.
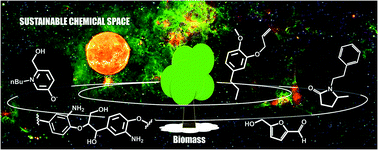
Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 4724-4738
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC00936D
Bio-based building blocks from 5-hydroxymethylfurfural via 1-hydroxyhexane-2,5-dione as intermediate
1-Hydroxy-2,5-hexanedione, obtained in good yield from renewable 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, is a versatile building block for a variety of new compounds.
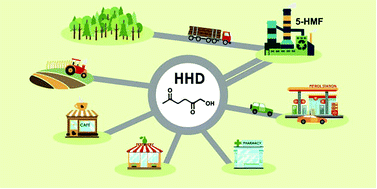
Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 6024-6034
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9SC01309A
Mechanisms of catalytic reduction of CO2 with heme and nonheme metal complexes
This critical review discusses the thermal and photocatalytic mechanisms of one-, two-, four-, six- and eight-electron reduction of CO2 with metal complex catalysts.
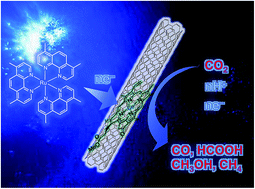
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 6017-6034
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC02220H
Inedible saccharides: a platform for CO2 capturing
Renewable materials, viz. cellulose, chitin, chitosan and cyclodextrins are promising alternatives to petroleum-based feedstocks for CO2 sequestration.
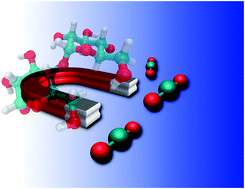
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 1088-1100
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC04706A
Selective cleavage of lignin and lignin model compounds without external hydrogen, catalyzed by heterogeneous nickel catalysts
This work reports an economical and environmentally friendly, external hydrogen-free method for the selective cleavage of lignin and lignin model compounds into value-added chemicals.
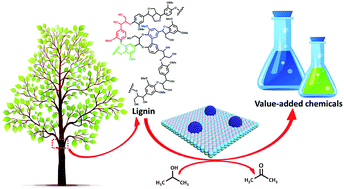
Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 4458-4468
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9SC00691E
Flux melting of metal–organic frameworks
We show flux melting by using a liquid MOF as a solvent for a secondary, non-melting MOF component.
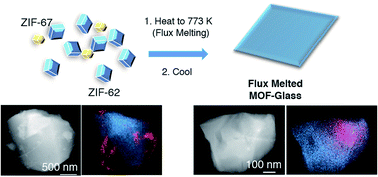
Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 3592-3601
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC04044C
CO2 capture by Mn(I) and Re(I) complexes with a deprotonated triethanolamine ligand
CO2 capture at low concentration by catalysts is potentially useful for developing photocatalytic and electrocatalytic CO2 reduction systems.
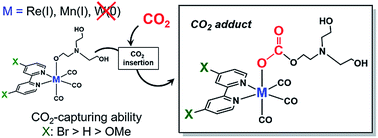
Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 3080-3088
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC04389B
Transforming atmospheric CO2 into alternative fuels: a metal-free approach under ambient conditions
The present work established the metal-free approach to capture CO2 from air and its reduction into alternative fuel under ambient conditions.
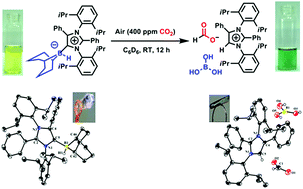
Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 1879-1884
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC03581D
Bio-inspired design: bulk iron–nickel sulfide allows for efficient solvent-dependent CO2 reduction
The electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2RR) to valuable bulk chemicals is set to become a vital factor in the prevention of environmental pollution and the selective storage of sustainable energy.

Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 1075-1081
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC03555E
Hetero-metallic active sites coupled with strongly reductive polyoxometalate for selective photocatalytic CO2-to-CH4 conversion in water
Two reductive polyoxometalate (POM)-based heterogeneous photo-catalysts display highly selective CO2-to-CH4 conversion in water.
Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 185-190
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC03471K
The chemical identity, state and structure of catalytically active centers during the electrochemical CO2 reduction on porous Fe–nitrogen–carbon (Fe–N–C) materials
We report novel structure–activity relationships and explore the chemical state and structure of catalytically active sites under operando conditions during the electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR) catalyzed by a series of porous iron–nitrogen–carbon (FeNC) catalysts.
