Themed collection Molecular scale electronics

Themed collection on molecular scale electronics
Tim Su, Michael Inkpen and Haixing Li introduce the Journal of Materials Chemistry C themed collection Molecular Scale Electronics.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 7830-7832
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TC90061H
Single-molecule non-volatile memories: an overview and future perspectives
A single-molecule non-volatile memory is a crucial component of future nanoscale information storage. This article provides an overview of the design, mechanism and prospects of single-molecule non-volatile memories.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 751-764
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC03724J
The regulation effect of coordination number on the conductance of single-molecule junctions
The molecules with multiple anchoring sites offer opportunities for conductance regulation of single-molecule junctions via a switch between different coordination numbers.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 60-65
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC03618A
Spin polarized current in chiral organic radical monolayers
An enantiopure organic radical monolayer on gold exhibits efficient spin selectivity properties in electron transport. This result makes thia[4]azahelicenes promising candidates for the development of chiral spintronic molecular-based devices.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 10029-10035
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TC00944D
Triplet formation inhibits amplified spontaneous emission in perylene-based polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
Three similar polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon display outstanding emission properties, but only one displays amplified stimulated emission. The lack of available triplet states hinders the triplet formation allowing the amplified stimulated emission.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 5239-5246
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC04740G
Antiaromatic non-alternant heterocyclic compounds as molecular wires
We have theoretically studied the electron-transport properties of a family of molecular junctions containing the non-alternant antiaromatic pentalene moiety stabilised with various 5-membered heterocycles.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 4306-4315
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC04266A
Reliable I/V characteristics and long lifetime of porphyrin-based single-molecule junctions
In this work diamino-porphyrin derivatives, in their free base or cobalt complex forms, have been used to construct SMJs.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 4326-4335
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC04142E
Oxazine: an anchoring group serving as functional kernels to construct single-molecule switches
High-performance single-molecule switches constructed with carbon electrodes can be realized via de/rehydrogenation of the oxazine anchoring groups, not depending on specific molecular backbones.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 2194-2202
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC03720G
Interaction strength in molecular junctions consisting of π-stacked antiaromatic molecules
The interaction force was measured as the adhesive force acting between norcorrole molecules anchored to the probe surface and the sample surface. This study reveals substantial interactions in π-stacked antiaromatics at the single-molecule scale.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 1640-1643
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC04166B
Theoretical investigation of width effects in the electronic and transport properties of carbon nanoribbons with 5-8-5 carbon rings: a first-principles study
An increase in width enhances stability and acts like uniaxial tensile strain. Sub-bandgap regions trigger optoelectronic device applications and negative differential resistance. Nanodevice behavior depends on the width.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 1459-1473
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC03701K
High-performance molecular spin filters based on a square-planar four-coordinate Fe complex and covalent pyrazine anchoring groups
We propose a promising method to generate highly spin-polarized currents by connecting a magnetic molecule to carbon electrodes with appropriate anchors, whose HOMOs and LUMOs have distinct features of spatial distribution for the two spin types.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 1297-1308
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC03719C
Robust large area molecular junctions based on transparent and flexible electrodes
Towards transparent and flexible large area molecular electronic devices.
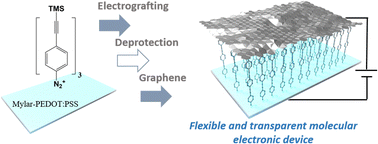
J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 1325-1333
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC02237D
Charge transfer properties of novel linear carbon chain-based dyes
Dyes with unique donor and acceptor groups outperformed phenothiazine (PTZ)-containing counterparts. 2-amine pyrrole donor induced faster charge transfer (qCT) than PTZ. qCT values reveal that the pyridinium acceptor group enhances charge separation.
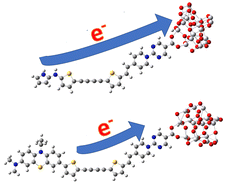
J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 903-912
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC03740A
Elucidating the effects of the sidechain substitution direction on the optoelectronic properties of isomeric diketopyrrolopyrrole-based conjugated polymers for near-infrared organic phototransistors
Compared to P3BT-out, P3BT-in with sidechains in the inner way has better molecular planarity, narrower bandgap, and stronger light absorption ability, resulting in an increased electron mobility and higher near-infrared photoresponsivity.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 489-497
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC03736C
Understanding trends in conductivity in four isostructural multifunctional crystals of Se substituted bis-dithiazolyl radicals
To understand the trends in conductivity in bisdithiazolyl-type radical-based molecular materials, one needs to master a holistic view of the parameters governing the charge transport process (namely, λ, HDA, topology of conduction paths, and ρc).

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 468-480
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC03710J
Conductive ionogel for the study of charge transport through SAM-based junctions in aqueous solution
Ionogel as a novel top electrode is suitable for junction testing in aqueous solution for self-assembled monolayers and protein junctions.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 481-488
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC03733A
Photoinduced energy and electron transfer at graphene quantum dot/azobenzene interfaces
The photophysical properties of azobenzene–graphene quantum dot interfaces show enhanced photoinduced hole and energy transfer rates for the trans isomer, making it the acvite specie compared to the cis isomer.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 143-153
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC03667G
Extended π-conjugation: a key to magnetic anisotropy preservation in highly reactive porphyrins
The findings herein reported highlight the role played by planarization in quenching the reactivity and preserving the magnetic anisotropy. The effect is associated with the weakening of the ligand field, which accompanies the π-conjugation increase.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2023,11, 15521-15530
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC02726K
A generalized neural network approach for separation of molecular breaking traces
The presented generalized neural network is a reliable and efficient tool for the separation of tunneling-only traces from break-junction data sets.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2023,11, 15564-15570
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC02346J
Exploring the impact of select anchor groups for norbornadiene/quadricyclane single-molecule switches
To achieve the ultimate limit of device miniaturization, it is necessary to have a comprehensive understanding of the structure–property relationship in functional molecular systems used in single-molecule electronics.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2023,11, 15412-15418
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC02652C
High Seebeck coefficient from isolated oligo-phenyl arrays on single layered graphene via stepwise assembly
Organic thin films composed of highly ordered molecular arrays hold tremendous potential for thermoelectric energy harvesting.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2023,11, 14652-14660
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC02842A
A conceptual framework for designing and analyzing complex molecular circuits
A computational framework to design molecular breadboards is presented. We demonstrate that the conductance of constituent circuits in a bis-terpyridine breadboard can be varied by changing the position of electrode anchoring nitrogen atoms.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2023,11, 14680-14694
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC02651E
About this collection
This Journal of Materials Chemistry C collection is guest edited by Timothy A. Su (University of California, Riverside), Michael S. Inkpen (University of Southern California), and Haixing Li (City University of Hong Kong).
The concept of using molecules as electronic components has received significant attention over the past 3 decades, initially motivated by the decreasing size of semiconductor-based circuit elements in line with Moore’s Law. It is now recognized that molecular devices can demonstrate properties unique from those observed in conventional electronics, resulting from quantum interference effects, changes in molecular redox state and/or the immediate nanoscale environment (solvent, temperature, light, magnetic field). With robust and reproducible measurement techniques now established, and great gains made in reconciling experimental and theoretical results, attention has turned to the discovery of useful wires, switches, diodes, and resistors – and how best to utilize them. This Journal of Materials Chemistry C collection captures the cutting-edge innovations in synthesis, measurement, data science, and theory that are driving this field forward.