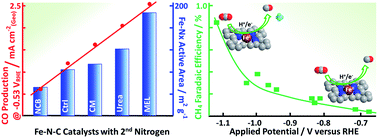
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 5064-5073
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC00491A
Solar H2 generation in water with a CuCrO2 photocathode modified with an organic dye and molecular Ni catalyst
H2 generation using a Ni catalyst on dye-sensitised CuCrO2 highlights the benefits of using delafossite semiconductors for solar fuel production.
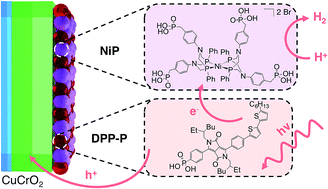
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 1439-1447
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC04476C
Overcoming double-step CO2 adsorption and minimizing water co-adsorption in bulky diamine-appended variants of Mg2(dobpdc)
Judicious choice of framework structure allows for single CO2 adsorption steps with bulky primary,secondary diamines appended to metal–organic frameworks.
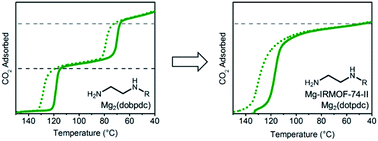
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 160-174
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC04266C
Alkene hydrogenation activity of enoate reductases for an environmentally benign biosynthesis of adipic acid
We demonstrate the first enzymatic hydrogenation of 2-hexenedioic acid and muconic acid to adipic acid using enoate reductases (ERs).
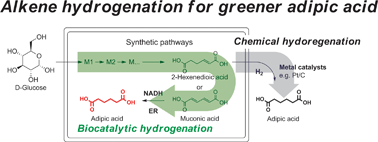
Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 1406-1413
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC02842J
Putting an ultrahigh concentration of amine groups into a metal–organic framework for CO2 capture at low pressures
Hydrazine can be grafted in CPO-27-Mg/MOF-74-Mg to provide an ultrahigh concentration of amine groups on the pore surface, giving an exceptionally high CO2 capture performance, especially at extremely low pressures.

Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 6528-6533
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC00836D
Coupling fullerene into porous aromatic frameworks for gas selective sorption
Fullerene molecules were connected to form fullerene-based PAFs. The porous structure could adsorb H2 and exhibit some selectivity of CO2.
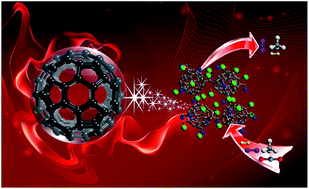
Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 3751-3756
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC00134C
Hydrolysis of woody biomass by a biomass-derived reusable heterogeneous catalyst
A carbon catalyst prepared by air oxidation of woody biomass hydrolyses woody biomass, and the reaction residue is transformed back to the catalyst by the same air oxidation method.
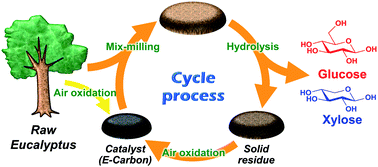
Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 692-696
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC03377B
Turning it off! Disfavouring hydrogen evolution to enhance selectivity for CO production during homogeneous CO2 reduction by cobalt–terpyridine complexes
Understanding the activity and selectivity of molecular catalysts for CO2 reduction to fuels is an important scientific endeavour in addressing the growing global energy demand.
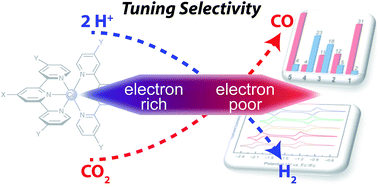
Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 2522-2531
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4SC03766A
About this collection
This collection of articles highlights research published in Chemical Science, attempting to address the global challenge of a low carbon future, where fossil-fuel use is reduced or eliminated and carbon dioxide emissions are minimised. The collection covers a range of different approaches including fundamental research into carbon capture, renewable energy sources, biofuels as alternative carbon sources, and catalytic processes for carbon dioxide reduction amongst others. This original research is also supplemented by a number of Minireviews and Perspectives which aim to demonstrate the variety of ways that scientists from around the world are choosing to tackle this issue using ideas and tools from across the chemical sciences.